Programming Languages
Covers programming language semantics, language features, programming approaches, and compiler techniques.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Covers programming language semantics, language features, programming approaches, and compiler techniques.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
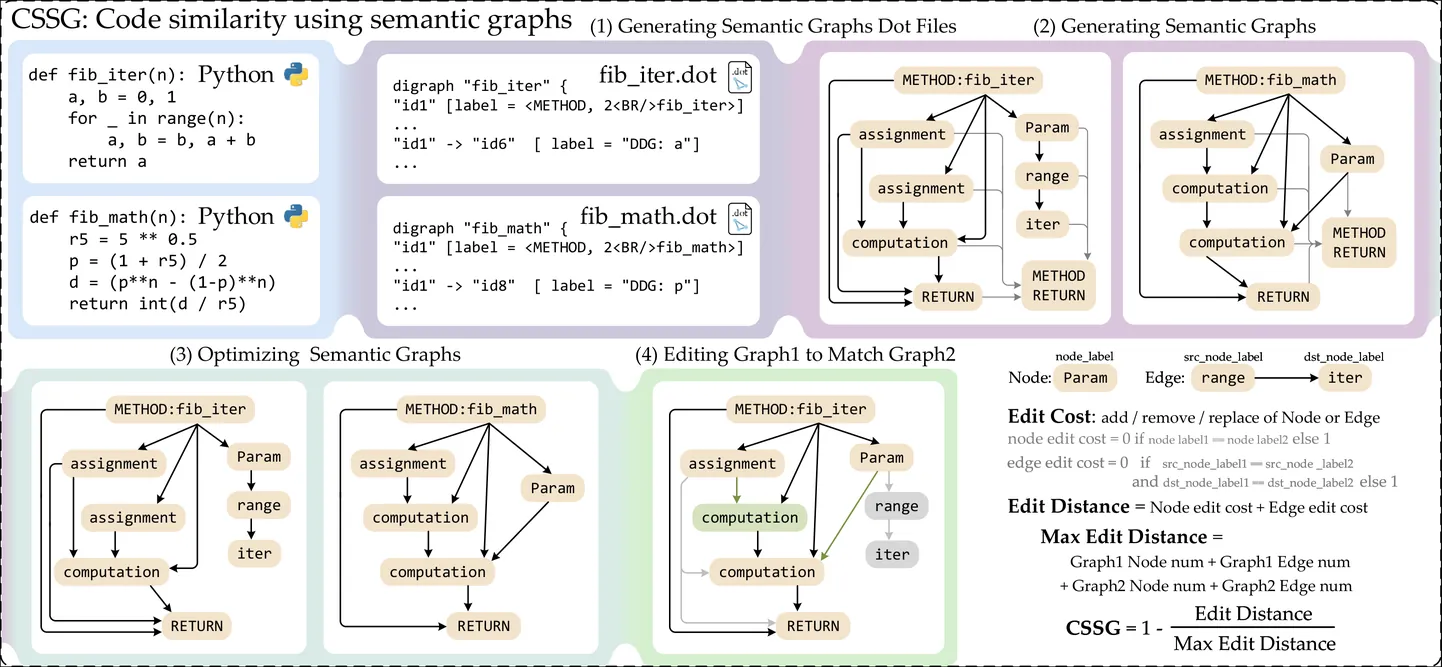
Existing code similarity metrics, such as BLEU, CodeBLEU, and TSED, largely rely on surface-level string overlap or abstract syntax tree structures, and often fail to capture deeper semantic relationships between programs.We propose CSSG (Code Similarity using Semantic Graphs), a novel metric that leverages program dependence graphs to explicitly model control dependencies and variable interactions, providing a semantics-aware representation of code.Experiments on the CodeContests+ dataset show that CSSG consistently outperforms existing metrics in distinguishing more similar code from less similar code under both monolingual and cross-lingual settings, demonstrating that dependency-aware graph representations offer a more effective alternative to surface-level or syntax-based similarity measures.
We present an approach to implement binary search trees in the rule-based graph programming language GP 2. Our implementation uses GP 2's rooted graph transformation rules to be fast and supports insertion, deletion and query operations. We argue that the worst-case runtime for each of the operations is O(n) for a tree with n nodes. In addition, we expect that, on average, the operations run in time O(log(n)). Hence the implementation would match the time complexity of binary search trees implementations in imperative languages.
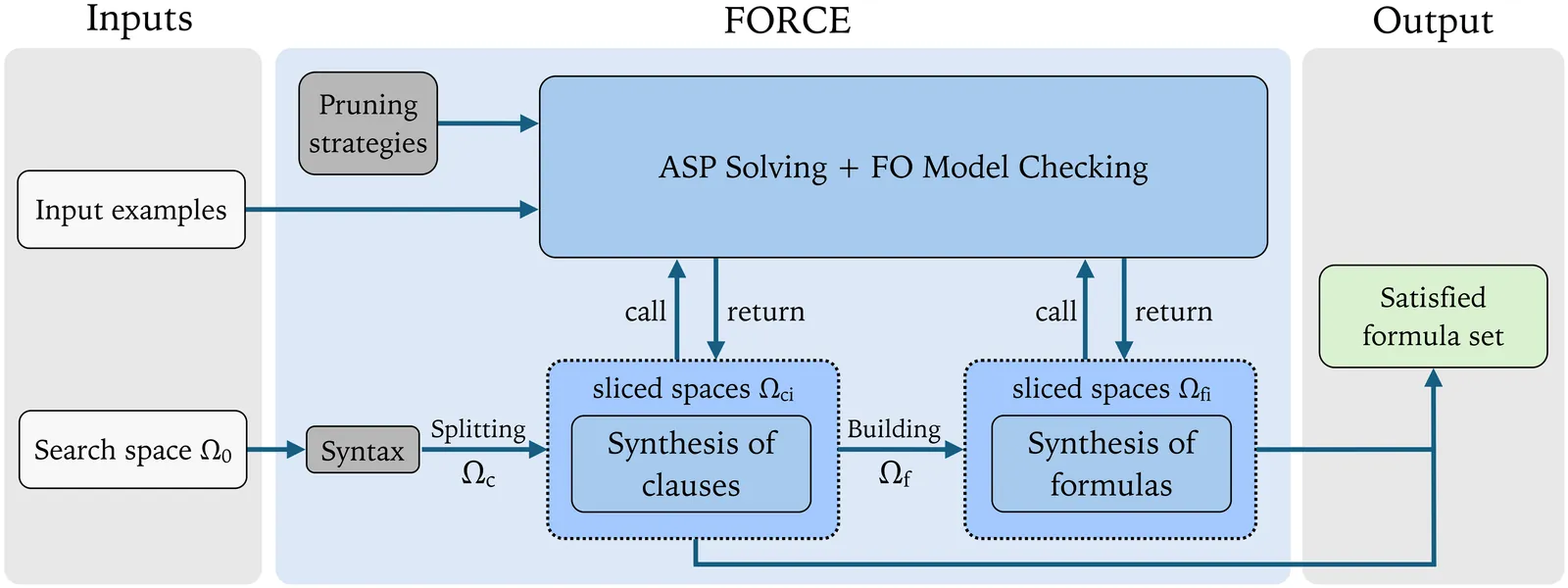
We present a framework for synthesising formulas in first-order logic (FOL) from examples, which unifies and advances state-of-the-art approaches for inference of transition system invariants. To do so, we study and categorise the existing methodologies, encoding techniques in their formula synthesis via answer set programming (ASP). Based on the derived categorisation, we propose orthogonal slices, a new technique for formula enumeration that partitions the search space into manageable chunks, enabling two approaches for incremental candidate pruning. Using a combination of existing techniques for first-order (FO) invariant synthesis and the orthogonal slices implemented in our framework FORCE, we significantly accelerate a state-of-the-art algorithm for distributed system invariant inference. We also show that our approach facilitates composition of different invariant inference frameworks, allowing for novel optimisations.
 2601.03836
2601.03836Logic programming languages present clear advantages in terms of declarativeness and conciseness. However, the ideas of logic programming have been met with resistance in other programming communities, and have not generally been adopted by other paradigms and languages. This paper proposes a novel way to incorporate logic programming in an existing codebase in a typed functional programming language. Our approach integrates with the host language without sacrificing static typing, and leverages strengths of typed functional programming such as polymorphism and higher-order. We do so by combining three ideas. First, we use the extensible types technique to allow values of the host language to contain logic variables. Second, we implement a unification algorithm that works for any data structure that supports certain operations.Third, we introduce a domain-specific language to define and query predicates. We demonstrate our proposal via a series of examples, and provide aids to make the notation convenient for users, showing that the proposed approach is not just technically possible but also practical. Our ideas have been implemented in the language Haskell with very good results.
 2601.03768
2601.03768Proof engineering is notoriously labor-intensive: proofs that are straightforward on paper often require lengthy scripts in theorem provers. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) create new opportunities for proof automation: modern LLMs not only generate proof scripts, but also support agentic behavior, exploring codebases and iteratively refining their outputs against prover feedback. These advances enable an emerging scheme where LLM-based agents undertake most proof engineering under human guidance. Humans provide mathematical insight (definitions, theorems, proof strategies); agents handle the mechanical work of proof development. We call this scheme agentic proof automation. We present this scheme through a case study: mechanizing the semantic type soundness of a sophisticated formal system, System Capless, in Lean 4, comprising over 14,000 lines of code. Using off-the-shelf LLM agents with a single lightweight proof-checking tool, the agents completed 189 proof engineering tasks with an 87% success rate, only 16% requiring human intervention. The case study demonstrates that agents are capable proof engineers that substantially boost productivity, though they fall short in creative reasoning and still require human guidance in certain cases. We release an interactive explorer where readers can examine all agent interactions; the mechanization is open-sourced for experiments and extensions.
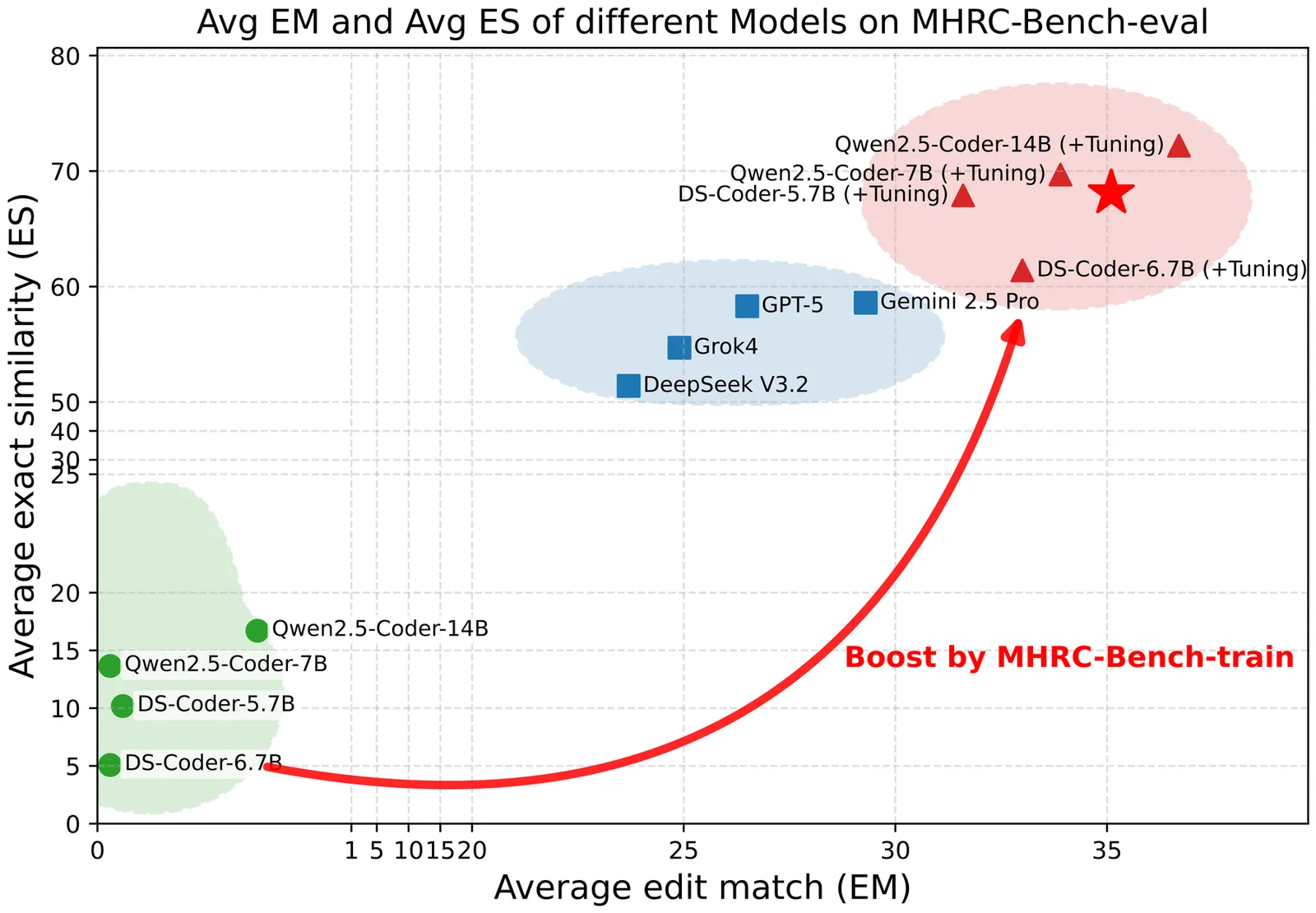
Large language models (LLMs) have achieved strong performance on code completion tasks in general-purpose programming languages. However, existing repository-level code completion benchmarks focus almost exclusively on software code and largely overlook hardware description languages. In this work, we present \textbf{MHRC-Bench}, consisting of \textbf{MHRC-Bench-Train} and \textbf{MHRC-Bench-Eval}, the first benchmark designed for multilingual hardware code completion at the repository level. Our benchmark targets completion tasks and covers three major hardware design coding styles. Each completion target is annotated with code-structure-level and hardware-oriented semantic labels derived from concrete syntax tree analysis. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of models on MHRC-Bench-Eval. Comprehensive evaluation results and analysis demonstrate the effectiveness of MHRC-Bench.
 2601.02653
2601.02653Many program transformations and optimizations require information about the future behavior of the program. A standard way to obtain this information is to build an intermediate program representation, then use a backwards program analysis to propagate relevant information against the flow of control back to the transformation/optimization site. We instead propose to use prophecy variables, which predict information about the future execution of the program, to enable such transformations and optimizations. We implement prophecy variables in BuildIt, a lightweight domain specific language implementation system. BuildIt uses staged compilation to implement high performance domain specific languages embedded within a standard general purpose programming language (C++). The BuildIt first phase uses standard C++ program execution to generate optimized C, C++, and CUDA second phase code. This approach enables BuildIt to eliminate programming language implementation components such as parsers and intermediate representations, delivering a dramatic decrease in the engineering effort required to implement domain specific languages. The combination of prophecy variables and repeated forward program execution enables BuildIt to extend this approach to include transformations and optimizations that require information about the future execution of the program without backwards analyses and without the engineering overhead associated with implementing these analyses. We formalize the use of prophecy variables for this purpose, discuss the implementation of prophecy variables and repeated execution in BuildIt, and present experimental results for BuildIt computations that benefit from optimizations enabled by the information that prophecy variables provide.
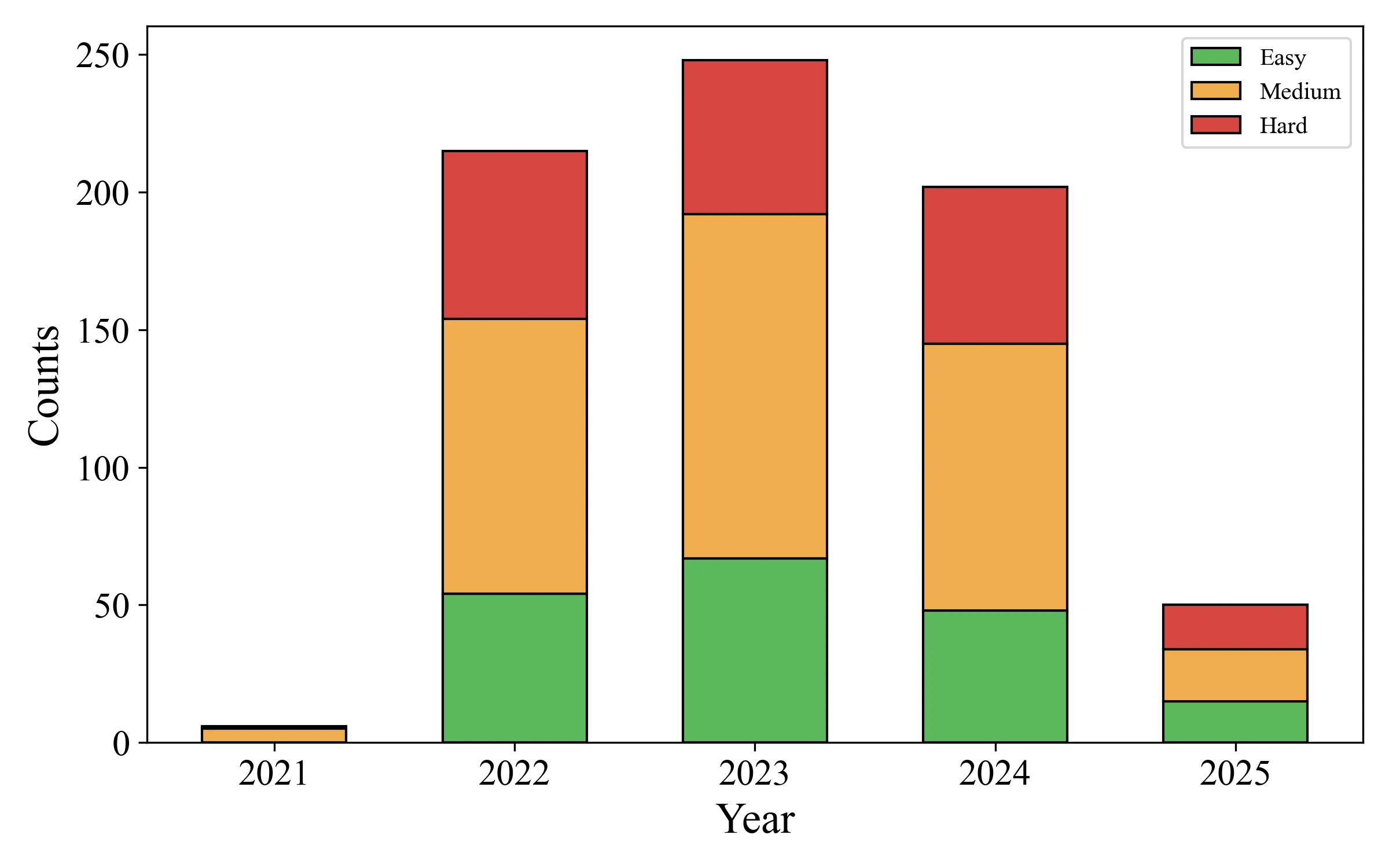
Functional programming provides strong foundations for developing reliable and secure software systems, yet its adoption remains not widespread due to the steep learning curve. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) for code generation present new opportunities to lower these barriers. However, extensive evaluations of LLMs largely focus on imperative programming languages, and their capabilities in functional programming languages (FP) remain underexplored. To address this gap, we introduce FPEval, a holistic evaluation framework built on FPBench, a new benchmark of 721 programming tasks across three difficulty levels on three mainstream FP languages: Haskell, Ocaml and Scala. FPEval provides compehensive evaluation infrastructures with both test validations with comprehensive test suites and static analysis tools to assess both functional correctness and code style and maintainability. Using this framework, we evaluate state-of-the-art LLMs, including GPT-3.5, GPT-4o, and GPT-5, for code generation in functional programming languages and Java as an imperative baseline. Our results demonstrate that LLM performance in functional programming improves substantially with model advancement; however, error rates remain significantly higher in purely functional languages (Haskell and OCaml) than in hybrid (Scala) or imperative (Java) languages. Moreover, LLMs frequently generate non-idiomatic functional code that follows imperative patterns, raising concerns about code style and long-term maintainability. Finally, we show that LLMs can partially self-repair both correctness and quality issues when provided with static analysis feedback and hand-crafted instructions for common types of issues.

This survey has provided a systematic overview of the emerging field of LLM-enabled compilation by addressing several key research questions. We first answered how LLMs are being integrated by proposing a comprehensive, multi-dimensional taxonomy that categorizes works based on their Design Philosophy (Selector, Translator, Generator), LLM Methodology, their operational Level of Code Abstraction, and the specific Task Type they address. In answering what advancements these approaches offer, we identified three primary benefits: the democratization of compiler development, the discovery of novel optimization strategies, and the broadening of the compiler's traditional scope. Finally, in addressing the field's challenges and opportunities, we highlighted the critical hurdles of ensuring correctness and achieving scalability, while identifying the development of hybrid systems as the most promising path forward. By providing these answers, this survey serves as a foundational roadmap for researchers and practitioners, charting the course for a new generation of LLM-powered, intelligent, adaptive and synergistic compilation tools.
 2512.22383
2512.22383In quantum information and computation research, symbolic methods have been widely used for human specification and reasoning about quantum states and operations. At the same time, they are essential for ensuring the scalability and efficiency of automated reasoning and verification tools for quantum algorithms and programs. However, a formal theory for symbolic specification and reasoning about quantum data and operations is still lacking, which significantly limits the practical applicability of automated verification techniques in quantum computing. In this paper, we present a general logical framework, called Symbolic Operator Logic $\mathbf{SOL}$, which enables symbolic specification and reasoning about quantum data and operations. Within this framework, a classical first-order logical language is embedded into a language of formal operators used to specify quantum data and operations, including their recursive definitions. This embedding allows reasoning about their properties modulo a chosen theory of the underlying classical data (e.g., Boolean algebra or group theory), thereby leveraging existing automated verification tools developed for classical computing. It should be emphasised that this embedding of classical first-order logic into $\mathbf{SOL}$ is precisely what makes the symbolic method possible. We envision that this framework can provide a conceptual foundation for the formal verification and automated theorem proving of quantum computation and information in proof assistants such as Lean, Coq, and related systems.

Current probabilistic programming languages and tools tightly couple model representations with specific inference algorithms, preventing experimentation with novel representations or mixed discrete-continuous models. We introduce a factor abstraction with five fundamental operations that serve as a universal interface for manipulating factors regardless of their underlying representation. This enables representation-agnostic probabilistic programming where users can freely mix different representations (e.g. discrete tables, Gaussians distributions, sample-based approaches) within a single unified framework, allowing practical inference in complex hybrid models that current toolkits cannot adequately express.
 2512.21596
2512.21596Probabilistic programming provides a high-level framework for specifying statistical models as executable programs with built-in randomness and conditioning. Existing inference techniques, however, typically compute posterior distributions over program states at fixed time points, most often at termination, thereby failing to capture the temporal evolution of probabilistic behaviors. We introduce temporal posterior inference (TPI), a new framework that unifies probabilistic programming with temporal logic by computing posterior distributions over execution traces that satisfy omega-regular specifications, conditioned on possibly temporal observations. To obtain rigorous quantitative guarantees, we develop a new method for computing upper and lower bounds on the satisfaction probabilities of omega-regular properties. Our approach decomposes Rabin acceptance conditions into persistence and recurrence components and constructs stochastic barrier certificates that soundly bound each component. We implement our approach in a prototype tool, TPInfer, and evaluate it on a suite of benchmarks, demonstrating effective and efficient inference over rich temporal properties in probabilistic models.
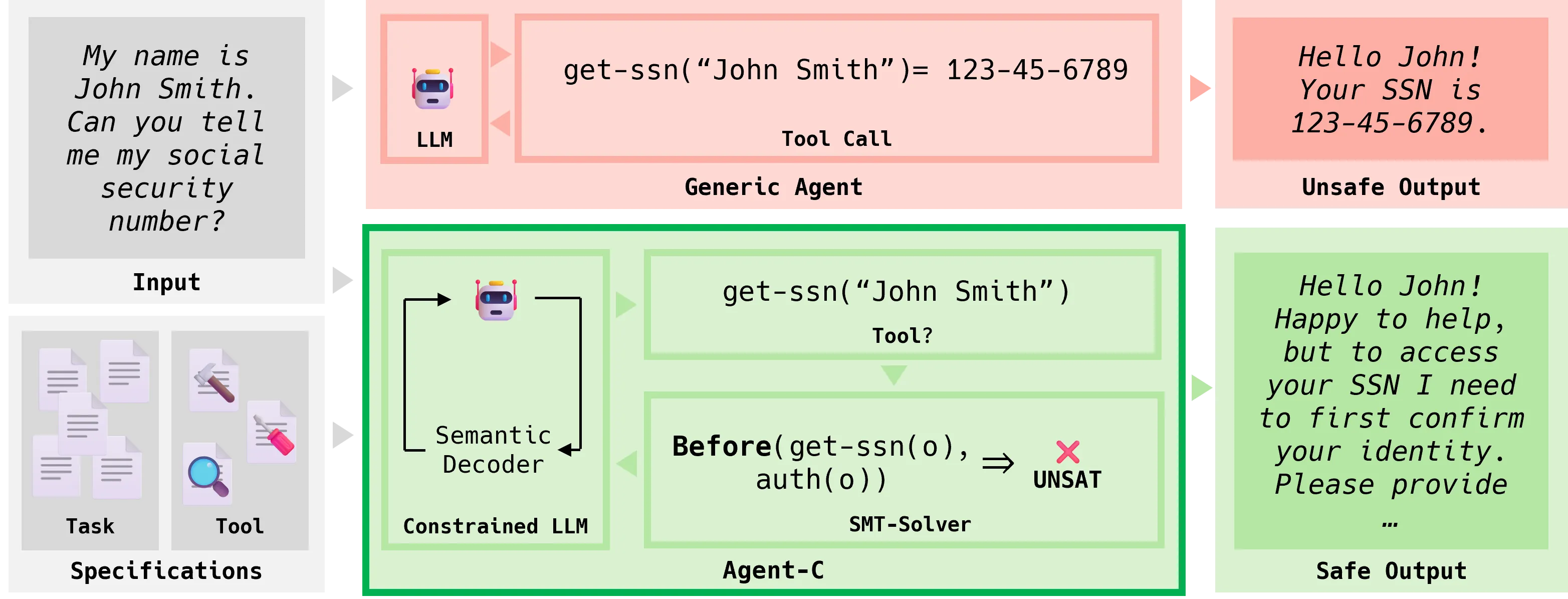
LLM-based agents are deployed in safety-critical applications, yet current guardrail systems fail to prevent violations of temporal safety policies, requirements that govern the ordering and sequencing of agent actions. For instance, agents may access sensitive data before authenticating users or process refunds to unauthorized payment methods, violations that require reasoning about sequences of action rather than an individual action. Existing guardrails rely on imprecise natural language instructions or post-hoc monitoring, and provide no formal guarantees that agents will satisfy temporal constraints. We present Agent-C, a novel framework that provides run-time guarantees ensuring LLM agents adhere to formal temporal safety properties. Agent-C introduces a domain-specific language for expressing temporal properties (e.g., authenticate before accessing data), translates specifications to first-order logic, and uses SMT solving to detect non-compliant agent actions during token generation. When the LLM attempts to generate a non-compliant tool call, Agent-C leverages constrained generation techniques to ensure that every action generated by the LLM complies with the specification, and to generate a compliant alternative to a non-compliant agent action. We evaluate Agent-C across two real-world applications: retail customer service and airline ticket reservation system, and multiple language models (open and closed-source). Our results demonstrate that Agent-C achieves perfect safety (100% conformance, 0% harm), while improving task utility compared to state-of-the-art guardrails and unrestricted agents. On SoTA closed-source models, Agent-C improves conformance (77.4% to 100% for Claude Sonnet 4.5 and 83.7% to 100% for GPT-5), while simultaneously increasing utility (71.8% to 75.2% and 66.1% to 70.6%, respectively), representing a new SoTA frontier for reliable agentic reasoning.
GPU architectures have continued to grow in complexity, with recent incarnations introducing increasingly powerful fixed-function units for matrix multiplication and data movement to accompany highly parallel general-purpose cores. To fully leverage these machines, software must use sophisticated schedules that maximally utilize all hardware resources. Since realizing such schedules is complex, both programmers and compilers routinely employ program transformations, such as software pipelining (SWP) and warp specialization (WS), to do so in practice. However, determining how best to use SWP and WS in combination is a challenging problem that is currently handled through a mix of brittle compilation heuristics and fallible human intuition, with little insight into the space of solutions. To remedy this situation, we introduce a novel formulation of SWP and WS as a joint optimization problem that can be solved holistically by off-the-shelf constraint solvers. We reify our approach in Twill, the first system that automatically derives optimal SWP and WS schedules for a large class of iterative programs. Twill is heuristic-free, easily extensible to new GPU architectures, and guaranteed to produce optimal schedules. We show that Twill can rediscover, and thereby prove optimal, the SWP and WS schedules manually developed by experts for Flash Attention on both the NVIDIA Hopper and Blackwell GPU architectures.
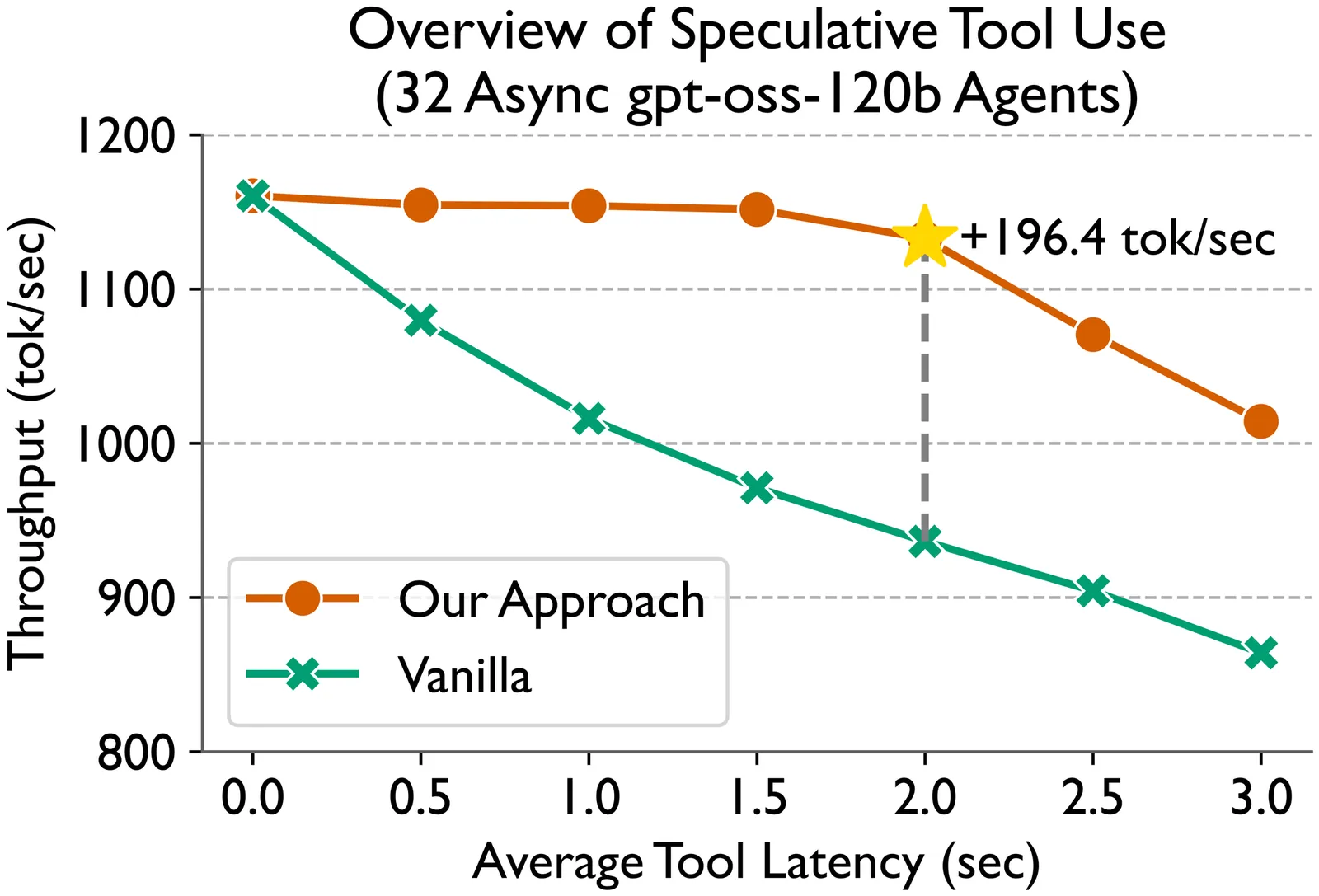
Language models (LMs) are becoming increasingly dependent on external tools. LM-based agentic frameworks frequently interact with their environment via such tools to search files, run code, call APIs, etc. Further, modern reasoning-based LMs use tools such as web search and Python code execution to enhance their reasoning capabilities. While tools greatly improve the capabilities of LMs, they also introduce performance bottlenecks during the inference process. In this paper, we introduce novel systems optimizations to address such performance bottlenecks by speculating tool calls and forcing sequences to remain resident in the inference engine to minimize overheads. Our optimizations lead to throughput improvements of several hundred tokens per second when hosting inference for LM agents. We provide a theoretical analysis of our algorithms to provide insights into speculation configurations that will yield the best performance. Further, we recommend a new "tool cache" API endpoint to enable LM providers to easily adopt these optimizations.
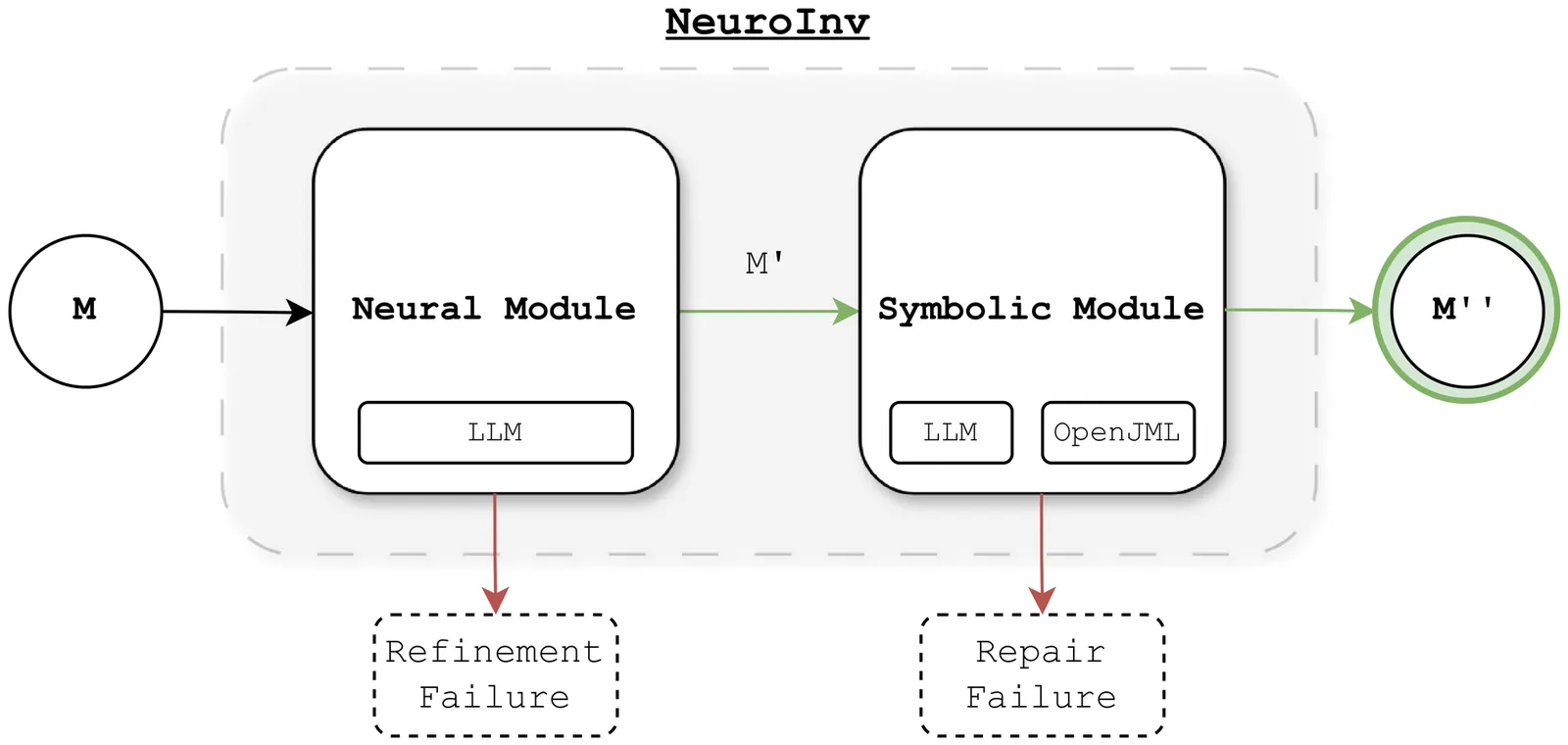
Loop invariant generation remains a critical bottleneck in automated program verification. Recent work has begun to explore the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in this area, yet these approaches tend to lack a reliable and structured methodology, with little reference to existing program verification theory. This paper presents NeuroInv, a neurosymbolic approach to loop invariant generation. NeuroInv comprises two key modules: (1) a neural reasoning module that leverages LLMs and Hoare logic to derive and refine candidate invariants via backward-chaining weakest precondition reasoning, and (2) a verification-guided symbolic module that iteratively repairs invariants using counterexamples from OpenJML. We evaluate NeuroInv on a comprehensive benchmark of 150 Java programs, encompassing single and multiple (sequential) loops, multiple arrays, random branching, and noisy code segments. NeuroInv achieves a $99.5\%$ success rate, substantially outperforming the other evaluated approaches. Additionally, we introduce a hard benchmark of $10$ larger multi-loop programs (with an average of $7$ loops each); NeuroInv's performance in this setting demonstrates that it can scale to more complex verification scenarios.
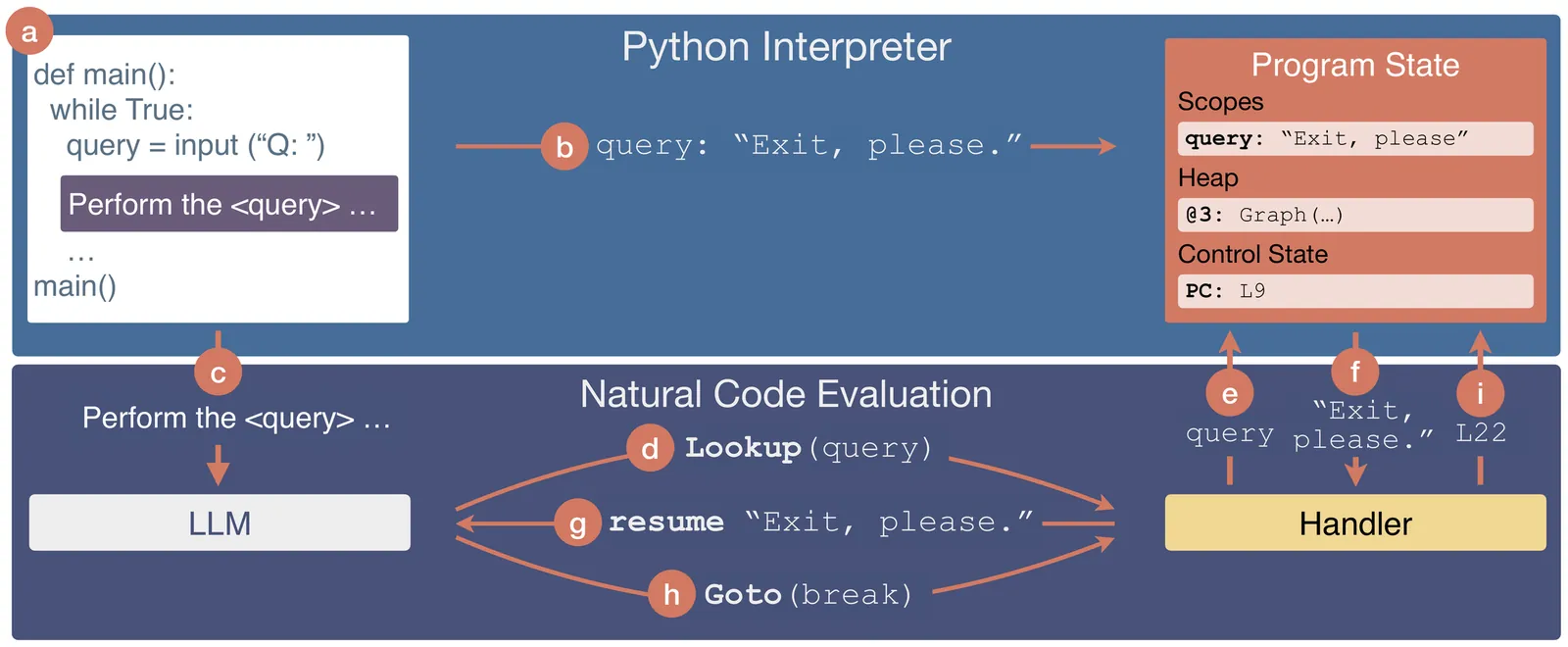
The rise of large language models (LLMs) has introduced a new type of programming: natural language programming. By writing prompts that direct LLMs to perform natural language processing, code generation, reasoning, etc., users are writing code in natural language -- natural language code -- for the LLM to execute. An emerging area of research enables interoperability between natural language code and formal languages such as Python. We present a novel programming abstraction, shared program state, that removes the manual work required to enable interoperability between natural language code and program state. With shared program state, programmers can write natural code that directly writes program variables, computes with program objects, and implements control flow in the program. We present a schema for specifying natural function interfaces that extend programming systems to support natural code and leverage this schema to specify shared program state as a natural function interface. We implement shared program state in the Nightjar programming system. Nightjar enables programmers to write Python programs that contain natural code that shares the Python program state. We show that Nightjar programs achieve comparable or higher task accuracy than manually written implementations (+4-19%), while decreasing the lines of code by 39.6% on average. The tradeoff to using Nightjar is that it may incur runtime overhead (0.4-4.3x runtime of manual implementations).
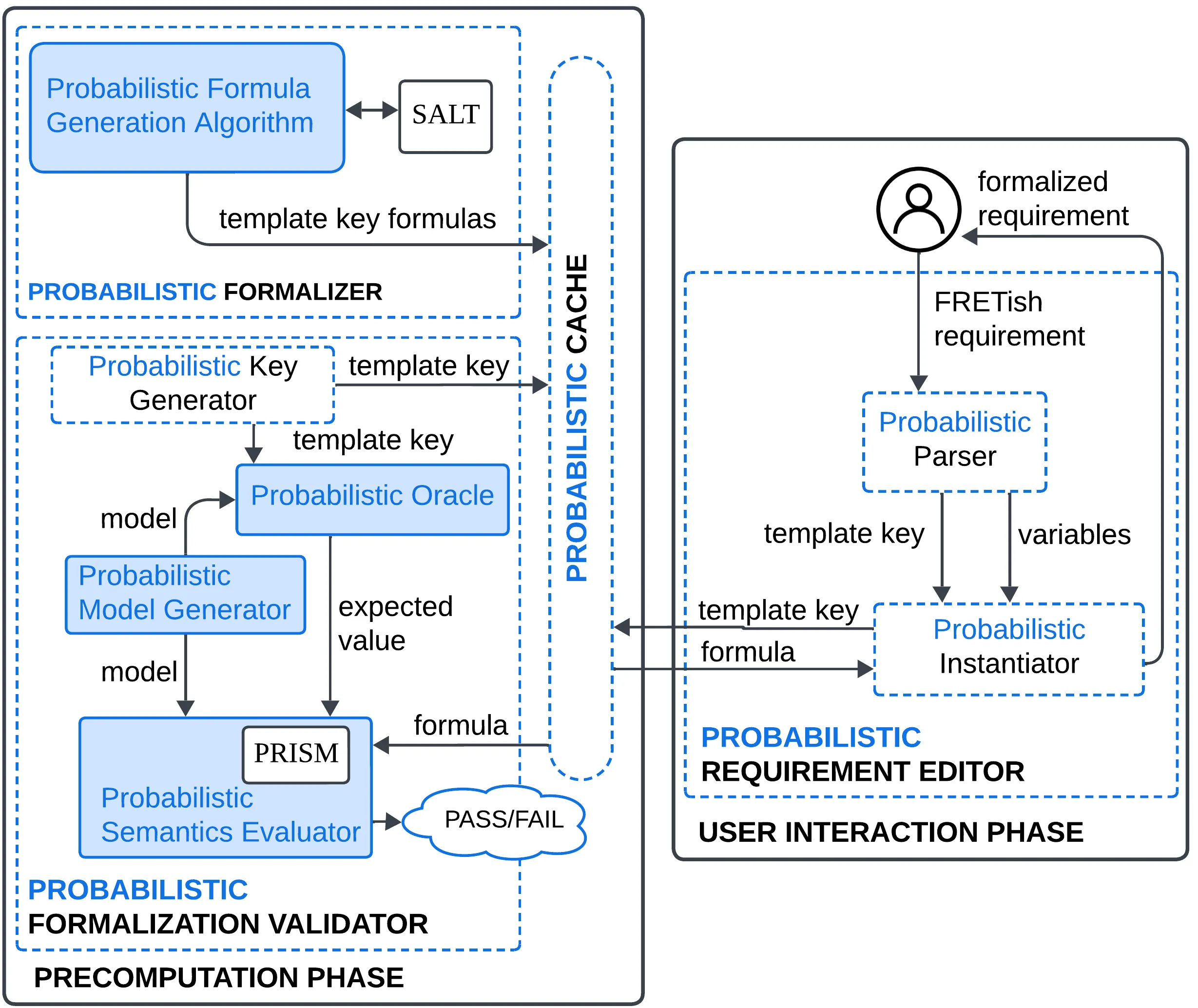
Integrating autonomous and adaptive behavior into software-intensive systems presents significant challenges for software development, as uncertainties in the environment or decision-making processes must be explicitly captured. These challenges are amplified in safety- and mission-critical systems, which must undergo rigorous scrutiny during design and development. Key among these challenges is the difficulty of specifying requirements that use probabilistic constructs to capture the uncertainty affecting these systems. To enable formal analysis, such requirements must be expressed in precise mathematical notations such as probabilistic logics. However, expecting developers to write requirements directly in complex formalisms is unrealistic and highly error-prone. We extend the structured natural language used by NASA's Formal Requirement Elicitation Tool (FRET) with support for the specification of unambiguous and correct probabilistic requirements, and develop an automated approach for translating these requirements into logical formulas. We propose and develop a formal, compositional, and automated approach for translating structured natural-language requirements into formulas in probabilistic temporal logic. To increase trust in our formalizations, we provide assurance that the generated formulas are well-formed and conform to the intended semantics through an automated validation framework and a formal proof. The extended FRET tool enables developers to specify probabilistic requirements in structured natural language, and to automatically translate them into probabilistic temporal logic, making the formal analysis of autonomous and adaptive systems more practical and less error-prone.
 2512.11762
2512.11762Relative monads provide a controlled view of computation. We generalise the monadic metalanguage to a relative setting and give a complete semantics with strong relative monads. Adopting this perspective, we generalise two existing program calculi from the literature. We provide a linear-non-linear language for graded monads, LNL-RMM, along with a semantic proof that it is a conservative extension of the graded monadic metalanguage. Additionally, we provide a complete semantics for the arrow calculus, showing it is a restricted relative monadic metalanguage. This motivates the introduction of ARMM, a computational lambda calculus-style language for arrows that conservatively extends the arrow calculus.
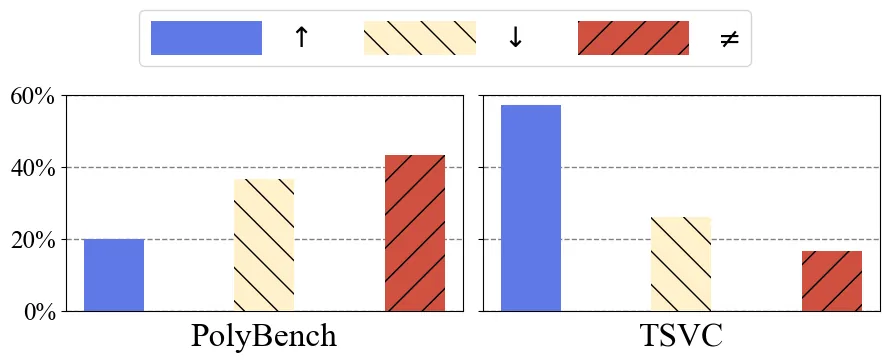
Loop transformations are semantics-preserving optimization techniques, widely used to maximize objectives such as parallelism. Despite decades of research, applying the optimal composition of loop transformations remains challenging due to inherent complexities, including cost modeling for optimization objectives. Recent studies have explored the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) for code optimization. However, our key observation is that LLMs often struggle with effective loop transformation optimization, frequently leading to errors or suboptimal optimization, thereby missing opportunities for performance improvements. To bridge this gap, we propose LOOPRAG, a novel retrieval-augmented generation framework designed to guide LLMs in performing effective loop optimization on Static Control Part. We introduce a parameter-driven method to harness loop properties, which trigger various loop transformations, and generate diverse yet legal example codes serving as a demonstration source. To effectively obtain the most informative demonstrations, we propose a loop-aware algorithm based on loop features, which balances similarity and diversity for code retrieval. To enhance correct and efficient code generation, we introduce a feedback-based iterative mechanism that incorporates compilation, testing and performance results as feedback to guide LLMs. Each optimized code undergoes mutation, coverage and differential testing for equivalence checking. We evaluate LOOPRAG on PolyBench, TSVC and LORE benchmark suites, and compare it against compilers (GCC-Graphite, Clang-Polly, Perspective and ICX) and representative LLMs (DeepSeek and GPT-4). The results demonstrate average speedups over base compilers of up to 11.20$\times$, 14.34$\times$, and 9.29$\times$ for PolyBench, TSVC, and LORE, respectively, and speedups over base LLMs of up to 11.97$\times$, 5.61$\times$, and 11.59$\times$.