Data Structures and Algorithms
Covers data structures and analysis of algorithms.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Covers data structures and analysis of algorithms.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
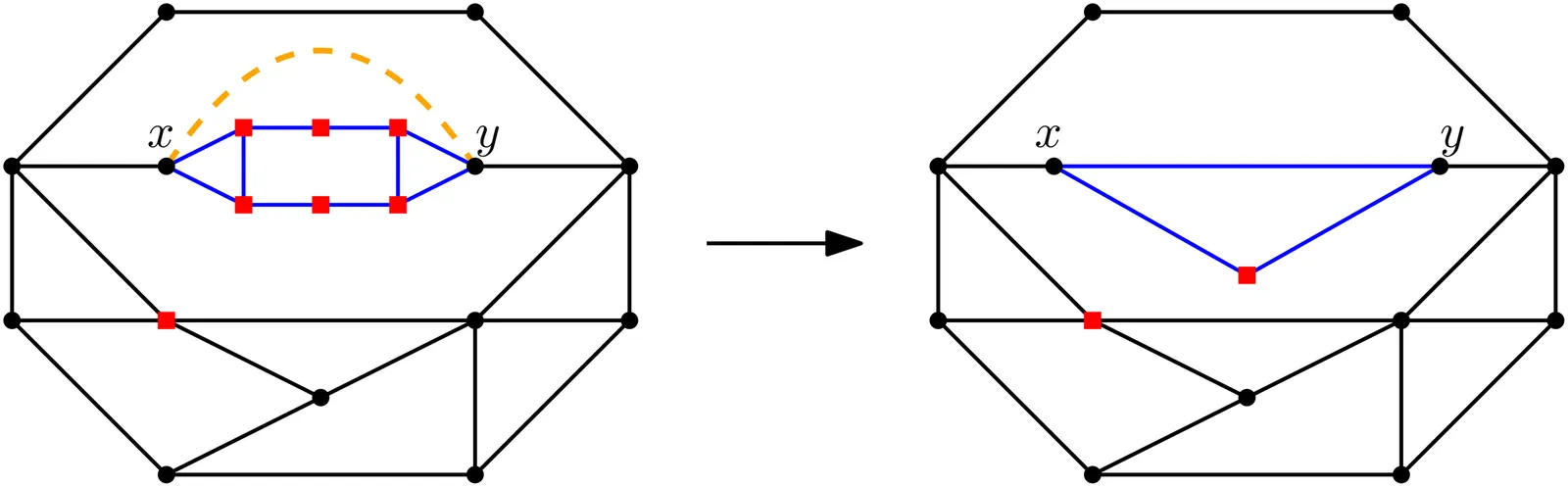
Given a planar graph, a subset of its vertices called terminals, and $k \in \mathbb{N}$, the Face Cover Number problem asks whether the terminals lie on the boundaries of at most $k$ faces of some embedding of the input graph. When a plane graph is given in the input, the problem is known to have a polynomial kernel~\cite{GarneroST17}. In this paper, we present the first polynomial kernel for Face Cover Number when the input is a planar graph (without a fixed embedding). Our approach overcomes the challenge of not having a predefined set of face boundaries by building a kernel bottom-up on an SPR-tree while preserving the essential properties of the face cover along the way.
To achieve fast recovery from link failures, most modern communication networks feature fully decentralized fast re-routing mechanisms. These re-routing mechanisms rely on pre-installed static re-routing rules at the nodes (the routers), which depend only on local failure information, namely on the failed links incident to the node. Ideally, a network is perfectly resilient: the re-routing rules ensure that packets are always successfully routed to their destinations as long as the source and the destination are still physically connected in the underlying network after the failures. Unfortunately, there are examples where achieving perfect resilience is not possible. Surprisingly, only very little is known about the algorithmic aspect of when and how perfect resilience can be achieved. We investigate the computational complexity of analyzing such local fast re-routing mechanisms. Our main result is a negative one: we show that even checking whether a given set of static re-routing rules ensures perfect resilience is coNP-complete. We also show coNP-completeness of the so-called ideal resilience, a weaker notion of resilience often considered in the literature. Additionally, we investigate other fundamental variations of the problem. In particular, we show that our coNP-completeness proof also applies to scenarios where the re-routing rules have specific patterns (known as skipping in the literature). On the positive side, for scenarios where nodes do not have information about the link from which a packet arrived (the so-called in-port), we present linear-time algorithms for both the verification and synthesis problem for perfect resilience.
 2601.03643
2601.03643A $k$-connectivity oracle for a graph $G=(V,E)$ is a data structure that given $s,t \in V$ determines whether there are at least $k+1$ internally disjoint $st$-paths in $G$. For undirected graphs, Pettie, Saranurak & Yin [STOC 2022, pp. 151-161] proved that any $k$-connectivity oracle requires $Ω(kn)$ bits of space. They asked whether $Ω(kn)$ bits are still necessary if $G$ is $k$-connected. We will show by a very simple proof that this is so even if $G$ is $k$-connected, answering this open question.
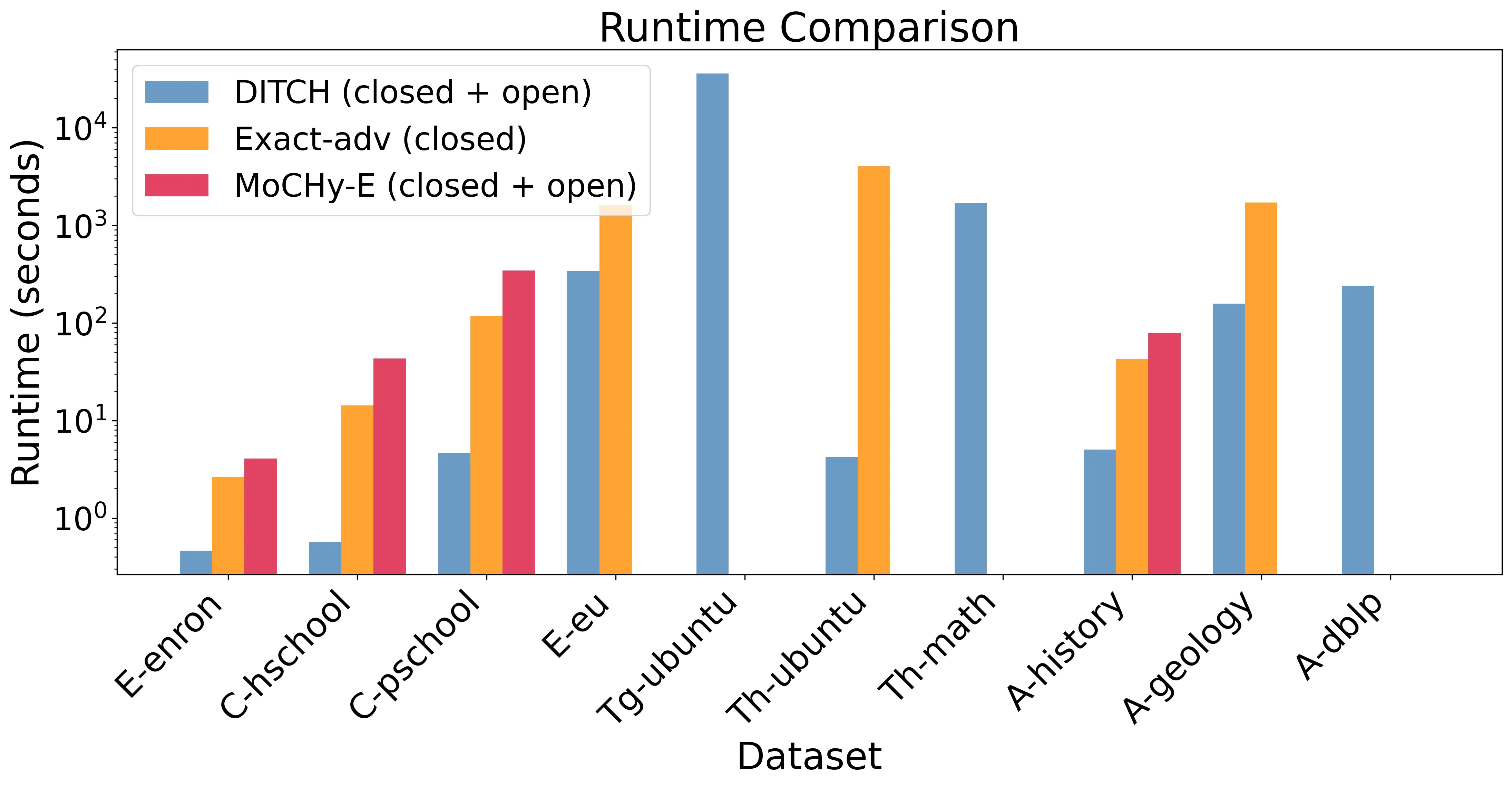
Counting the number of small patterns is a central task in network analysis. While this problem is well studied for graphs, many real-world datasets are naturally modeled as hypergraphs, motivating the need for efficient hypergraph motif counting algorithms. In particular, we study the problem of counting hypertriangles - collections of three pairwise-intersecting hyperedges. These hypergraph patterns have a rich structure with multiple distinct intersection patterns unlike graph triangles. Inspired by classical graph algorithms based on orientations and degeneracy, we develop a theoretical framework that generalizes these concepts to hypergraphs and yields provable algorithms for hypertriangle counting. We implement these ideas in DITCH (Degeneracy Inspired Triangle Counter for Hypergraphs) and show experimentally that it is 10-100x faster and more memory efficient than existing state-of-the-art methods.
We study $τ$-Bounded-Density Edge Deletion ($τ$-BDED), where given an undirected graph $G$, the task is to remove as few edges as possible to obtain a graph $G'$ where no subgraph of $G'$ has density more than $τ$. The density of a (sub)graph is the number of edges divided by the number of vertices. This problem was recently introduced and shown to be NP-hard for $τ\in \{2/3, 3/4, 1 + 1/25\}$, but polynomial-time solvable for $τ\in \{0,1/2,1\}$ [Bazgan et al., JCSS 2025]. We provide a complete dichotomy with respect to the target density $τ$: 1. If $2τ\in \mathbb{N}$ (half-integral target density) or $τ< 2/3$, then $τ$-BDED is polynomial-time solvable. 2. Otherwise, $τ$-BDED is NP-hard. We complement the NP-hardness with fixed-parameter tractability with respect to the treewidth of $G$. Moreover, for integral target density $τ\in \mathbb{N}$, we show $τ$-BDED to be solvable in randomized $O(m^{1 + o(1)})$ time. Our algorithmic results are based on a reduction to a new general flow problem on restricted networks that, depending on $τ$, can be solved via Maximum s-t-Flow or General Factors. We believe this connection between these variants of flow and matching to be of independent interest.
 2601.03020
2601.03020The regular expression matching problem asks whether a given regular expression of length $m$ matches a given string of length $n$. As is well known, the problem can be solved in $O(nm)$ time using Thompson's algorithm. Moreover, recent studies have shown that the matching problem for regular expressions extended with a practical extension called lookaround can be solved in the same time complexity. In this work, we consider three well-known extensions to regular expressions called backreference, intersection and complement, and we show that, unlike in the case of lookaround, the matching problem for regular expressions extended with any of the three (for backreference, even when restricted to one capturing group) cannot be solved in $O(n^{2-\varepsilon} \mathrm{poly}(m))$ time for any constant $\varepsilon > 0$ under the Orthogonal Vectors Conjecture. Moreover, we study the matching problem for regular expressions extended with complement in more detail, which is also known as extended regular expression (ERE) matching. We show that there is no ERE matching algorithm that runs in $O(n^{ω-\varepsilon} \mathrm{poly}(m))$ time ($2 \le ω< 2.3716$ is the exponent of square matrix multiplication) for any constant $\varepsilon > 0$ under the $k$-Clique Hypothesis, and there is no combinatorial ERE matching algorithm that runs in $O(n^{3-\varepsilon} \mathrm{poly}(m))$ time for any constant $\varepsilon > 0$ under the Combinatorial $k$-Clique Hypothesis. This shows that the $O(n^3 m)$-time algorithm introduced by Hopcroft and Ullman in 1979 and recently improved by Bille et al. to run in $O(n^ωm)$ time using fast matrix multiplication was already optimal in a sense, and sheds light on why the theoretical computer science community has struggled to improve the time complexity of ERE matching with respect to $n$ and $m$ for more than 45 years.
In moldable job scheduling, we are provided $m$ identical machines and $n$ jobs that can be executed on a variable number of machines. The execution time of each job depends on the number of machines assigned to execute that job. For the specific problem of monotone moldable job scheduling, jobs are assumed to have a processing time that is non-increasing in the number of machines. The previous best-known algorithms are: (1) a polynomial-time approximation scheme with time complexity $Ω(n^{g(1/\varepsilon)})$, where $g(\cdot)$ is a super-exponential function [Jansen and Thöle '08; Jansen and Land '18], (2) a fully polynomial approximation scheme for the case of $m \geq 8\frac{n}{\varepsilon}$ [Jansen and Land '18], and (3) a $\frac{3}{2}$ approximation with time complexity $O(nm\log(mn))$ [Wu, Zhang, and Chen '23]. We present a new practically efficient algorithm with an approximation ratio of $\approx (1.4593 + \varepsilon)$ and a time complexity of $O(nm \log \frac{1}{\varepsilon})$. Our result also applies to the contiguous variant of the problem. In addition to our theoretical results, we implement the presented algorithm and show that the practical performance is significantly better than the theoretical worst-case approximation ratio.
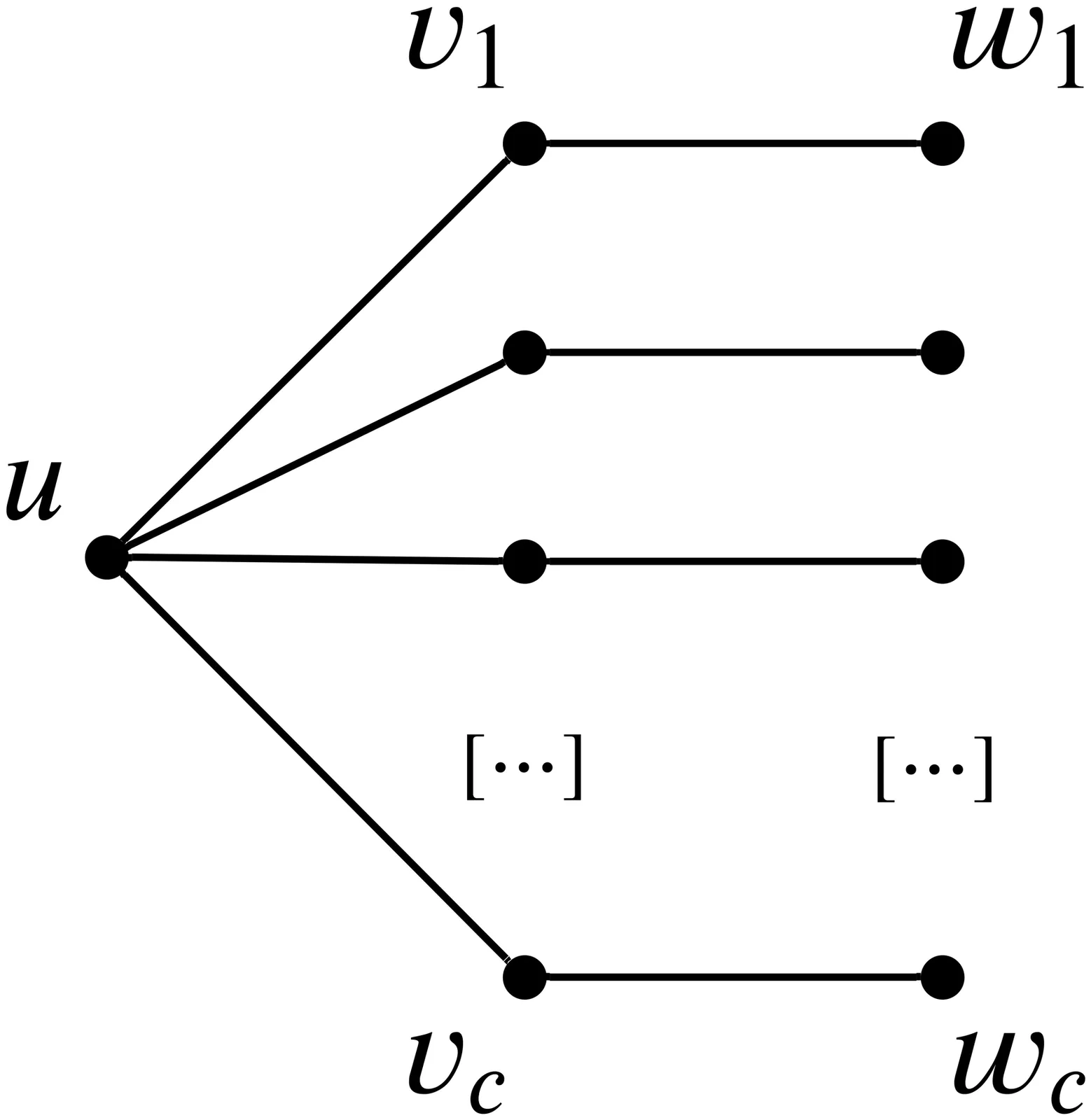
We study the parameterized complexity of the Cograph Deletion problem, which asks whether one can delete at most $k$ edges from a graph to make it $P_4$-free. This is a well-known graph modification problem with applications in computation biology and social network analysis. All current parameterized algorithms use a similar strategy, which is to find a $P_4$ and explore the local structure around it to perform an efficient recursive branching. The best known algorithm achieves running time $O^*(2.303^k)$ and requires an automated search of the branching cases due to their complexity. Since it appears difficult to further improve the current strategy, we devise a new approach using modular decompositions. We solve each module and the quotient graph independently, with the latter being the core problem. This reduces the problem to solving on a prime graph, in which all modules are trivial. We then use a characterization of Chudnovsky et al. stating that any large enough prime graph has one of seven structures as an induced subgraph. These all have many $P_4$s, with the quantity growing linearly with the graph size, and we show that these allow a recursive branch tree algorithm to achieve running time $O^*((2 + ε)^k)$ for any $ε> 0$. This appears to be the first algorithmic application of the prime graph characterization and it could be applicable to other modification problems. Towards this goal, we provide the exact set of graph classes $\H$ for which the $\H$-free editing problem can make use of our reduction to a prime graph, opening the door to improvements for other modification problems.
We introduce the first iterative algorithm for constructing a $\varepsilon$-coreset that guarantees deterministic $\ell_p$ subspace embedding for any $p \in [1,\infty)$ and any $\varepsilon > 0$. For a given full rank matrix $\mathbf{X} \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times d}$ where $n \gg d$, $\mathbf{X}' \in \mathbb{R}^{m \times d}$ is an $(\varepsilon,\ell_p)$-subspace embedding of $\mathbf{X}$, if for every $\mathbf{q} \in \mathbb{R}^d$, $(1-\varepsilon)\|\mathbf{Xq}\|_{p}^{p} \leq \|\mathbf{X'q}\|_{p}^{p} \leq (1+\varepsilon)\|\mathbf{Xq}\|_{p}^{p}$. Specifically, in this paper, $\mathbf{X}'$ is a weighted subset of rows of $\mathbf{X}$ which is commonly known in the literature as a coreset. In every iteration, the algorithm ensures that the loss on the maintained set is upper and lower bounded by the loss on the original dataset with appropriate scalings. So, unlike typical coreset guarantees, due to bounded loss, our coreset gives a deterministic guarantee for the $\ell_p$ subspace embedding. For an error parameter $\varepsilon$, our algorithm takes $O(\mathrm{poly}(n,d,\varepsilon^{-1}))$ time and returns a deterministic $\varepsilon$-coreset, for $\ell_p$ subspace embedding whose size is $O\left(\frac{d^{\max\{1,p/2\}}}{\varepsilon^{2}}\right)$. Here, we remove the $\log$ factors in the coreset size, which had been a long-standing open problem. Our coresets are optimal as they are tight with the lower bound. As an application, our coreset can also be used for approximately solving the $\ell_p$ regression problem in a deterministic manner.
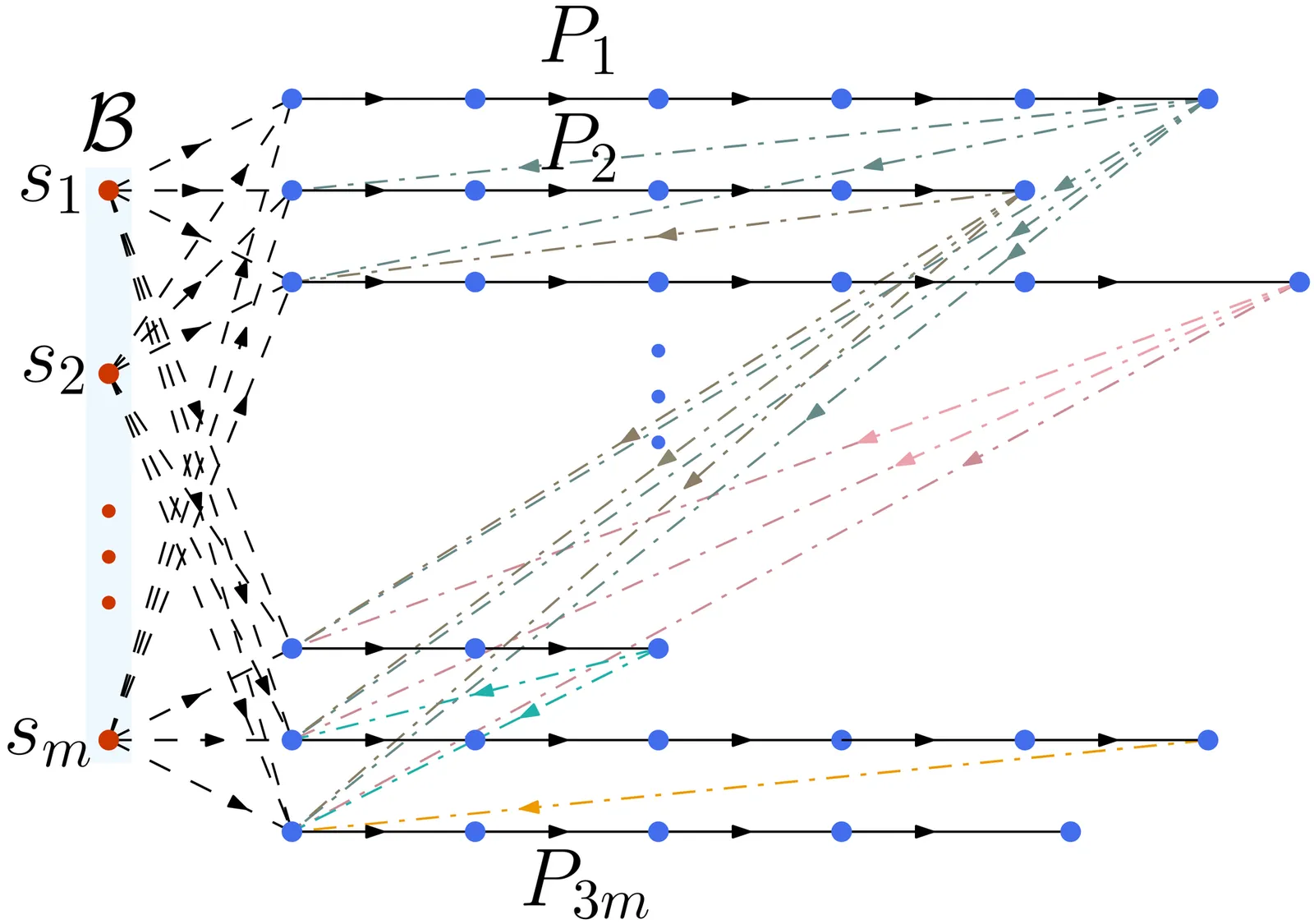
The kidney exchange mechanism allows many patient-donor pairs who are otherwise incompatible with each other to come together and exchange kidneys along a cycle. However, due to infrastructure and legal constraints, kidney exchange can only be performed in small cycles in practice. In reality, there are also some altruistic donors who do not have any paired patients. This allows us to also perform kidney exchange along paths that start from some altruistic donor. Unfortunately, the computational task is NP-complete. To overcome this computational barrier, an important line of research focuses on designing faster algorithms, both exact and using the framework of parameterized complexity. The standard parameter for the kidney exchange problem is the number $t$ of patients that receive a healthy kidney. The current fastest known deterministic FPT algorithm for this problem, parameterized by $t$, is $O^\star\left(14^t\right)$. In this work, we improve this by presenting a deterministic FPT algorithm that runs in time $O^\star\left((4e)^t\right)\approx O^\star\left(10.88^t\right)$. This problem is also known to be W[1]-hard parameterized by the treewidth of the underlying undirected graph. A natural question here is whether the kidney exchange problem admits an FPT algorithm parameterized by the pathwidth of the underlying undirected graph. We answer this negatively in this paper by proving that this problem is W[1]-hard parameterized by the pathwidth of the underlying undirected graph. We also present some parameterized intractability results improving the current understanding of the problem under the framework of parameterized complexity.
Subgraph complementation is an operation that toggles all adjacencies inside a selected vertex set. Given a graph \(G\) and a target class \(\mathcal{C}\), the Minimum Subgraph Complementation problem asks for a minimum-size vertex set \(S\) such that complementing the subgraph induced by \(S\) transforms \(G\) into a graph belonging to \(\mathcal{C}\). While the decision version of Subgraph Complementation has been extensively studied and is NP-complete for many graph classes, the algorithmic complexity of its optimization variant has remained largely unexplored. In this paper, we study MSC from an algorithmic perspective. We present polynomial-time algorithms for MSC in several nontrivial settings. Our results include polynomial-time solvability for transforming graphs between bipartite, co-bipartite, and split graphs, as well as for complementing bipartite regular graphs into chordal graphs. We also show that MSC to the class of graphs of fixed degeneracy can be solved in polynomial time when the input graph is a forest. Moreover, we investigate MSC with respect to connectivity and prove that MSC to the class of disconnected graphs and to the class of 2-connected graphs can be solved in polynomial time for arbitrary inputs.
Recently, Lafond and Luo [MFCS 2023] defined the $\mathcal{G}$-modular cardinality of a graph $G$ as the minimum size of a partition of $V(G)$ into modules that belong to a graph class $\mathcal{G}$. We analyze the complexity of calculating parameters that generalize interval graphs when parameterized by the $\mathcal{G}$-modular cardinality, where $\mathcal{G}$ corresponds either to the class of interval graphs or to the union of complete graphs. Namely, we analyze the complexity of computing the thinness and the simultaneous interval number of a graph. We present a linear kernel for the Thinness problem parameterized by the interval-modular cardinality and an FPT algorithm for Simultaneous Interval Number when parameterized by the cluster-modular cardinality plus the solution size. The interval-modular cardinality of a graph is not greater than the cluster-modular cardinality, which in turn generalizes the neighborhood diversity and the twin-cover number. Thus, our results imply a linear kernel for Thinness when parameterized by the neighborhood diversity of the input graph, FPT algorithms for Thinness when parameterized by the twin-cover number and vertex cover number, and FPT algorithms for Simultaneous Interval Number when parameterized by the neighborhood diversity plus the solution size, twin-cover number, and vertex cover number. To the best of our knowledge, prior to our work no parameterized algorithms (FPT or XP) for computing the thinness or the simultaneous interval number were known. On the negative side, we observe that Thinness and Simultaneous Interval Number parameterized by treewidth, pathwidth, bandwidth, (linear) mim-width, clique-width, modular-width, or even the thinness or simultaneous interval number themselves, admit no polynomial kernels assuming NP $\not\subseteq$ coNP/poly.
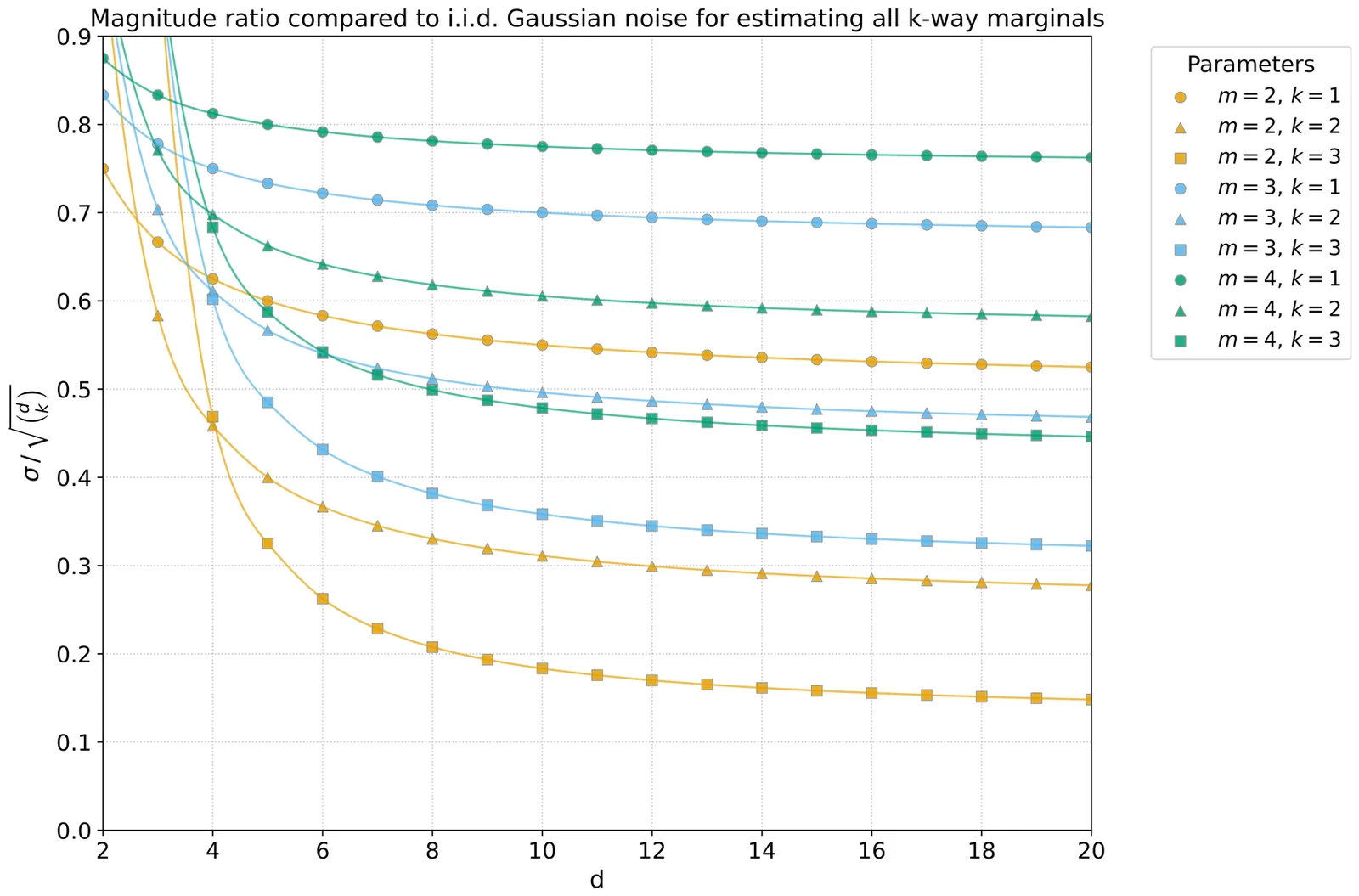
We revisit the task of releasing marginal queries under differential privacy with additive (correlated) Gaussian noise. We first give a construction for answering arbitrary workloads of weighted marginal queries, over arbitrary domains. Our technique is based on releasing queries in the Fourier basis with independent noise with carefully calibrated variances, and reconstructing the marginal query answers using the inverse Fourier transform. We show that our algorithm, which is a factorization mechanism, is exactly optimal among all factorization mechanisms, both for minimizing the sum of weighted noise variances, and for minimizing the maximum noise variance. Unlike algorithms based on optimizing over all factorization mechanisms via semidefinite programming, our mechanism runs in time polynomial in the dataset and the output size. This construction recovers results of Xiao et al. [Neurips 2023] with a simpler algorithm and optimality proof, and a better running time. We then extend our approach to a generalization of marginals which we refer to as product queries. We show that our algorithm is still exactly optimal for this more general class of queries. Finally, we show how to embed extended marginal queries, which allow using a threshold predicate on numerical attributes, into product queries. We show that our mechanism is almost optimal among all factorization mechanisms for extended marginals, in the sense that it achieves the optimal (maximum or average) noise variance up to lower order terms.
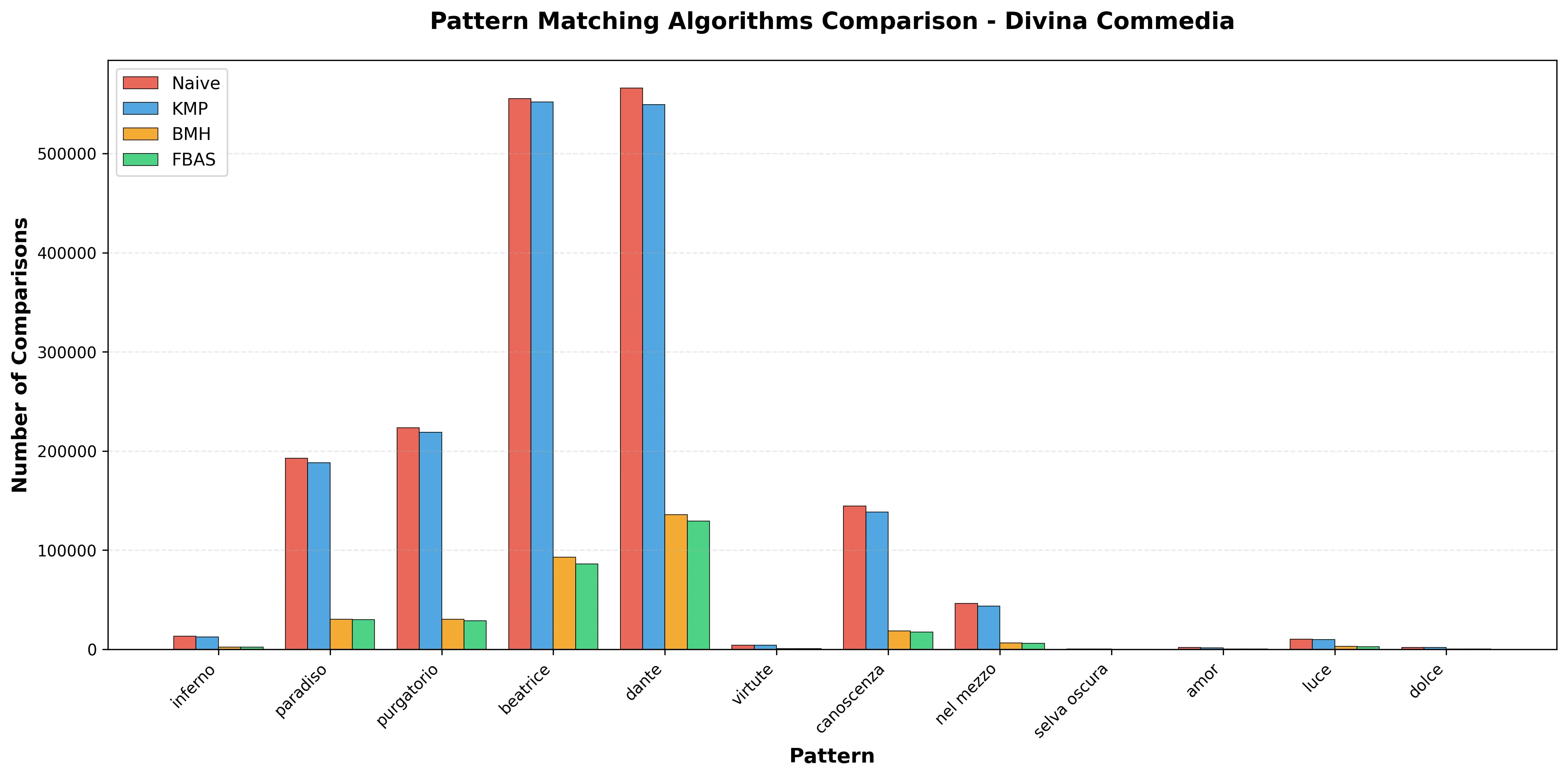
In this work, we propose an enhancement to the Boyer-Moore-Horspool algorithm tailored for natural language text. The approach involves preprocessing the search pattern to identify its statistically least frequent character, referred to as the "anchor." During the search, verification is first performed at this high-entropy position, allowing the algorithm to quickly discard non-matching windows. This fail-fast strategy reduces unnecessary comparisons, improving overall efficiency. Our implementation shows that incorporating basic linguistic statistics into classical pattern-matching techniques can boost performance without increasing complexity to the shift heuristics.
Approximate nearest neighbor search (ANN) is a common way to retrieve relevant search results, especially now in the context of large language models and retrieval augmented generation. One of the most widely used algorithms for ANN is based on constructing a multi-layer graph over the dataset, called the Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW). While this algorithm supports insertion of new data, it does not support deletion of existing data. Moreover, deletion algorithms described by prior work come at the cost of increased query latency, decreased recall, or prolonged deletion time. In this paper, we propose a new theoretical framework for graph-based ANN based on random walks. We then utilize this framework to analyze a randomized deletion approach that preserves hitting time statistics compared to the graph before deleting the point. We then turn this theoretical framework into a deterministic deletion algorithm, and show that it provides better tradeoff between query latency, recall, deletion time, and memory usage through an extensive collection of experiments.
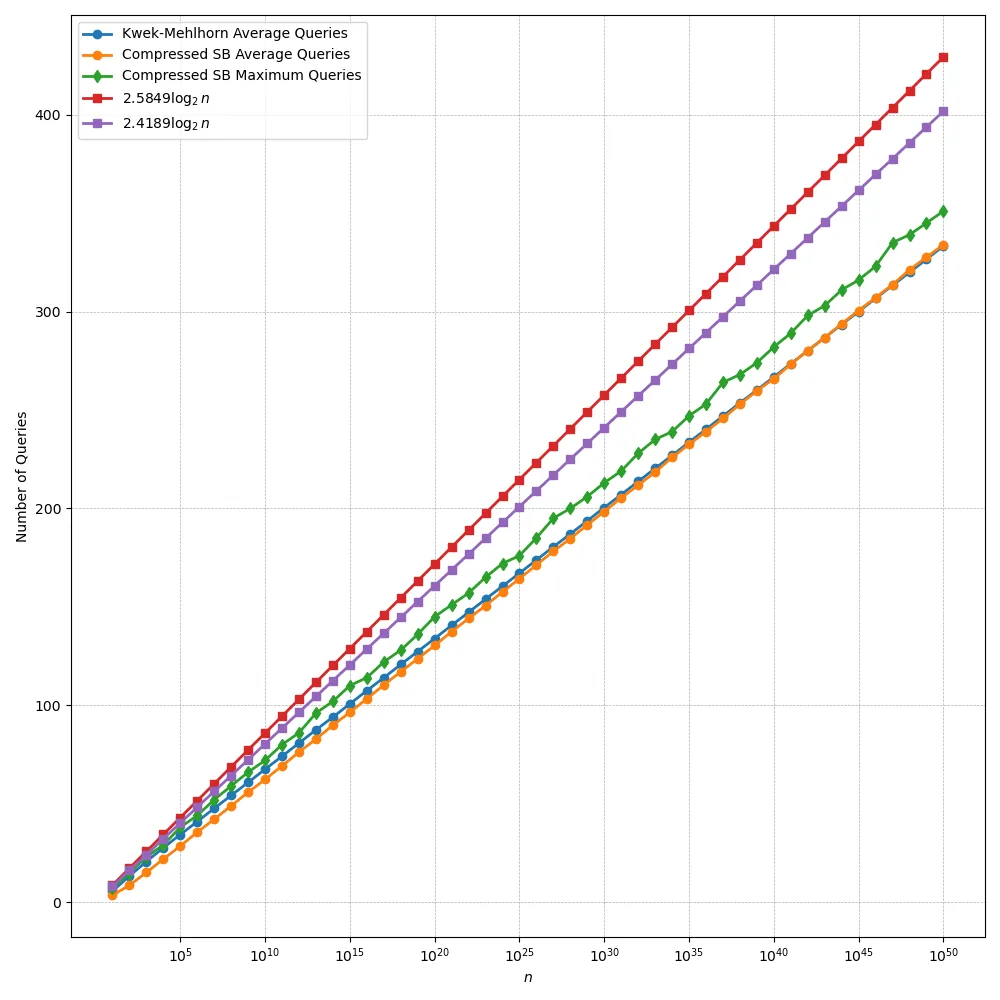
We revisit the problem of rational search: given an unknown rational number $α= \frac{a}{b} \in (0,1)$ with $b \leq n$, the goal is to identify $α$ using comparison queries of the form ``$β\leq α$?''. The problem has been studied several decades ago and optimal query algorithms are known. We present a new algorithm for rational search based on a compressed traversal of the Stern--Brocot tree, which appeared to have been overlooked in the literature. This approach also naturally extends to two related problems that, to the best of our knowledge, have not been previously addressed: (i) unbounded rational search, where the bound $n$ is unknown, and (ii) computing the best (in a precise sense) rational approximation of an unknown real number using only comparison queries.
 2512.16875
2512.16875We study the problem of finding confidence ellipsoids for an arbitrary distribution in high dimensions. Given samples from a distribution $D$ and a confidence parameter $α$, the goal is to find the smallest volume ellipsoid $E$ which has probability mass $\Pr_{D}[E] \ge 1-α$. Ellipsoids are a highly expressive class of confidence sets as they can capture correlations in the distribution, and can approximate any convex set. This problem has been studied in many different communities. In statistics, this is the classic minimum volume estimator introduced by Rousseeuw as a robust non-parametric estimator of location and scatter. However in high dimensions, it becomes NP-hard to obtain any non-trivial approximation factor in volume when the condition number $β$ of the ellipsoid (ratio of the largest to the smallest axis length) goes to $\infty$. This motivates the focus of our paper: can we efficiently find confidence ellipsoids with volume approximation guarantees when compared to ellipsoids of bounded condition number $β$? Our main result is a polynomial time algorithm that finds an ellipsoid $E$ whose volume is within a $O(β^{γd})$ multiplicative factor of the volume of best $β$-conditioned ellipsoid while covering at least $1-O(α/γ)$ probability mass for any $γ< α$. We complement this with a computational hardness result that shows that such a dependence seems necessary up to constants in the exponent. The algorithm and analysis uses the rich primal-dual structure of the minimum volume enclosing ellipsoid and the geometric Brascamp-Lieb inequality. As a consequence, we obtain the first polynomial time algorithm with approximation guarantees on worst-case instances of the robust subspace recovery problem.

We study the problem of computing Chamfer distance in the fully dynamic setting, where two set of points $A, B \subset \mathbb{R}^{d}$, each of size up to $n$, dynamically evolve through point insertions or deletions and the goal is to efficiently maintain an approximation to $\mathrm{dist}_{\mathrm{CH}}(A,B) = \sum_{a \in A} \min_{b \in B} \textrm{dist}(a,b)$, where $\textrm{dist}$ is a distance measure. Chamfer distance is a widely used dissimilarity metric for point clouds, with many practical applications that require repeated evaluation on dynamically changing datasets, e.g., when used as a loss function in machine learning. In this paper, we present the first dynamic algorithm for maintaining an approximation of the Chamfer distance under the $\ell_p$ norm for $p \in \{1,2 \}$. Our algorithm reduces to approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search with little overhead. Plugging in standard ANN bounds, we obtain $(1+ε)$-approximation in $\tilde{O}(ε^{-d})$ update time and $O(1/ε)$-approximation in $\tilde{O}(d n^{ε^2} ε^{-4})$ update time. We evaluate our method on real-world datasets and demonstrate that it performs competitively against natural baselines.

Democracy relies on making collective decisions through voting. In addition, voting procedures have further applications, for example in the training of artificial intelligence. An essential criterion for determining the winner of a fair election is that all alternatives are treated equally: this is called neutrality. The established Ranked Pairs voting method cannot simultaneously guarantee neutrality and be computationally tractable for election with ties. River, the recently introduced voting method, shares desirable properties with Ranked Pairs and has further advantages, such as a new property related to resistance against manipulation. Both Ranked Pairs and River use a weighted margin graph to model the election. Ties in the election can lead to edges of equal margin. To order the edges in such a case, a tiebreaking scheme must be employed. Many tiebreaks violate neutrality or other important properties. A tiebreaking scheme that preserves neutrality is Parallel Universe Tiebreaking (PUT). Ranked Pairs with PUT is NP-hard to compute. The main result of this thesis shows that River with PUT can be computed in polynomial worst-case runtime: We can check whether an alternative is a River PUT winner, by running River with a specially constructed ordering of the edges. To construct this ordering, we introduce the semi-River diagram which contains the edges that can appear in any River diagram for some arbitrary tiebreak. On this diagram we can compute the River winners, by applying a variant of Prims algorithm per alternative. Additionally, we give an algorithm improve the previous naive runtime of River from $\mathcal{O}(n^4)$ to $\mathcal{O}(n^2 \log n)$, where n is the number of alternatives.
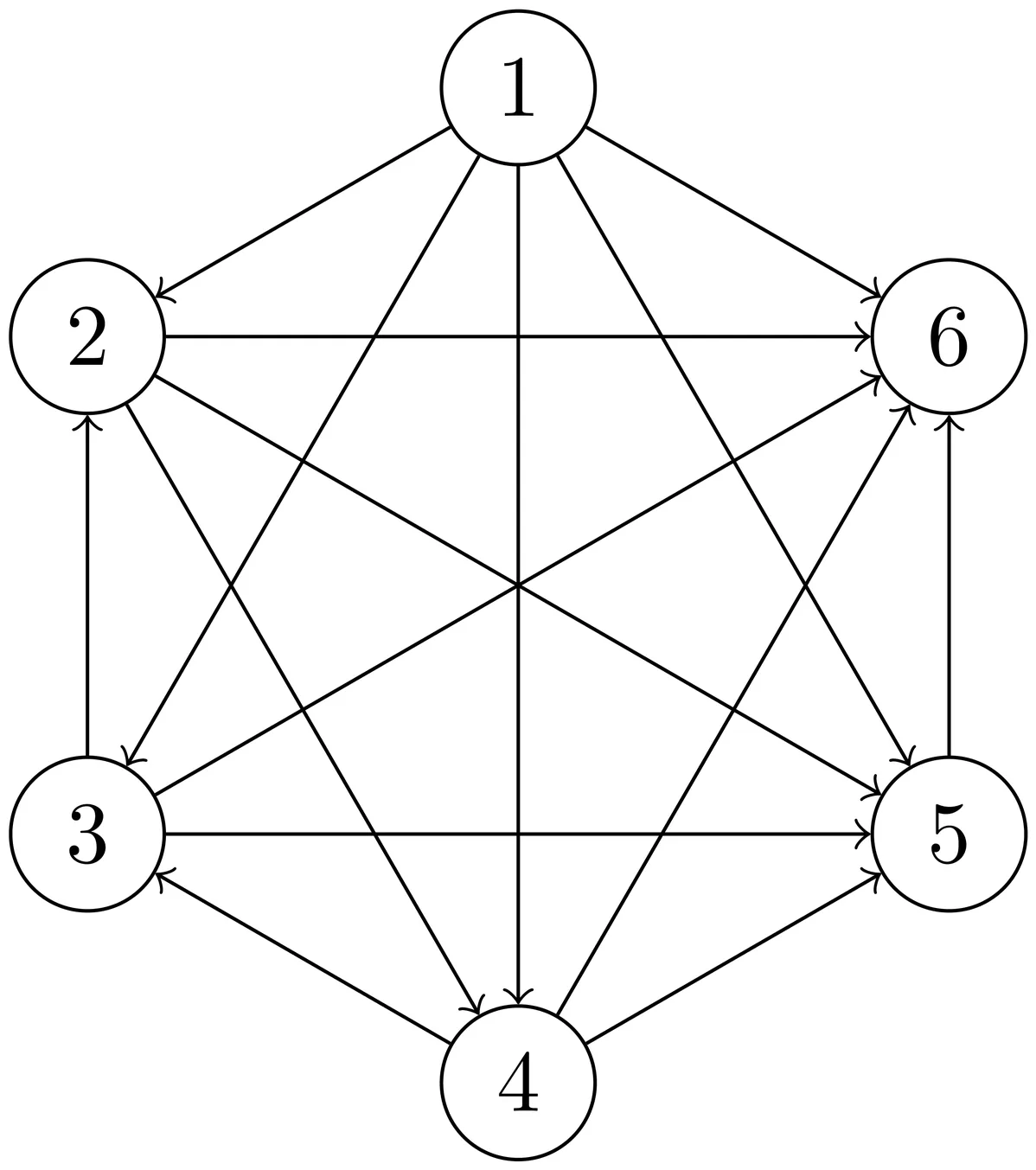
The score set of a tournament is defined as the set of its distinct out-degrees. In 1978, Reid proposed the conjecture that for any set of nonnegative integers $D$, there exists a tournament $T$ with a degree set $D$. In 1989, Yao presented an arithmetical proof of the conjecture, but a general polynomial-time construction algorithm is not known. This paper proposes a necessary and sufficient condition and a separate necessary condition, based on the existing Landau's theorem for the problem of reconstructing score sequences from score sets of tournament graphs. The necessary condition introduces a structured set that enables the use of group-theoretic techniques, offering not only a framework for solving the reconstruction problem but also a new perspective for approaching similar problems. In particular, the same theoretical approach can be extended to reconstruct valid score sets given constraints on the frequency of distinct scores in tournaments. Based on these conditions, we have developed three algorithms that demonstrate the practical utility of our framework: a polynomial-time algorithm and a scalable algorithm for reconstructing score sequences, and a polynomial-time network-building method that finds all possible score sequences for a given score set. Moreover, the polynomial-time algorithm for reconstructing the score sequence of a tournament for a given score set can be used to verify Reid's conjecture. These algorithms have practical applications in sports analysis, ranking prediction, and machine learning tasks such as learning-to-rank models and data imputation, where the reconstruction of partial rankings or sequences is essential for recommendation systems and anomaly detection.