Logic in Computer Science
Covers all aspects of logic in computer science, including finite model theory, logics of programs, modal logic, and program verification.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Covers all aspects of logic in computer science, including finite model theory, logics of programs, modal logic, and program verification.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
 2601.03849
2601.03849LPTP (Logic Program Theorem Prover) is an interactive natural-deduction-based theorem prover for pure Prolog programs with negation as failure, unification with the occurs check, and a restricted but extensible set of built-in predicates. With LPTP, one can formally prove termination and partial correctness of such Prolog programs. LPTP was designed in the mid-1990's by Robert F. Staerk. It is written in ISO-Prolog and comes with an Emacs user-interface. From a theoretical point of view, in his publications about LPTP, Staerk associates a set of first-order axioms IND(P) to the considered Prolog program P. IND(P) contains the Clark's equality theory for P, definitions of success, failure and termination for each user-defined logic procedure in P, axioms relating these three points of view, and an axiom schema for proving inductive properties. LPTP is thus a dedicated proof editor where these axioms are hard-wired. We propose to translate these axioms as first-order formulas (FOFs), and apply automated theorem provers to check the property of interest. Using FOF as an intermediary language, we experiment the use of automated theorem provers for Prolog program verification. We evaluate the approach over a benchmark of about 400 properties of Prolog programs from the library available with LPTP. Both the compiler which generates a set of FOF files from a given input Prolog program together with its properties and the benchmark are publicly available.
We present automated theorem provers for the first-order logic of here and there (HT). They are based on a native sequent calculus for the logic of HT and an axiomatic embedding of the logic of HT into intuitionistic logic. The analytic proof search in the sequent calculus is optimized by using free variables and skolemization. The embedding is used in combination with sequent, tableau and connection calculi for intuitionistic first-order logic. All provers are evaluated on a large benchmark set of first-order formulas, providing a foundation for the development of more efficient HT provers.
The logical semantics of normal logic programs has traditionally been based on the notions of Clark's completion and two-valued or three-valued canonical models, including supported, stable, regular, and well-founded models. Two-valued interpretations can also be seen as states evolving under a program's update operator, producing a transition graph whose fixed points and cycles capture stable and oscillatory behaviors, respectively. We refer to this view as dynamical semantics since it characterizes the program's meaning in terms of state-space trajectories, as first introduced in the stable (supported) class semantics. Recently, we have established a formal connection between Datalog^\neg programs (i.e., normal logic programs without function symbols) and Boolean networks, leading to the introduction of the trap space concept for Datalog^\neg programs. In this paper, we generalize the trap space concept to arbitrary normal logic programs, introducing trap space semantics as a new approach to their interpretation. This new semantics admits both model-theoretic and dynamical characterizations, providing a comprehensive approach to understanding program behavior. We establish the foundational properties of the trap space semantics and systematically relate it to the established model-theoretic semantics, including the stable (supported), stable (supported) partial, regular, and L-stable model semantics, as well as to the dynamical stable (supported) class semantics. Our results demonstrate that the trap space semantics offers a unified and precise framework for proving the existence of supported classes, strict stable (supported) classes, and regular models, in addition to uncovering and formalizing deeper relationships among the existing semantics of normal logic programs.
 2601.03841
2601.03841DatalogMTL with negation is an extension of Datalog with metric temporal operators enriched with unstratifiable negation. In this paper, we define the stable, well-founded, Kripke-Kleene, and supported model semantics for DatalogMTL with negation in a very simple and straightforward way, by using the solid mathematical formalism of Approximation Fixpoint Theory (AFT). Moreover, we prove that the stable model semantics obtained via AFT coincides with the one defined in previous work, through the employment of pairs of interpretations stemming from the logic of here-and-there.
Expressive querying of machine learning models - viewed as a form of intentional data - enables their verification and interpretation using declarative languages, thereby making learned representations of data more accessible. Motivated by the querying of feedforward neural networks, we investigate logics for weighted structures. In the absence of a bound on neural network depth, such logics must incorporate recursion; thereto we revisit the functional fixpoint mechanism proposed by Grädel and Gurevich. We adopt it in a Datalog-like syntax; we extend normal forms for fixpoint logics to weighted structures; and show an equivalent "loose" fixpoint mechanism that allows values of inductively defined weight functions to be overwritten. We propose a "scalar" restriction of functional fixpoint logic, of polynomial-time data complexity, and show it can express all PTIME model-agnostic queries over reduced networks with polynomially bounded weights. In contrast, we show that very simple model-agnostic queries are already NP-complete. Finally, we consider transformations of weighted structures by iterated transductions.
 2601.03298
2601.03298This is a brief description of a project that has already autoformalized a large portion of the general topology from the Munkres textbook (which has in total 241 pages in 7 chapters and 39 sections). The project has been running since November 21, 2025 and has as of January 4, 2026, produced 160k lines of formalized topology. Most of it (about 130k lines) have been done in two weeks,from December 22 to January 4, for an LLM subscription cost of about \$100. This includes a 3k-line proof of Urysohn's lemma, a 2k-line proof of Urysohn's Metrization theorem, over 10k-line proof of the Tietze extension theorem, and many more (in total over 1.5k lemmas/theorems). The approach is quite simple and cheap: build a long-running feedback loop between an LLM and a reasonably fast proof checker equipped with a core foundational library. The LLM is now instantiated as ChatGPT (mostly 5.2) or Claude Sonnet (4.5) run through the respective Codex or Claude Code command line interfaces. The proof checker is Chad Brown's higher-order set theory system Megalodon, and the core library is Brown's formalization of basic set theory and surreal numbers (including reals, etc). The rest is some prompt engineering and technical choices which we describe here. Based on the fast progress, low cost, virtually unknown ITP/library, and the simple setup available to everyone, we believe that (auto)formalization may become quite easy and ubiquitous in 2026, regardless of which proof assistant is used.
In this paper, we address the complexity barrier inherent in Fourier-Motzkin elimination (FME) and cylindrical algebraic decomposition (CAD) when eliminating a block of (existential) quantifiers. To mitigate this, we propose exploiting structural sparsity in the variable dependency graph of quantified formulas. Utilizing tools from parameterized algorithms, we investigate the role of treewidth, a parameter that measures the graph's tree-likeness, in the process of quantifier elimination. A novel dynamic programming framework, structured over a tree decomposition of the dependency graph, is developed for applying FME and CAD, and is also extensible to general quantifier elimination procedures. Crucially, we prove that when the treewidth is a constant, the framework achieves a significant exponential complexity improvement for both FME and CAD, reducing the worst-case complexity bound from doubly exponential to single exponential. Preliminary experiments on sparse linear real arithmetic (LRA) and nonlinear real arithmetic (NRA) benchmarks confirm that our algorithm outperforms the existing popular heuristic-based approaches on instances exhibiting low treewidth.
 2512.24980
2512.24980We introduce a two-sort weighted modal logic for possibilistic reasoning with fuzzy formal contexts. The syntax of the logic includes two types of weighted modal operators corresponding to classical necessity ($\Box$) and sufficiency ($\boxminus$) modalities and its formulas are interpreted in fuzzy formal contexts based on possibility theory. We present its axiomatization that is \emph{sound} with respect to the class of all fuzzy context models. In addition, both the necessity and sufficiency fragments of the logic are also individually complete with respect to the class of all fuzzy context models. We highlight the expressive power of the logic with some illustrative examples. As a formal context is the basic construct of formal concept analysis (FCA), we generalize three main notions in FCA, i.e., formal concepts, object oriented concepts, and property oriented concepts, to their corresponding $c$-cut concepts in fuzzy formal contexts. Then, we show that our logical language can represent all three of these generalized notions. Finally, we demonstrate the possibility of extending our logic to reasoning with multi-relational fuzzy contexts, in which the Boolean combinations of different fuzzy relations are allowed.
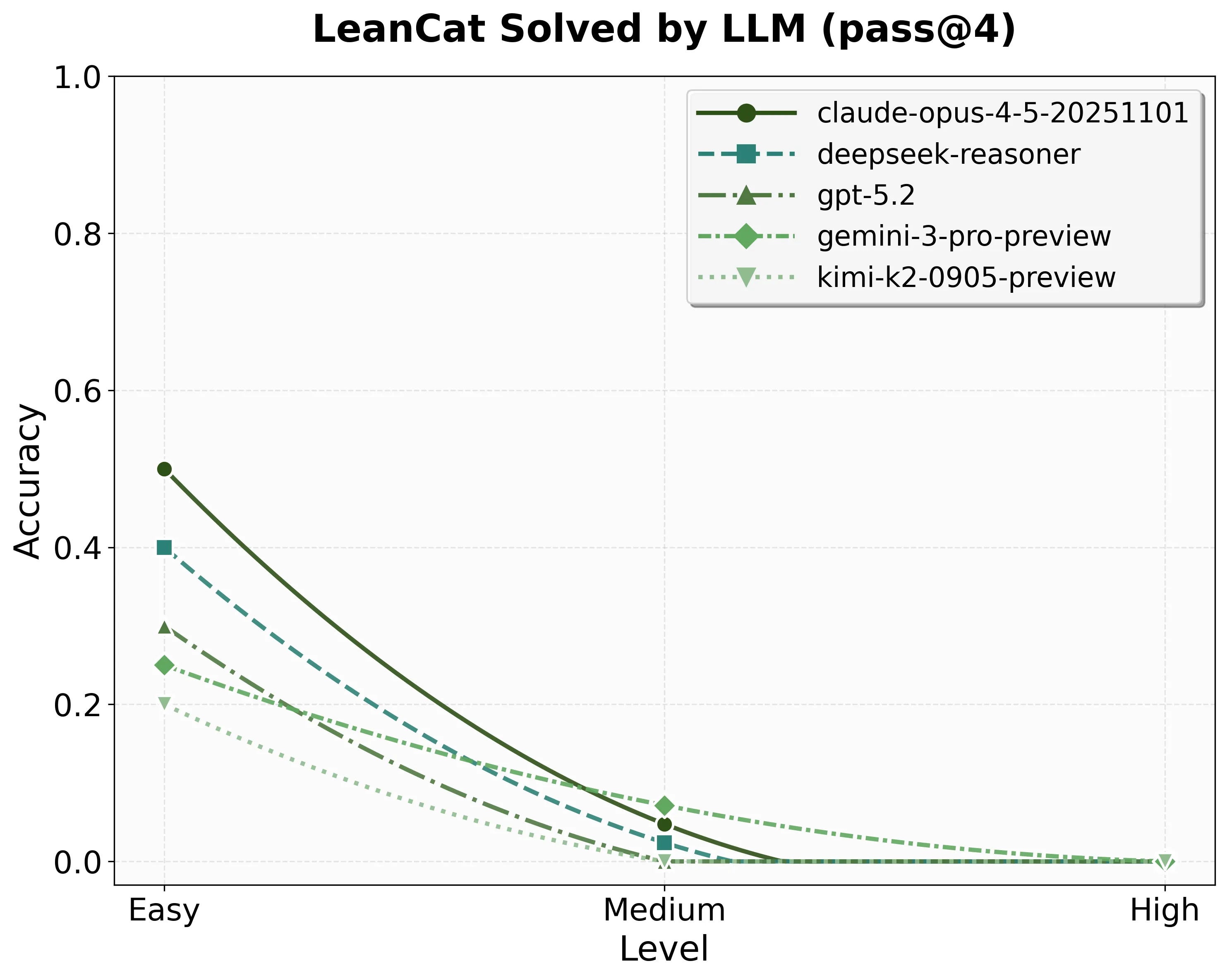
Large language models (LLMs) have made rapid progress in formal theorem proving, yet current benchmarks under-measure the kind of abstraction and library-mediated reasoning that organizes modern mathematics. In parallel with FATE's emphasis on frontier algebra, we introduce LeanCat, a Lean benchmark for category-theoretic formalization -- a unifying language for mathematical structure and a core layer of modern proof engineering -- serving as a stress test of structural, interface-level reasoning. Part I: 1-Categories contains 100 fully formalized statement-level tasks, curated into topic families and three difficulty tiers via an LLM-assisted + human grading process. The best model solves 8.25% of tasks at pass@1 (32.50%/4.17%/0.00% by Easy/Medium/High) and 12.00% at pass@4 (50.00%/4.76%/0.00%). We also evaluate LeanBridge which use LeanExplore to search Mathlib, and observe consistent gains over single-model baselines. LeanCat is intended as a compact, reusable checkpoint for tracking both AI and human progress toward reliable, research-level formalization in Lean.
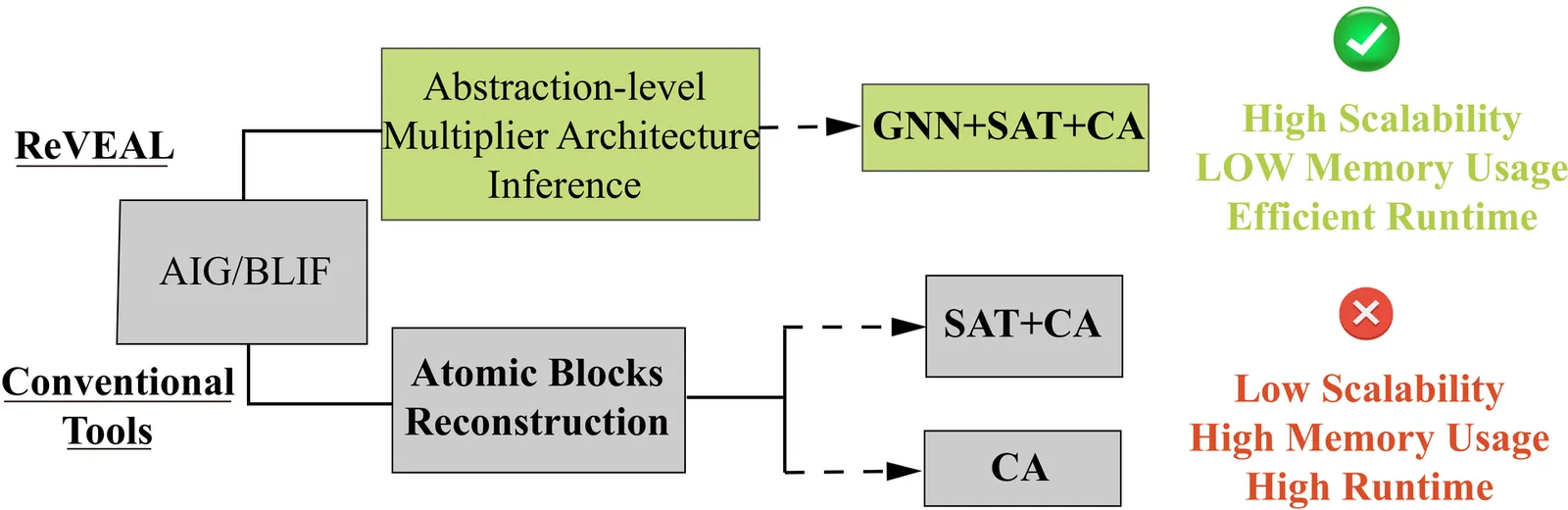
We present ReVEAL, a graph-learning-based method for reverse engineering of multiplier architectures to improve algebraic circuit verification techniques. Our framework leverages structural graph features and learning-driven inference to identify architecture patterns at scale, enabling robust handling of large optimized multipliers. We demonstrate applicability across diverse multiplier benchmarks and show improvements in scalability and accuracy compared to traditional rule-based approaches. The method integrates smoothly with existing verification flows and supports downstream algebraic proof strategies.
The correct use of a Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) interface in embedded applications is crucial to prevent malfunctions, crashes, or even hardware damage. Software model checking has been successfully applied to check interface specifications in application programs, but its employment in industrial practice is hindered by its unpredictability (whether it succeeds for a given application program or not). In this paper, we present a novel approach to address this problem by checking the HAL interface specification continuously and right from the start of the development. I.e., we develop an embedded application in several iterations without a formal connection between the steps. The steps start from a program skeleton which does nothing but calling HAL functions. Actual functionality is added consecutively. The HAL interface specification is checked in each step of the sequence. The idea of the approach is to exploit a specific feature of software model checking: Its attempt to compute exactly the abstraction that is needed for the check to succeed may carry over from one step to the next, even if there is no formal connection between the steps. The experience from a preliminary experimental evaluation of our approach in the development of embedded applications is very promising. Following our approach, the check succeeds in each step and in particular in the final application program.
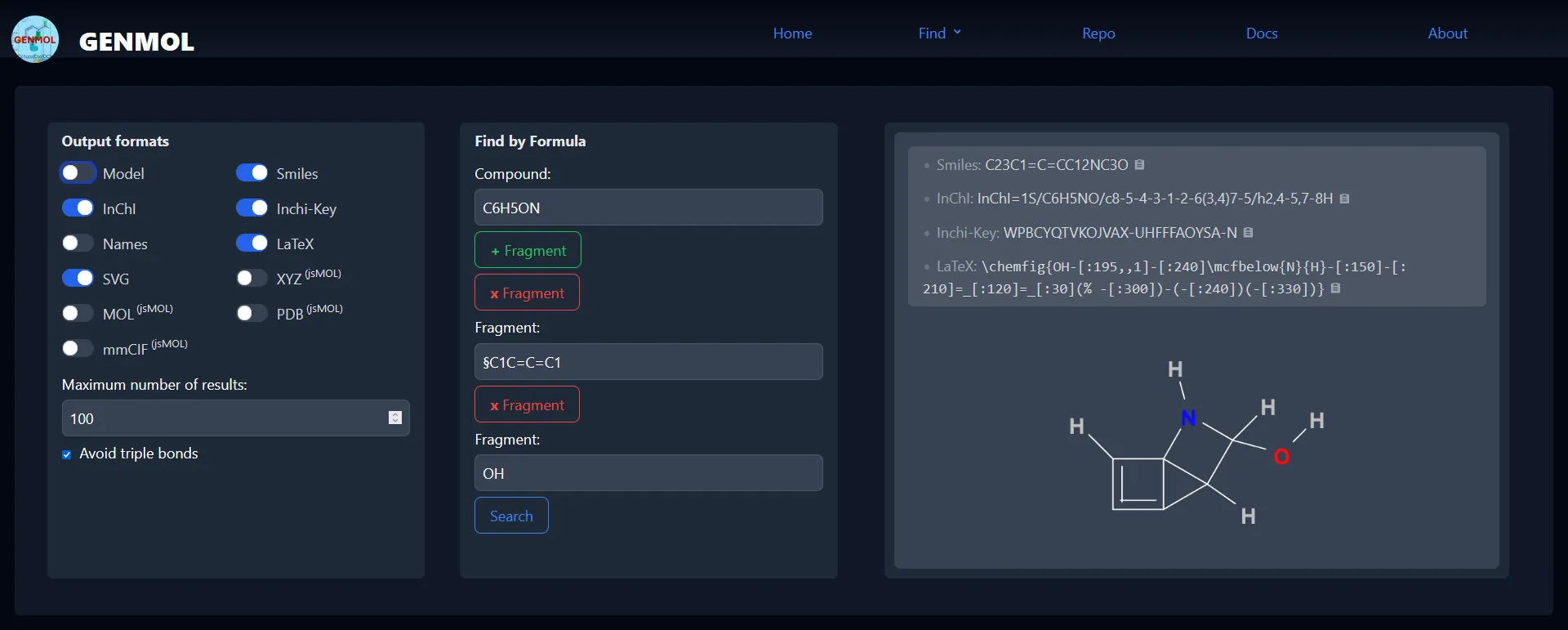
We present a new use of Answer Set Programming (ASP) to discover the molecular structure of chemical samples based on the relative abundance of elements and structural fragments, as measured in mass spectrometry. To constrain the exponential search space for this combinatorial problem, we develop canonical representations of molecular structures and an ASP implemen- tation that uses these definitions. We evaluate the correctness of our implementation over a large set of known molecular structures, and we compare its quality and performance to other ASP symmetry-breaking methods and to a commercial tool from analytical chemistry. Under consideration in Theory and Practice of Logic Programming (TPLP).
 2512.16697
2512.16697We provide a formulation of the univalence axiom in a universe category model of dependent type theory that is convenient to verify in homotopy-theoretic settings. We further develop a strengthening of the univalence axiom, called pointed univalence, that is both computationally desirable and semantically natural, and verify its closure under Artin-Wraith gluing and formation of inverse diagrams.
Rigorous modelling of natural and industrial systems still conveys various challenges related to abstractions, methods to proceed with and easy-to-use tools to build, compose and reason on models. Operads are mathematical structures that provide such abstractions to compose various objects and garanteeing well-formedness. Concrete implementations of operads will offer practical means to exploit operads and to use them for various technical applications. Going from the mathematical structures, we develop with Event-B a complete refinement chain that implements algebraic operads and their basic operations. The result of this work, can be used from the methodological point of view to handle similar implementations for symbolic computation questions, and also to reason on symbolic computation applications supported by operads structures.
Dynamic logic is a logic for reasoning about programs. A cyclic proof system is a proof system that allows proofs containing cycles and is an alternative to a proof system containing (co-)induction. This paper introduces a sequent calculus and a non-labelled cyclic proof system for an extension of propositional dynamic logic obtained by adding backwards modal operators. We prove the soundness and completeness of these systems and show that cut-elimination fails in both. Moreover, we show the cut-elimination property of the cyclic proof system for propositional dynamic logic obtained by restricting ours.
We provide a novel semantics for belief using simplicial complexes. In our framework, belief satisfies the \textsf{KD45} axioms and rules as well as the ``knowledge implies belief'' axiom ($Kφ\lthen Bφ$); in addition, we adopt the (standard) assumption that each facet in our simplicial models has exactly one vertex of every color. No existing model of belief in simplicial complexes that we are aware of is able to satisfy all of these conditions without trivializing belief to coincide with knowledge. We also address the common technical assumption of ``properness'' for relational structures made in the simplicial semantics literature, namely, that no two worlds fall into the same knowledge cell for all agents; we argue that there are conceptually sensible belief frames in which this assumption is violated, and use the result of ``A Note on Proper Relational Structures'' to bypass this restriction. We conclude with a discussion of how an alternative ``simplicial sets'' framework could allow us to bypass properness altogether and perhaps provide a more streamlined simplicial framework for representing belief.
Embedded applications often use a Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) to access hardware. Improper use of the HAL can lead to incorrect hardware operations, resulting in system failure and potentially serious damage to the hardware. The question is how one can obtain prioritize, among a possibly large set of HAL interface requirements, those that are indisputably relevant for preventing this kind of system failure. In this paper, we introduce a formal notion of relevance. This allows us to leverage a formal method, i.e., software model checking, to produce a mathematical proof that a requirement is indisputably relevant. We propose an approach to extract provably relevant requirements from issue reports on system failures. We present a case study to demonstrate that the approach is feasible in principle. The case study uses three examples of issue reports on embedded applications that use the SPI bus via the spidev HAL. The overall contribution of this paper is to pave the way for the study of approaches to a new kind of prioritization aimed at preventing a specific kind of system failure.
Petri nets are a modeling formalism capable of describing complex distributed systems and there exists a large number of both academic and industrial tools that enable automatic verification of model properties. Typical questions include reachability analysis and model checking against logics like LTL and CTL. However, these logics fall short when describing properties like non-interference and observational determinism that require simultaneous reasoning about multiple traces of the model and can thus only be expressed as hyperproperties. We introduce, to the best of our knowledge, the first HyperLTL model checker for Petri nets. The tool is fully integrated into the verification framework TAPAAL and we describe the semantics of the hyperlogic, present the tool's architecture and GUI, and evaluate the performance of the HyperLTL verification engine on two benchmarks of problems originating from the computer networking domain.
In this paper, we investigate how language models can perform case-based reasoning (CBR) on non-factorized case bases. We introduce a novel framework, argumentative agentic models for case-based reasoning (AAM-CBR), which extends abstract argumentation for case-based reasoning (AA-CBR). Unlike traditional approaches that require factorization of previous cases, AAM-CBR leverages language models to determine case coverage and extract factors based on new cases. This enables factor-based reasoning without exposing or preprocessing previous cases, thus improving both flexibility and privacy. We also present initial experiments to assess AAM-CBR performance by comparing the proposed framework with a baseline that uses a single-prompt approach to incorporate both new and previous cases. The experiments are conducted based on a synthetic credit card application dataset. The result shows that AAM-CBR surpasses the baseline only when the new case contains a richer set of factors. The finding indicates that language models can handle case-based reasoning with a limited number of factors, but face challenges as the number of factors increase. Consequently, integrating symbolic reasoning with language models, as implemented in AAM-CBR, is crucial for effectively handling cases involving many factors.
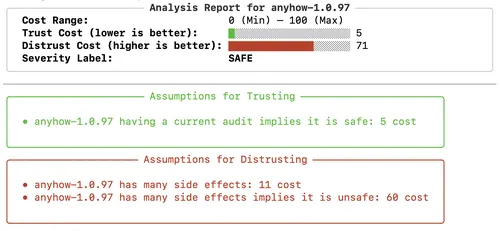
Supply chain attacks threaten open-source software ecosystems. This paper proposes a formal framework for quantifying trust in third-party software dependencies that is both formally checkable - formalized in satisfiability modulo theories (SMT) - while at the same time incorporating human factors, like the number of downloads, authors, and other metadata that are commonly used to identify trustworthy software in practice. We use data from both software analysis tools and metadata to build a first-order relational model of software dependencies; to obtain an overall "trust cost" combining these factors, we propose a formalization based on the minimum trust problem which asks for the minimum cost of a set of assumptions which can be used to prove that the code is safe. We implement these ideas in Cargo Sherlock, targeted for Rust libraries (crates), incorporating a list of candidate assumptions motivated by quantifiable trust metrics identified in prior work. Our evaluation shows that Cargo Sherlock can be used to identify synthetically generated supply chain attacks and known incidents involving typosquatted and poorly AI-maintained crates, and that its performance scales to Rust crates with many dependencies.