Performance
Covers performance measurement, evaluation, and simulation of computer systems.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Covers performance measurement, evaluation, and simulation of computer systems.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
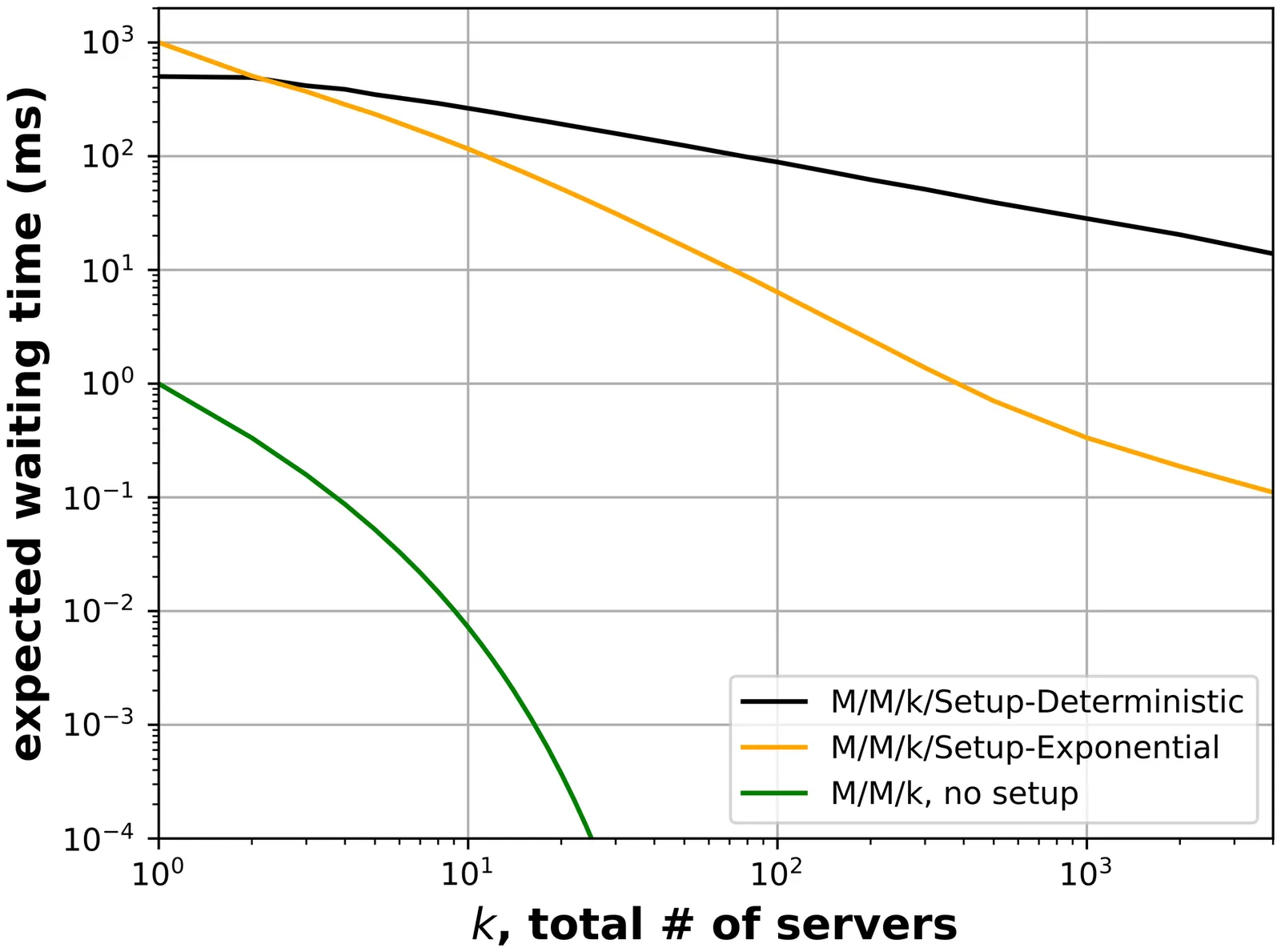
In many systems, servers do not turn on instantly; instead, a setup time must pass before a server can begin work. These "setup times" can wreak havoc on a system's queueing; this is especially true in modern systems, where servers are regularly turned on and off as a way to reduce operating costs (energy, labor, CO2, etc.). To design modern systems which are both efficient and performant, we need to understand how setup times affect queues. Unfortunately, despite successes in understanding setup in a single-server system, setup in a multiserver system remains poorly understood. To circumvent the main difficulty in analyzing multiserver setup, all existing results assume that setup times are memoryless, i.e. distributed Exponentially. However, in most practical settings, setup times are close to Deterministic, and the widely used Exponential-setup assumption leads to unrealistic model behavior and a dramatic underestimation of the true harm caused by setup times. This paper provides a comprehensive characterization of the average waiting time in a multiserver system with Deterministic setup times, the M/M/k/Setup-Deterministic. In particular, we derive upper and lower bounds on the average waiting time in this system, and show these bounds are within a multiplicative constant of each other. These bounds are the first closed-form characterization of waiting time in any finite-server system with setup times. Further, we demonstrate how to combine our upper and lower bounds to derive a simple and accurate approximation for the average waiting time. These results are all made possible via a new technique for analyzing random time integrals that we named the Method of Intervening Stopping Times, or MIST.
Achieving high efficiency on AI operators demands precise control over computation and data movement. However, existing scheduling languages are locked into specific compiler ecosystems, preventing fair comparison, reuse, and evaluation across frameworks. No unified interface currently decouples scheduling specification from code generation and measurement. We introduce XTC, a platform that unifies scheduling and performance evaluation across compilers. With its common API and reproducible measurement framework, XTC enables portable experimentation and accelerates research on optimization strategies.
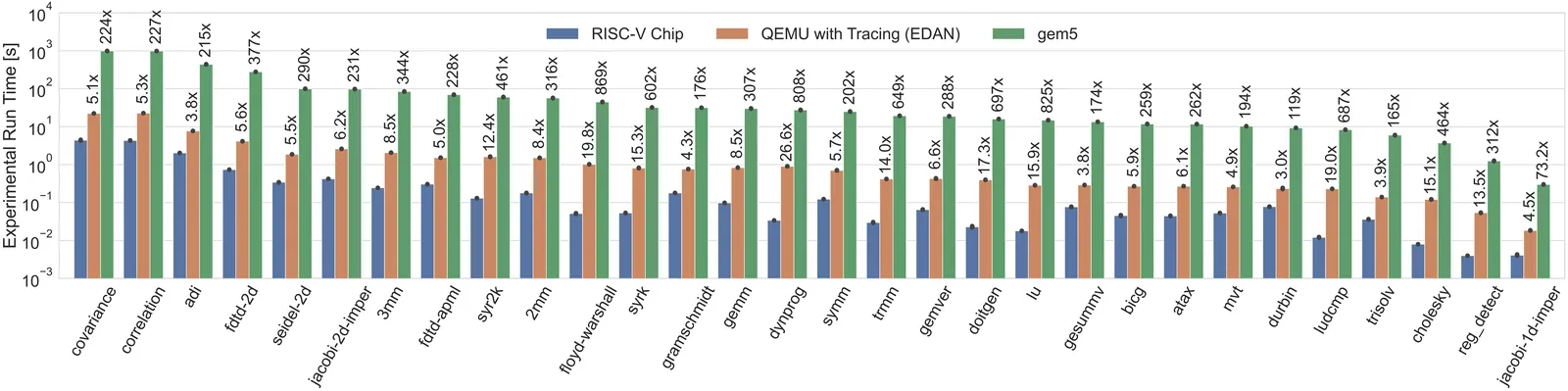
Resource disaggregation is a promising technique for improving the efficiency of large-scale computing systems. However, this comes at the cost of increased memory access latency due to the need to rely on the network fabric to transfer data between remote nodes. As such, it is crucial to ascertain an application's memory latency sensitivity to minimize the overall performance impact. Existing tools for measuring memory latency sensitivity often rely on custom ad-hoc hardware or cycle-accurate simulators, which can be inflexible and time-consuming. To address this, we present EDAN (Execution DAG Analyzer), a novel performance analysis tool that leverages an application's runtime instruction trace to generate its corresponding execution DAG. This approach allows us to estimate the latency sensitivity of sequential programs and investigate the impact of different hardware configurations. EDAN not only provides us with the capability of calculating the theoretical bounds for performance metrics, but it also helps us gain insight into the memory-level parallelism inherent to HPC applications. We apply EDAN to applications and benchmarks such as PolyBench, HPCG, and LULESH to unveil the characteristics of their intrinsic memory-level parallelism and latency sensitivity.
The performance of algorithms, methods, and models tends to depend heavily on the distribution of cases on which they are applied, this distribution being specific to the applicative domain. After performing an evaluation in several domains, it is highly informative to compute a (weighted) mean performance and, as shown in this paper, to scrutinize what happens during this averaging. To achieve this goal, we adopt a probabilistic framework and consider a performance as a probability measure (e.g., a normalized confusion matrix for a classification task). It appears that the corresponding weighted mean is known to be the summarization, and that only some remarkable scores assign to the summarized performance a value equal to a weighted arithmetic mean of the values assigned to the domain-specific performances. These scores include the family of ranking scores, a continuum parameterized by user preferences, and that the weights to consider in the arithmetic mean depend on the user preferences. Based on this, we rigorously define four domains, named easiest, most difficult, preponderant, and bottleneck domains, as functions of user preferences. After establishing the theory in a general setting, regardless of the task, we develop new visual tools for two-class classification.
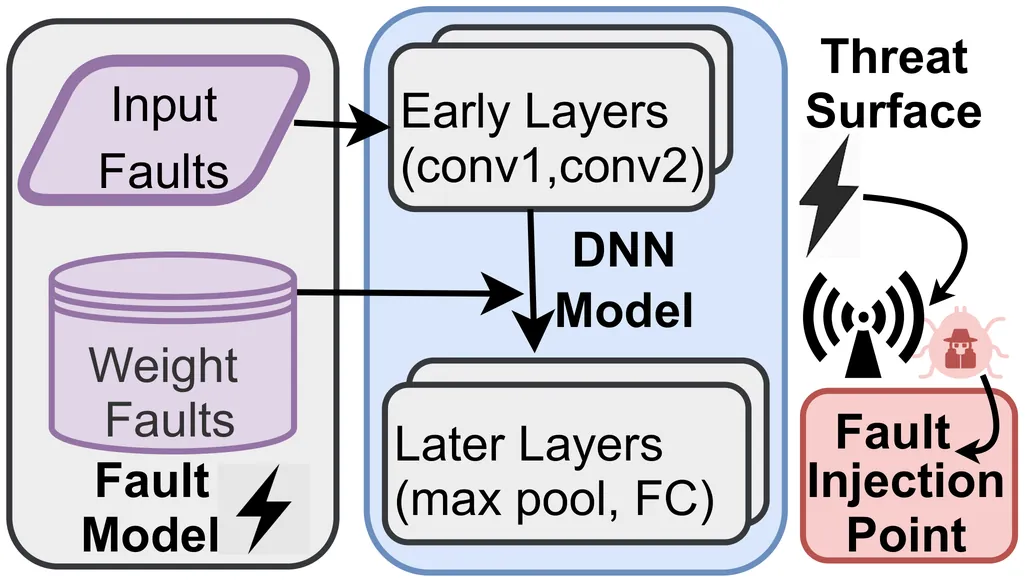
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are increasingly deployed across distributed and resource-constrained platforms, such as System-on-Chip (SoC) accelerators and edge-cloud systems. DNNs are often partitioned and executed across heterogeneous processing units to optimize latency and energy. However, the reliability of these partitioned models under hardware faults and communication errors remains a critical yet underexplored topic, especially in safety-critical applications. In this paper, we propose an accuracy-aware, fault-resilient DNN partitioning framework targeting multi-objective optimization using NSGA-II, where accuracy degradation under fault conditions is introduced as a core metric alongside energy and latency. Our framework performs runtime fault injection during optimization and utilizes a feedback loop to prioritize fault-tolerant partitioning. We evaluate our approach on benchmark CNNs including AlexNet, SqueezeNet and ResNet18 on hardware accelerators, and demonstrate up to 27.7% improvement in fault tolerance with minimal increase in performance overhead. Our results highlight the importance of incorporating resilience into DNN partitioning, and thereby paving the way for robust AI inference in error-prone environments.
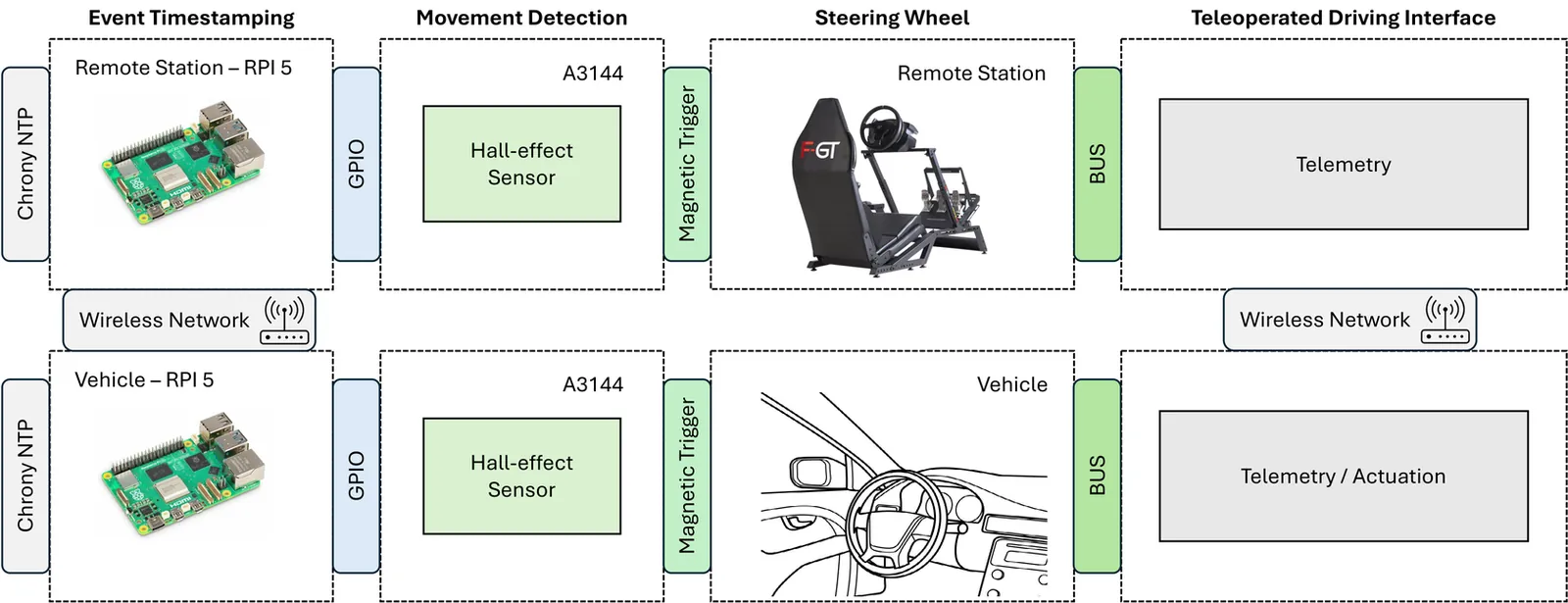
Latency is a key performance factor for the teleoperation of Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CAVs). It affects how quickly an operator can perceive changes in the driving environment and apply corrective actions. Most existing work focuses on Glass-to-Glass (G2G) latency, which captures delays only in the video pipeline. However, there is no standard method for measuring Motion-to-Motion (M2M) latency, defined as the delay between the physical steering movement of the remote operator and the corresponding steering motion in the vehicle. This paper presents an M2M latency measurement framework that uses Hall-effect sensors and two synchronized Raspberry Pi~5 devices. The system records interrupt-based timestamps on both sides to estimate M2M latency, independently of the underlying teleoperation architecture. Precision tests show an accuracy of 10--15~ms, while field results indicate that actuator delays dominate M2M latency, with median values above 750~ms.
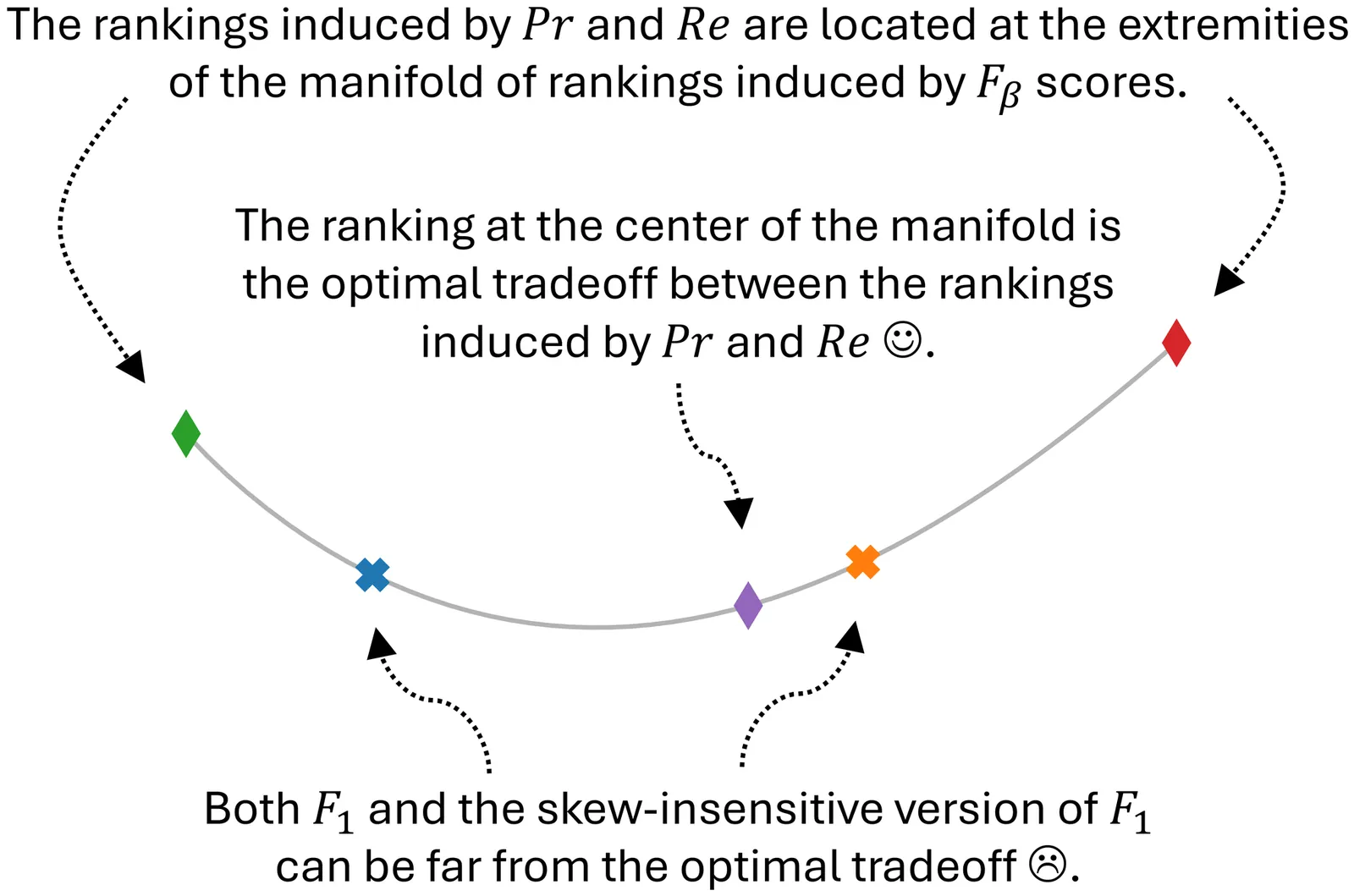
Ranking methods or models based on their performance is of prime importance but is tricky because performance is fundamentally multidimensional. In the case of classification, precision and recall are scores with probabilistic interpretations that are both important to consider and complementary. The rankings induced by these two scores are often in partial contradiction. In practice, therefore, it is extremely useful to establish a compromise between the two views to obtain a single, global ranking. Over the last fifty years or so,it has been proposed to take a weighted harmonic mean, known as the F-score, F-measure, or $F_β$. Generally speaking, by averaging basic scores, we obtain a score that is intermediate in terms of values. However, there is no guarantee that these scores lead to meaningful rankings and no guarantee that the rankings are good tradeoffs between these base scores. Given the ubiquity of $F_β$ scores in the literature, some clarification is in order. Concretely: (1) We establish that $F_β$-induced rankings are meaningful and define a shortest path between precision- and recall-induced rankings. (2) We frame the problem of finding a tradeoff between two scores as an optimization problem expressed with Kendall rank correlations. We show that $F_1$ and its skew-insensitive version are far from being optimal in that regard. (3) We provide theoretical tools and a closed-form expression to find the optimal value for $β$ for any distribution or set of performances, and we illustrate their use on six case studies.
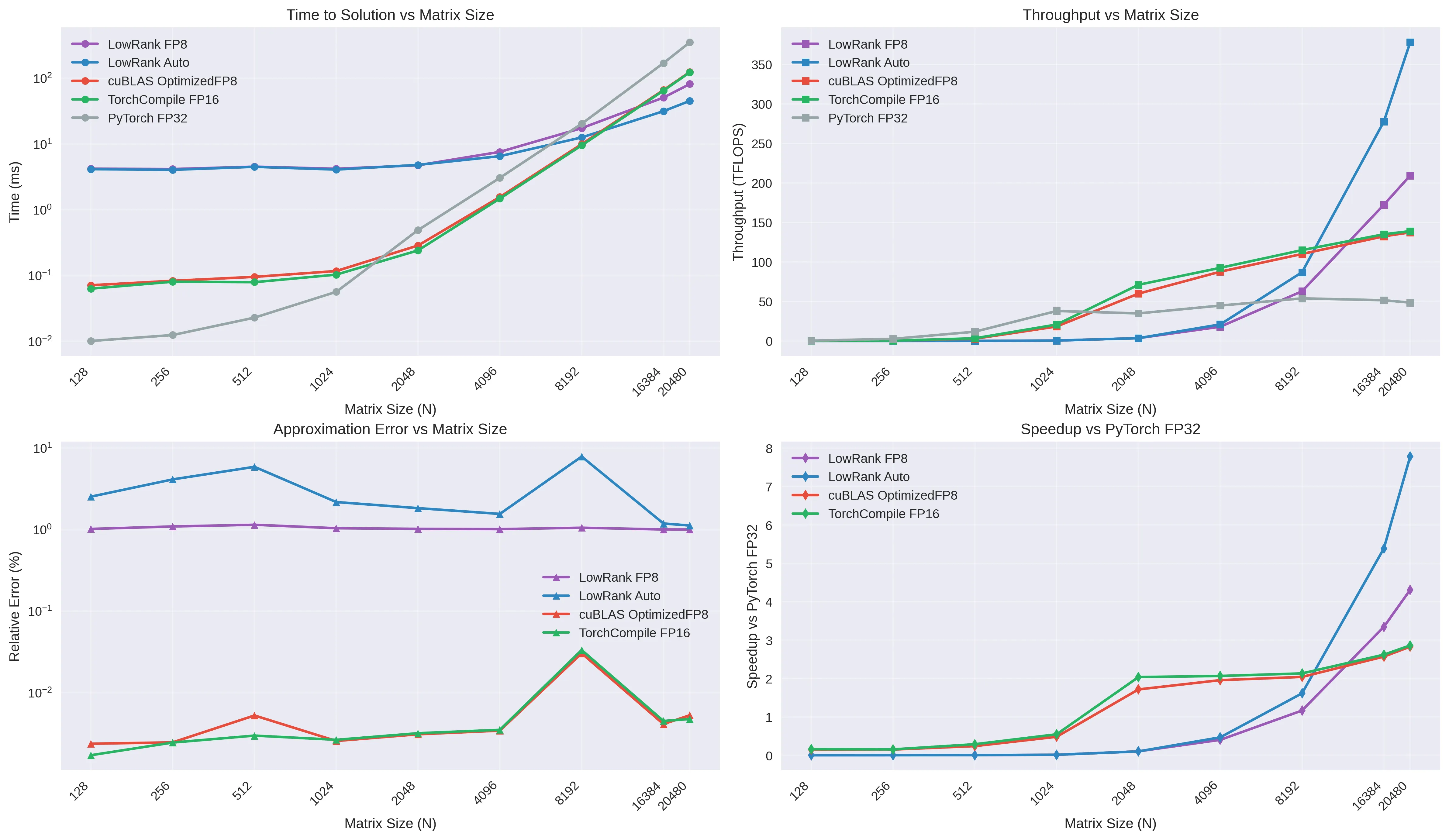
Large matrix multiplication is a cornerstone of modern machine learning workloads, yet traditional approaches suffer from cubic computational complexity (e.g., $\mathcal{O}(n^3)$ for a matrix of size $n\times n$). We present Low-Rank GEMM, a novel approach that leverages low-rank matrix approximations to achieve sub-quadratic complexity while maintaining hardware-accelerated performance through FP8 precision and intelligent kernel selection. On a NVIDIA RTX 4090, our implementation achieves up to 378 TFLOPS on matrices up to $N=20480$, providing 75\% memory savings and $7.8\times$ speedup over PyTorch FP32 for large matrices. The system automatically adapts to hardware capabilities, selecting optimal decomposition methods (SVD, randomized SVD) and precision levels based on matrix characteristics and available accelerators. Comprehensive benchmarking on NVIDIA RTX 4090 demonstrates that Low-Rank GEMM becomes the fastest approach for matrices $N\geq10240$, surpassing traditional cuBLAS implementations through memory bandwidth optimization rather than computational shortcuts.
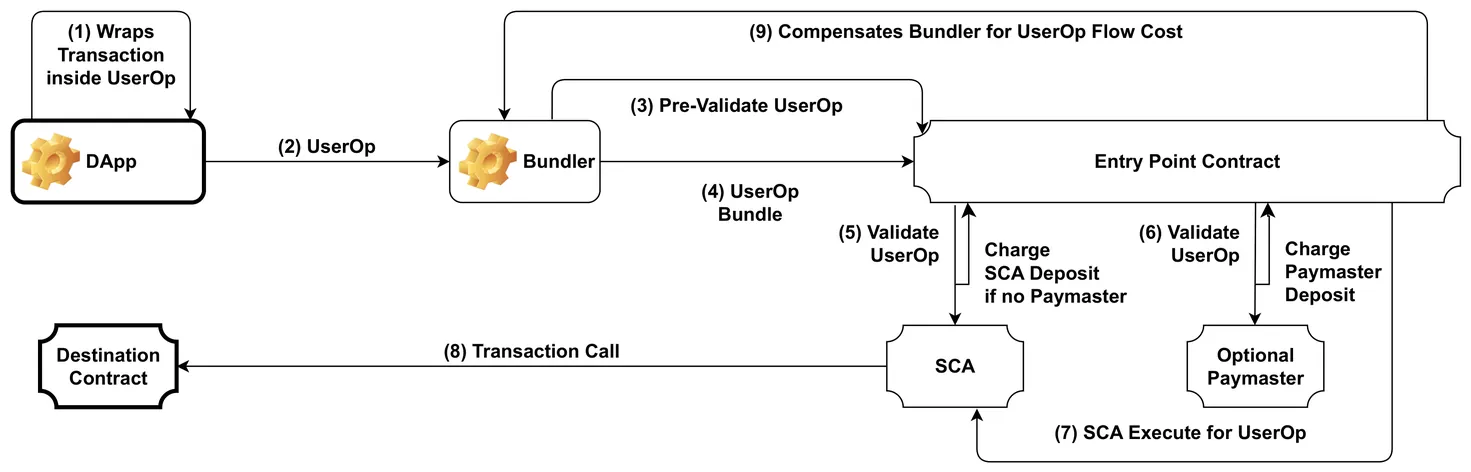
Ethereum is currently the main blockchain ecosystem providing decentralised trust guarantees for applications ranging from finance to e-government. A common criticism of blockchain networks has been their energy consumption and operational costs. The switch from Proof-of-Work (PoW) protocol to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) protocol has significantly reduced this issue, though concerns remain, especially with network expansions via additional layers. The ERC-4337 standard is a recent proposal that facilitates end-user access to Ethereum-backed applications. It introduces a middleware called a bundler, operated as a third-party service, where part of its operational cost is represented by its power consumption. While bundlers have served over 500 million requests in the past two years, fewer than 15 official bundler providers exist, compared to over 100 regular Ethereum access providers. In this paper, we provide a first look at the active power consumption overhead that a bundler would add to an Ethereum access service. Using SmartWatts, a monitoring system leveraging Running Average Power Limit (RAPL) hardware interfaces, we empirically determine correlations between the bundler workload and its active power consumption.
This work explores the use of the AMD Xilinx Versal Adaptable Intelligent Engine(AIE) to accelerate Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) inference for latency-Constrained applications. We present a custom workload distribution framework across the AIE's vector processors and propose a hybrid AIE - Programmable Logic (PL) design to optimize computational efficiency. Our approach highlights the potential of deploying adaptable neural networks in real-time environments such as online preprocessing in the readout chain of a physics experiment, offering a flexible alternative to traditional fixed-function algorithms.
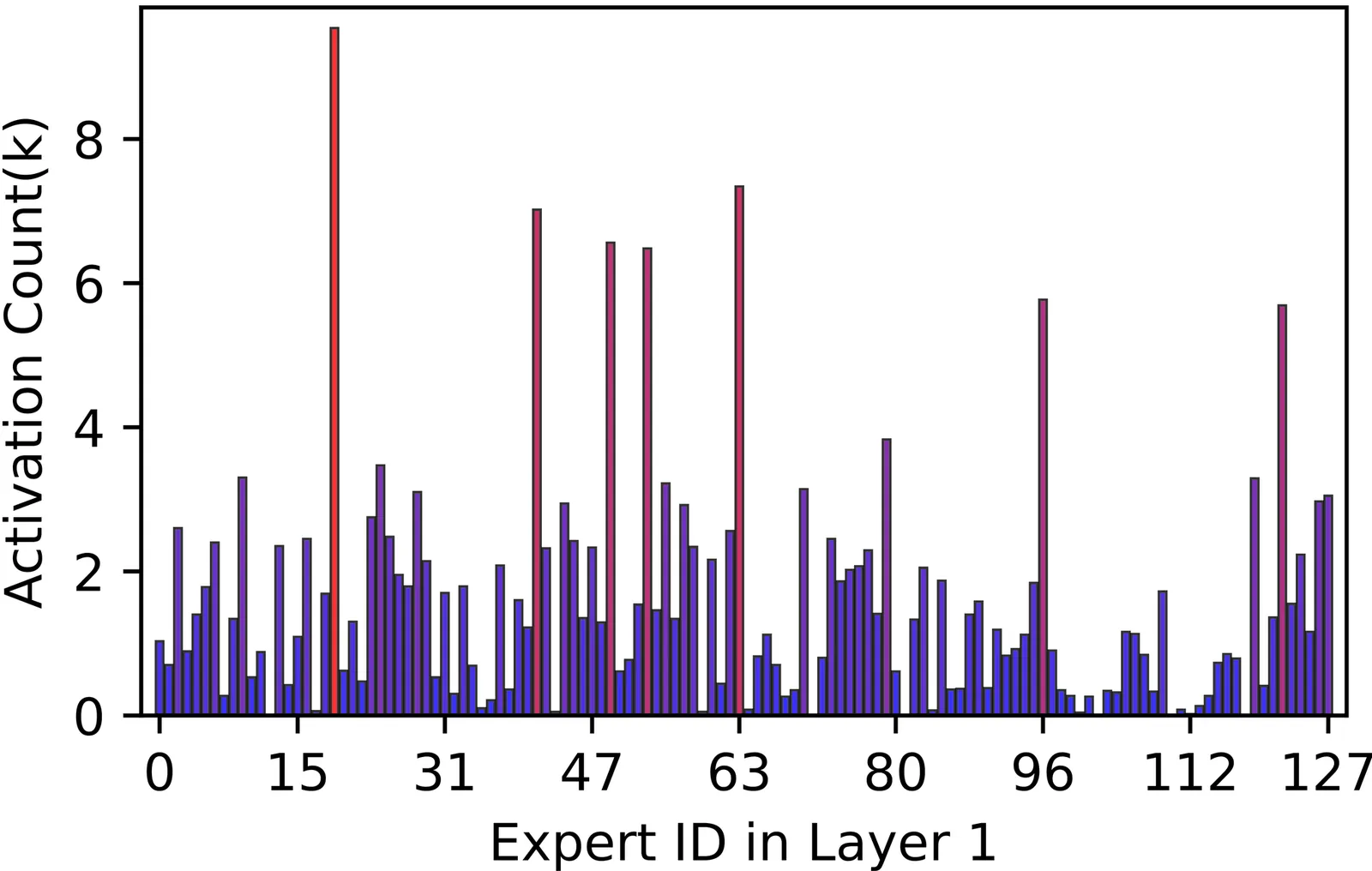
Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models scale LLM capacity efficiently, but deployment on consumer GPUs is limited by the large memory footprint of inactive experts. Static post-training quantization reduces storage costs but cannot adapt to shifting activation patterns, causing accuracy loss under aggressive compression. So we present DynaExq, a runtime system that treats expert precision as a first-class, dynamically managed resource. DynaExq combines (1) a hotness-aware precision controller that continuously aligns expert bit-widths with long-term activation statistics, (2) a fully asynchronous precision-switching pipeline that overlaps promotion and demotion with MoE computation, and (3) a fragmentation-free memory pooling mechanism that supports hybrid-precision experts with deterministic allocation. Together, these components enable stable, non-blocking precision transitions under strict HBM budgets. Across Qwen3-30B and Qwen3-80B MoE models and six representative benchmarks, DynaExq deploys large LLMs on single RTX 5090 and A6000 GPUs and improves accuracy by up to 4.03 points over static low-precision baselines. The results show that adaptive, workload-aware quantization is an effective strategy for memory-constrained MoE serving.
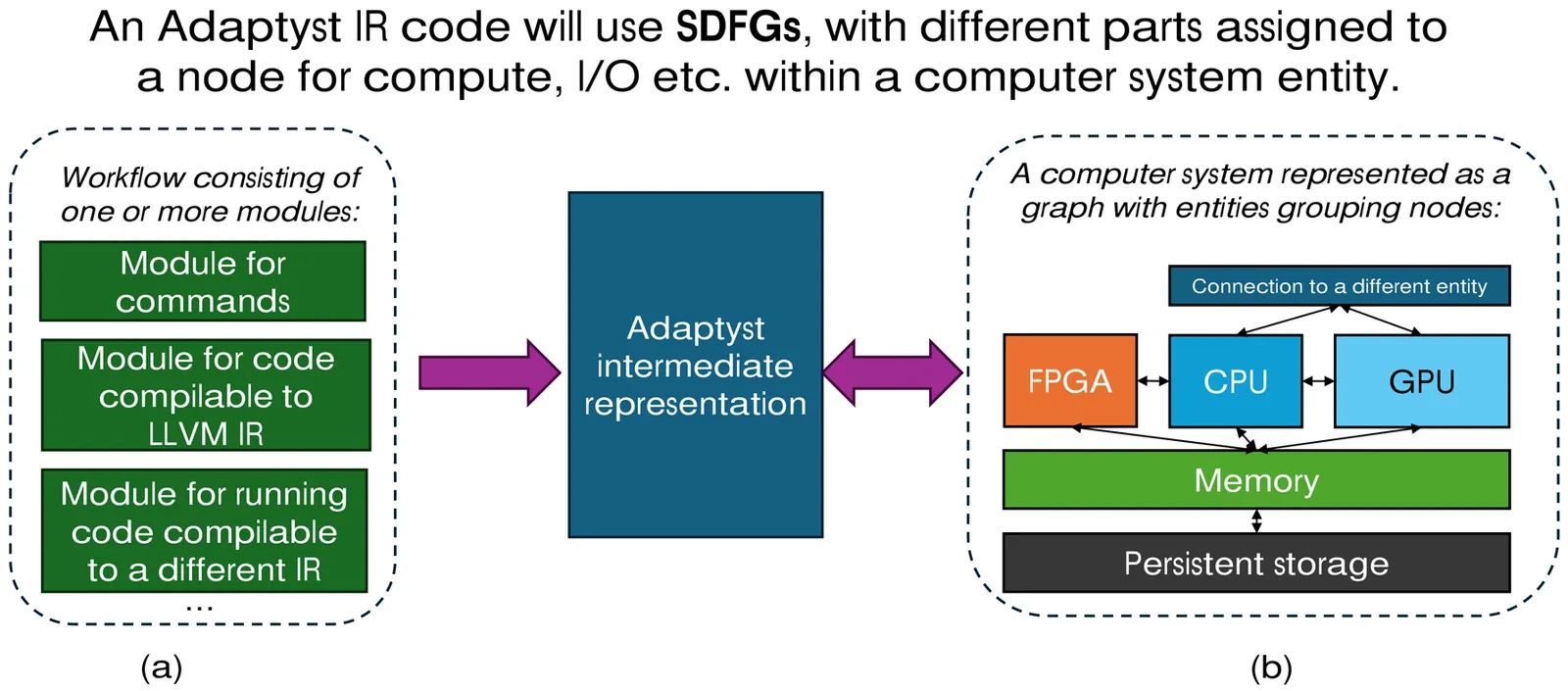
Heterogeneous computing integrates diverse processing elements, such as CPUs, GPUs, and FPGAs, within a single system, aiming to leverage the strengths of each architecture to optimize performance and energy consumption. In this context, efficient performance analysis plays a critical role in determining the most suitable platform for dispatching tasks, ensuring that workloads are allocated to the processing units where they can execute most effectively. Adaptyst is a novel ongoing effort at CERN, with the aim to develop an open-source, architecture-agnostic performance analysis for scientific workloads. This study explores the performance and implementation complexity of two built-in eBPF-based methods such as Uprobes and USDT, with the aim of outlining a roadmap for future integration into Adaptyst and advancing toward heterogeneous performance analysis capabilities.
The rise of AI and its growing computational demands have driven the integration of domain-specific accelerators (such as GPUs, TPUs, and NPUs) across the entire computing infrastructure. Following the precedent set by the GPGPU which popularized GPUs for general-purpose tasks, this research asks whether this phenomenon can be replicated with specialized accelerators like NPUs in new contexts. This paper evaluates the potential of the Apple Neural Engine (ANE) designed for high energy efficiency in Machine Learning workloads, in the context of general-purpose HPC applications. We evaluate the performance and energy consumption of classic HPC algorithms such as GEMM, Jacobi or Multigrid methods on Apple's ANE across the M1 and the latest M4 architectures. Results confirm that, when algorithms are properly adapted, the ANE achieves competitive performance (up to 3.8 TFlops on the M4-Pro, comparable to the GPU's 4.7 TFlops on the same SoC for GEMM operation) while demonstrating significantly superior energy efficiency (e.g., GEMM consumes 5.2 Watts on the ANE versus 24 Watts on GPU counterpart in M4 architectures).
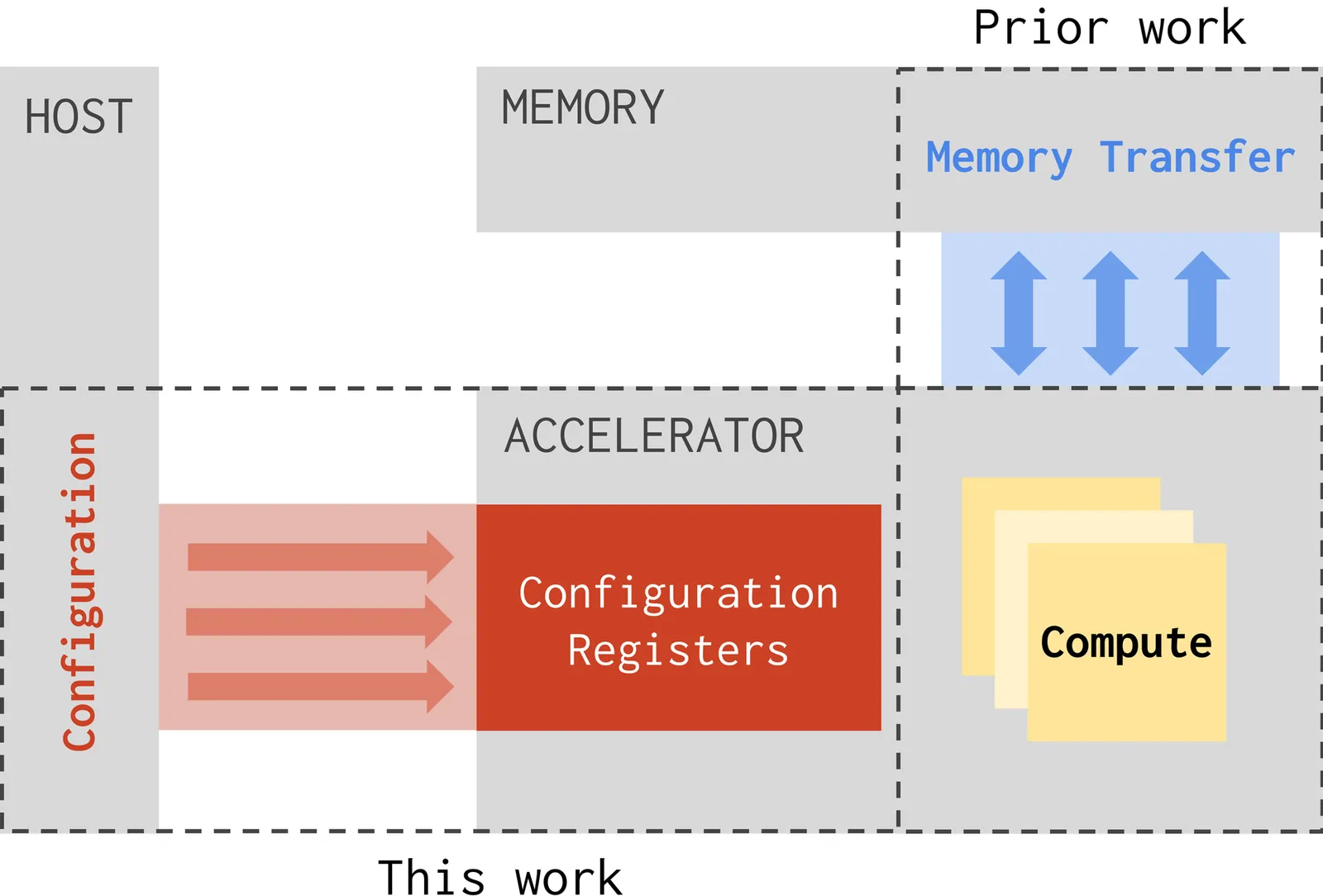
Contemporary compute platforms increasingly offload compute kernels from CPU to integrated hardware accelerators to reach maximum performance per Watt. Unfortunately, the time the CPU spends on setup control and synchronization has increased with growing accelerator complexity. For systems with complex accelerators, this means that performance can be configuration-bound. Faster accelerators are more severely impacted by this overlooked performance drop, which we call the configuration wall. Prior work evidences this wall and proposes ad-hoc solutions to reduce configuration overhead. However, these solutions are not universally applicable, nor do they offer comprehensive insights into the underlying causes of performance degradation. In this work, we first introduce a widely-applicable variant of the well-known roofline model to quantify when system performance is configuration-bound. To move systems out of the performance-bound region, we subsequently propose a domain-specific compiler abstraction and associated optimization passes. We implement the abstraction and passes in the MLIR compiler framework to run optimized binaries on open-source architectures to prove its effectiveness and generality. Experiments demonstrate a geomean performance boost of 2x on the open-source OpenGeMM system, by eliminating redundant configuration cycles and by automatically hiding the remaining configuration cycles. Our work provides key insights in how accelerator performance is affected by setup mechanisms, thereby facilitating automatic code generation for circumventing the configuration wall.
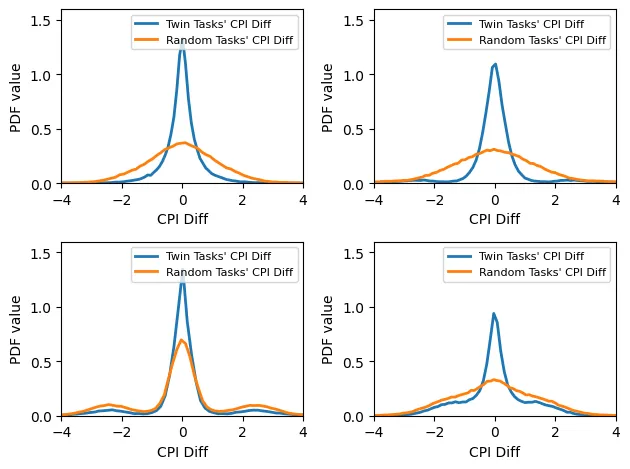
Modern warehouse-scale datacenters commonly collocate multiple jobs on shared machines to improve resource utilization. However, such collocation often leads to performance interference caused by antagonistic jobs that overconsume shared resources. Existing antagonist-detection approaches either rely on offline profiling, which is costly and unscalable, or use a sample-from-production approach, which suffers from noisy measurements and fails under multi-victim scenarios. We present PANDA, a noise-resilient antagonist identification framework for production-scale datacenters. Like prior correlation-based methods, PANDA uses cycles per instruction (CPI) as its performance metric, but it differs by (i) leveraging global historical knowledge across all machines to suppress sampling noise and (ii) introducing a machine-level CPI metric that captures shared-resource contention among multiple co-located tasks. Evaluation on a recent Google production trace shows that PANDA ranks true antagonists far more accurately than prior methods -- improving average suspicion percentile from 50-55% to 82.6% -- and achieves consistent antagonist identification under multi-victim scenarios, all with negligible runtime overhead.
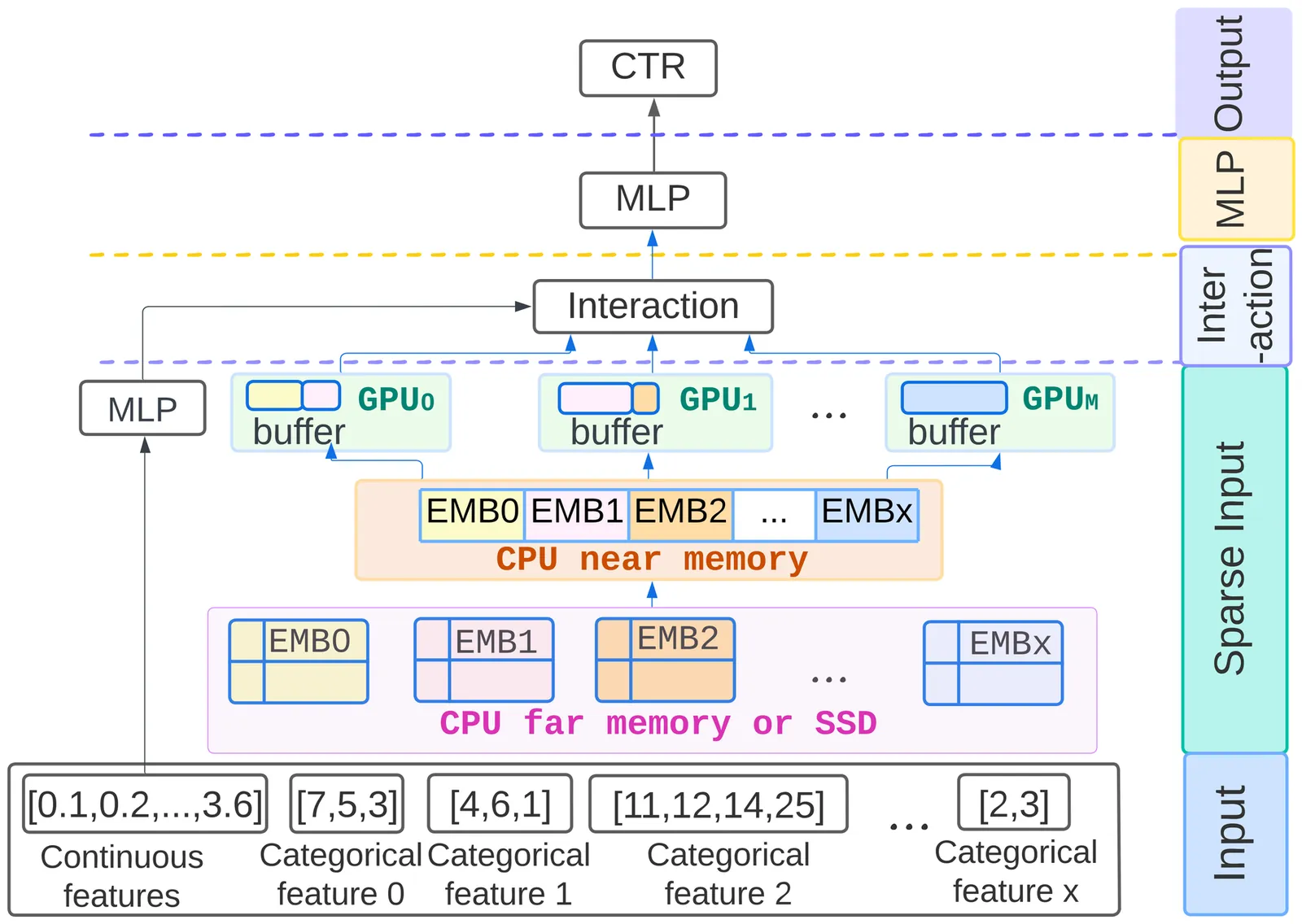
Deep learning recommendation models (DLRMs) are widely used in industry, and their memory capacity requirements reach the terabyte scale. Tiered memory architectures provide a cost-effective solution but introduce challenges in embedding-vector placement due to complex embedding-access patterns. We propose RecMG, a machine learning (ML)-guided system for vector caching and prefetching on tiered memory. RecMG accurately predicts accesses to embedding vectors with long reuse distances or few reuses. The design of RecMG focuses on making ML feasible in the context of DLRM inference by addressing unique challenges in data labeling and navigating the search space for embedding-vector placement. By employing separate ML models for caching and prefetching, plus a novel differentiable loss function, RecMG narrows the prefetching search space and minimizes on-demand fetches. Compared to state-of-the-art temporal, spatial, and ML-based prefetchers, RecMG reduces on-demand fetches by 2.2x, 2.8x, and 1.5x, respectively. In industrial-scale DLRM inference scenarios, RecMG effectively reduces end-to-end DLRM inference time by up to 43%.
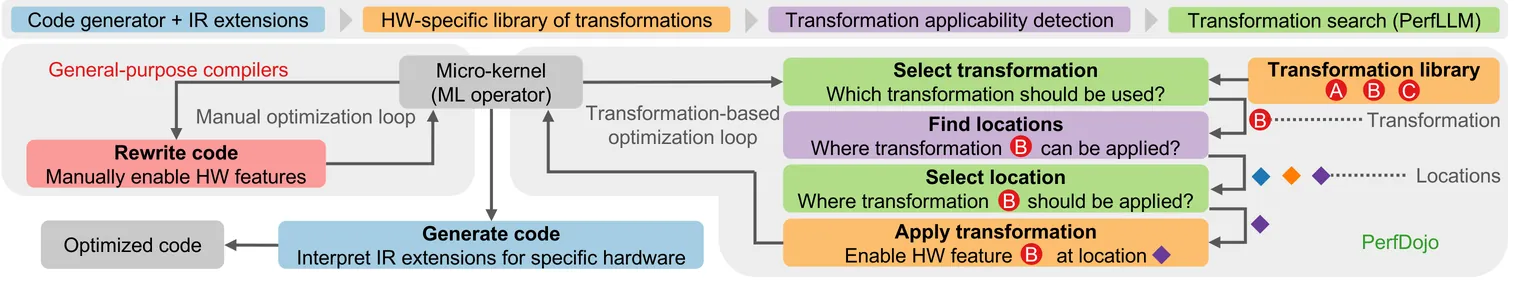
The increasing complexity of machine learning models and the proliferation of diverse hardware architectures (CPUs, GPUs, accelerators) make achieving optimal performance a significant challenge. Heterogeneity in instruction sets, specialized kernel requirements for different data types and model features (e.g., sparsity, quantization), and architecture-specific optimizations complicate performance tuning. Manual optimization is resource-intensive, while existing automatic approaches often rely on complex hardware-specific heuristics and uninterpretable intermediate representations, hindering performance portability. We introduce PerfLLM, a novel automatic optimization methodology leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). Central to this is PerfDojo, an environment framing optimization as an RL game using a human-readable, mathematically-inspired code representation that guarantees semantic validity through transformations. This allows effective optimization without prior hardware knowledge, facilitating both human analysis and RL agent training. We demonstrate PerfLLM's ability to achieve significant performance gains across diverse CPU (x86, Arm, RISC-V) and GPU architectures.
Heavy-tailed distributions, prevalent in a lot of real-world applications such as finance, telecommunications, queuing theory, and natural language processing, are challenging to model accurately owing to their slow tail decay. Bernstein phase-type (BPH) distributions, through their analytical tractability and good approximations in the non-tail region, can present a good solution, but they suffer from an inability to reproduce these heavy-tailed behaviors exactly, thus leading to inadequate performance in important tail areas. On the contrary, while highly adaptable to heavy-tailed distributions, hyperexponential (HE) models struggle in the body part of the distribution. Additionally, they are highly sensitive to initial parameter selection, significantly affecting their precision. To solve these issues, we propose a novel hybrid model of BPH and HE distributions, borrowing the most desirable features from each for enhanced approximation quality. Specifically, we leverage an optimization to set initial parameters for the HE component, significantly enhancing its robustness and reducing the possibility that the associated procedure results in an invalid HE model. Experimental validation demonstrates that the novel hybrid approach is more performant than individual application of BPH or HE models. More precisely, it can capture both the body and the tail of heavy-tailed distributions, with a considerable enhancement in matching parameters such as mean and coefficient of variation. Additional validation through experiments utilizing queuing theory proves the practical usefulness, accuracy, and precision of our hybrid approach.
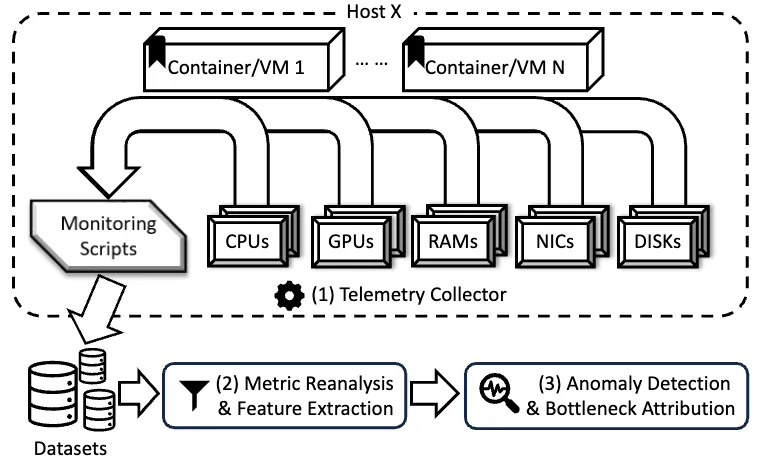
Modern machine learning (ML) has grown into a tightly coupled, full-stack ecosystem that combines hardware, software, network, and applications. Many users rely on cloud providers for elastic, isolated, and cost-efficient resources. Unfortunately, these platforms as a service use virtualization, which means operators have little insight into the users' workloads. This hinders resource optimizations by the operator, which is essential to ensure cost efficiency and minimize execution time. In this paper, we argue that workload knowledge is unnecessary for system-level optimization. We propose Reveal, which takes a hardware-centric approach, relying only on hardware signals - fully accessible by operators. Using low-level signals collected from the system, Reveal detects anomalies through an unsupervised learning pipeline. The pipeline is developed by analyzing over 30 popular ML models on various hardware platforms, ensuring adaptability to emerging workloads and unknown deployment patterns. Using Reveal, we successfully identified both network and system configuration issues, accelerating the DeepSeek model by 5.97%.
A well-designed scheduling policy can unlock significant performance improvements with no additional resources. Multiserver SRPT (SRPT-$k$) is known to achieve asymptotically optimal mean response time in the heavy traffic limit, as load approaches capacity. No better policy is known for the M/G/$k$ queue in any regime. We introduce a new policy, SRPT-Except-$k+1$ & Modified SRPT (SEK-SMOD), which is the first policy to provably achieve lower mean response time than SRPT-$k$. SEK-SMOD outperforms SRPT-$k$ across all loads and all job size distributions. The key idea behind SEK-SMOD is to prioritize large jobs over small jobs in specific scenarios to improve server utilization, and thereby improve the response time of subsequent jobs in expectation. Our proof is a novel application of hybrid worst-case and stochastic techniques to relative analysis, where we analyze the deviations of our proposed SEK-SMOD policy away from the SRPT-$k$ baseline policy. Furthermore, we design Practical-SEK (a simplified variant of SEK-SMOD) and empirically verify the improvement over SRPT-$k$ via simulation.