Trending in Systems & Networking
DataJoint 2.0: A Computational Substrate for Agentic Scientific Workflows
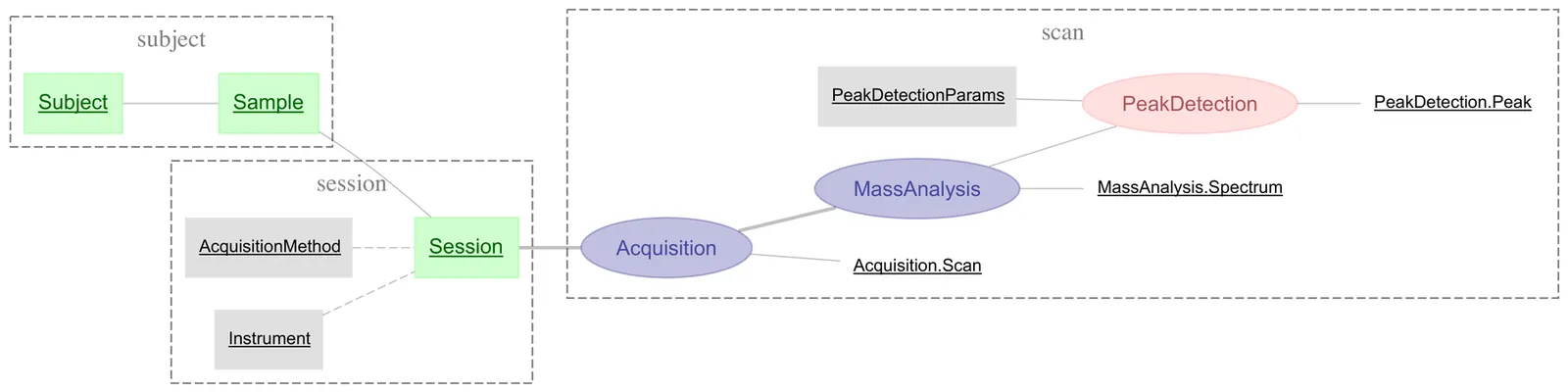
Operational rigor determines whether human-agent collaboration succeeds or fails. Scientific data pipelines need the equivalent of DevOps -- SciOps -- yet common approaches fragment provenance across disconnected systems without transactional guarantees. DataJoint 2.0 addresses this gap through the relational workflow model: tables represent workflow steps, rows represent artifacts, foreign keys prescribe execution order. The schema specifies not only what data exists but how it is derived -- a single formal system where data structure, computational dependencies, and integrity constraints are all queryable, enforceable, and machine-readable. Four technical innovations extend this foundation: object-augmented schemas integrating relational metadata with scalable object storage, semantic matching using attribute lineage to prevent erroneous joins, an extensible type system for domain-specific formats, and distributed job coordination designed for composability with external orchestration. By unifying data structure, data, and computational transformations, DataJoint creates a substrate for SciOps where agents can participate in scientific workflows without risking data corruption.
2602.16585
Feb 2026Databases
ThunderAgent: A Simple, Fast and Program-Aware Agentic Inference System
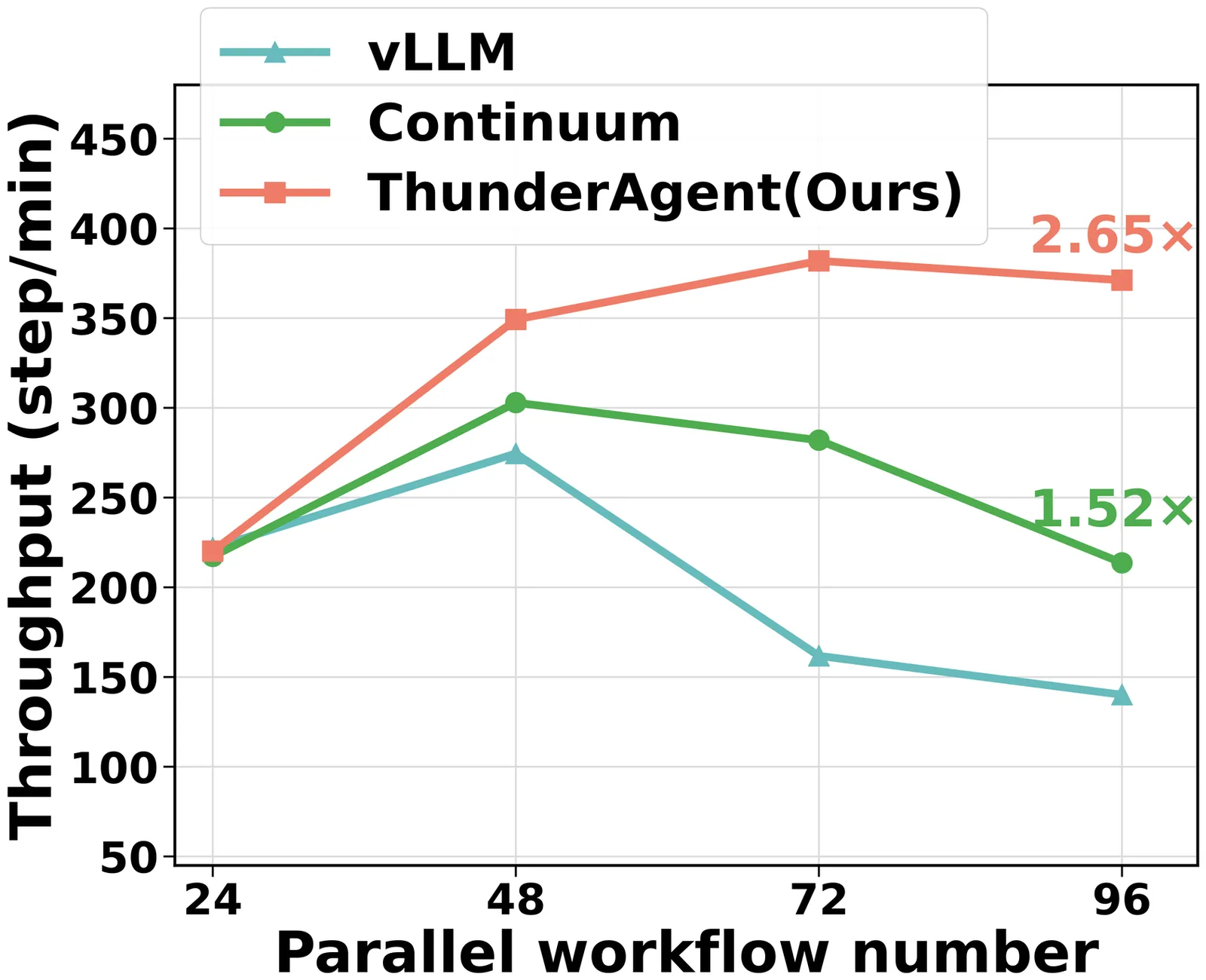
Large language models(LLMs) are now used to power complex multi-turn agentic workflows. Existing systems run agentic inference by loosely assembling isolated components: an LLM inference engine (e.g., vLLM) and a tool orchestrator (e.g., Kubernetes). Although agentic workflows involve multiple LLM and tool requests, these systems schedule and allocate resources separately on a per-request basis, without end-to-end knowledge of the workflow. This leads to sub-optimal management of KV cache and tool execution environments. To address the challenges, we propose ThunderAgent, a fast, simple, and program-aware agentic inference system. We first abstract agentic workflows as LLM Programs, enabling a unified view of heterogeneous resources, including KV caches, system states, and external tool assets such as disk memory and network ports. Built upon this abstraction, ThunderAgent introduces a program-aware scheduler and a tool resource manager designed to maximize KV cache hit rates, mitigate memory imbalances, and enable asynchronous environment preparation. Evaluations across coding, routing, and scientific discovery agents demonstrate that ThunderAgent achieves 1.5-3.6x throughput improvements in serving, 1.8-3.9x in RL rollout, and up to 4.2x disk memory savings compared to state-of-the-art inference systems. To facilitate reproducibility and support future development, we open-source the system implementations of the whole ThunderAgent at: https://github.com/Agentic-Kinetics/ThunderAgent.
2602.13692
Feb 2026Operating Systems
Fine-Tuning GPT-5 for GPU Kernel Generation
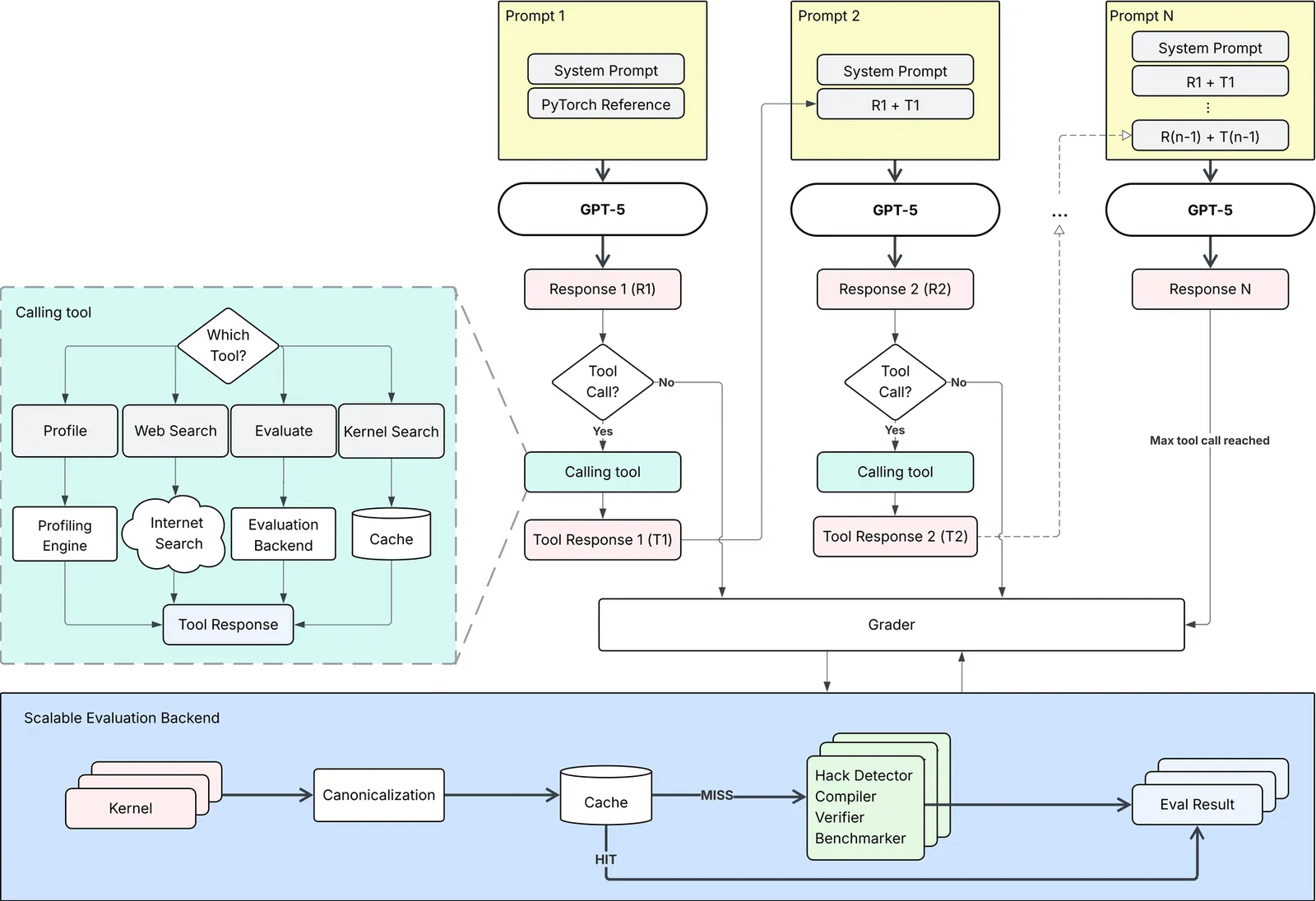
Developing efficient GPU kernels is essential for scaling modern AI systems, yet it remains a complex task due to intricate hardware architectures and the need for specialized optimization expertise. Although Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate strong capabilities in general sequential code generation, they face significant challenges in GPU code generation because of the scarcity of high-quality labeled training data, compiler biases when generating synthetic solutions, and limited generalization across hardware generations. This precludes supervised fine-tuning (SFT) as a scalable methodology for improving current LLMs. In contrast, reinforcement learning (RL) offers a data-efficient and adaptive alternative but requires access to relevant tools, careful selection of training problems, and a robust evaluation environment. We present Makora's environment and tools for reinforcement learning finetuning of frontier models and report our results from fine-tuning GPT-5 for Triton code generation. In the single-attempt setting, our fine-tuned model improves kernel correctness from 43.7% to 77.0% (+33.3 percentage points) and increases the fraction of problems outperforming TorchInductor from 14.8% to 21.8% (+7 percentage points) compared to baseline GPT-5, while exceeding prior state-of-the-art models on KernelBench. When integrated into a full coding agent, it is able to solve up to 97.4% of problems in an expanded KernelBench suite, outperforming the PyTorch TorchInductor compiler on 72.9% of problems with a geometric mean speedup of 2.12x. Our work demonstrates that targeted post-training with reinforcement learning can unlock LLM capabilities in highly specialized technical domains where traditional supervised learning is limited by data availability, opening new pathways for AI-assisted accelerator programming.
2602.11000
Feb 2026Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing
Benchmarking Large Language Models for Knowledge Graph Validation
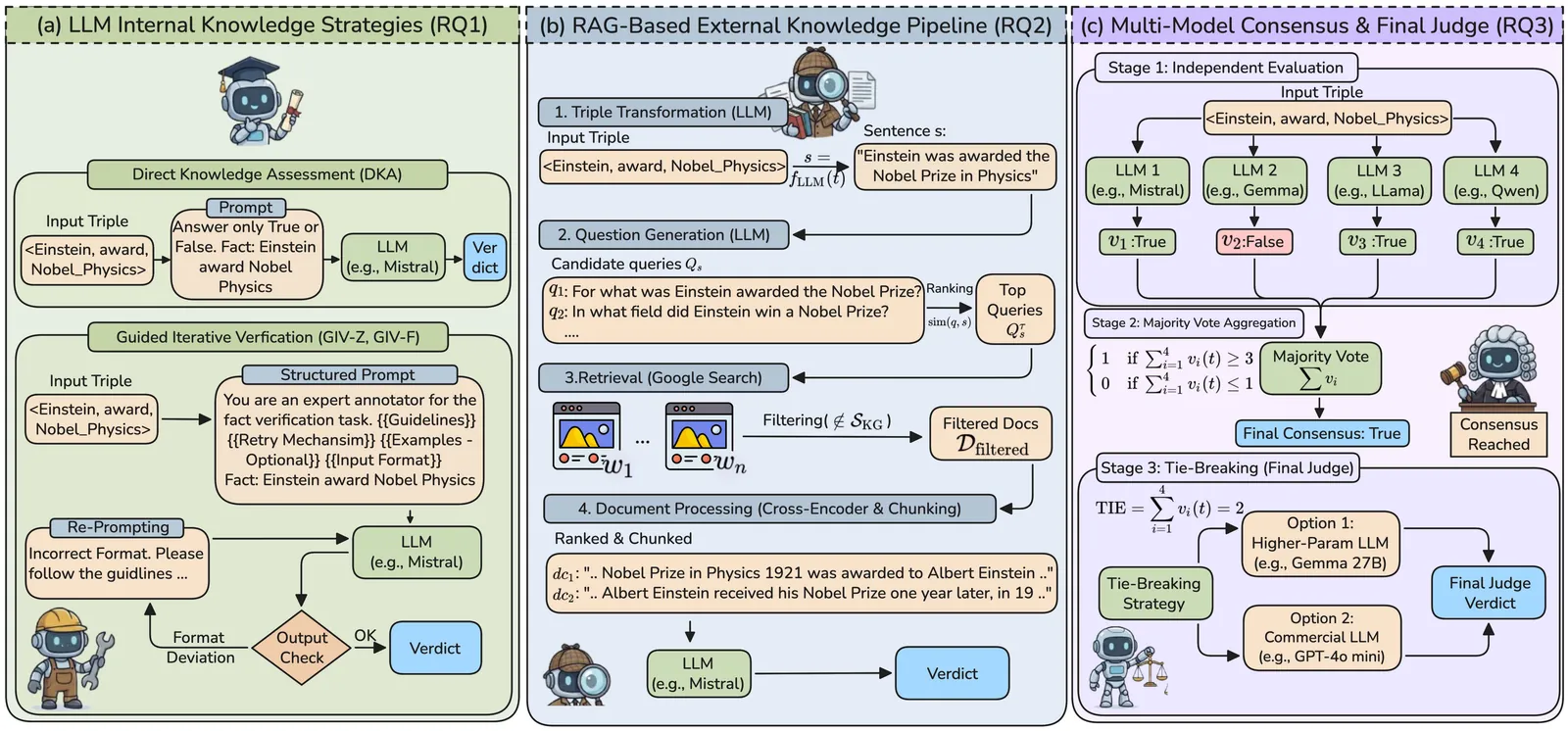
Knowledge Graphs (KGs) store structured factual knowledge by linking entities through relationships, crucial for many applications. These applications depend on the KG's factual accuracy, so verifying facts is essential, yet challenging. Expert manual verification is ideal but impractical on a large scale. Automated methods show promise but are not ready for real-world KGs. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer potential with their semantic understanding and knowledge access, yet their suitability and effectiveness for KG fact validation remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we introduce FactCheck, a benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs for KG fact validation across three key dimensions: (1) LLMs internal knowledge; (2) external evidence via Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG); and (3) aggregated knowledge employing a multi-model consensus strategy. We evaluated open-source and commercial LLMs on three diverse real-world KGs. FactCheck also includes a RAG dataset with 2+ million documents tailored for KG fact validation. Additionally, we offer an interactive exploration platform for analyzing verification decisions. The experimental analyses demonstrate that while LLMs yield promising results, they are still not sufficiently stable and reliable to be used in real-world KG validation scenarios. Integrating external evidence through RAG methods yields fluctuating performance, providing inconsistent improvements over more streamlined approaches -- at higher computational costs. Similarly, strategies based on multi-model consensus do not consistently outperform individual models, underscoring the lack of a one-fits-all solution. These findings further emphasize the need for a benchmark like FactCheck to systematically evaluate and drive progress on this difficult yet crucial task.
2602.10748
Feb 2026Databases
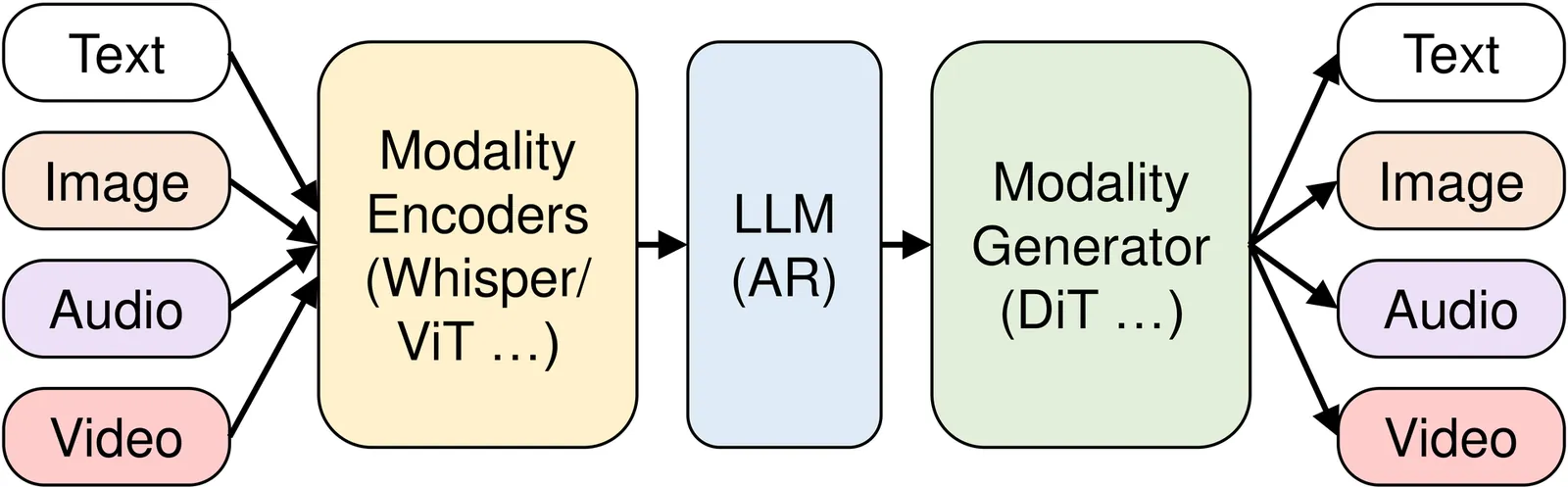
vLLM-Omni: Fully Disaggregated Serving for Any-to-Any Multimodal Models
Any-to-any multimodal models that jointly handle text, images, video, and audio represent a significant advance in multimodal AI. However, their complex architectures (typically combining multiple autoregressive LLMs, diffusion transformers, and other specialized components) pose substantial challenges for efficient model serving. Existing serving systems are mainly tailored to a single paradigm, such as autoregressive LLMs for text generation or diffusion transformers for visual generation. They lack support for any-to-any pipelines that involve multiple interconnected model components. As a result, developers must manually handle cross-stage interactions, leading to huge performance degradation. We present vLLM-Omni, a fully disaggregated serving system for any-to-any models. vLLM-Omni features a novel stage abstraction that enables users to decompose complex any-to-any architectures into interconnected stages represented as a graph, and a disaggregated stage execution backend that optimizes resource utilization and throughput across stages. Each stage is independently served by an LLM or diffusion engine with per-stage request batching, flexible GPU allocation, and unified inter-stage connectors for data routing. Experimental results demonstrate that vLLM-Omni reduces job completion time (JCT) by up to 91.4% compared to baseline methods. The code is public available at https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm-omni.
2602.02204
Feb 2026Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing
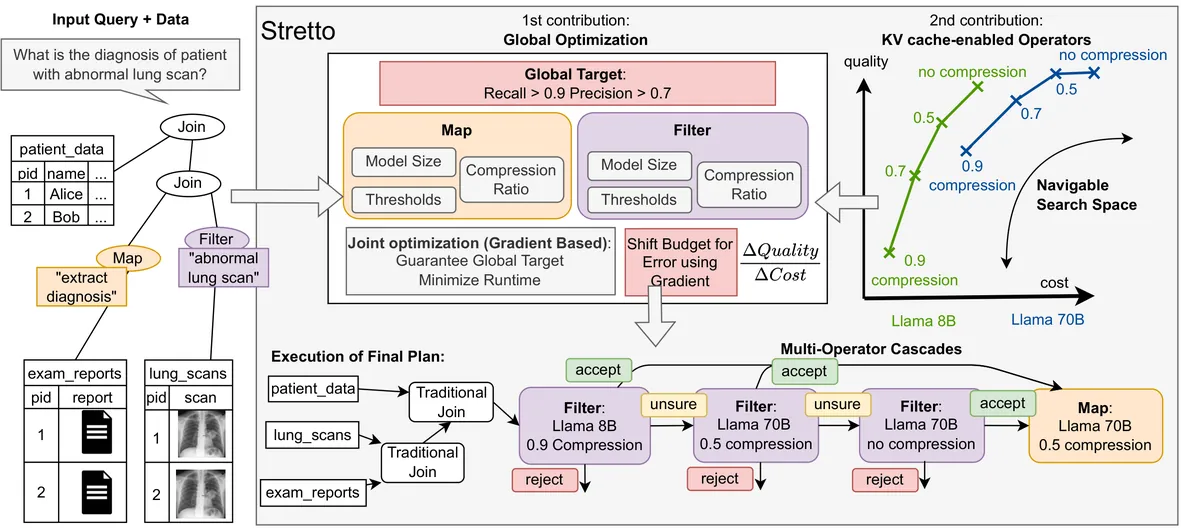
The Stretto Execution Engine for LLM-Augmented Data Systems
LLM-augmented data systems enable semantic querying over structured and unstructured data, but executing queries with LLM-powered operators introduces a fundamental runtime--accuracy trade-off. In this paper, we present Stretto, a new execution engine that provides end-to-end query guarantees while efficiently navigating this trade-off in a holistic manner. For this, Stretto formulates query planning as a constrained optimization problem and uses a gradient-based optimizer to jointly select operator implementations and allocate error budgets across pipelines. Moreover, to enable fine-grained execution choices, Stretto introduces a novel idea on how KV-caching can be used to realize a spectrum of different physical operators that transform a sparse design space into a dense continuum of runtime--accuracy trade-offs. Experiments show that Stretto outperforms state-of-the-art systems while consistently meeting quality guarantees.
2602.04430
Feb 2026Databases
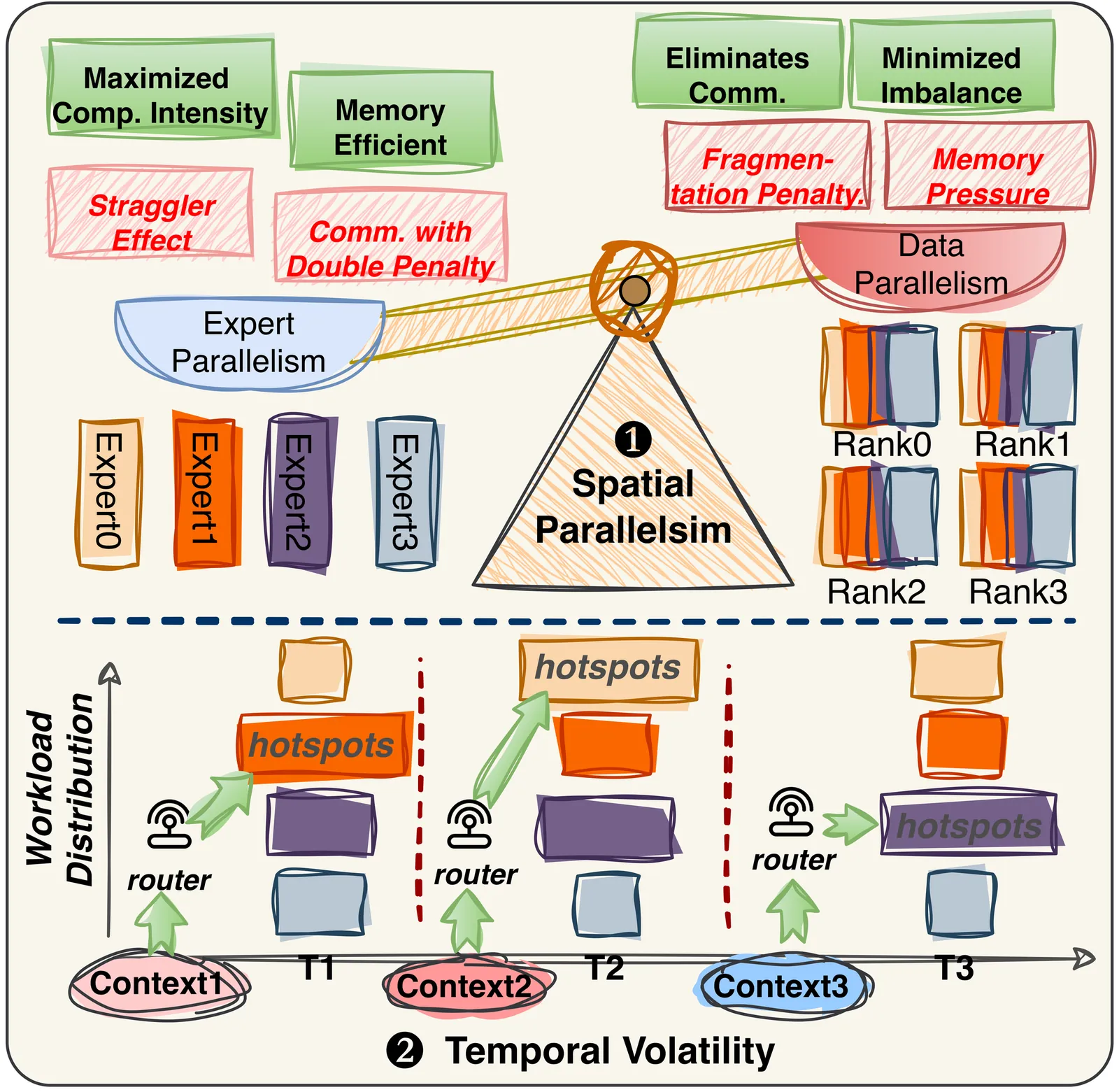
PROBE: Co-Balancing Computation and Communication in MoE Inference via Real-Time Predictive Prefetching
Mixture-of-Experts models have become a dominant architecture for scaling Large Language Models by activating only a sparse subset of experts per token. However, latency-critical MoE inference faces a fundamental tension: while expert parallelism improves memory efficiency, it also amplifies execution stragglers. In real-world serving, continuous batching and diverse concurrent requests induce rapid semantic shifts, causing expert hotspots to migrate abruptly across GPUs and triggering the 'double penalty' of coupled computational skew and network congestion. We propose PROBE, an inference system that co-balances computation and communication in real time. PROBE introduces Continuous Lookahead Pipelining, which proactively predicts, plans, and prefetches for upcoming layers while keeping all control overheads off the critical path. PROBE consists of: (1) a Gate-Initialized Lookahead Predictor that distills the target router to forecast next-layer expert activation with high fidelity; (2) a Hardware-Aware Balance Planning solver that jointly optimizes dynamic expert replication and token assignment under strict hiding-window constraints; and (3) a Phase-Locked Co-Scheduling policy that uses split-phase transmission to hide bandwidth-intensive expert transfers behind computation without contending with All-to-All collectives. Experiments show that PROBE reduces prefill latency by up to 1.32X and improves decoding throughput by up to 1.26X over state-of-the-art baselines, especially under extreme workload volatility.
2602.00509
Jan 2026Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing

SuperInfer: SLO-Aware Rotary Scheduling and Memory Management for LLM Inference on Superchips
Large Language Model (LLM) serving faces a fundamental tension between stringent latency Service Level Objectives (SLOs) and limited GPU memory capacity. When high request rates exhaust the KV cache budget, existing LLM inference systems often suffer severe head-of-line (HOL) blocking. While prior work explored PCIe-based offloading, these approaches cannot sustain responsiveness under high request rates, often failing to meet tight Time-To-First-Token (TTFT) and Time-Between-Tokens (TBT) SLOs. We present SuperInfer, a high-performance LLM inference system designed for emerging Superchips (e.g., NVIDIA GH200) with tightly coupled GPU-CPU architecture via NVLink-C2C. SuperInfer introduces RotaSched, the first proactive, SLO-aware rotary scheduler that rotates requests to maintain responsiveness on Superchips, and DuplexKV, an optimized rotation engine that enables full-duplex transfer over NVLink-C2C. Evaluations on GH200 using various models and datasets show that SuperInfer improves TTFT SLO attainment rates by up to 74.7% while maintaining comparable TBT and throughput compared to state-of-the-art systems, demonstrating that SLO-aware scheduling and memory co-design unlocks the full potential of Superchips for responsive LLM serving.
2601.20309
Jan 2026Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing
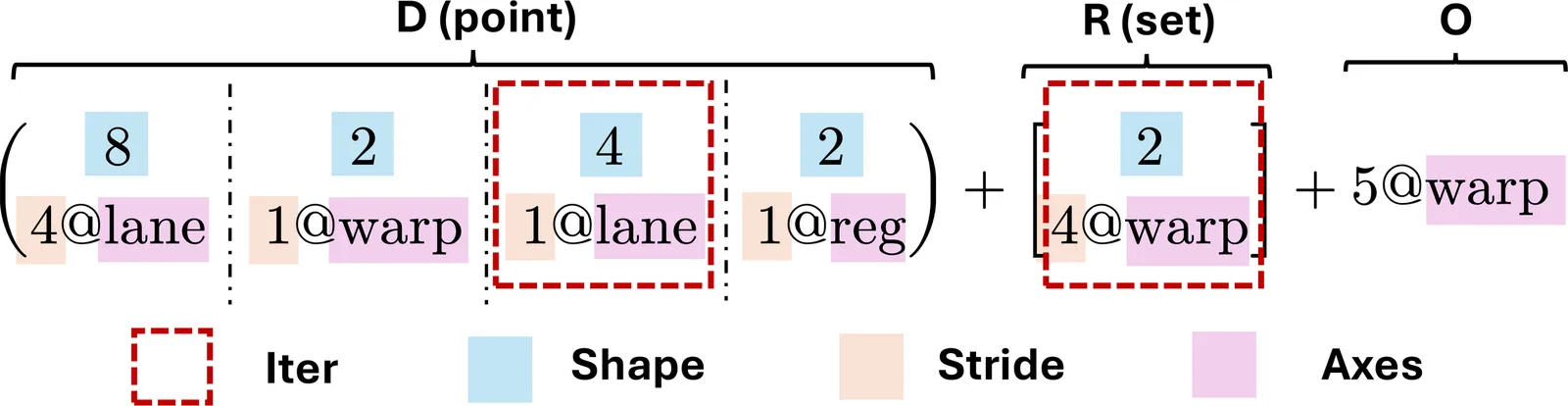
Axe: A Simple Unified Layout Abstraction for Machine Learning Compilers
Scaling modern deep learning workloads demands coordinated placement of data and compute across device meshes, memory hierarchies, and heterogeneous accelerators. We present Axe Layout, a hardware-aware abstraction that maps logical tensor coordinates to a multi-axis physical space via named axes. Axe unifies tiling, sharding, replication, and offsets across inter-device distribution and on-device layouts, enabling collective primitives to be expressed consistently from device meshes to threads. Building on Axe, we design a multi-granularity, distribution-aware DSL and compiler that composes thread-local control with collective operators in a single kernel. Experiments show that our unified approach can bring performance close to hand-tuned kernels on across latest GPU devices and multi-device environments and accelerator backends.
2601.19092
Jan 2026Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing

MegaFlow: Large-Scale Distributed Orchestration System for the Agentic Era
The rapid development of interactive and autonomous AI systems signals our entry into the agentic era. Training and evaluating agents on complex agentic tasks such as software engineering and computer use requires not only efficient model computation but also sophisticated infrastructure capable of coordinating vast agent-environment interactions. However, no open-source infrastructure can effectively support large-scale training and evaluation on such complex agentic tasks. To address this challenge, we present MegaFlow, a large-scale distributed orchestration system that enables efficient scheduling, resource allocation, and fine-grained task management for agent-environment workloads. MegaFlow abstracts agent training infrastructure into three independent services (Model Service, Agent Service, and Environment Service) that interact through unified interfaces, enabling independent scaling and flexible resource allocation across diverse agent-environment configurations. In our agent training deployments, MegaFlow successfully orchestrates tens of thousands of concurrent agent tasks while maintaining high system stability and achieving efficient resource utilization. By enabling such large-scale agent training, MegaFlow addresses a critical infrastructure gap in the emerging agentic AI landscape.
2601.07526
Jan 2026Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing
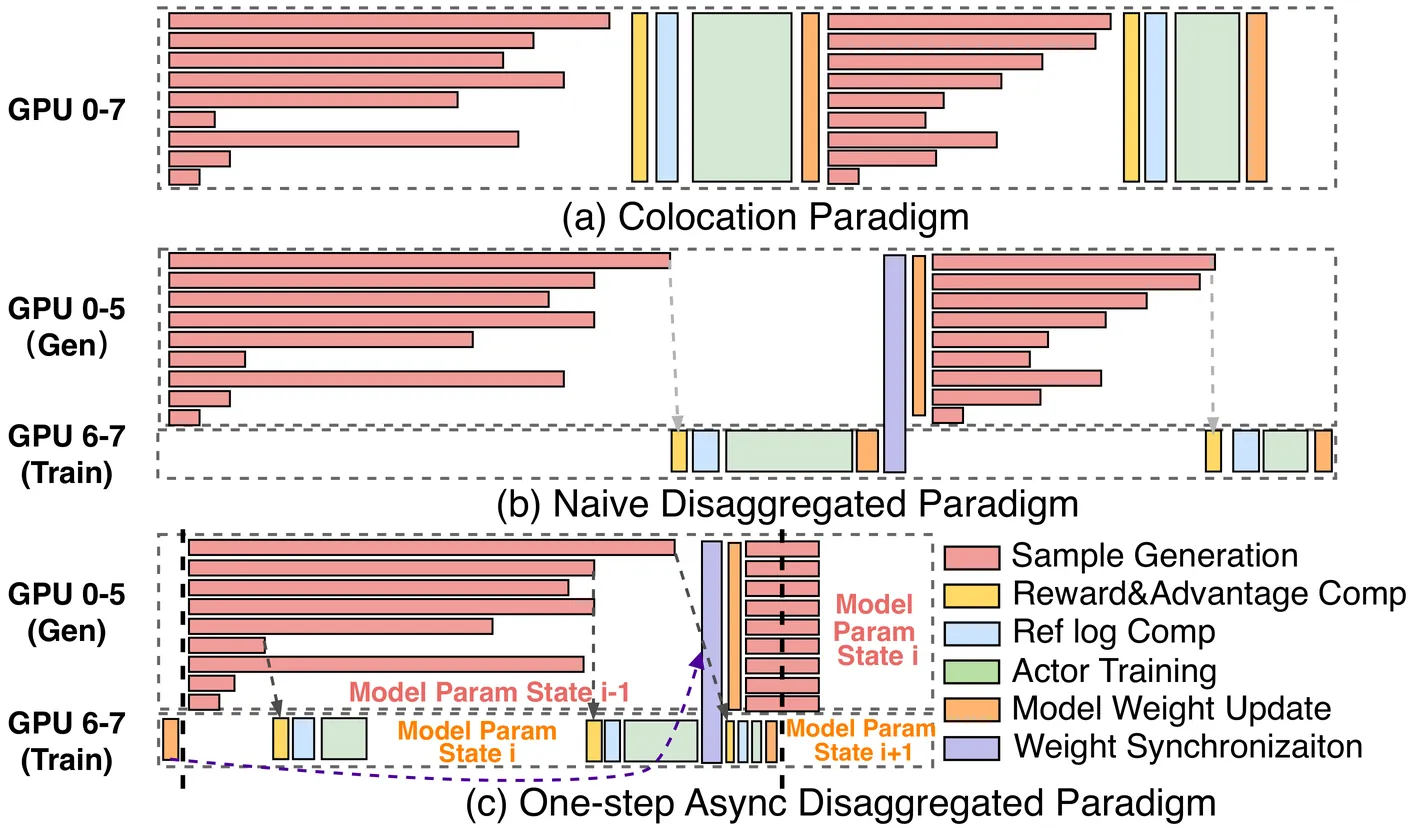
OrchestrRL: Dynamic Compute and Network Orchestration for Disaggregated RL
Post-training with reinforcement learning (RL) has greatly enhanced the capabilities of large language models. Disaggregating the generation and training stages in RL into a parallel, asynchronous pipeline offers the potential for flexible scaling and improved throughput. However, it still faces two critical challenges. First, the generation stage often becomes a bottleneck due to dynamic workload shifts and severe execution imbalances. Second, the decoupled stages result in diverse and dynamic network traffic patterns that overwhelm conventional network fabrics. This paper introduces OrchestrRL, an orchestration framework that dynamically manages compute and network rhythms in disaggregated RL. To improve generation efficiency, OrchestrRL employs an adaptive compute scheduler that dynamically adjusts parallelism to match workload characteristics within and across generation steps. This accelerates execution while continuously rebalancing requests to mitigate stragglers. To address the dynamic network demands inherent in disaggregated RL -- further intensified by parallelism switching -- we co-design RFabric, a reconfigurable hybrid optical-electrical fabric. RFabric leverages optical circuit switches at selected network tiers to reconfigure the topology in real time, enabling workload-aware circuits for (i) layer-wise collective communication during training iterations, (ii) generation under different parallelism configurations, and (iii) periodic inter-cluster weight synchronization. We evaluate OrchestrRL on a physical testbed with 48 H800 GPUs, demonstrating up to a 1.40x throughput improvement. Furthermore, we develop RLSim, a high-fidelity simulator, to evaluate RFabric at scale. Our results show that RFabric achieves superior performance-cost efficiency compared to static Fat-Tree networks, establishing it as a highly effective solution for large-scale RL workloads.
2601.01209
Jan 2026Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing
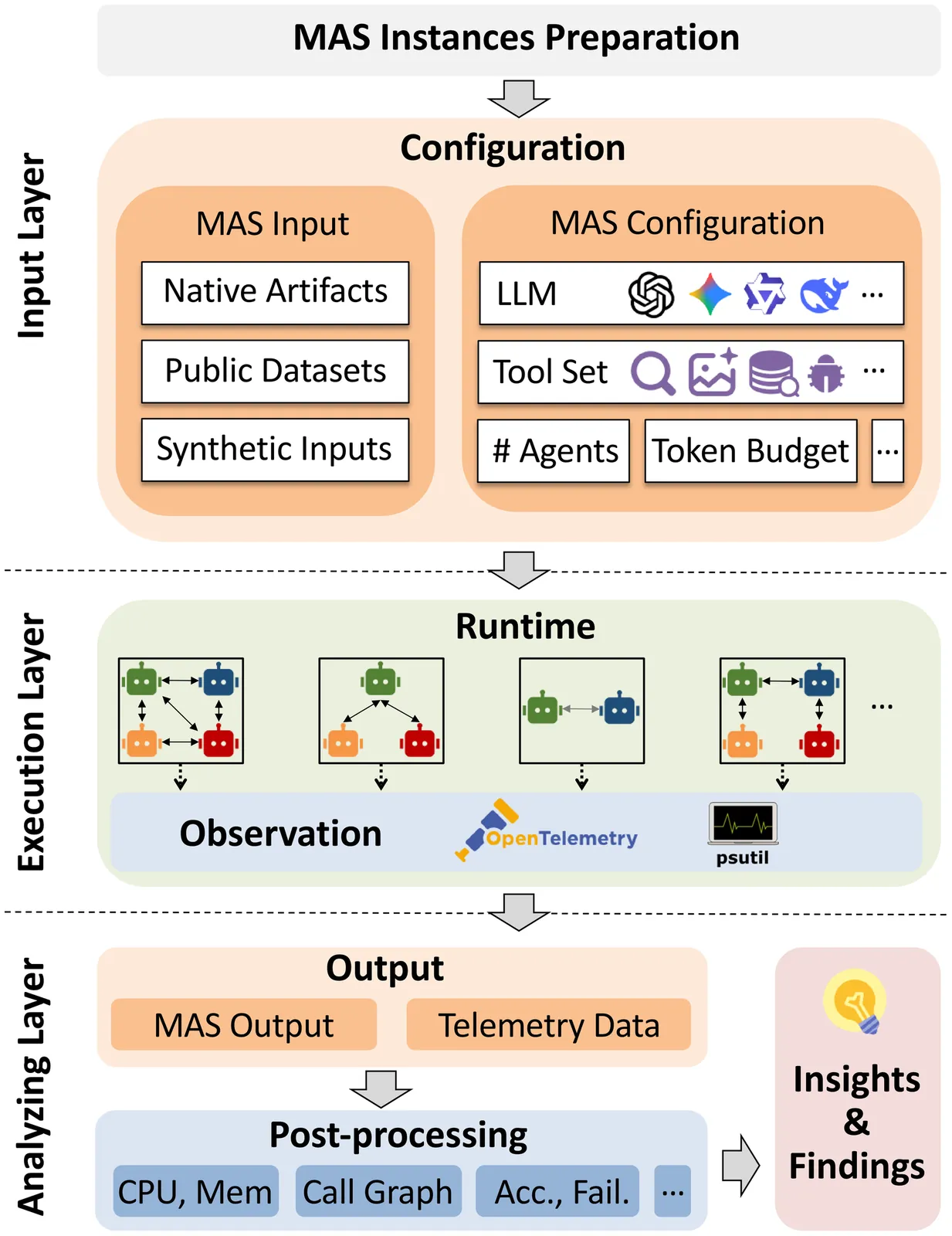
MAESTRO: Multi-Agent Evaluation Suite for Testing, Reliability, and Observability
We present MAESTRO, an evaluation suite for the testing, reliability, and observability of LLM-based MAS. MAESTRO standardizes MAS configuration and execution through a unified interface, supports integrating both native and third-party MAS via a repository of examples and lightweight adapters, and exports framework-agnostic execution traces together with system-level signals (e.g., latency, cost, and failures). We instantiate MAESTRO with 12 representative MAS spanning popular agentic frameworks and interaction patterns, and conduct controlled experiments across repeated runs, backend models, and tool configurations. Our case studies show that MAS executions can be structurally stable yet temporally variable, leading to substantial run-to-run variance in performance and reliability. We further find that MAS architecture is the dominant driver of resource profiles, reproducibility, and cost-latency-accuracy trade-off, often outweighing changes in backend models or tool settings. Overall, MAESTRO enables systematic evaluation and provides empirical guidance for designing and optimizing agentic systems.
2601.00481
Jan 2026Networking and Internet Architecture
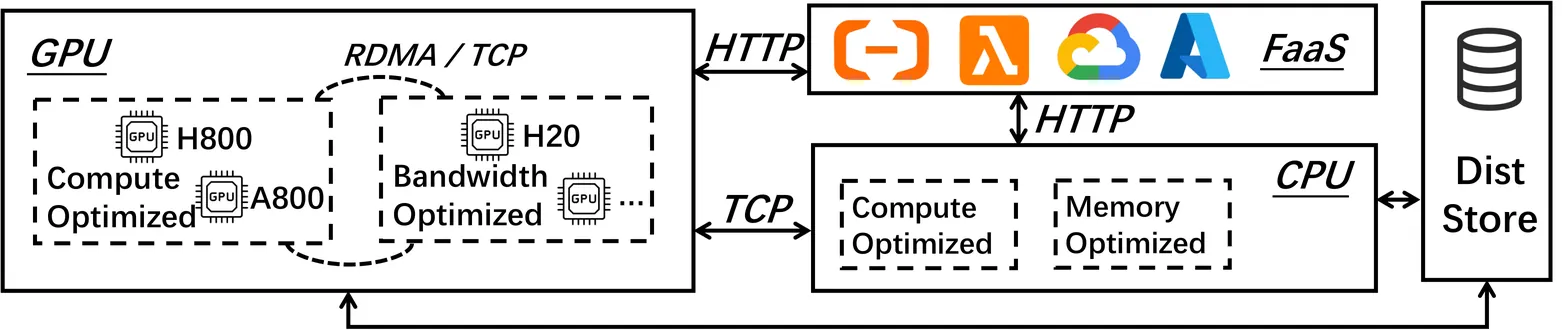
RollArt: Scaling Agentic RL Training via Disaggregated Infrastructure
Agentic Reinforcement Learning (RL) enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform autonomous decision-making and long-term planning. Unlike standard LLM post-training, agentic RL workloads are highly heterogeneous, combining compute-intensive prefill phases, bandwidth-bound decoding, and stateful, CPU-heavy environment simulations. We argue that efficient agentic RL training requires disaggregated infrastructure to leverage specialized, best-fit hardware. However, naive disaggregation introduces substantial synchronization overhead and resource underutilization due to the complex dependencies between stages. We present RollArc, a distributed system designed to maximize throughput for multi-task agentic RL on disaggregated infrastructure. RollArc is built on three core principles: (1) hardware-affinity workload mapping, which routes compute-bound and bandwidth-bound tasks to bestfit GPU devices, (2) fine-grained asynchrony, which manages execution at the trajectory level to mitigate resource bubbles, and (3) statefulness-aware computation, which offloads stateless components (e.g., reward models) to serverless infrastructure for elastic scaling. Our results demonstrate that RollArc effectively improves training throughput and achieves 1.35-2.05\(\times\) end-to-end training time reduction compared to monolithic and synchronous baselines. We also evaluate RollArc by training a hundreds-of-billions-parameter MoE model for Qoder product on an Alibaba cluster with more than 3,000 GPUs, further demonstrating RollArc scalability and robustness. The code is available at https://github.com/alibaba/ROLL.
2512.225601
Dec 2025Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing

ECCO: Leveraging Cross-Camera Correlations for Efficient Live Video Continuous Learning
Recent advances in video analytics address real-time data drift by continuously retraining specialized, lightweight DNN models for individual cameras. However, the current practice of retraining a separate model for each camera suffers from high compute and communication costs, making it unscalable. We present ECCO, a new video analytics framework designed for resource-efficient continuous learning. The key insight is that the data drift, which necessitates model retraining, often shows temporal and spatial correlations across nearby cameras. By identifying cameras that experience similar drift and retraining a shared model for them, ECCO can substantially reduce the associated compute and communication costs. Specifically, ECCO introduces: (i) a lightweight grouping algorithm that dynamically forms and updates camera groups; (ii) a GPU allocator that dynamically assigns GPU resources across different groups to improve retraining accuracy and ensure fairness; and (iii) a transmission controller at each camera that configures frame sampling and coordinates bandwidth sharing with other cameras based on its assigned GPU resources. We conducted extensive evaluations on three distinctive datasets for two vision tasks. Compared to leading baselines, ECCO improves retraining accuracy by 6.7%-18.1% using the same compute and communication resources, or supports 3.3 times more concurrent cameras at the same accuracy.
2512.11727
Dec 2025Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing
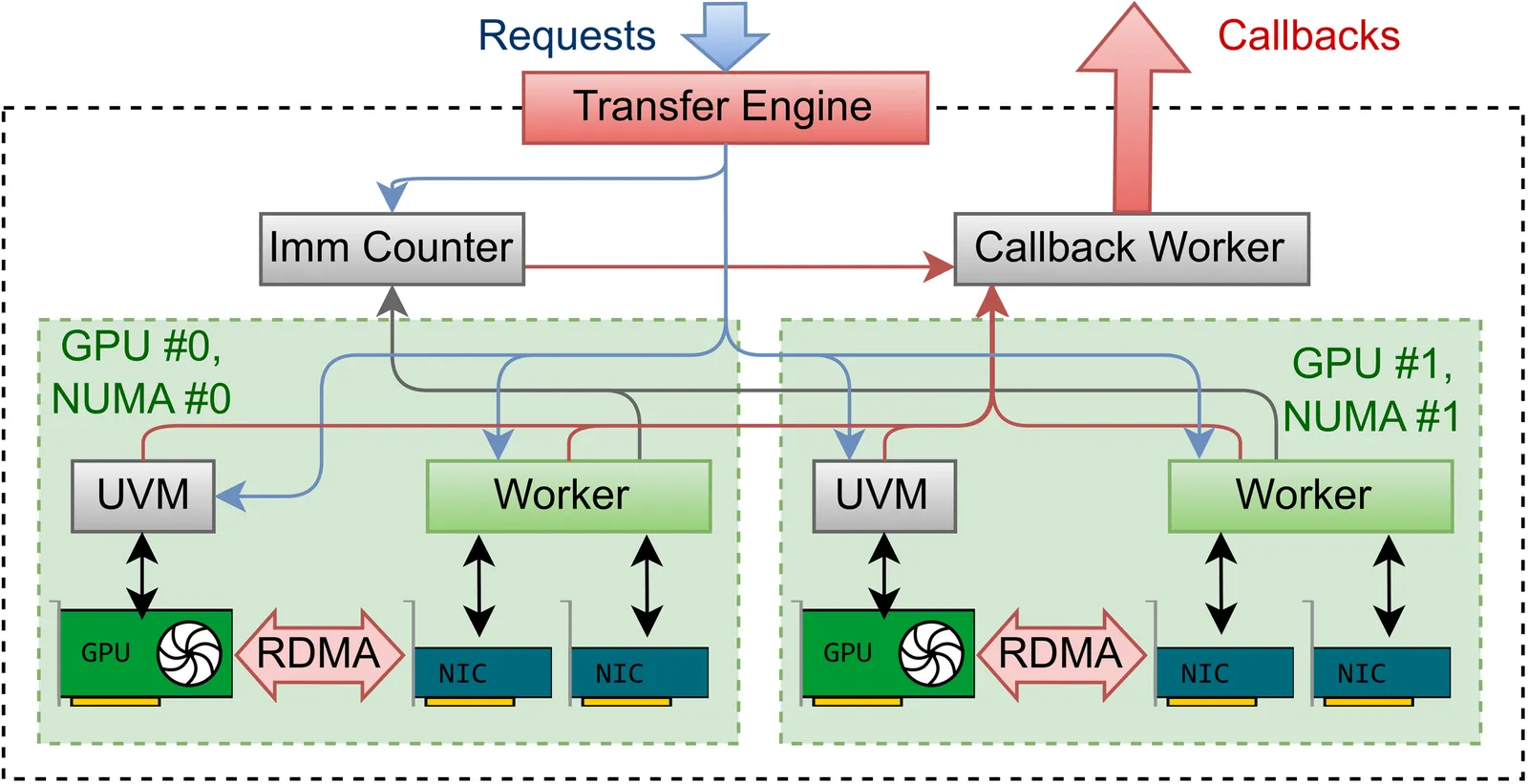
RDMA Point-to-Point Communication for LLM Systems
Emerging Large Language Model (LLM) system patterns, such as disaggregated inference, Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) routing, and asynchronous reinforcement fine-tuning, require flexible point-to-point communication beyond simple collectives. Existing implementations are locked to specific Network Interface Controllers (NICs), hindering integration into inference engines and portability across hardware providers. We present TransferEngine, which bridges the functionality of common NICs to expose a uniform interface. TransferEngine exposes one-sided WriteImm operations with a ImmCounter primitive for completion notification, without ordering assumptions of network transport, transparently managing multiple NICs per GPU. We demonstrate peak throughput of 400 Gbps on both NVIDIA ConnectX-7 and AWS Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA). We showcase TransferEngine through three production systems: (1) KvCache transfer for disaggregated inference with dynamic scaling, (2) RL weight updates achieving 1.3 seconds for trillion-parameter models, and (3) MoE dispatch/combine implementation exceeding DeepEP decode latency on ConnectX-7, with the first viable latencies on EFA. We demonstrate that our portable point-to-point communication complements collectives while avoiding lock-in.
2510.276562
Oct 2025Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing