Neural and Evolutionary Computing
Covers neural networks, connectionism, genetic algorithms, artificial life, adaptive behavior.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Covers neural networks, connectionism, genetic algorithms, artificial life, adaptive behavior.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
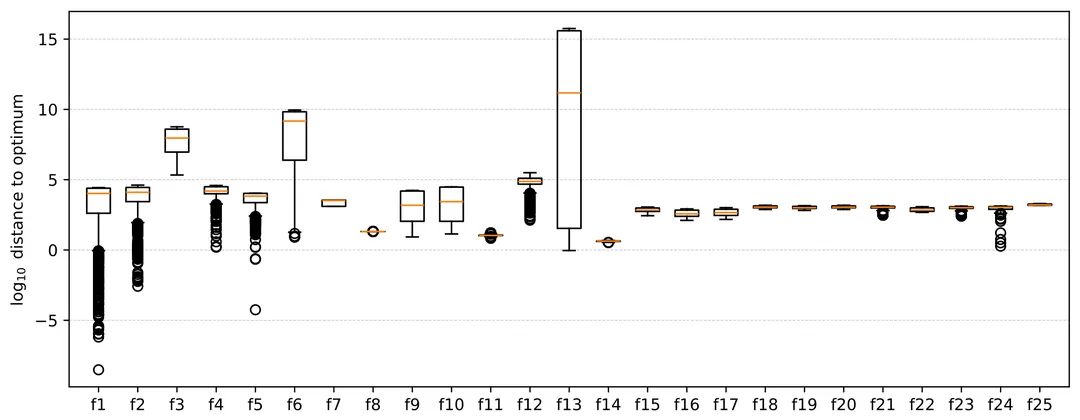
The PSO-X framework incorporates dozens of modules that have been proposed for solving single-objective continuous optimization problems using particle swarm optimization. While modular frameworks enable users to automatically generate and configure algorithms tailored to specific optimization problems, the complexity of this process increases with the number of modules in the framework and the degrees of freedom defined for their interaction. Understanding how modules affect the performance of algorithms for different problems is critical to making the process of finding effective implementations more efficient and identifying promising areas for further investigation. Despite their practical applications and scientific relevance, there is a lack of empirical studies investigating which modules matter most in modular optimization frameworks and how they interact. In this paper, we analyze the performance of 1424 particle swarm optimization algorithms instantiated from the PSO-X framework on the 25 functions in the CEC'05 benchmark suite with 10 and 30 dimensions. We use functional ANOVA to quantify the impact of modules and their combinations on performance in different problem classes. In practice, this allows us to identify which modules have greater influence on PSO-X performance depending on problem features such as multimodality, mathematical transformations and varying dimensionality. We then perform a cluster analysis to identify groups of problem classes that share similar module effect patterns. Our results show low variability in the importance of modules in all problem classes, suggesting that particle swarm optimization performance is driven by a few influential modules.
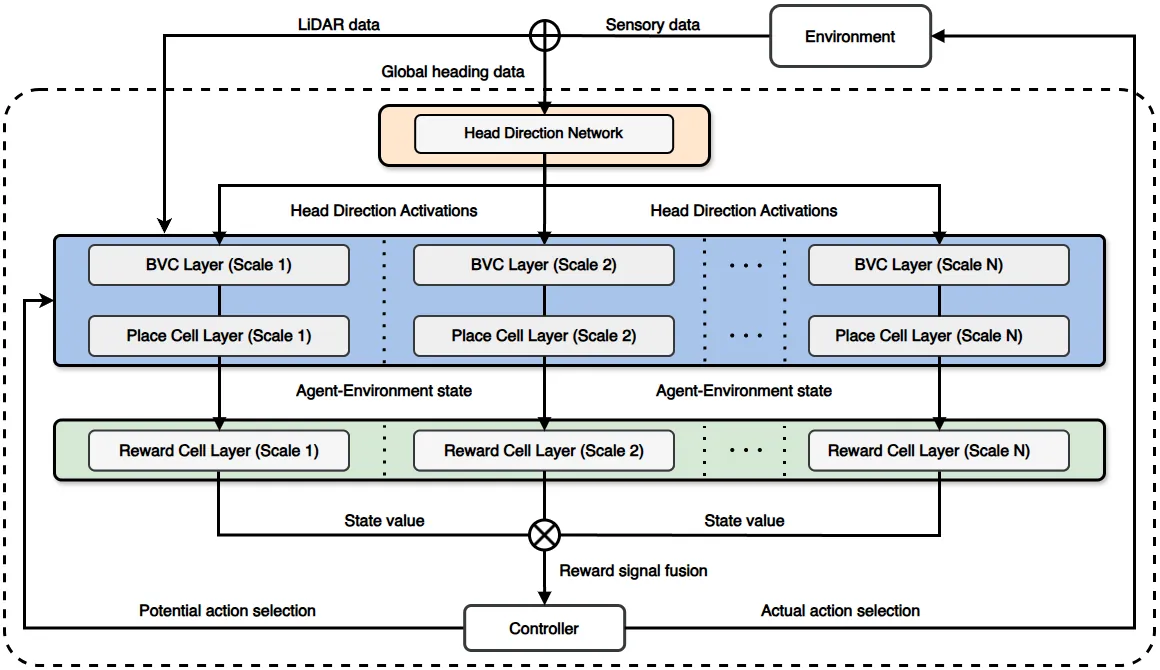
Autonomous navigation in complex and partially observable environments remains a central challenge in robotics. Several bio-inspired models of mapping and navigation based on place cells in the mammalian hippocampus have been proposed. This paper introduces a new robust model that employs parallel layers of place fields at multiple spatial scales, a replay-based reward mechanism, and dynamic scale fusion. Simulations show that the model improves path efficiency and accelerates learning compared to single-scale baselines, highlighting the value of multiscale spatial representations for adaptive robot navigation.
 2601.01916
2601.01916We propose a theoretical framework--Holographic Reservoir Computing (HRC)--which hypothesizes that the thermodynamic noise and timing dynamics in voltage-stressed Bitcoin mining ASICs (BM1366) could potentially serve as a physical reservoir computing substrate. We present the CHIMERA (Conscious Hybrid Intelligence via Miner-Embedded Resonance Architecture) system architecture, which treats the SHA-256 hashing pipeline not as an entropy source, but as a deterministic diffusion operator whose timing characteristics under controlled voltage and frequency conditions may exhibit computationally useful dynamics. We report preliminary observations of non-Poissonian variability in inter-arrival time statistics during edge-of-stability operation, which we term the "Silicon Heartbeat" hypothesis. Theoretical analysis based on Hierarchical Number System (HNS) representations suggests that such architectures could achieve O(log n) energy scaling compared to traditional von Neumann O(2^n) dependencies. However, we emphasize that these are theoretical projections requiring experimental validation. We present the implemented measurement infrastructure, acknowledge current limitations, and outline the experimental program necessary to confirm or refute these hypotheses. This work contributes to the emerging field of thermodynamic computing by proposing a novel approach to repurposing obsolete cryptographic hardware for neuromorphic applications.
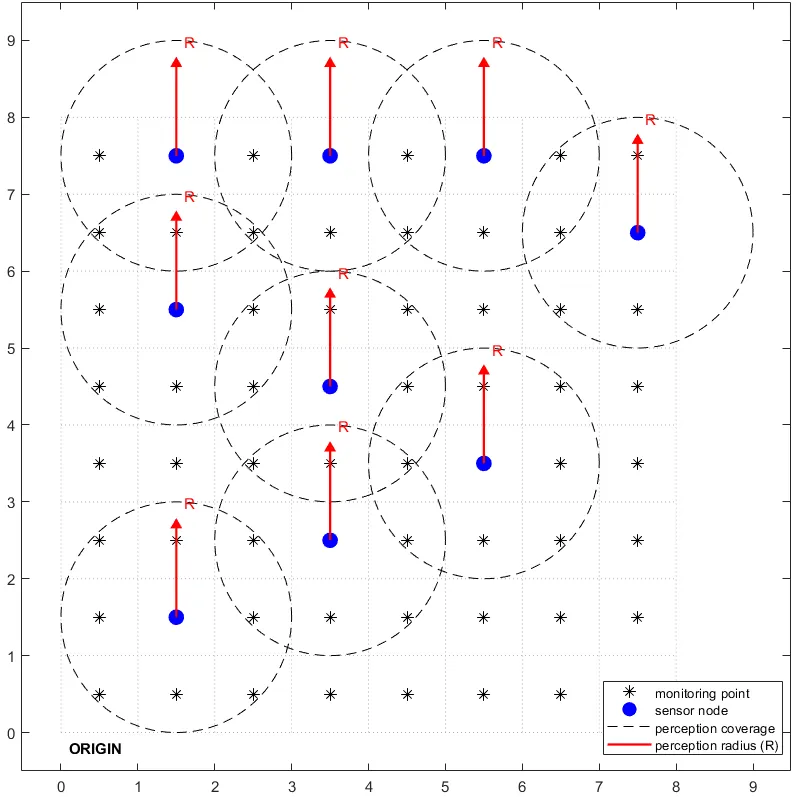
To enhance the coverage rate of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), this paper proposes an advanced optimization strategy based on a multi-strategy integrated Northern Goshawk Optimization (NGO) algorithm. Specifically, multivariate chaotic mapping is first employed to improve the randomness and uniformity of the initial population. To further bolster population diversity and prevent the algorithm from stagnating in local optima, a bidirectional population evolutionary dynamics strategy is incorporated following the pursuit-and-evasion phase, thereby facilitating the attainment of the global optimal solution. Extensive simulations were conducted to evaluate the performance of the proposed multi-strategy NGO in WSN coverage. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms existing benchmarks in terms of both coverage enhancement and node connectivity.
We present Yukthi Opus (YO), a multi-chain hybrid metaheuristic designed for NP-hard optimization under explicit evaluation budget constraints. YO integrates three complementary mechanisms in a structured two-phase architecture: Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) for global exploration, greedy local search for exploitation, and simulated annealing with adaptive reheating to enable controlled escape from local minima. A dedicated burn-in phase allocates evaluations to probabilistic exploration, after which a hybrid optimization loop refines promising candidates. YO further incorporates a spatial blacklist mechanism to avoid repeated evaluation of poor regions and a multi-chain execution strategy to improve robustness and reduce sensitivity to initialization. We evaluate YO on three benchmarks: the Rastrigin function (5D) with ablation studies, the Traveling Salesman Problem with 50 to 200 cities, and the Rosenbrock function (5D) with comparisons against established optimizers including CMA-ES, Bayesian optimization, and accelerated particle swarm optimization. Results show that MCMC exploration and greedy refinement are critical for solution quality, while simulated annealing and multi-chain execution primarily improve stability and variance reduction. Overall, YO achieves competitive performance on large and multimodal problems while maintaining predictable evaluation budgets, making it suitable for expensive black-box optimization settings.
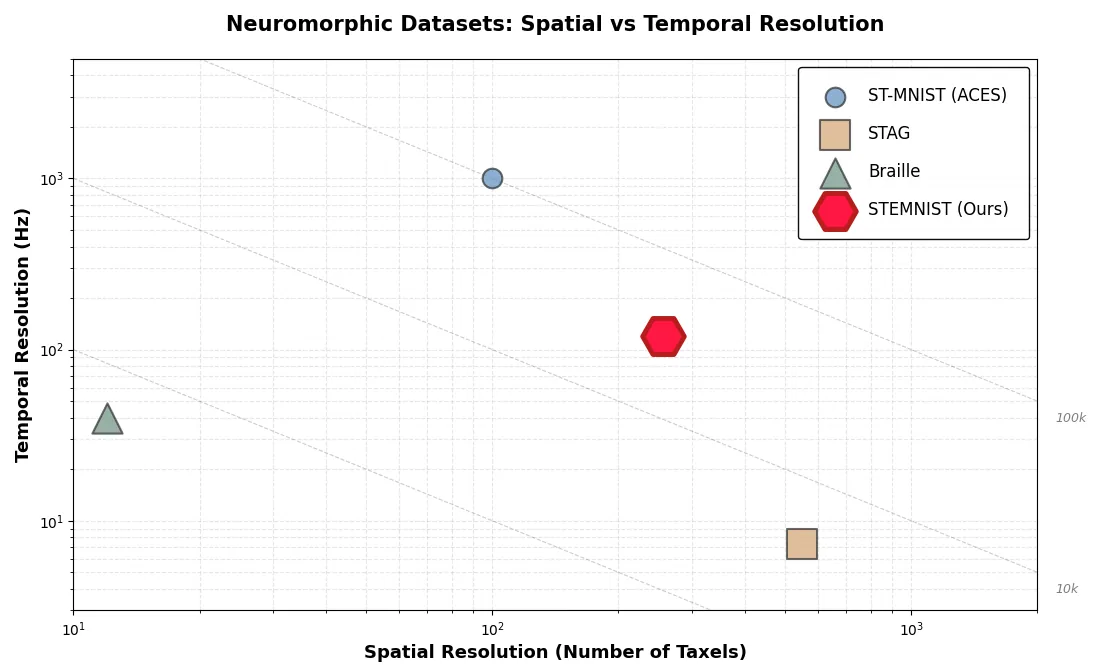
Tactile sensing is essential for robotic manipulation, prosthetics and assistive technologies, yet neuromorphic tactile datasets remain limited compared to their visual counterparts. We introduce STEMNIST, a large-scale neuromorphic tactile dataset extending ST-MNIST from 10 digits to 35 alphanumeric classes (uppercase letters A--Z and digits 1--9), providing a challenging benchmark for event-based haptic recognition. The dataset comprises 7,700 samples collected from 34 participants using a custom \(16\times 16\) tactile sensor array operating at 120 Hz, encoded as 1,005,592 spike events through adaptive temporal differentiation. Following EMNIST's visual character recognition protocol, STEMNIST addresses the critical gap between simplified digit classification and real-world tactile interaction scenarios requiring alphanumeric discrimination. Baseline experiments using conventional CNNs (90.91% test accuracy) and spiking neural networks (89.16%) establish performance benchmarks. The dataset's event-based format, unrestricted spatial variability and rich temporal structure makes it suitable for testing neuromorphic hardware and bio-inspired learning algorithms. STEMNIST enables reproducible evaluation of tactile recognition systems and provides a foundation for advancing energy-efficient neuromorphic perception in robotics, biomedical engineering and human-machine interfaces. The dataset, documentation and codes are publicly available to accelerate research in neuromorphic tactile computing.
Dynamic multi-objective optimization (DMOO) has recently attracted increasing interest from both academic researchers and engineering practitioners, as numerous real-world applications that evolve over time can be naturally formulated as dynamic multi-objective optimization problems (DMOPs). This growing trend necessitates advanced benchmarks for the rigorous evaluation of optimization algorithms under realistic conditions. This paper introduces a comprehensive and principled framework for constructing highly realistic and challenging DMOO benchmarks. The proposed framework features several novel components: a generalized formulation that allows the Pareto-optimal Set (PS) to change on hypersurfaces, a mechanism for creating controlled variable contribution imbalances to generate heterogeneous landscapes, and dynamic rotation matrices for inducing time-varying variable interactions and non-separability. Furthermore, we incorporate a temporal perturbation mechanism to simulate irregular environmental changes and propose a generalized time-linkage mechanism that systematically embeds historical solution quality into future problems, thereby capturing critical real-world phenomena such as error accumulation and time-deception. Extensive experimental results validate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, demonstrating its superiority over conventional benchmarks in terms of realism, complexity, and its capability for discriminating state-of-the-art algorithmic performance. This work establishes a new standard for dynamic multi-objective optimization benchmarking, providing a powerful tool for the development and evaluation of next-generation algorithms capable of addressing the complexities of real-world dynamic systems.
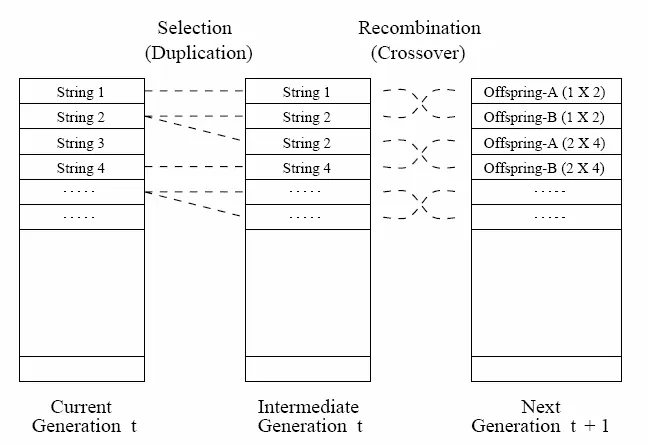
This paper presents a genetic algorithm (GA) approach to cost-optimal task scheduling in a production line. The system consists of a set of serial processing tasks, each with a given duration, unit execution cost, and precedence constraints, which must be assigned to an unlimited number of stations subject to a per-station duration bound. The objective is to minimize the total production cost, modeled as a station-wise function of task costs and the duration bound, while strictly satisfying all prerequisite and capacity constraints. Two chromosome encoding strategies are investigated: a station-based representation implemented using the JGAP library with SuperGene validity checks, and a task-based representation in which genes encode station assignments directly. For each encoding, standard GA operators (crossover, mutation, selection, and replacement) are adapted to preserve feasibility and drive the population toward lower-cost schedules. Experimental results on three classes of precedence structures-tightly coupled, loosely coupled, and uncoupled-demonstrate that the task-based encoding yields smoother convergence and more reliable cost minimization than the station-based encoding, particularly when the number of valid schedules is large. The study highlights the advantages of GA over gradient-based and analytical methods for combinatorial scheduling problems, especially in the presence of complex constraints and non-differentiable cost landscapes.
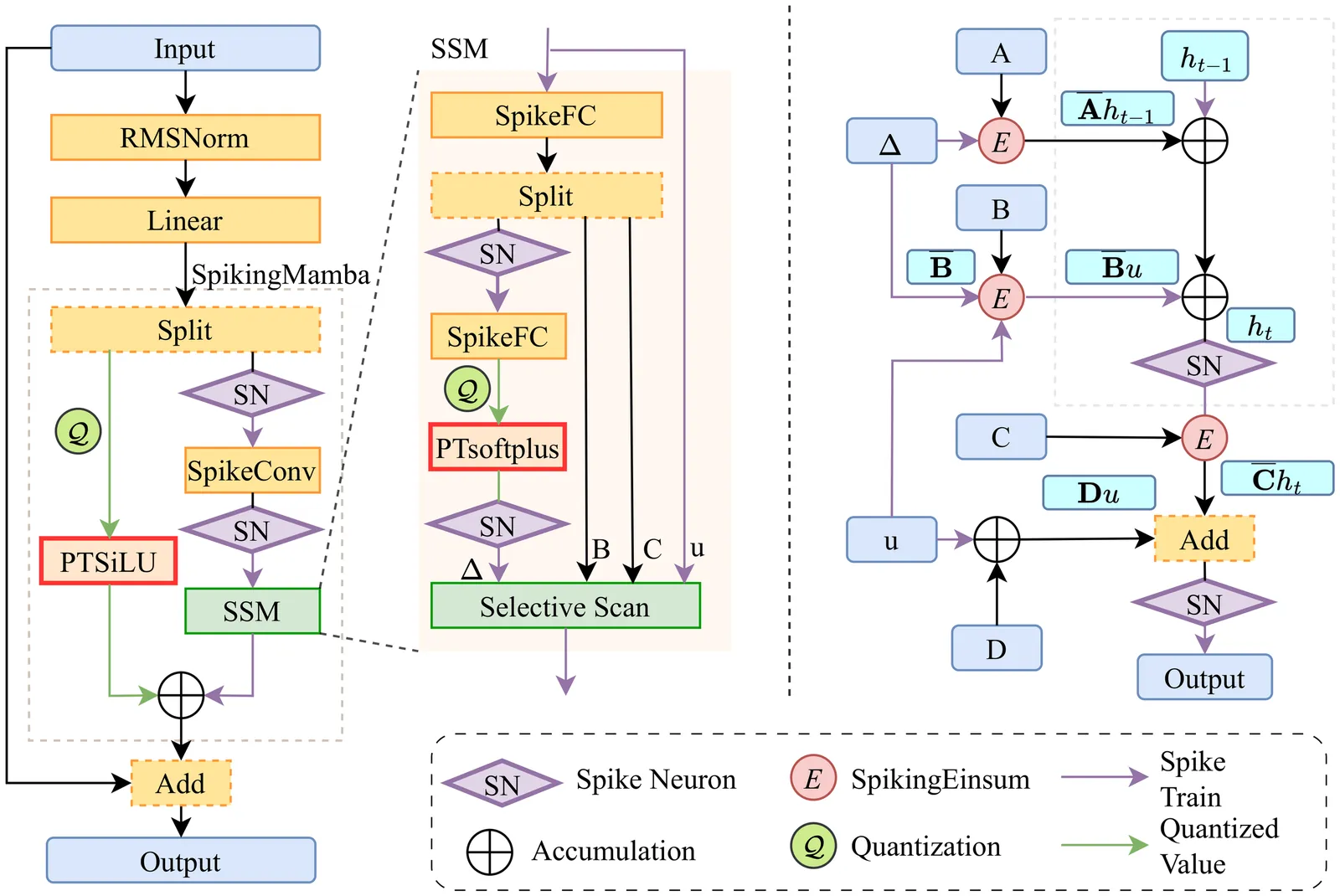
Time-series forecasting often operates under tight power and latency budgets in fields like traffic management, industrial condition monitoring, and on-device sensing. These applications frequently require near real-time responses and low energy consumption on edge devices. Spiking neural networks (SNNs) offer event-driven computation and ultra-low power by exploiting temporal sparsity and multiplication-free computation. Yet existing SNN-based time-series forecasters often inherit complex transformer blocks, thereby losing much of the efficiency benefit. To solve the problem, we propose SpikySpace, a spiking state-space model (SSM) that reduces the quadratic cost in the attention block to linear time via selective scanning. Further, we replace dense SSM updates with sparse spike trains and execute selective scans only on spike events, thereby avoiding dense multiplications while preserving the SSM's structured memory. Because complex operations such as exponentials and divisions are costly on neuromorphic chips, we introduce simplified approximations of SiLU and Softplus to enable a neuromorphic-friendly model architecture. In matched settings, SpikySpace reduces estimated energy consumption by 98.73% and 96.24% compared to two state-of-the-art transformer based approaches, namely iTransformer and iSpikformer, respectively. In standard time series forecasting datasets, SpikySpace delivers competitive accuracy while substantially reducing energy cost and memory traffic. As the first full spiking state-space model, SpikySpace bridges neuromorphic efficiency with modern sequence modeling, marking a practical and scalable path toward efficient time series forecasting systems.
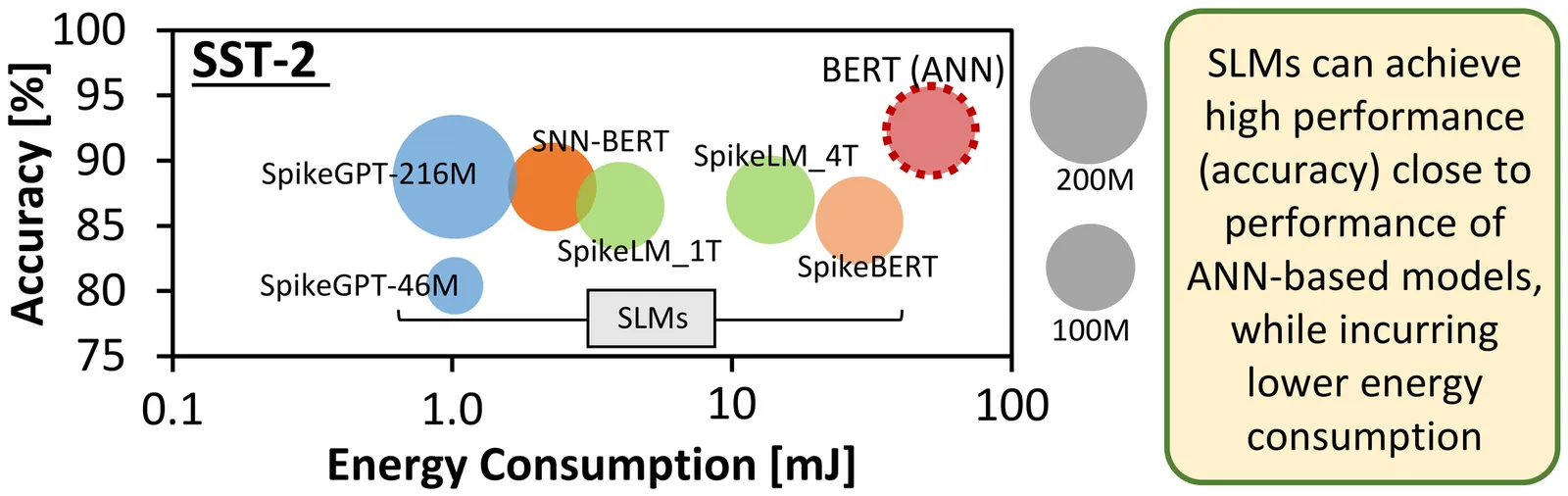
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been emerging as prominent AI models for solving many natural language tasks due to their high performance (e.g., accuracy) and capabilities in generating high-quality responses to the given inputs. However, their large computational cost, huge memory footprints, and high processing power/energy make it challenging for their embedded deployments. Amid several tinyLLMs, recent works have proposed spike-driven language models (SLMs) for significantly reducing the processing power/energy of LLMs. However, their memory footprints still remain too large for low-cost and resource-constrained embedded devices. Manual quantization approach may effectively compress SLM memory footprints, but it requires a huge design time and compute power to find the quantization setting for each network, hence making this approach not-scalable for handling different networks, performance requirements, and memory budgets. To bridge this gap, we propose QSLM, a novel framework that performs automated quantization for compressing pre-trained SLMs, while meeting the performance and memory constraints. To achieve this, QSLM first identifies the hierarchy of the given network architecture and the sensitivity of network layers under quantization, then employs a tiered quantization strategy (e.g., global-, block-, and module-level quantization) while leveraging a multi-objective performance-and-memory trade-off function to select the final quantization setting. Experimental results indicate that our QSLM reduces memory footprint by up to 86.5%, reduces power consumption by up to 20%, maintains high performance across different tasks (i.e., by up to 84.4% accuracy of sentiment classification on the SST-2 dataset and perplexity score of 23.2 for text generation on the WikiText-2 dataset) close to the original non-quantized model while meeting the performance and memory constraints.
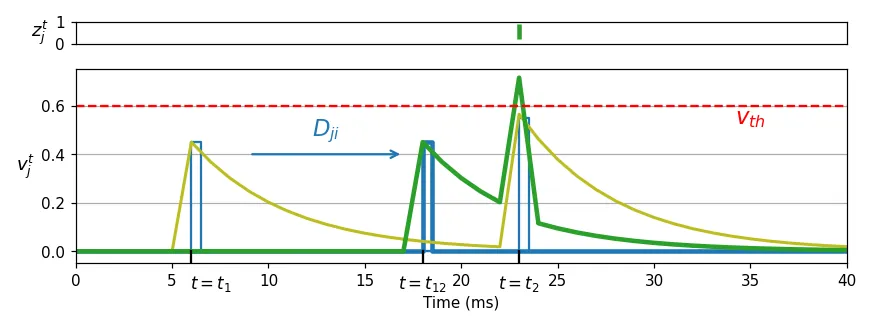
Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are dynamical systems that operate on spatiotemporal data, yet their learnable parameters are often limited to synaptic weights, contributing little to temporal pattern recognition. Learnable parameters that delay spike times can improve classification performance in temporal tasks, but existing methods rely on large networks and offline learning, making them unsuitable for real-time operation in resource-constrained environments. In this paper, we introduce synaptic and axonal delays to leaky integrate and fire (LIF)-based feedforward and recurrent SNNs, and propose three-factor learning rules to simultaneously learn delay parameters online. We employ a smooth Gaussian surrogate to approximate spike derivatives exclusively for the eligibility trace calculation, and together with a top-down error signal determine parameter updates. Our experiments show that incorporating delays improves accuracy by up to 20% over a weights-only baseline, and for networks with similar parameter counts, jointly learning weights and delays yields up to 14% higher accuracy. On the SHD speech recognition dataset, our method achieves similar accuracy to offline backpropagation-based approaches. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, it reduces model size by 6.6x and inference latency by 67%, with only a 2.4% drop in classification accuracy. Our findings benefit the design of power and area-constrained neuromorphic processors by enabling on-device learning and lowering memory requirements.
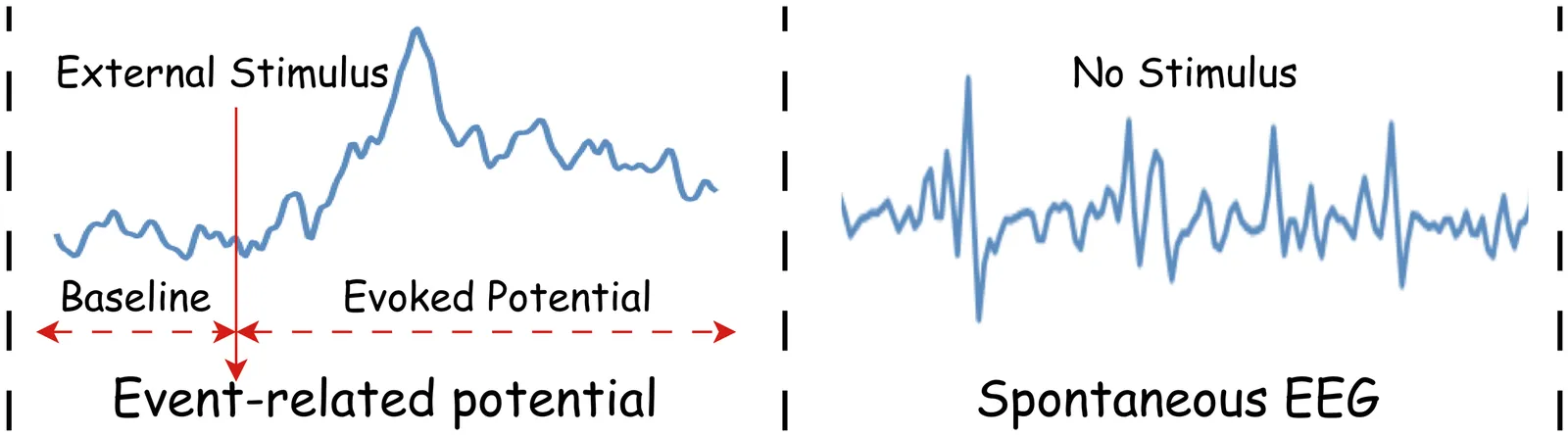
Event-related potential (ERP), a specialized paradigm of electroencephalographic (EEG), reflects neurological responses to external stimuli or events, generally associated with the brain's processing of specific cognitive tasks. ERP plays a critical role in cognitive analysis, the detection of neurological diseases, and the assessment of psychological states. Recent years have seen substantial advances in deep learning-based methods for spontaneous EEG and other non-time-locked task-related EEG signals. However, their effectiveness on ERP data remains underexplored, and many existing ERP studies still rely heavily on manually extracted features. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive benchmark study that systematically compares traditional manual features (followed by a linear classifier), deep learning models, and pre-trained EEG foundation models for ERP analysis. We establish a unified data preprocessing and training pipeline and evaluate these approaches on two representative tasks, ERP stimulus classification and ERP-based brain disease detection, across 12 publicly available datasets. Furthermore, we investigate various patch-embedding strategies within advanced Transformer architectures to identify embedding designs that better suit ERP data. Our study provides a landmark framework to guide method selection and tailored model design for future ERP analysis. The code is available at https://github.com/DL4mHealth/ERP-Benchmark.
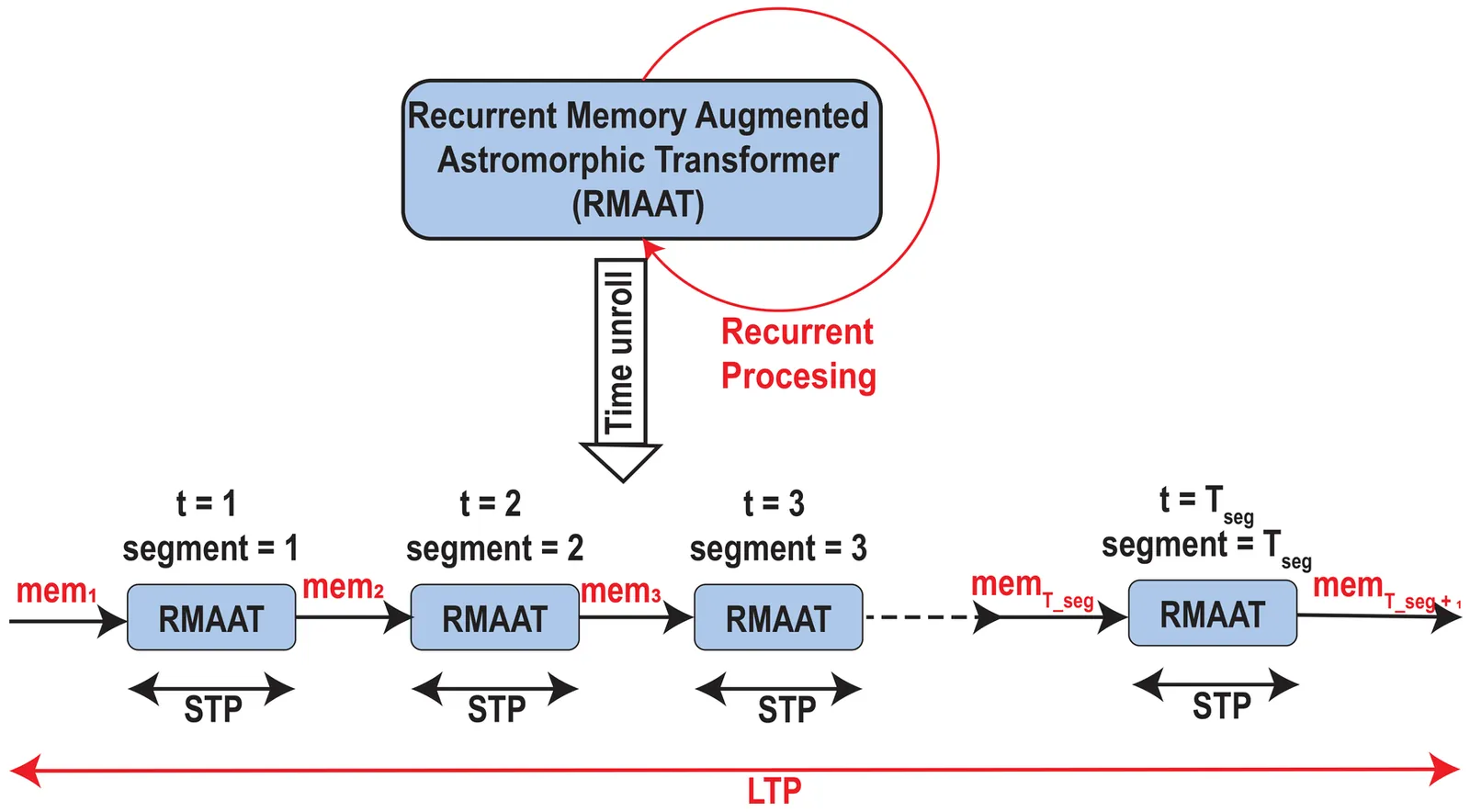
The quadratic complexity of self-attention mechanism presents a significant impediment to applying Transformer models to long sequences. This work explores computational principles derived from astrocytes-glial cells critical for biological memory and synaptic modulation-as a complementary approach to conventional architectural modifications for efficient self-attention. We introduce the Recurrent Memory Augmented Astromorphic Transformer (RMAAT), an architecture integrating abstracted astrocyte functionalities. RMAAT employs a recurrent, segment-based processing strategy where persistent memory tokens propagate contextual information. An adaptive compression mechanism, governed by a novel retention factor derived from simulated astrocyte long-term plasticity (LTP), modulates these tokens. Attention within segments utilizes an efficient, linear-complexity mechanism inspired by astrocyte short-term plasticity (STP). Training is performed using Astrocytic Memory Replay Backpropagation (AMRB), a novel algorithm designed for memory efficiency in recurrent networks. Evaluations on the Long Range Arena (LRA) benchmark demonstrate RMAAT's competitive accuracy and substantial improvements in computational and memory efficiency, indicating the potential of incorporating astrocyte-inspired dynamics into scalable sequence models.
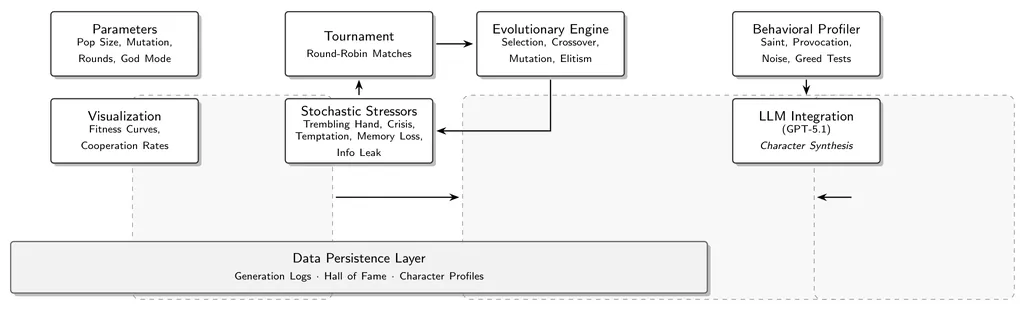
Standard simulations of the Iterated Prisoners Dilemma (IPD) operate in deterministic, noise-free environments, producing strategies that may be theoretically optimal but fragile when confronted with real-world uncertainty. This paper addresses two critical gaps in evolutionary game theory research: (1) the absence of realistic environmental stressors during strategy evolution, and (2) the Interpretability Gap, where evolved genetic strategies remain opaque binary sequences devoid of semantic meaning. We introduce a novel framework combining stochastic environmental perturbations (God Mode) with Large Language Model (LLM)-based behavioral profiling to transform evolved genotypes into interpretable character archetypes. Our experiments demonstrate that strategies evolved under chaotic conditions exhibit superior resilience and present distinct behavioral phenotypes, ranging from Ruthless Capitalists to Diplomatic Enforcers. These phenotypes are readily classified by LLMs but remain nearly impossible to interpret through manual genome inspection alone. This work bridges evolutionary computation with explainable AI and provides a template for automated agent characterization in multi-agent systems.
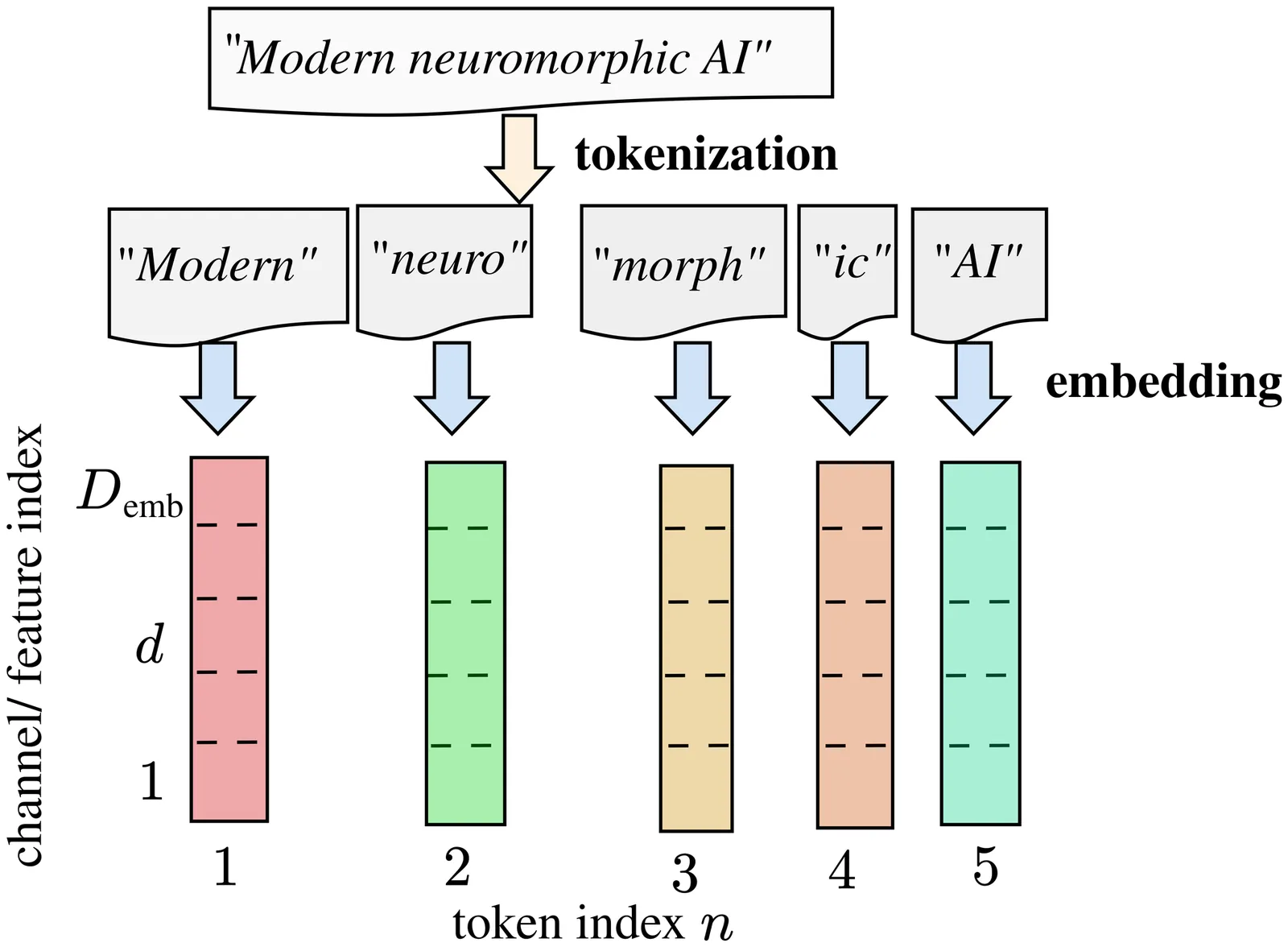
The rapid growth of artificial intelligence (AI) has brought novel data processing and generative capabilities but also escalating energy requirements. This challenge motivates renewed interest in neuromorphic computing principles, which promise brain-like efficiency through discrete and sparse activations, recurrent dynamics, and non-linear feedback. In fact, modern AI architectures increasingly embody neuromorphic principles through heavily quantized activations, state-space dynamics, and sparse attention mechanisms. This paper elaborates on the connections between neuromorphic models, state-space models, and transformer architectures through the lens of the distinction between intra-token processing and inter-token processing. Most early work on neuromorphic AI was based on spiking neural networks (SNNs) for intra-token processing, i.e., for transformations involving multiple channels, or features, of the same vector input, such as the pixels of an image. In contrast, more recent research has explored how neuromorphic principles can be leveraged to design efficient inter-token processing methods, which selectively combine different information elements depending on their contextual relevance. Implementing associative memorization mechanisms, these approaches leverage state-space dynamics or sparse self-attention. Along with a systematic presentation of modern neuromorphic AI models through the lens of intra-token and inter-token processing, training methodologies for neuromorphic AI models are also reviewed. These range from surrogate gradients leveraging parallel convolutional processing to local learning rules based on reinforcement learning mechanisms.
Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategy (CMA-ES) is a highly effective optimization technique. A primary challenge when applying CMA-ES in high dimensionality is sampling from a multivariate normal distribution with an arbitrary covariance matrix, which involves its decomposition. The cubic complexity of this process is the main obstacle to applying CMA-ES in highdimensional spaces. We introduce a version of CMA-ES that uses no covariance matrix at all. In the proposed matrix-free CMA-ES, an archive stores the vectors of differences between individuals and the midpoint, normalized by the step size. New individuals are generated as the weighted combinations of the vectors from the archive. We prove that the probability distribution of individuals generated by the proposed method is identical to that of the standard CMA-ES. Experimental results show that reducing the archive size to store only a fixed number of the most recent populations is sufficient, without compromising optimization efficiency. The matrix-free and matrix-based CMA-ES achieve comparable results on the quadratic function when the step-size adaptation is turned off. When coupled with the step-size adaptation method, the matrix-free CMA-ES converges faster than the matrix-based, and usually yields the results of a comparable or superior quality, according to the results obtained for the CEC'2017 benchmark suite. Presented approach simplifies the algorithm, offers a novel perspective on covariance matrix adaptation, and serves as a stepping stone toward even more efficient methods.
 2512.24722
2512.24722The hippocampus appears to implement two core but highly distinct functions in the brain: long term memory retrieval and planning and spatial navigation. Naively, these functions appear very different algorithmically. In this short note, we demonstrate that two powerful algorithms that have each independently been proposed to underlie the hippocampal operation for each function -- personalized page-rank for memory retrieval, and successor representations for planning and navigation, are in fact isomorphic and utilize the same underlying representation -- the stationary distribution of a random walk on a graph. We hypothesize that the core computational function of the hippocampus is to compute this representation on arbitrary input graphs.
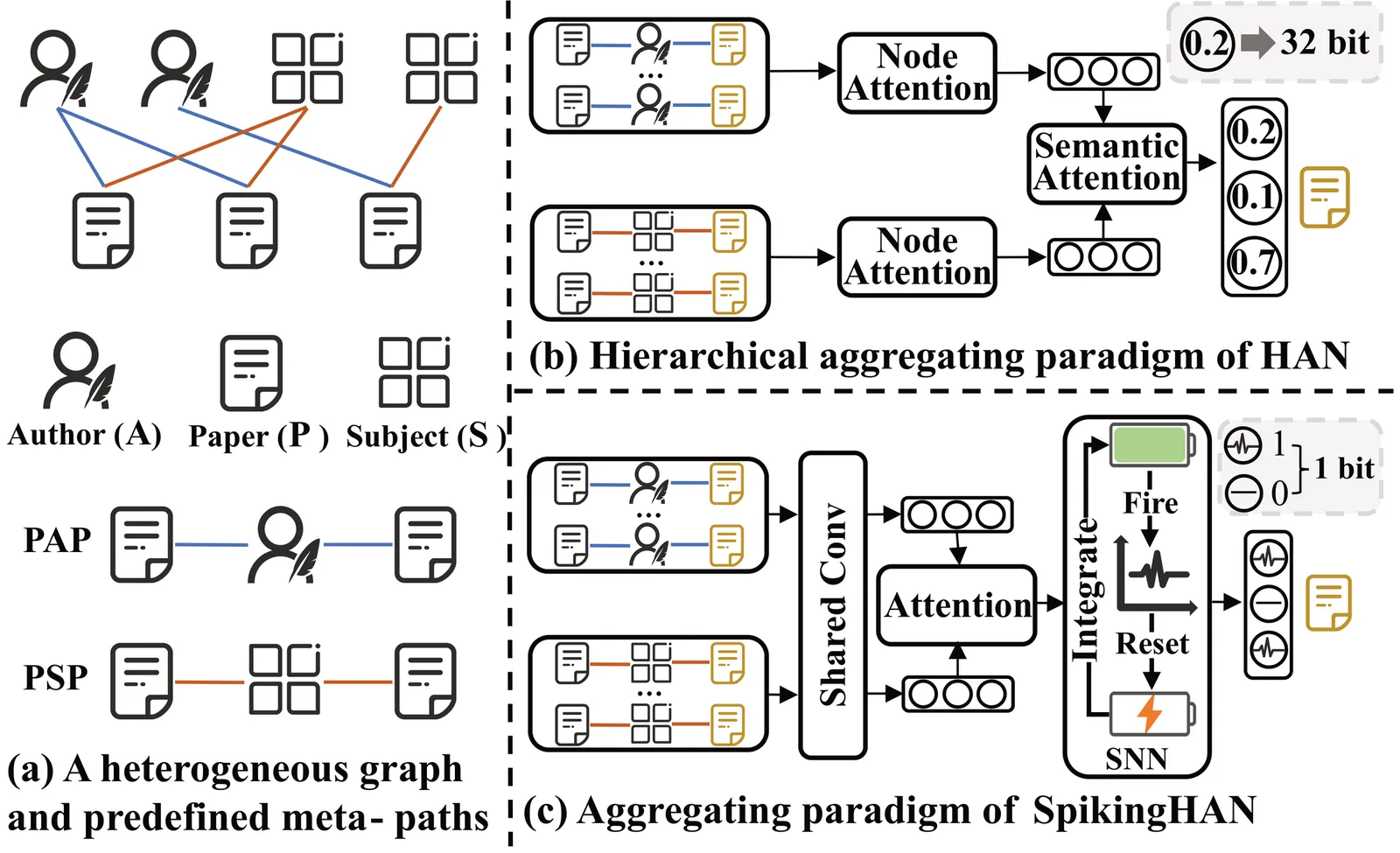
Real-world graphs or networks are usually heterogeneous, involving multiple types of nodes and relationships. Heterogeneous graph neural networks (HGNNs) can effectively handle these diverse nodes and edges, capturing heterogeneous information within the graph, thus exhibiting outstanding performance. However, most methods of HGNNs usually involve complex structural designs, leading to problems such as high memory usage, long inference time, and extensive consumption of computing resources. These limitations pose certain challenges for the practical application of HGNNs, especially for resource-constrained devices. To mitigate this issue, we propose the Spiking Heterogeneous Graph Attention Networks (SpikingHAN), which incorporates the brain-inspired and energy-saving properties of Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) into heterogeneous graph learning to reduce the computing cost without compromising the performance. Specifically, SpikingHAN aggregates metapath-based neighbor information using a single-layer graph convolution with shared parameters. It then employs a semantic-level attention mechanism to capture the importance of different meta-paths and performs semantic aggregation. Finally, it encodes the heterogeneous information into a spike sequence through SNNs, simulating bioinformatic processing to derive a binarized 1-bit representation of the heterogeneous graph. Comprehensive experimental results from three real-world heterogeneous graph datasets show that SpikingHAN delivers competitive node classification performance. It achieves this with fewer parameters, quicker inference, reduced memory usage, and lower energy consumption. Code is available at https://github.com/QianPeng369/SpikingHAN.
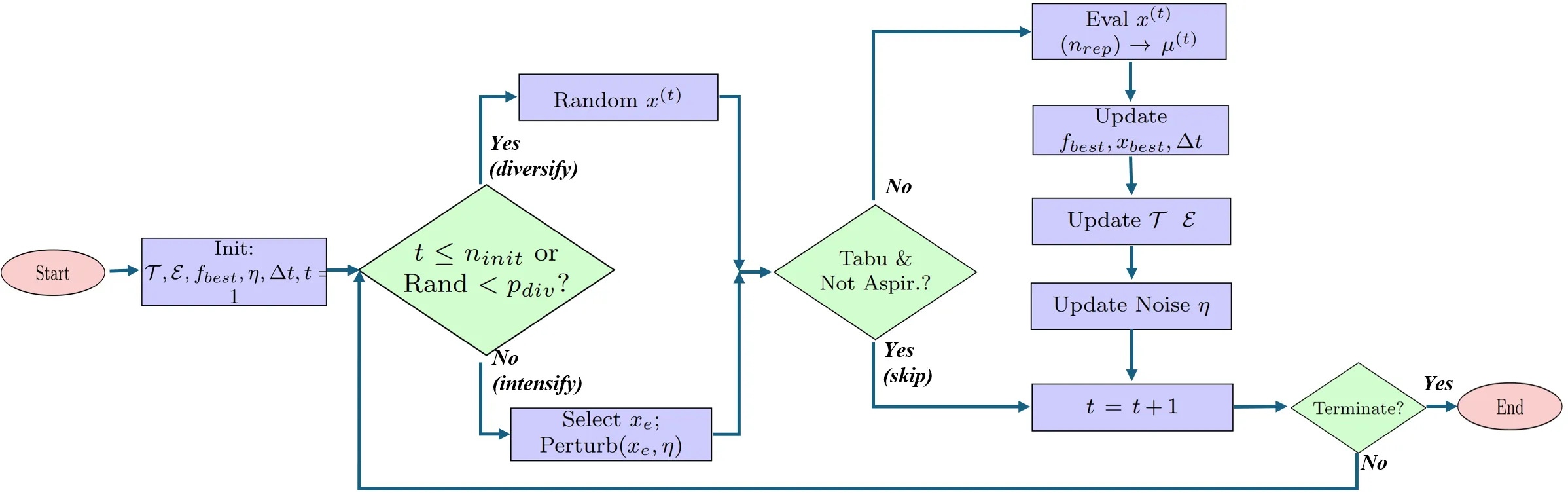
Simulation optimization (SO) is frequently challenged by noisy evaluations, high computational costs, and complex, multimodal search landscapes. This paper introduces Tabu-Enhanced Simulation Optimization (TESO), a novel metaheuristic framework integrating adaptive search with memory-based strategies. TESO leverages a short-term Tabu List to prevent cycling and encourage diversification, and a long-term Elite Memory to guide intensification by perturbing high-performing solutions. An aspiration criterion allows overriding tabu restrictions for exceptional candidates. This combination facilitates a dynamic balance between exploration and exploitation in stochastic environments. We demonstrate TESO's effectiveness and reliability using an queue optimization problem, showing improved performance compared to benchmarks and validating the contribution of its memory components. Source code and data are available at: https://github.com/bulentsoykan/TESO.
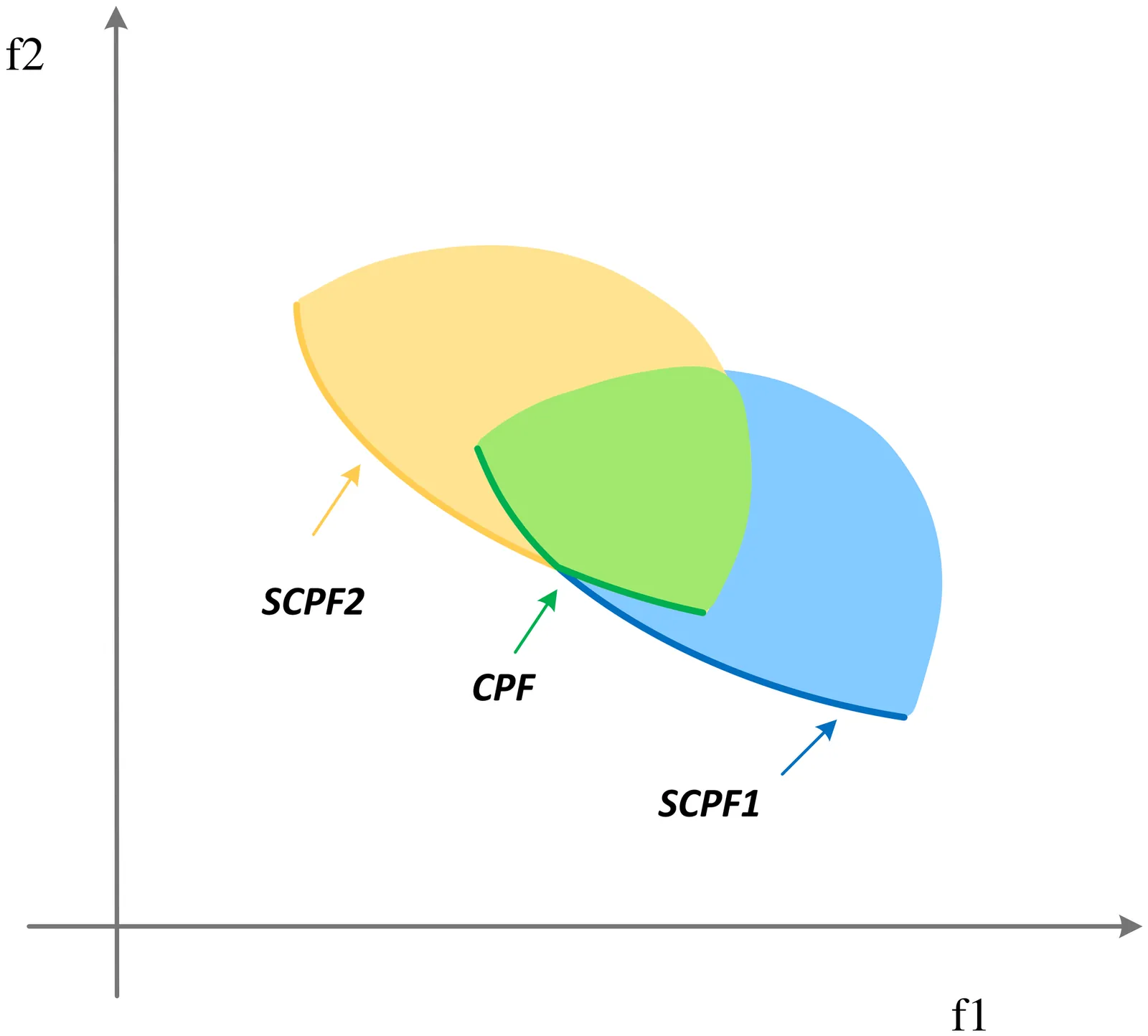
Real-world Constrained Multi-objective Optimization Problems (CMOPs) often contain multiple constraints, and understanding and utilizing the coupling between these constraints is crucial for solving CMOPs. However, existing Constrained Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithms (CMOEAs) typically ignore these couplings and treat all constraints as a single aggregate, which lacks interpretability regarding the specific geometric roles of constraints. To address this limitation, we first analyze how different constraints interact and show that the final Constrained Pareto Front (CPF) depends not only on the Pareto fronts of individual constraints but also on the boundaries of infeasible regions. This insight implies that CMOPs with different coupling types must be solved from different search directions. Accordingly, we propose a novel algorithm named Decoupling Constraint from Two Directions (DCF2D). This method periodically detects constraint couplings and spawns an auxiliary population for each relevant constraint with an appropriate search direction. Extensive experiments on seven challenging CMOP benchmark suites and on a collection of real-world CMOPs demonstrate that DCF2D outperforms five state-of-the-art CMOEAs, including existing decoupling-based methods.