Robotics
Covers all aspects of robotics, including robotic systems design, motion planning, and robot learning.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Covers all aspects of robotics, including robotic systems design, motion planning, and robot learning.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Many embedded devices operate under resource constraints and in dynamic environments, requiring local decision-making capabilities. Enabling devices to make independent decisions in such environments can improve the responsiveness of the system and reduce the dependence on constant external control. In this work, we integrate an autonomous agent, programmed using AgentSpeak, with a small two-wheeled robot that explores a maze using its own decision-making and sensor data. Experimental results show that the agent successfully solved the maze in 59 seconds using 287 reasoning cycles, with decision phases taking less than one millisecond. These results indicate that the reasoning process is efficient enough for real-time execution on resource-constrained hardware. This integration demonstrates how high-level agent-based control can be applied to resource-constrained embedded systems for autonomous operation.
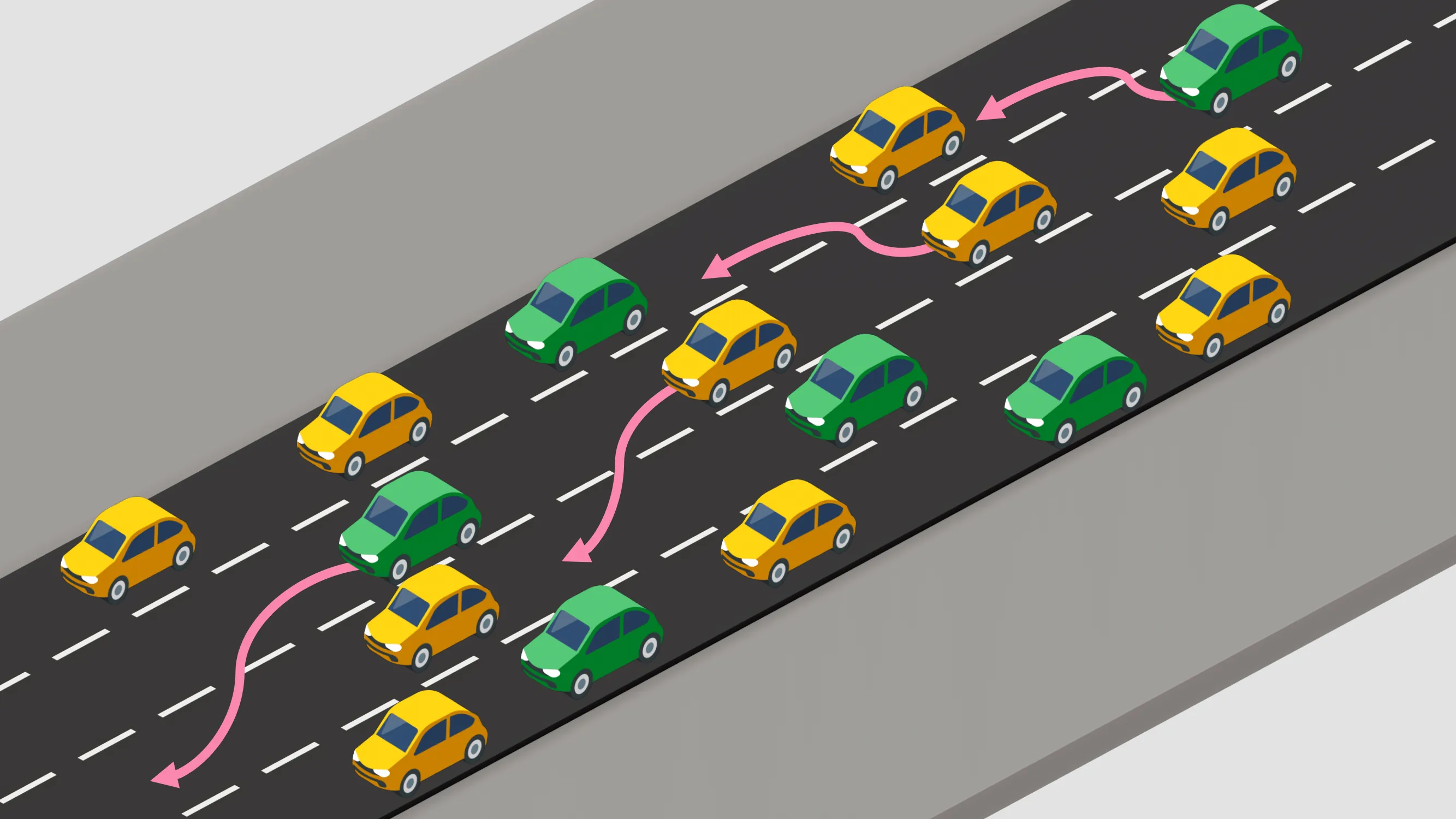
Emergency vehicles require rapid passage through congested traffic, yet existing strategies fail to adapt to dynamic conditions. We propose a novel hierarchical graph neural network (GNN)-based multi-agent reinforcement learning framework to coordinate connected vehicles for emergency corridor formation. Our approach uses a high-level planner for global strategy and low-level controllers for trajectory execution, utilizing graph attention networks to scale with variable agent counts. Trained via Multi-Agent Proximal Policy Optimization (MAPPO), the system reduces emergency vehicle travel time by 28.3% compared to baselines and 44.6% compared to uncoordinated traffic in simulations. The design achieves near-zero collision rates (0.3%) while maintaining 81% of background traffic efficiency. Ablation and generalization studies confirm the framework's robustness across diverse scenarios. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of combining GNNs with hierarchical learning for intelligent transportation systems.

As world models gain momentum in Embodied AI, an increasing number of works explore using video foundation models as predictive world models for downstream embodied tasks like 3D prediction or interactive generation. However, before exploring these downstream tasks, video foundation models still have two critical questions unanswered: (1) whether their generative generalization is sufficient to maintain perceptual fidelity in the eyes of human observers, and (2) whether they are robust enough to serve as a universal prior for real-world embodied agents. To provide a standardized framework for answering these questions, we introduce the Embodied Turing Test benchmark: WoW-World-Eval (Wow,wo,val). Building upon 609 robot manipulation data, Wow-wo-val examines five core abilities, including perception, planning, prediction, generalization, and execution. We propose a comprehensive evaluation protocol with 22 metrics to assess the models' generation ability, which achieves a high Pearson Correlation between the overall score and human preference (>0.93) and establishes a reliable foundation for the Human Turing Test. On Wow-wo-val, models achieve only 17.27 on long-horizon planning and at best 68.02 on physical consistency, indicating limited spatiotemporal consistency and physical reasoning. For the Inverse Dynamic Model Turing Test, we first use an IDM to evaluate the video foundation models' execution accuracy in the real world. However, most models collapse to $\approx$ 0% success, while WoW maintains a 40.74% success rate. These findings point to a noticeable gap between the generated videos and the real world, highlighting the urgency and necessity of benchmarking World Model in Embodied AI.
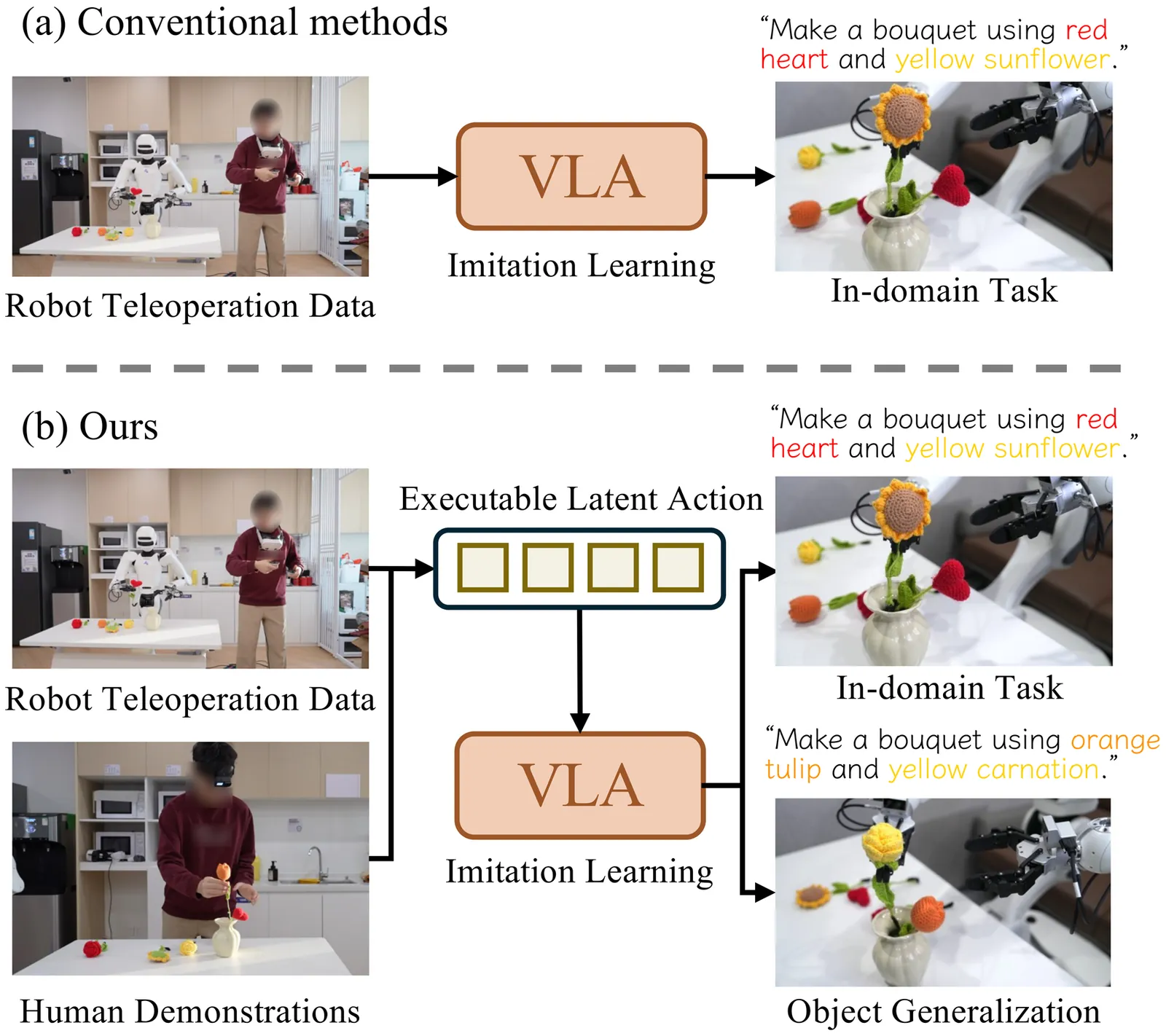
Generalist Vision-Language-Action models are currently hindered by the scarcity of robotic data compared to the abundance of human video demonstrations. Existing Latent Action Models attempt to leverage video data but often suffer from visual entanglement, capturing noise rather than manipulation skills. To address this, we propose Contrastive Latent Action Pretraining (CLAP), a framework that aligns the visual latent space from videos with a proprioceptive latent space from robot trajectories. By employing contrastive learning, CLAP maps video transitions onto a quantized, physically executable codebook. Building on this representation, we introduce a dual-formulation VLA framework offering both CLAP-NTP, an autoregressive model excelling at instruction following and object generalization, and CLAP-RF, a Rectified Flow-based policy designed for high-frequency, precise manipulation. Furthermore, we propose a Knowledge Matching (KM) regularization strategy to mitigate catastrophic forgetting during fine-tuning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CLAP significantly outperforms strong baselines, enabling the effective transfer of skills from human videos to robotic execution. Project page: https://lin-shan.com/CLAP/.
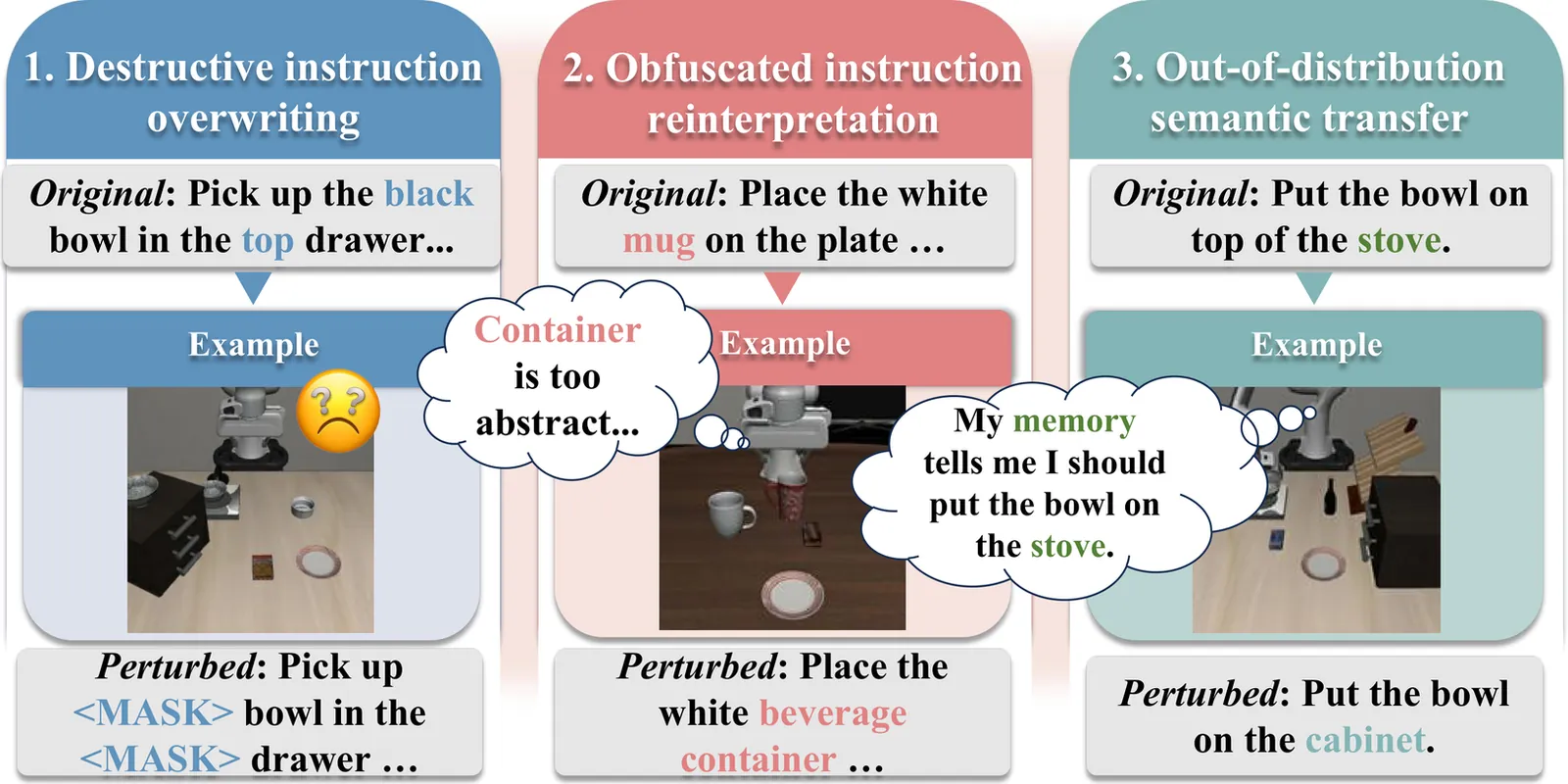
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have demonstrated impressive capabilities in generalized robotic control; however, they remain notoriously brittle to linguistic perturbations. We identify a critical ``modality collapse'' phenomenon where strong visual priors overwhelm sparse linguistic signals, causing agents to overfit to specific instruction phrasings while ignoring the underlying semantic intent. To address this, we propose \textbf{Residual Semantic Steering (RSS)}, a probabilistic framework that disentangles physical affordance from semantic execution. RSS introduces two theoretical innovations: (1) \textbf{Monte Carlo Syntactic Integration}, which approximates the true semantic posterior via dense, LLM-driven distributional expansion, and (2) \textbf{Residual Affordance Steering}, a dual-stream decoding mechanism that explicitly isolates the causal influence of language by subtracting the visual affordance prior. Theoretical analysis suggests that RSS effectively maximizes the mutual information between action and intent while suppressing visual distractors. Empirical results across diverse manipulation benchmarks demonstrate that RSS achieves state-of-the-art robustness, maintaining performance even under adversarial linguistic perturbations.
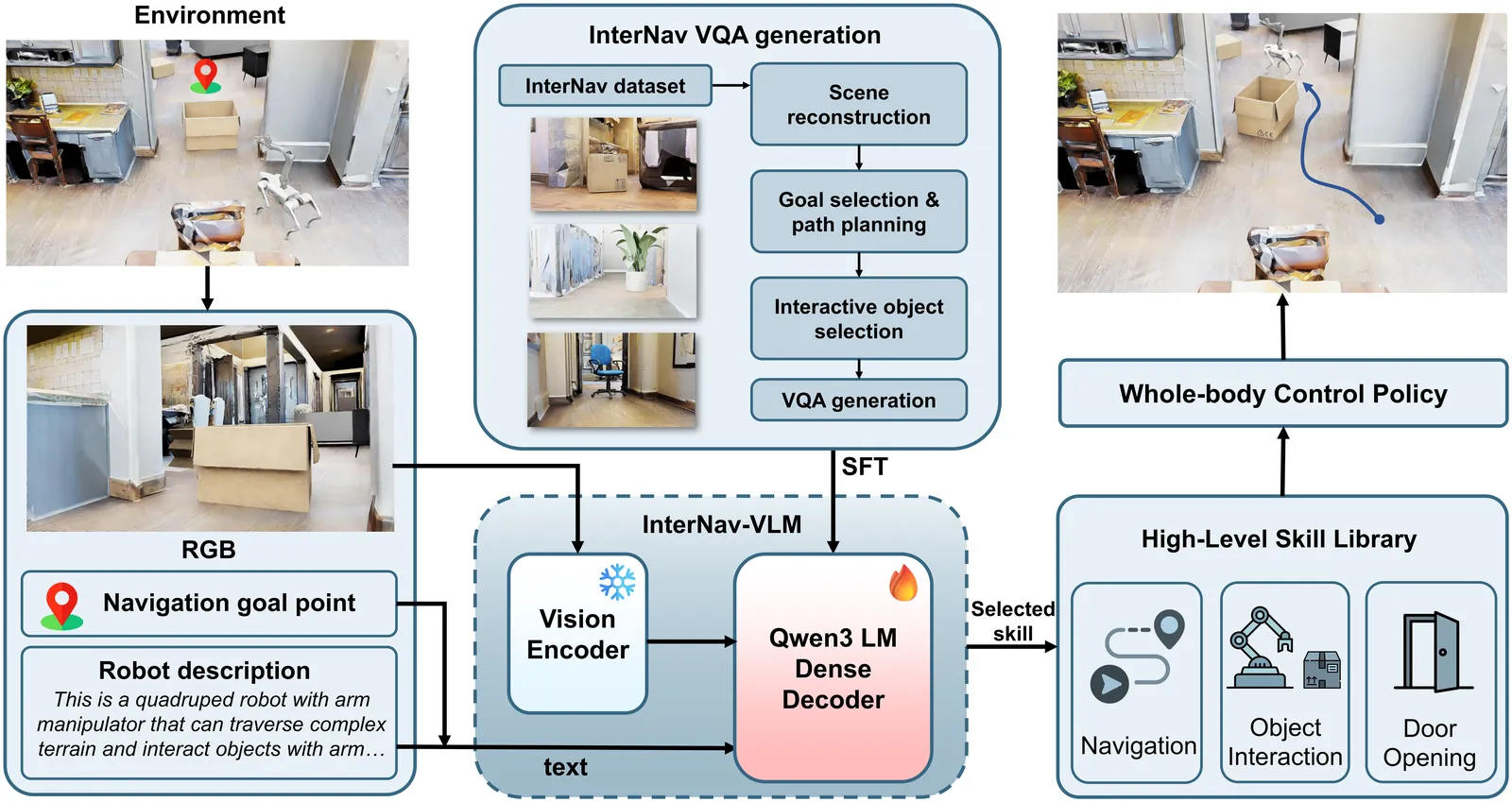
Recent Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in robotic planning. However, they typically function as semantic reasoners, lacking an intrinsic understanding of the specific robot's physical capabilities. This limitation is particularly critical in interactive navigation, where robots must actively modify cluttered environments to create traversable paths. Existing VLM-based navigators are predominantly confined to passive obstacle avoidance, failing to reason about when and how to interact with objects to clear blocked paths. To bridge this gap, we propose Counterfactual Interactive Navigation via Skill-aware VLM (CoINS), a hierarchical framework that integrates skill-aware reasoning and robust low-level execution. Specifically, we fine-tune a VLM, named InterNav-VLM, which incorporates skill affordance and concrete constraint parameters into the input context and grounds them into a metric-scale environmental representation. By internalizing the logic of counterfactual reasoning through fine-tuning on the proposed InterNav dataset, the model learns to implicitly evaluate the causal effects of object removal on navigation connectivity, thereby determining interaction necessity and target selection. To execute the generated high-level plans, we develop a comprehensive skill library through reinforcement learning, specifically introducing traversability-oriented strategies to manipulate diverse objects for path clearance. A systematic benchmark in Isaac Sim is proposed to evaluate both the reasoning and execution aspects of interactive navigation. Extensive simulations and real-world experiments demonstrate that CoINS significantly outperforms representative baselines, achieving a 17\% higher overall success rate and over 80\% improvement in complex long-horizon scenarios compared to the best-performing baseline

This paper presents a neuromorphic, event-driven tactile sensing system for soft, large-area skin, based on the Dynamic Vision Sensors (DVS) integrated with a flexible silicone optical waveguide skin. Instead of repetitively scanning embedded photoreceivers, this design uses a stereo vision setup comprising two DVS cameras looking sideways through the skin. Such a design produces events as changes in brightness are detected, and estimates press positions on the 2D skin surface through triangulation, utilizing Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) to find the center of mass of contact events resulting from pressing actions. The system is evaluated over a 4620 mm2 probed area of the skin using a meander raster scan. Across 95 % of the presses visible to both cameras, the press localization achieved a Root-Mean-Squared Error (RMSE) of 4.66 mm. The results highlight the potential of this approach for wide-area flexible and responsive tactile sensors in soft robotics and interactive environments. Moreover, we examined how the system performs when the amount of event data is strongly reduced. Using stochastic down-sampling, the event stream was reduced to 1/1024 of its original size. Under this extreme reduction, the average localization error increased only slightly (from 4.66 mm to 9.33 mm), and the system still produced valid press localizations for 85 % of the trials. This reduction in pass rate is expected, as some presses no longer produce enough events to form a reliable cluster for triangulation. These results show that the sensing approach remains functional even with very sparse event data, which is promising for reducing power consumption and computational load in future implementations. The system exhibits a detection latency distribution with a characteristic width of 31 ms.

Ensuring the functional safety of Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) requires motion planning modules that not only operate within strict real-time constraints but also maintain controllability in case of system faults. Existing safeguarding concepts, such as Online Verification (OV), provide safety layers that detect infeasible planning outputs. However, they lack an active mechanism to ensure safe operation in the event that the main planner fails. This paper presents a first step toward an active safety extension for fail-operational Autonomous Driving (AD). We deploy a lightweight sampling-based trajectory planner on an automotive-grade, embedded platform running a Real-Time Operating System (RTOS). The planner continuously computes trajectories under constrained computational resources, forming the foundation for future emergency planning architectures. Experimental results demonstrate deterministic timing behavior with bounded latency and minimal jitter, validating the feasibility of trajectory planning on safety-certifiable hardware. The study highlights both the potential and the remaining challenges of integrating active fallback mechanisms as an integral part of next-generation safeguarding frameworks. The code is available at: https://github.com/TUM-AVS/real-time-motion-planning
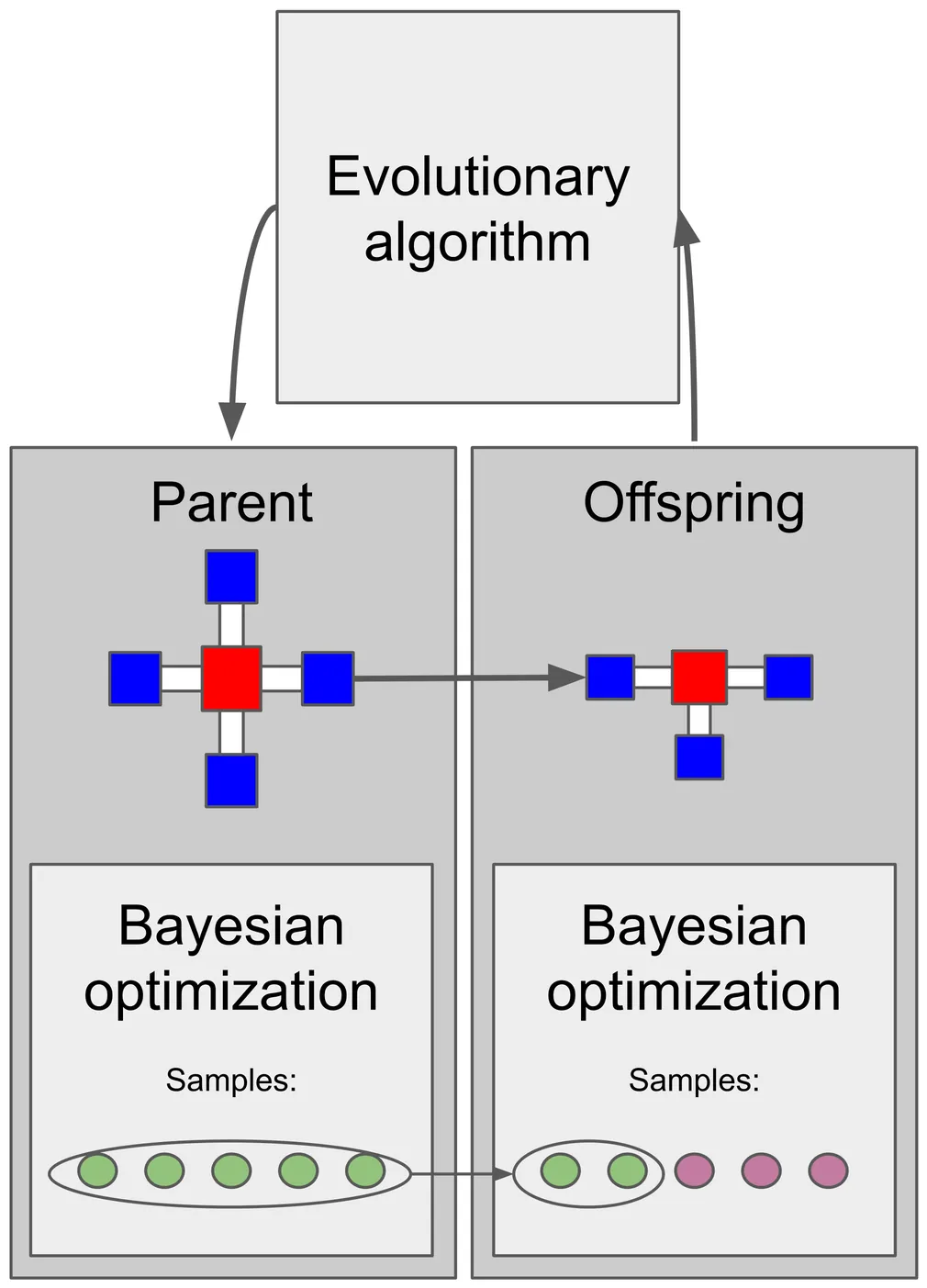
In evolutionary robotics, robot morphologies are designed automatically using evolutionary algorithms. This creates a body-brain optimization problem, where both morphology and control must be optimized together. A common approach is to include controller optimization for each morphology, but starting from scratch for every new body may require a high controller learning budget. We address this by using Bayesian optimization for controller optimization, exploiting its sample efficiency and strong exploration capabilities, and using sample inheritance as a form of Lamarckian inheritance. Under a deliberately low controller learning budget for each morphology, we investigate two types of sample inheritance: (1) transferring all the parent's samples to the offspring to be used as prior without evaluating them, and (2) reevaluating the parent's best samples on the offspring. Both are compared to a baseline without inheritance. Our results show that reevaluation performs best, with prior-based inheritance also outperforming no inheritance. Analysis reveals that while the learning budget is too low for a single morphology, generational inheritance compensates for this by accumulating learned adaptations across generations. Furthermore, inheritance mainly benefits offspring morphologies that are similar to their parents. Finally, we demonstrate the critical role of the environment, with more challenging environments resulting in more stable walking gaits. Our findings highlight that inheritance mechanisms can boost performance in evolutionary robotics without needing large learning budgets, offering an efficient path toward more capable robot design.
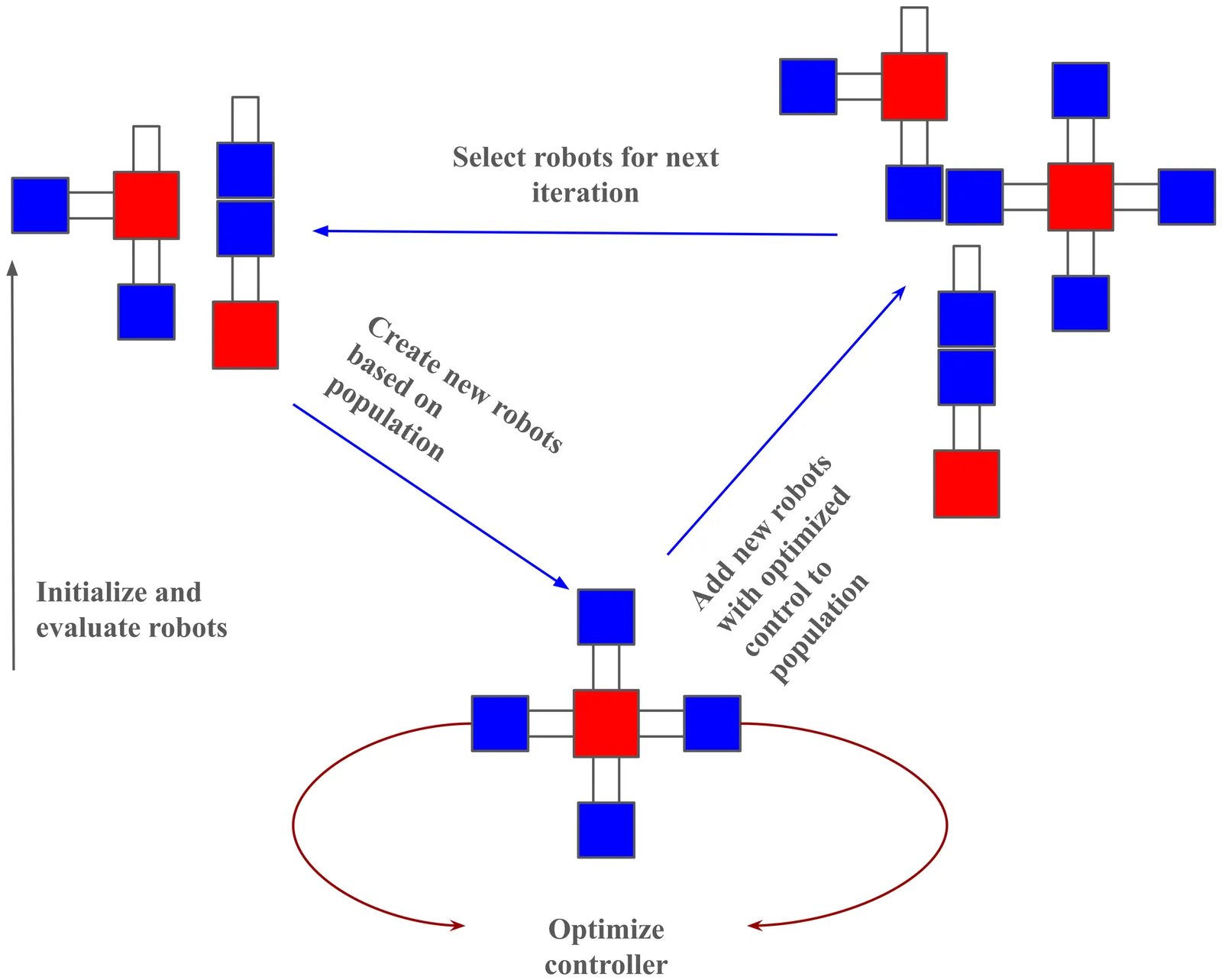
Evolutionary Robotics offers the possibility to design robots to solve a specific task automatically by optimizing their morphology and control together. However, this co-optimization of body and control is challenging, because controllers need some time to adapt to the evolving morphology - which may make it difficult for new and promising designs to enter the evolving population. A solution to this is to add intra-life learning, defined as an additional controller optimization loop, to each individual in the evolving population. A related problem is the lack of diversity often seen in evolving populations as evolution narrows the search down to a few promising designs too quickly. This problem can be mitigated by implementing full generational replacement, where offspring robots replace the whole population. This solution for increasing diversity usually comes at the cost of lower performance compared to using elitism. In this work, we show that combining such generational replacement with intra-life learning can increase diversity while retaining performance. We also highlight the importance of performance metrics when studying learning in morphologically evolving robots, showing that evaluating according to function evaluations versus according to generations of evolution can give different conclusions.
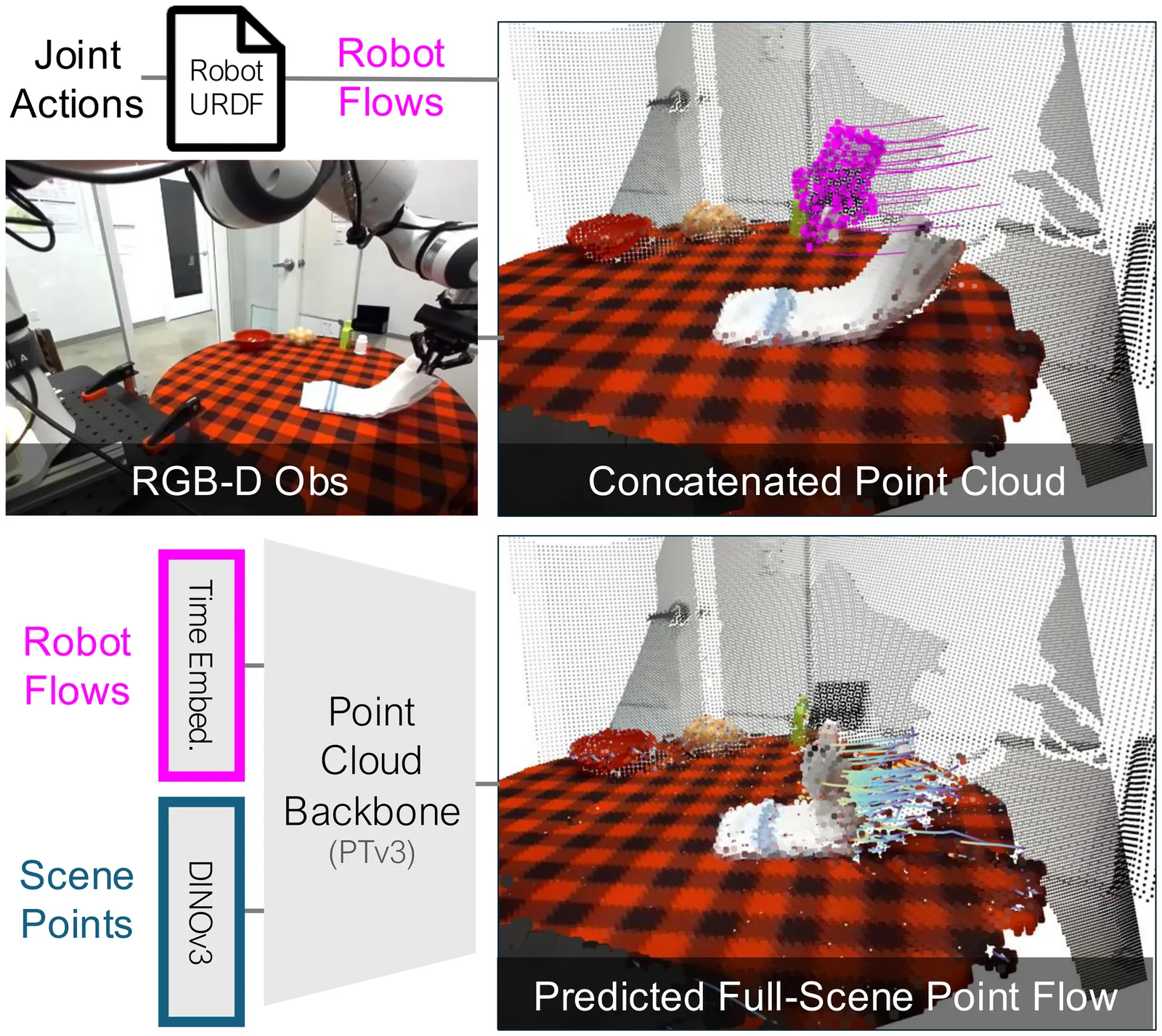
Humans anticipate, from a glance and a contemplated action of their bodies, how the 3D world will respond, a capability that is equally vital for robotic manipulation. We introduce PointWorld, a large pre-trained 3D world model that unifies state and action in a shared 3D space as 3D point flows: given one or few RGB-D images and a sequence of low-level robot action commands, PointWorld forecasts per-pixel displacements in 3D that respond to the given actions. By representing actions as 3D point flows instead of embodiment-specific action spaces (e.g., joint positions), this formulation directly conditions on physical geometries of robots while seamlessly integrating learning across embodiments. To train our 3D world model, we curate a large-scale dataset spanning real and simulated robotic manipulation in open-world environments, enabled by recent advances in 3D vision and simulated environments, totaling about 2M trajectories and 500 hours across a single-arm Franka and a bimanual humanoid. Through rigorous, large-scale empirical studies of backbones, action representations, learning objectives, partial observability, data mixtures, domain transfers, and scaling, we distill design principles for large-scale 3D world modeling. With a real-time (0.1s) inference speed, PointWorld can be efficiently integrated in the model-predictive control (MPC) framework for manipulation. We demonstrate that a single pre-trained checkpoint enables a real-world Franka robot to perform rigid-body pushing, deformable and articulated object manipulation, and tool use, without requiring any demonstrations or post-training and all from a single image captured in-the-wild. Project website at https://point-world.github.io/.
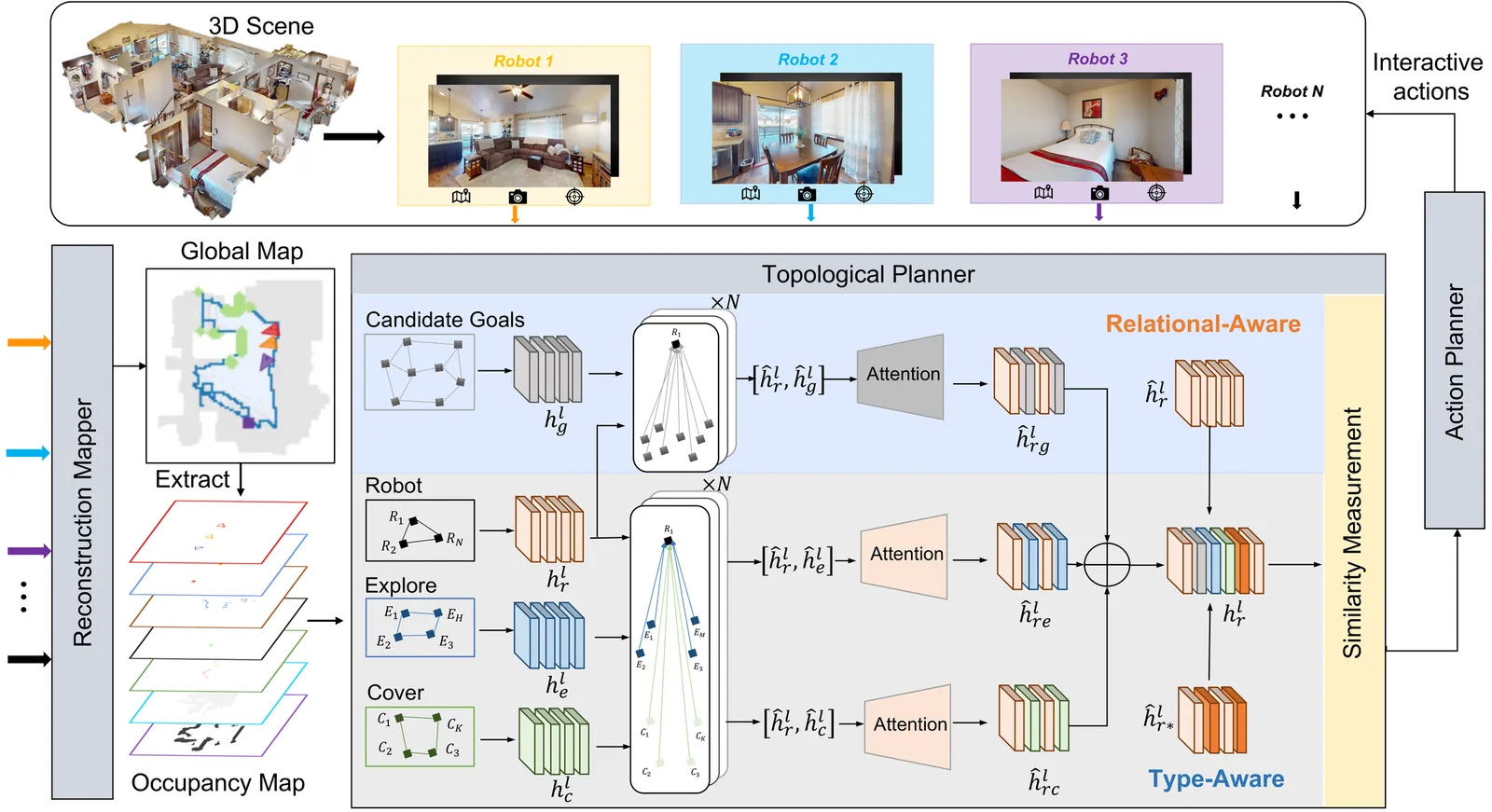
In multi-robot collaborative area search, a key challenge is to dynamically balance the two objectives of exploring unknown areas and covering specific targets to be rescued. Existing methods are often constrained by homogeneous graph representations, thus failing to model and balance these distinct tasks. To address this problem, we propose a Dual-Attention Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network (DA-HGNN) trained using deep reinforcement learning. Our method constructs a heterogeneous graph that incorporates three entity types: robot nodes, frontier nodes, and interesting nodes, as well as their historical states. The dual-attention mechanism comprises the relational-aware attention and type-aware attention operations. The relational-aware attention captures the complex spatio-temporal relationships among robots and candidate goals. Building on this relational-aware heterogeneous graph, the type-aware attention separately computes the relevance between robots and each goal type (frontiers vs. points of interest), thereby decoupling the exploration and coverage from the unified tasks. Extensive experiments conducted in interactive 3D scenarios within the iGibson simulator, leveraging the Gibson and MatterPort3D datasets, validate the superior scalability and generalization capability of the proposed approach.
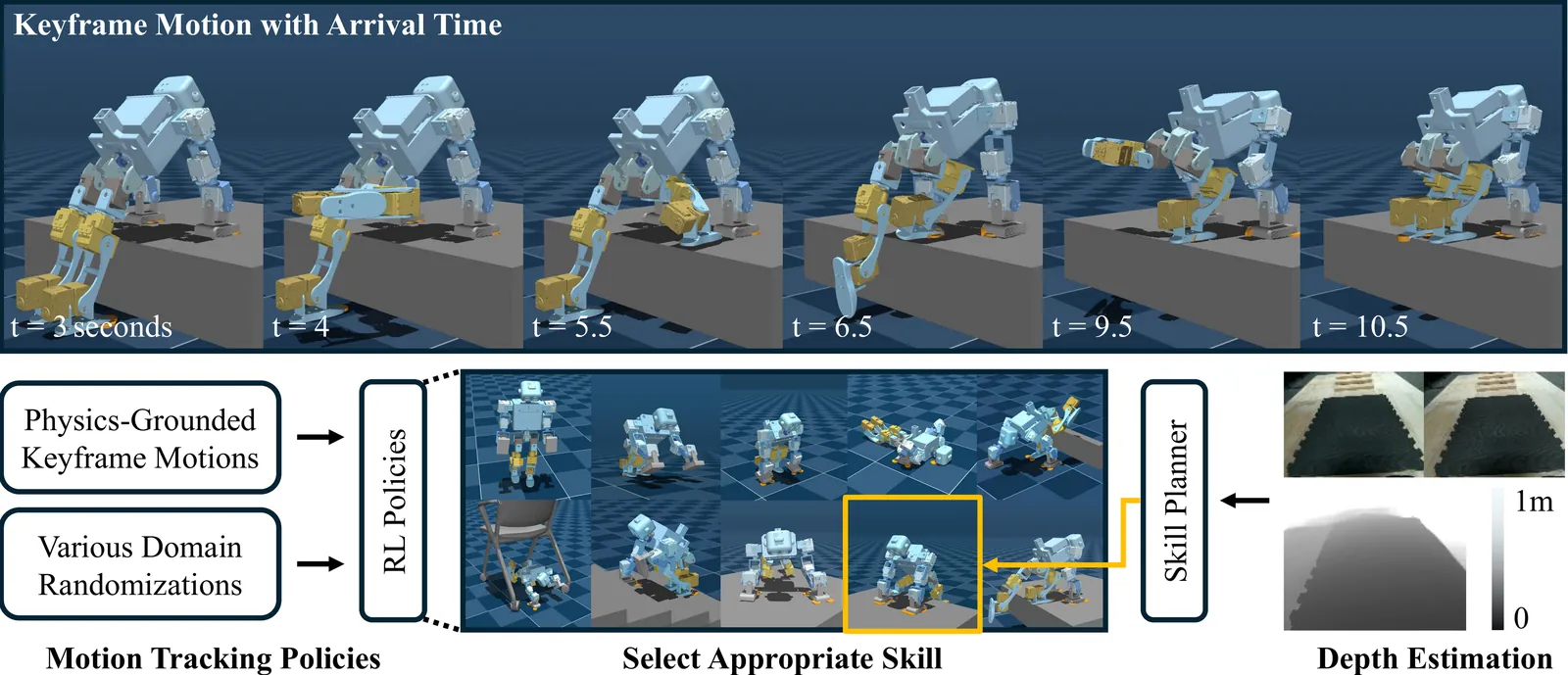
Most locomotion methods for humanoid robots focus on leg-based gaits, yet natural bipeds frequently rely on hands, knees, and elbows to establish additional contacts for stability and support in complex environments. This paper introduces Locomotion Beyond Feet, a comprehensive system for whole-body humanoid locomotion across extremely challenging terrains, including low-clearance spaces under chairs, knee-high walls, knee-high platforms, and steep ascending and descending stairs. Our approach addresses two key challenges: contact-rich motion planning and generalization across diverse terrains. To this end, we combine physics-grounded keyframe animation with reinforcement learning. Keyframes encode human knowledge of motor skills, are embodiment-specific, and can be readily validated in simulation or on hardware, while reinforcement learning transforms these references into robust, physically accurate motions. We further employ a hierarchical framework consisting of terrain-specific motion-tracking policies, failure recovery mechanisms, and a vision-based skill planner. Real-world experiments demonstrate that Locomotion Beyond Feet achieves robust whole-body locomotion and generalizes across obstacle sizes, obstacle instances, and terrain sequences.
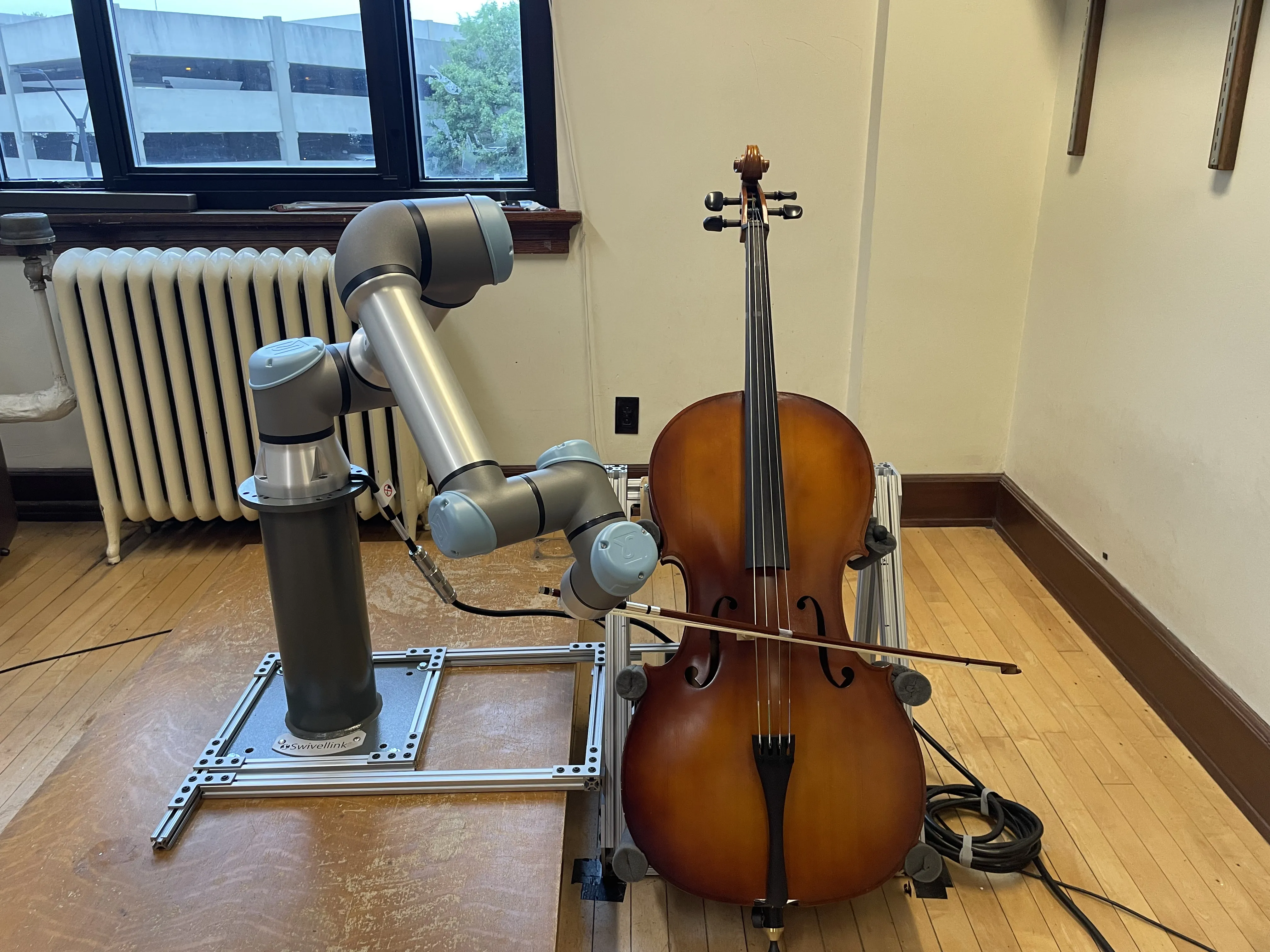

Robot musicians require precise control to obtain proper note accuracy, sound quality, and musical expression. Performance of string instruments, such as violin and cello, presents a significant challenge due to the precise control required over bow angle and pressure to produce the desired sound. While prior robotic cellists focus on accurate bowing trajectories, these works often rely on expensive motion capture techniques, and fail to sightread music in a human-like way. We propose a novel end-to-end MIDI score to robotic motion pipeline which converts musical input directly into collision-aware bowing motions for a UR5e robot cellist. Through use of Universal Robot Freedrive feature, our robotic musician can achieve human-like sound without the need for motion capture. Additionally, this work records live joint data via Real-Time Data Exchange (RTDE) as the robot plays, providing labeled robotic playing data from a collection of five standard pieces to the research community. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in comparison to human performers, we introduce the Musical Turing Test, in which a collection of 132 human participants evaluate our robot's performance against a human baseline. Human reference recordings are also released, enabling direct comparison for future studies. This evaluation technique establishes the first benchmark for robotic cello performance. Finally, we outline a residual reinforcement learning methodology to improve upon baseline robotic controls, highlighting future opportunities for improved string-crossing efficiency and sound quality.
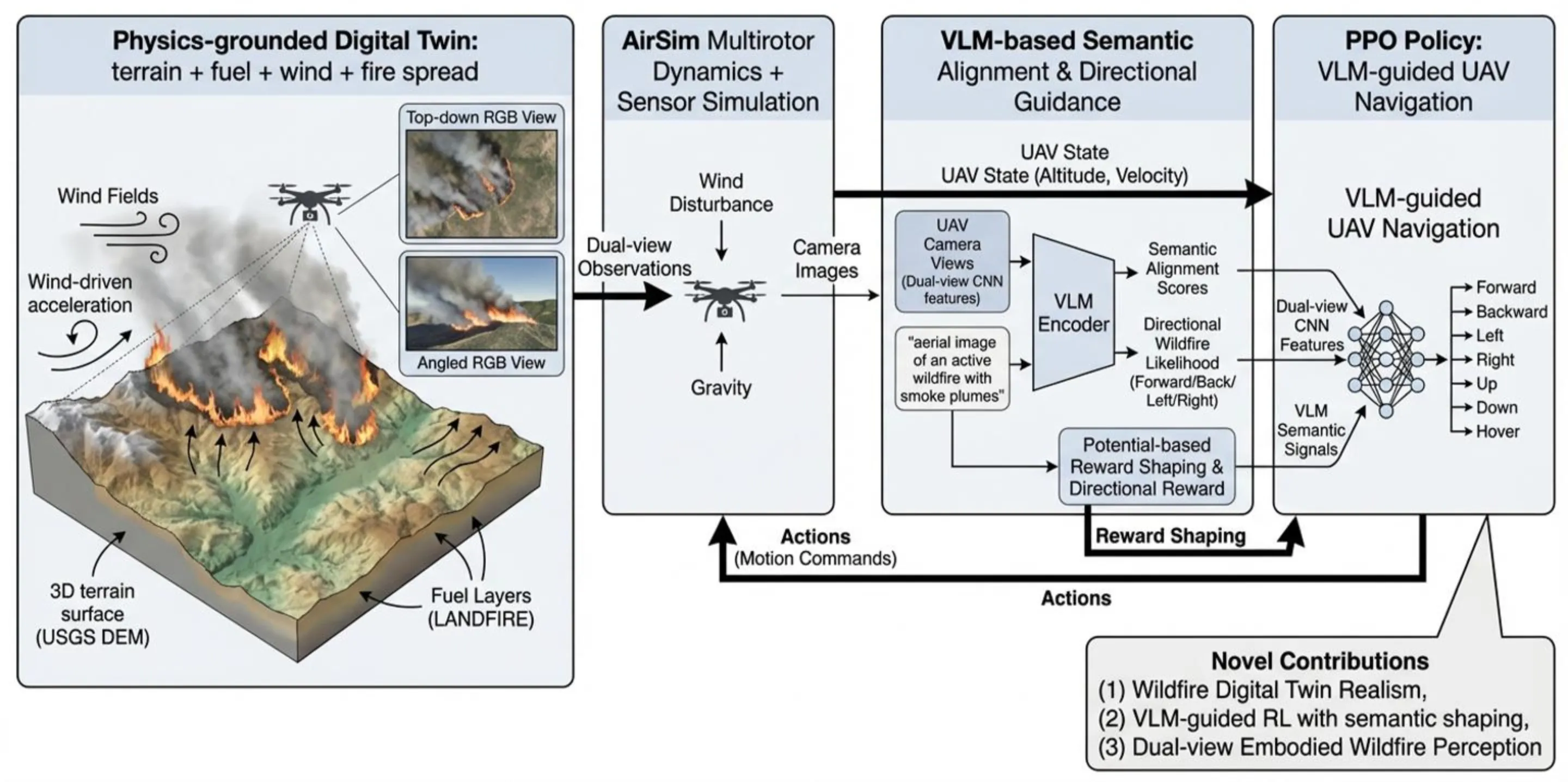
Wildfire monitoring demands autonomous systems capable of reasoning under extreme visual degradation, rapidly evolving physical dynamics, and scarce real-world training data. Existing UAV navigation approaches rely on simplified simulators and supervised perception pipelines, and lack embodied agents interacting with physically realistic fire environments. We introduce FIRE-VLM, the first end-to-end vision-language model (VLM) guided reinforcement learning (RL) framework trained entirely within a high-fidelity, physics-grounded wildfire digital twin. Built from USGS Digital Elevation Model (DEM) terrain, LANDFIRE fuel inventories, and semi-physical fire-spread solvers, this twin captures terrain-induced runs, wind-driven acceleration, smoke plume occlusion, and dynamic fuel consumption. Within this environment, a PPO agent with dual-view UAV sensing is guided by a CLIP-style VLM. Wildfire-specific semantic alignment scores, derived from a single prompt describing active fire and smoke plumes, are integrated as potential-based reward shaping signals. Our contributions are: (1) a GIS-to-simulation pipeline for constructing wildfire digital twins; (2) a VLM-guided RL agent for UAV firefront tracking; and (3) a wildfire-aware reward design that combines physical terms with VLM semantics. Across five digital-twin evaluation tasks, our VLM-guided policy reduces time-to-detection by up to 6 times, increases time-in-FOV, and is, to our knowledge, the first RL-based UAV wildfire monitoring system demonstrated in kilometer-scale, physics-grounded digital-twin fires.
Water level monitoring is critical for flood management, water resource allocation, and ecological assessment, yet traditional methods remain costly and limited in coverage. This work explores radar-based sensing as a low-cost alternative for water level estimation, leveraging its non-contact nature and robustness to environmental conditions. Commercial radar sensors are evaluated in real-world field tests, applying statistical filtering techniques to improve accuracy. Results show that a single radar sensor can achieve centimeter-scale precision with minimal calibration, making it a practical solution for autonomous water monitoring using drones and robotic platforms.
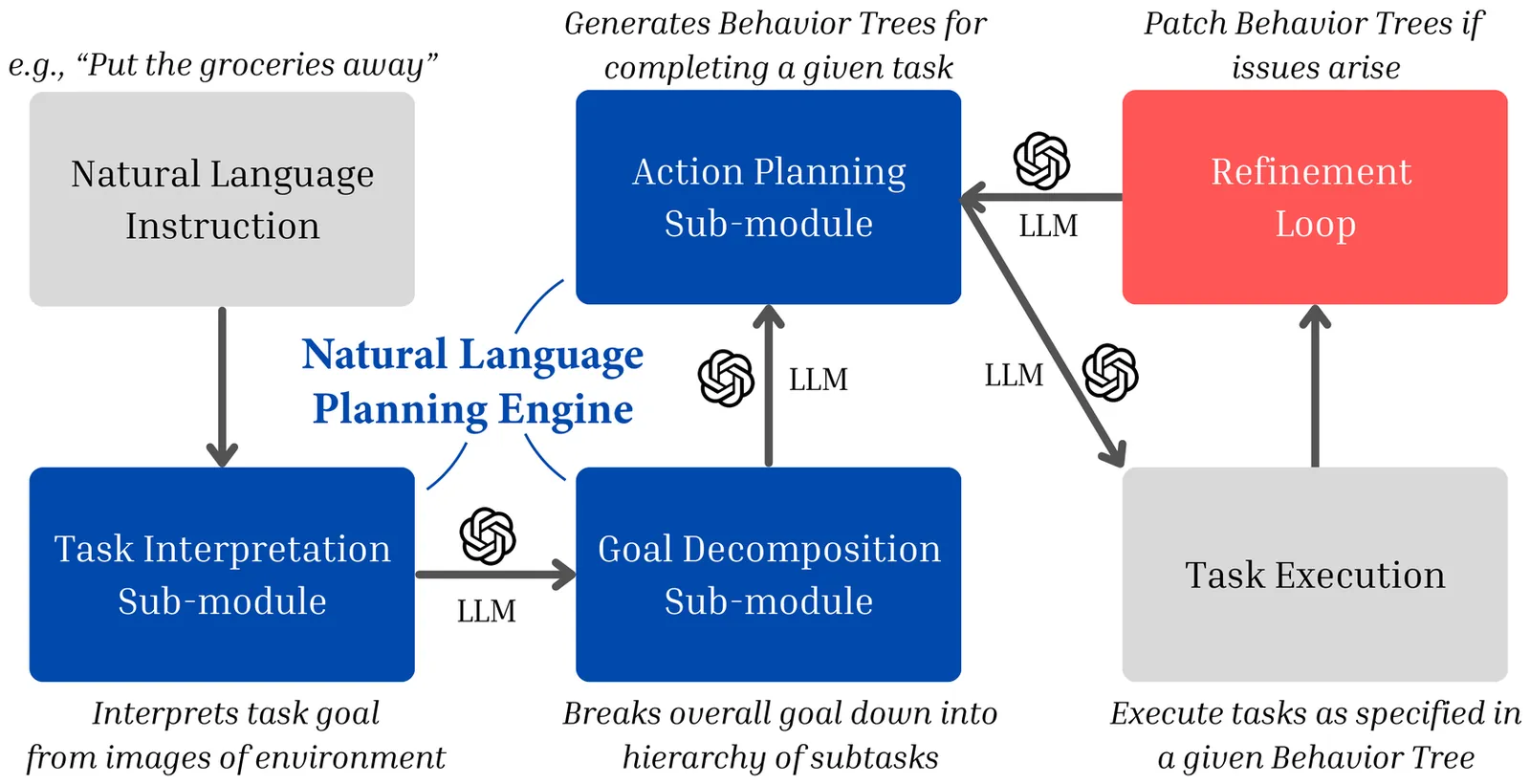
In this work, we introduce and formalize the Zero-Knowledge Task Planning (ZKTP) problem, i.e., formulating a sequence of actions to achieve some goal without task-specific knowledge. Additionally, we present a first investigation and approach for ZKTP that leverages a large language model (LLM) to decompose natural language instructions into subtasks and generate behavior trees (BTs) for execution. If errors arise during task execution, the approach also uses an LLM to adjust the BTs on-the-fly in a refinement loop. Experimental validation in the AI2-THOR simulator demonstrate our approach's effectiveness in improving overall task performance compared to alternative approaches that leverage task-specific knowledge. Our work demonstrates the potential of LLMs to effectively address several aspects of the ZKTP problem, providing a robust framework for automated behavior generation with no task-specific setup.
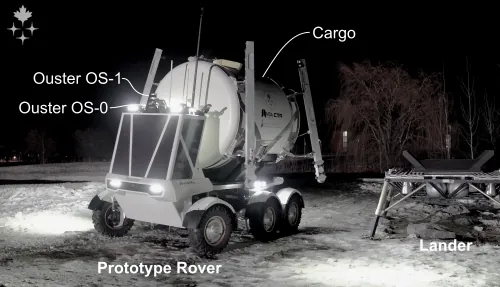
In future operations on the lunar surface, automated vehicles will be required to transport cargo between known locations. Such vehicles must be able to navigate precisely in safe regions to avoid natural hazards, human-constructed infrastructure, and dangerous dark shadows. Rovers must be able to park their cargo autonomously within a small tolerance to achieve a successful pickup and delivery. In this field test, Lidar Teach and Repeat provides an ideal autonomy solution for transporting cargo in this way. A one-tonne path-to-flight rover was driven in a semi-autonomous remote-control mode to create a network of safe paths. Once the route was taught, the rover immediately repeated the entire network of paths autonomously while carrying cargo. The closed-loop performance is accurate enough to align the vehicle to the cargo and pick it up. This field report describes a two-week deployment at the Canadian Space Agency's Analogue Terrain, culminating in a simulated lunar operation to evaluate the system's capabilities. Successful cargo collection and delivery were demonstrated in harsh environmental conditions.
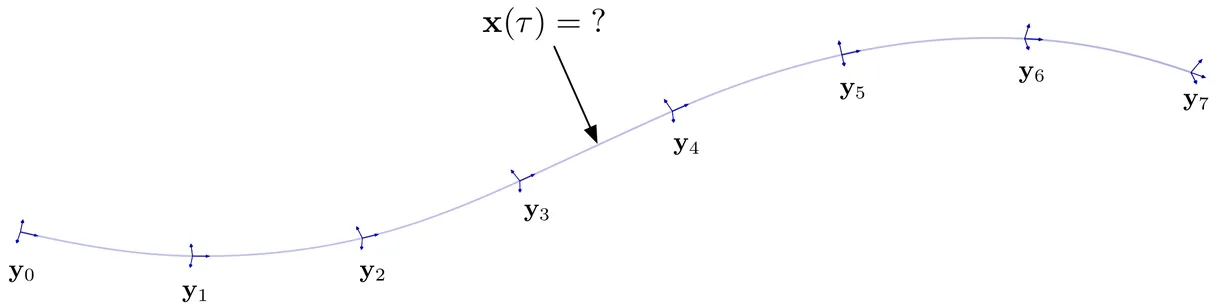
Continuous-time state estimation has been shown to be an effective means of (i) handling asynchronous and high-rate measurements, (ii) introducing smoothness to the estimate, (iii) post hoc querying the estimate at times other than those of the measurements, and (iv) addressing certain observability issues related to scanning-while-moving sensors. A popular means of representing the trajectory in continuous time is via a Gaussian process (GP) prior, with the prior's mean and covariance functions generated by a linear time-varying (LTV) stochastic differential equation (SDE) driven by white noise. When the state comprises elements of Lie groups, previous works have resorted to a patchwork of local GPs each with a linear time-invariant SDE kernel, which while effective in practice, lacks theoretical elegance. Here we revisit the full LTV GP approach to continuous-time trajectory estimation, deriving a global GP prior on Lie groups via the Magnus expansion, which offers a more elegant and general solution. We provide a numerical comparison between the two approaches and discuss their relative merits.
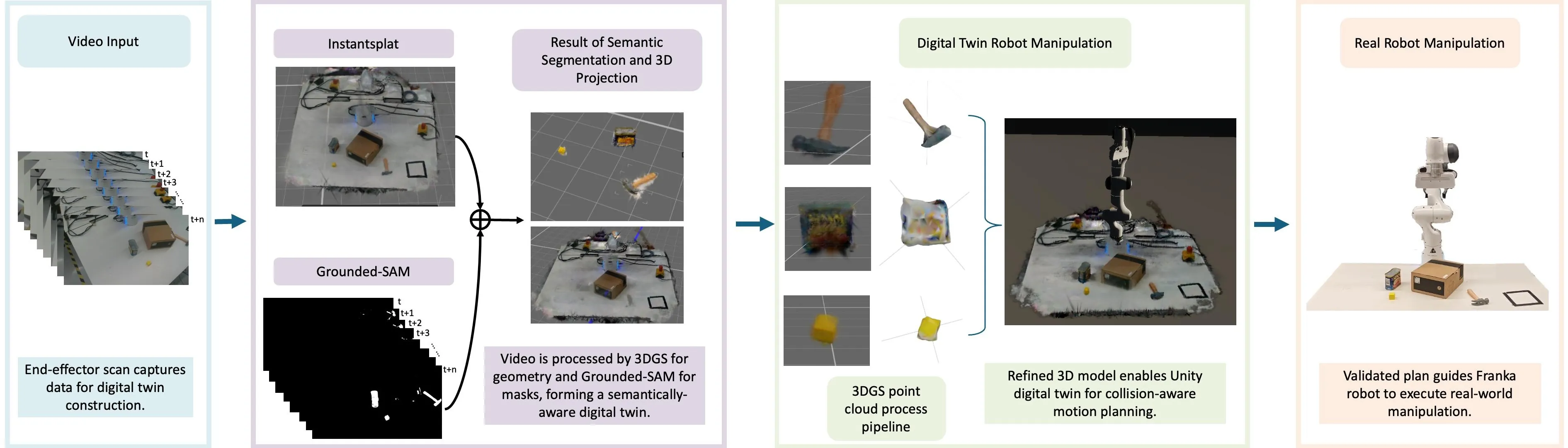
Developing high-fidelity, interactive digital twins is crucial for enabling closed-loop motion planning and reliable real-world robot execution, which are essential to advancing sim-to-real transfer. However, existing approaches often suffer from slow reconstruction, limited visual fidelity, and difficulties in converting photorealistic models into planning-ready collision geometry. We present a practical framework that constructs high-quality digital twins within minutes from sparse RGB inputs. Our system employs 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) for fast, photorealistic reconstruction as a unified scene representation. We enhance 3DGS with visibility-aware semantic fusion for accurate 3D labelling and introduce an efficient, filter-based geometry conversion method to produce collision-ready models seamlessly integrated with a Unity-ROS2-MoveIt physics engine. In experiments with a Franka Emika Panda robot performing pick-and-place tasks, we demonstrate that this enhanced geometric accuracy effectively supports robust manipulation in real-world trials. These results demonstrate that 3DGS-based digital twins, enriched with semantic and geometric consistency, offer a fast, reliable, and scalable path from perception to manipulation in unstructured environments.