Superconductivity
Superconductivity: theory, models, experiment. Cross-linked with physics.supr-con.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Superconductivity: theory, models, experiment. Cross-linked with physics.supr-con.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
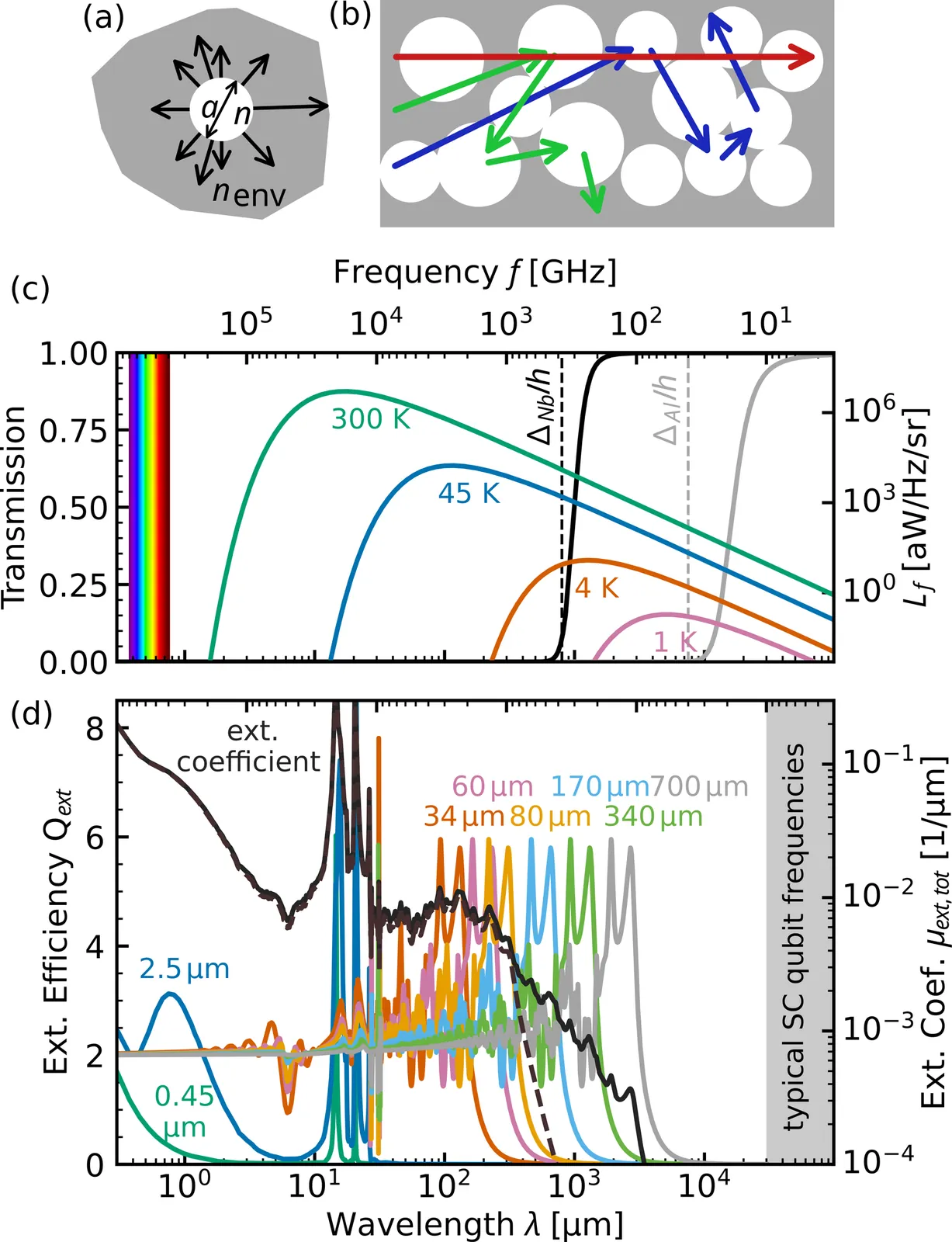
The fragile quantum states of low-temperature quantum applications require protection from infrared radiation caused by higher-temperature stages or other sources. We propose a material system that can efficiently block radiation up to the optical range while transmitting photons at low gigahertz frequencies. It is based on the effect that incident photons are strongly scattered when their wavelength is comparable to the size of particles embedded in a weakly absorbing medium (Mie-scattering). The goal of this work is to tailor the absorption and transmission spectrum of an non-magnetic epoxy resin containing sapphire spheres by simulating its dependence on the size distribution. Additionally, we fabricate several material compositions, characterize them, as well as other materials, at optical, infrared, and gigahertz frequencies. In the infrared region (stop band) the attenuation of the Mie-scattering optimized material is high and comparable to that of other commonly used filter materials. At gigahertz frequencies (pass-band), the prototype filter exhibits a high transmission at millikelvin temperatures, with an insertion loss of less than $0.4\,$dB below $10\,$GHz.
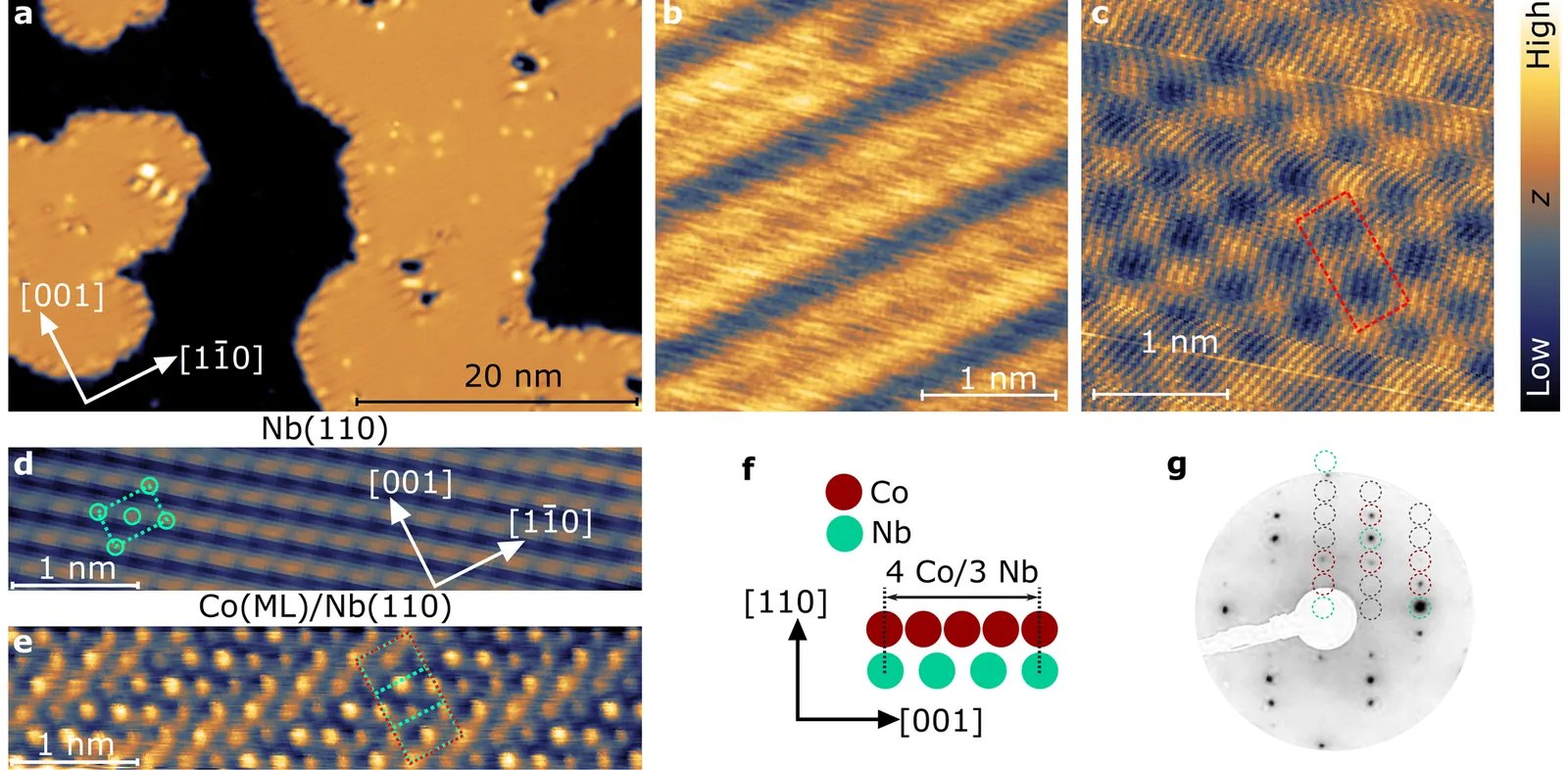
The potential application of topological superconductivity in quantum transport and quantum information has fueled an intense investigation of hybrid materials with emergent electronic properties, including magnet-superconductor heterostructures. Here, we report evidence of a topological nodal-point superconducting phase in a one-atom-thick in-plane ferromagnet in direct proximity to a conventional $s$-wave superconductor. Low-temperature scanning tunneling spectroscopy data reveal the presence of a double-peak low-energy feature in the local density of states of the hybrid system, which is rationalized via model calculations to be an emergent topological nodal-point superconducting phase with tilted Weyl cones. Our results further establish the combination of in-plane ferromagnetism and conventional superconductivity as a route to design two-dimensional topological quantum phases.
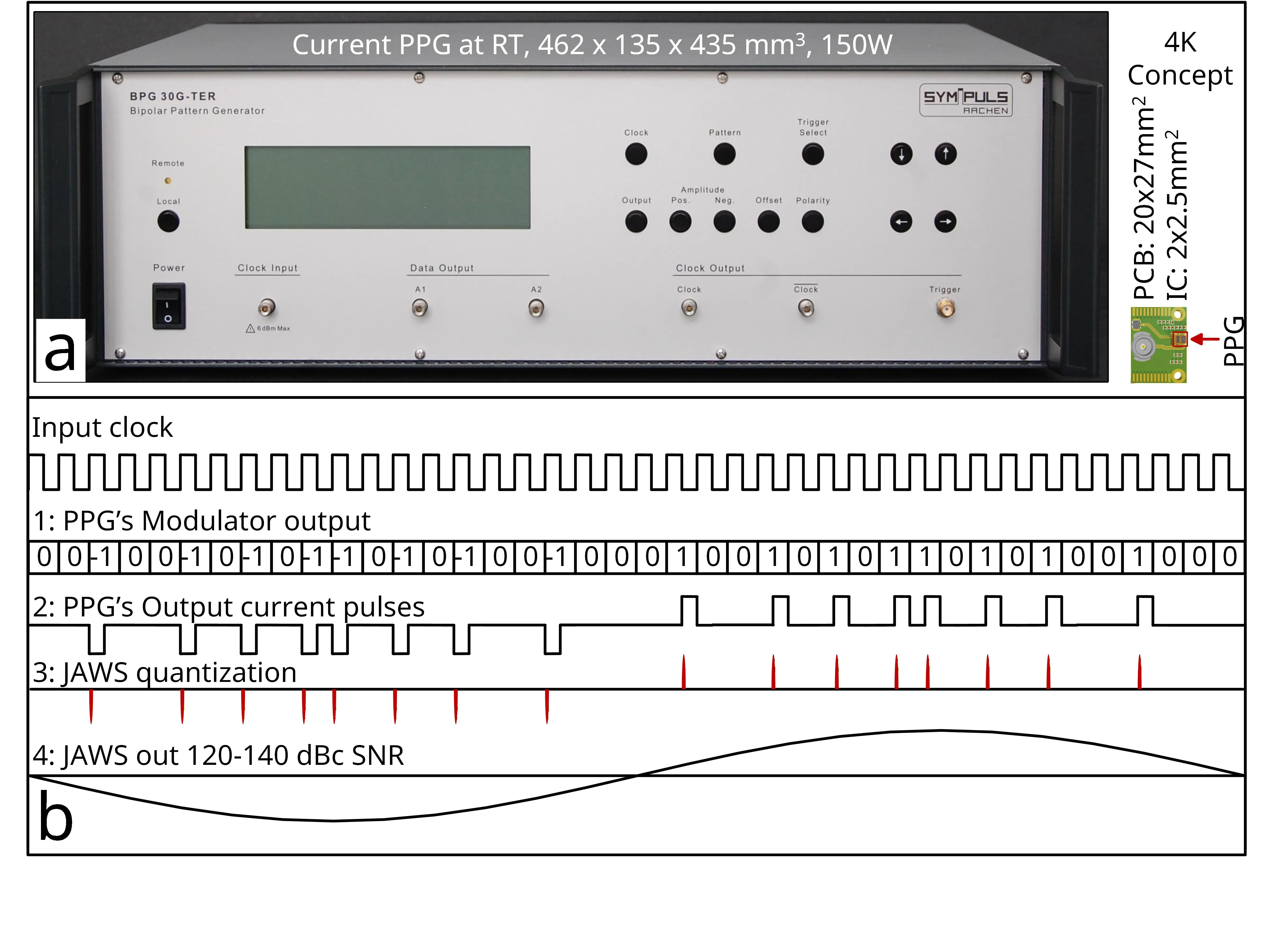
We combine a cryogenic BiCMOS integrated circuit, which generates high-speed return-to-zero (RTZ) pulses, with a superconducting Josephson junction array. The BiCMOS circuit acts as a cryogenic pulse pattern generator, delivering data rates of 30 Gb/s, while consuming 302 mW at 4 K. Each electrical pulse of the serializer effectively transfers one magnetic flux quantum through every Josephson junction, so that the average output voltage of the array produces well-defined plateaus (Shapiro steps) in its current-to-voltage characteristic. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first integration of a Josephson junction array with a cryogenic BiCMOS chip. The presented results pave the way toward a hybrid and fully integrated Josephson arbitrary waveform synthesizer (JAWS) that can generate ultra-low-noise signals for quantum voltage metrology and quantum information systems.
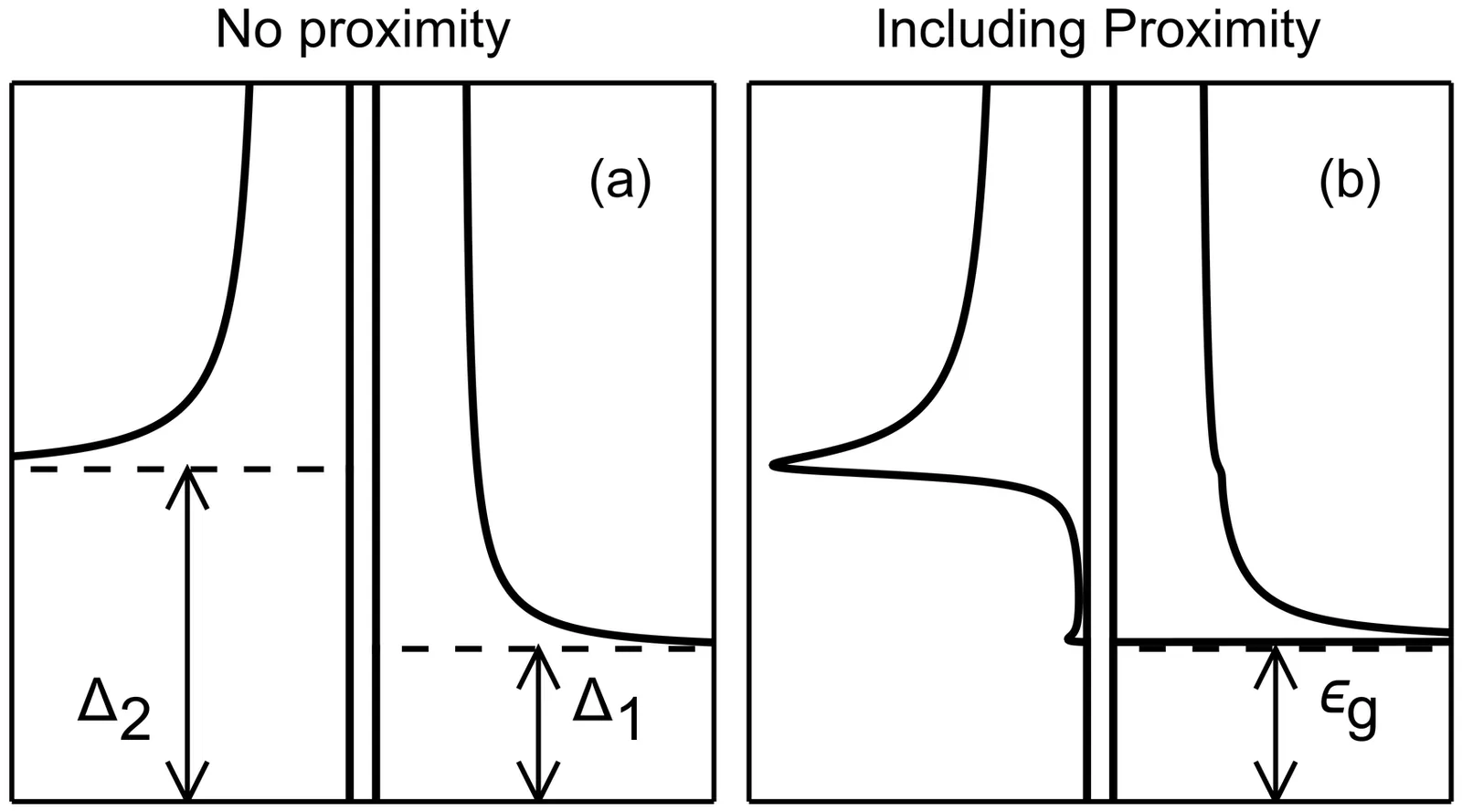
The standard mean-field treatment of low-temperature superconductors leads to a square-root divergent density of states at the gap value. This feature can lead to unphysical logarithmic divergences in various quantities, such as currents and qubit transition rates. We revisit their possible regularization based on the proximity effect between two superconducting films with different gaps. We derive analytical approximations for the density of states in each superconducting film. We find that the smearing of the density of states grows with the gap asymmetry. As a concrete example, we discuss the regularization of transition rates in qubits with frequency close to resonance with the gap asymmetry between the two films, and the consequent smoothening of the jump discontinuity in the qubit frequency shift.
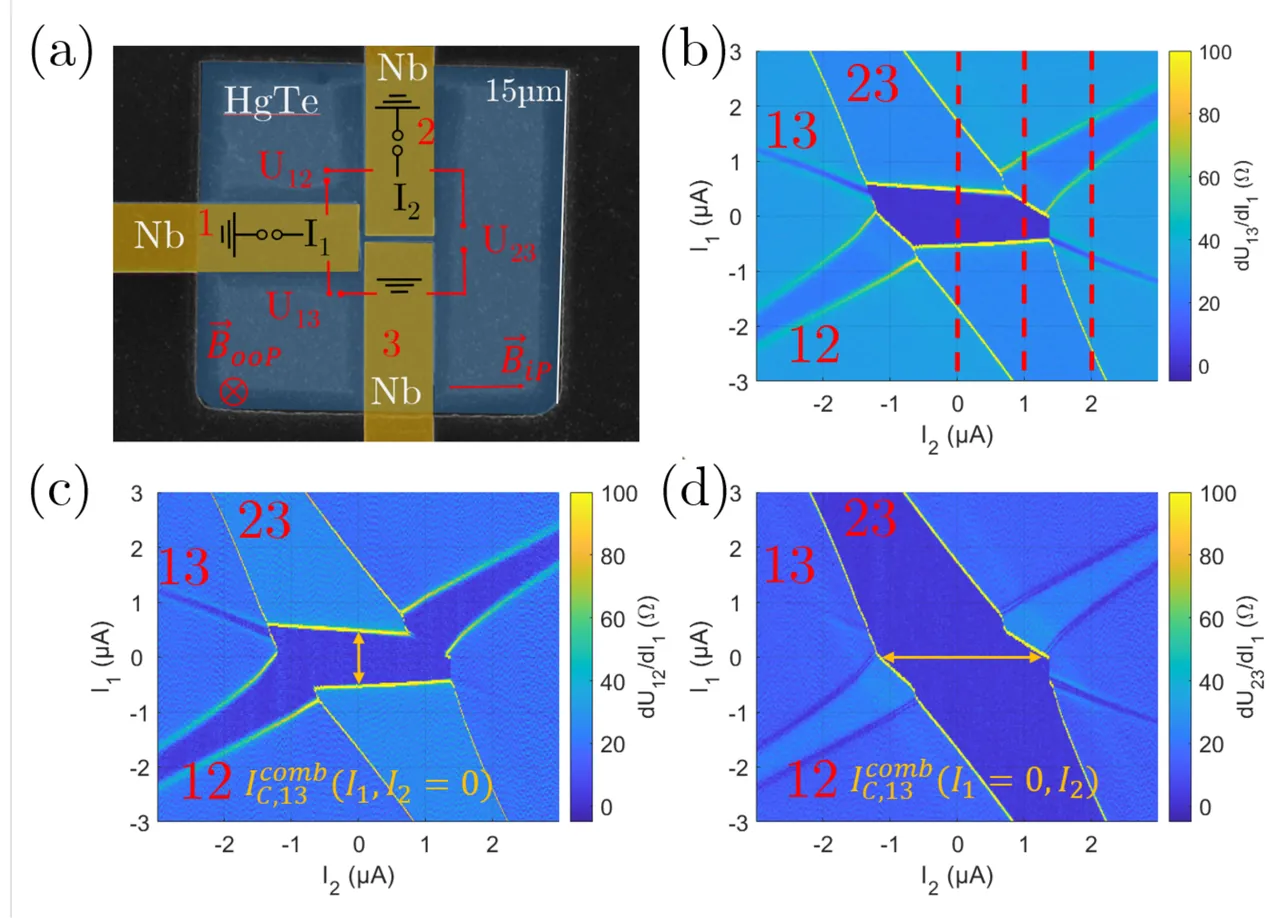
We investigate HgTe/Nb-based three-terminal Josephson junctions in T-shaped and X-shaped geometries and their critical current contours (CCCs). By decomposing the CCCs into the contributions from individual junctions, we uncover how bias current and magnetic field jointly determine the collective Josephson behavior. A perpendicular magnetic field induces a tunable crossover between SQUID-like and Fraunhofer-like interference patterns, controlled by the applied bias. Moreover, magnetic flux produces pronounced deformations of the CCC, enabling symmetry control in the $(I_1,I_2)$ plane. Remarkably, we identify a regime of strongly enhanced Josephson diode efficiency, reaching values up to $η\approx 0.8$ at low bias and magnetic field. The experimental results are quantitatively reproduced by resistively shunted junction (RSJ) simulations, which capture the coupled dynamics of current and flux in these multi-terminal superconducting systems.
We investigate the statistical properties of the vortex pinning potential in a thin superconducting film. Modeling intrinsic inhomogeneities by a random-temperature Ginzburg-Landau functional with short-range Gaussian disorder, we derive the pinning landscape $E(\mathbf{R})$ by determining how the vortex core adapts to randomness. Within the hard-core approximation, applicable for weak disorder, the energy landscape exhibits Gaussian statistics. In this regime, the mean areal density of its minima is given by $n_\text{min}\approx(6ξ)^{-2}$, indicating that the typical spacing between neighboring minima is significantly larger than the vortex core size $ξ$. Going beyond the hard-core approximation, we allow the vortex order parameter to relax in response to the inhomogeneities. As a result, the pinning potential statistics become non-Gaussian. We calculate the leading correction due to the core deformation, which reduces the density of minima with a relative magnitude scaling as $(T_c-T)^{-1/2}$.
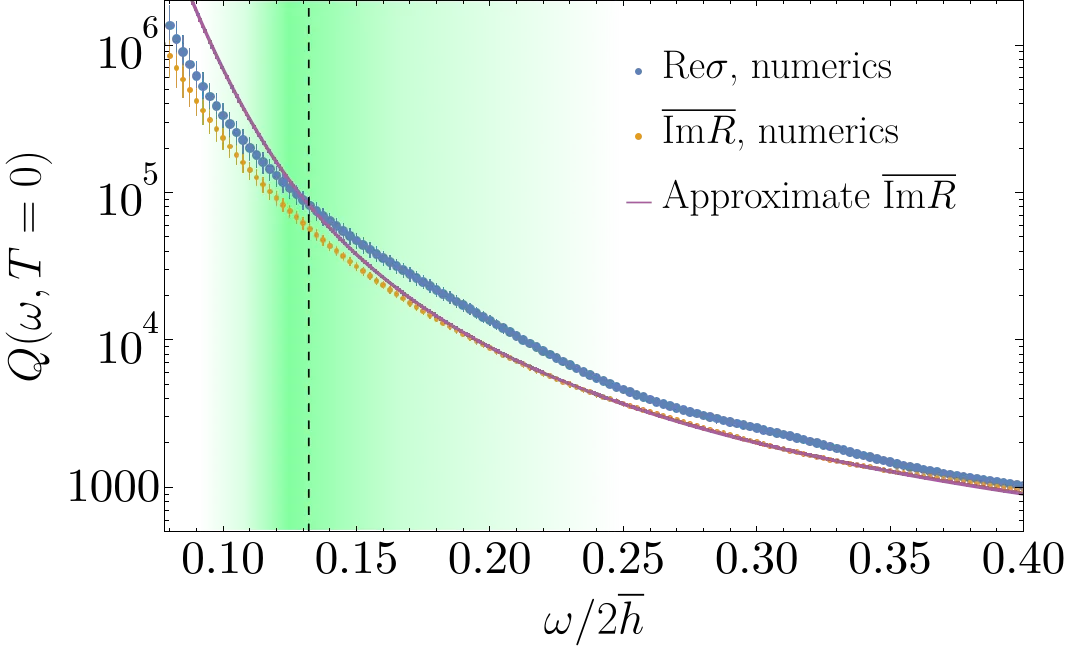
We develop a theory of the temperature $T$ and frequency $ω$ dependence of ac dissipation in strongly disordered superconductors featuring a pseudogap $Δ_{P}$ in the single-particle spectrum. Our theory applies to the regime $T,\,\hbarω\llΔ_{\text{typ}}\llΔ_{P}$, where $Δ_{\text{typ}}$ is the typical superconducting gap. The dissipation is expressed in terms of the quality factor $Q(T,ω)$ of microwave resonators made of these materials. We show that low-$ω$ dissipation is dominated by a new type of bulk localized collective modes. Due to the strongly nonuniform spectral density of these modes, $Q$ decreases sharply with frequency, while its temperature dependence exhibits a two-level-system-like growth as a function of $T$ for $T\ll T_{c}$. Our theory is applicable to InO$_x$, TiN, NbN, and similar strongly disordered materials. We further argue that the experimentally observed behavior of disordered films of granular Aluminum is explained by similar physics, although this case requires a separate theoretical analysis.
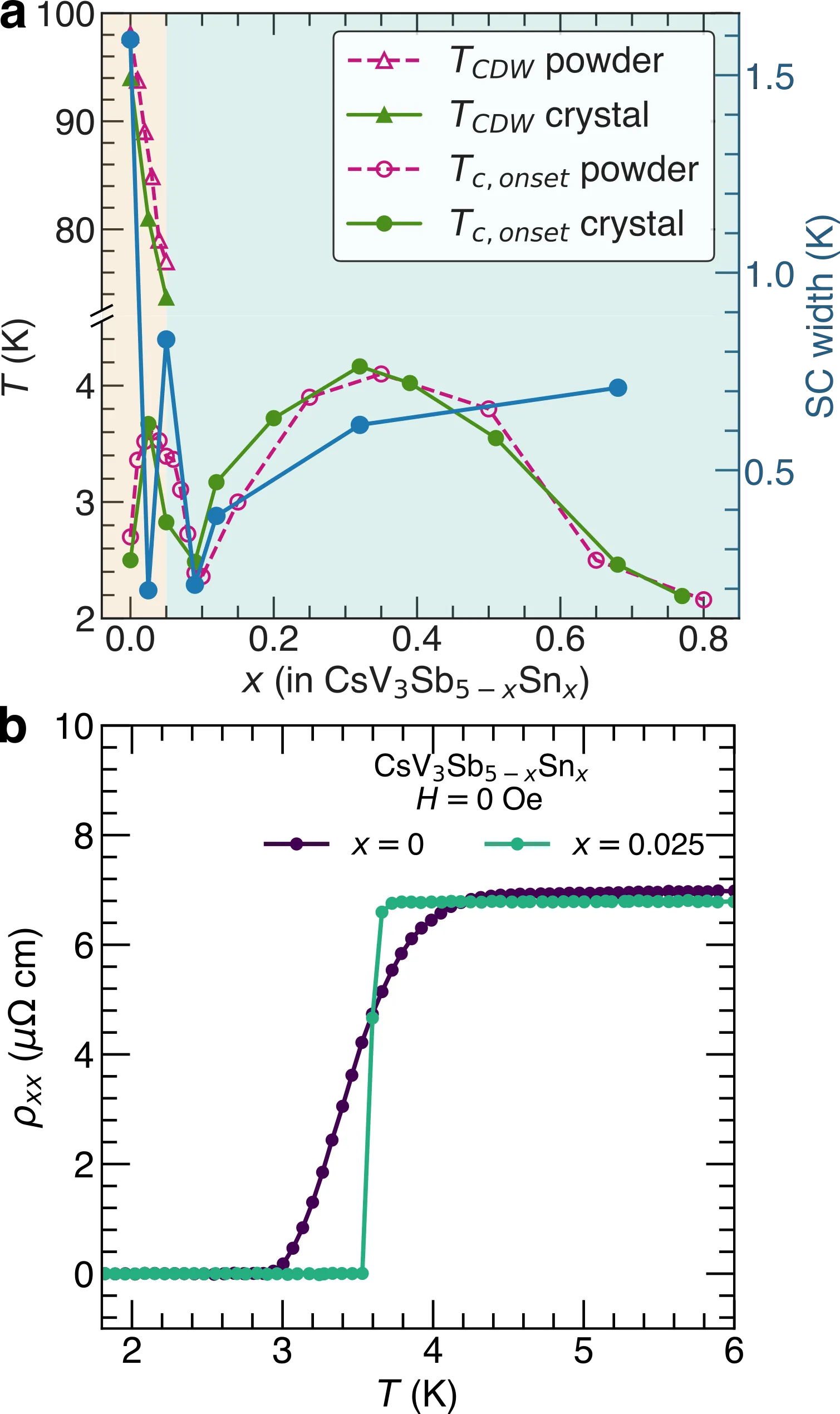
The kagome metal CsV$_3$Sb$_5$ shows an unconventional interplay between charge density wave (CDW) order and superconductivity. Tuning the band filling is known to rapidly suppress long-range CDW order and drive the formation of two superconducting ``domes" upon increasing hole concentration. Here we determine the detailed evolution of charge correlations across this phase diagram and resolve their interplay with the superconducting state. Upon light hole-doping, the suppression of a metastable $2\times 2\times 4$ CDW state coincides with the suppression of superconducting fluctuations present in the parent CsV$_3$Sb$_5$ compound. Continued doping suppresses long-range $2\times 2\times 2$ CDW order, leaving remnant short-range, quasi-1D correlations that persist across the second superconducting dome. These higher temperature charge correlations are seemingly essential to the lower temperature superconducting state, as charge correlations vanish coincident with superconductivity as a function of hole-doping. A multidomain model of short-range V-V dimer formation within the kagome plane is proposed in the second superconducting dome, where rotational and translational symmetry remain locally broken even in the absence of long-range CDW order.
 2512.11073
2512.11073We develop a systematic theoretical approach to incorporate the effects of a static white-noise disorder into the BCS-BEC crossover near the critical temperature ($T_c$) of the superfluid transition. Starting from a functional-integral formulation in momentum-frequency space, we derive an effective thermodynamic potential that fully accounts for Gaussian fluctuations of the order-parameter field and its coupling to the disorder potential. The effective action, expanded to second order in both the disorder potential and the bosonic field, naturally involves third- and fourth-order terms arising from the logarithmic expansion near $T_c$. This formalism, valid across the entire BCS-BEC crossover, reproduces the well-established BCS and BEC limits and yields self-energy expressions consistent with previous analyses for non-interacting point bosons and tightly bound fermion pairs. The approach applies equally to continuum and lattice systems and provides a natural framework for generalizations to multiband models.
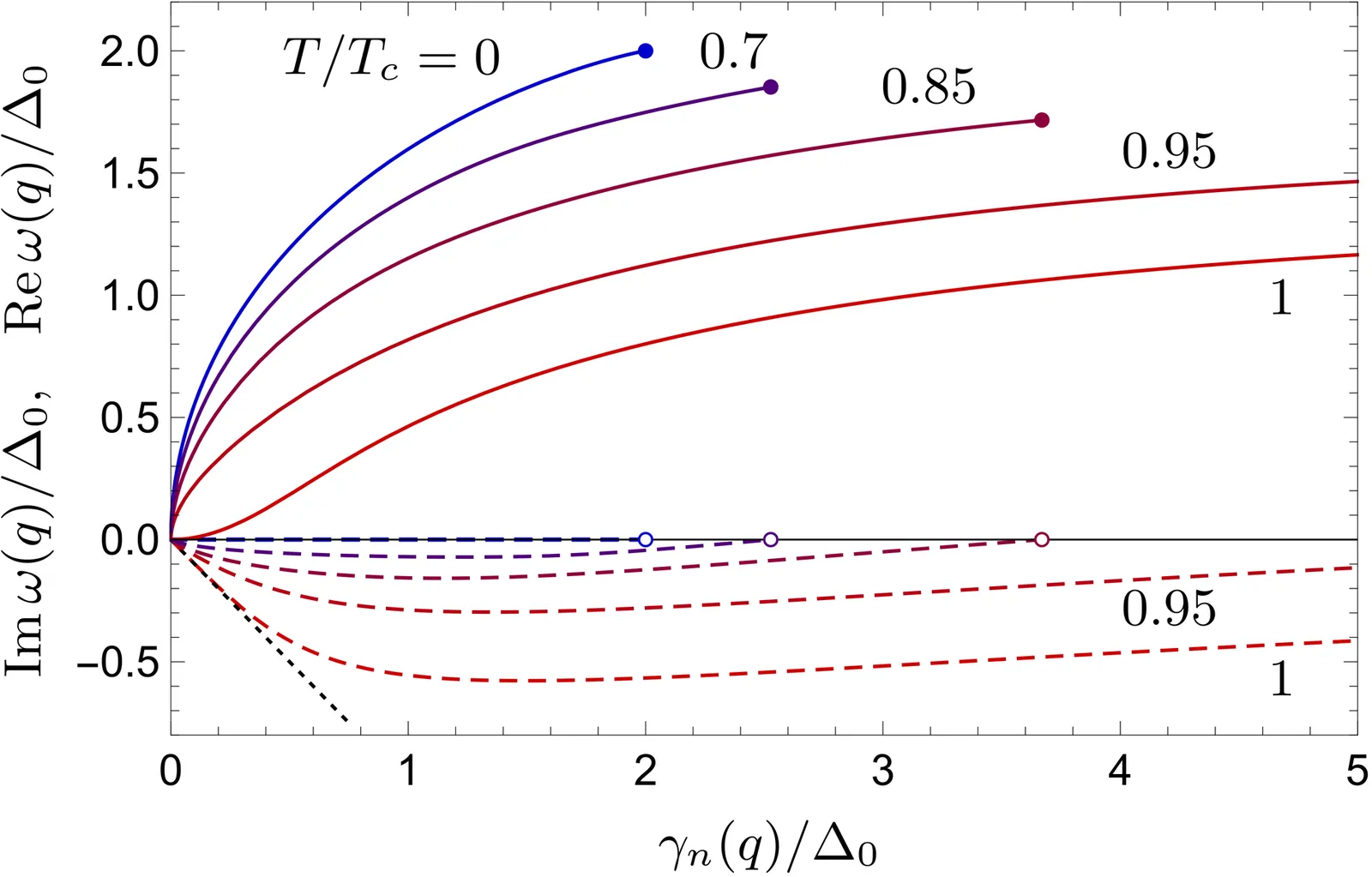
We develop a theory for the plasmon spectrum in dirty superconductors across the entire temperature range. Starting with the microscopic Keldysh sigma model description, we link the plasmon dispersion $ω(q)$ to the optical conductivity $σ(ω,T)$ of a superconductor, which requires analytical continuation to the lower half-plane of complex frequency. This approach reveals a discontinuity at the superconducting transition: a jump in both the real and imaginary parts of $ω(q)$ at $T_c$. For any temperature below $T_c$, the plasmon dispersion terminates at a critical wave vector $q_c(T)$ where plasmons remains undamped, with weakly $T$-dependent $ω[q_c(T)] \approx 2Δ(0)$. Plasmons significantly attenuate only within a narrow 5% temperature window near $T_c$, with the propagating mode recovering at large $q$.
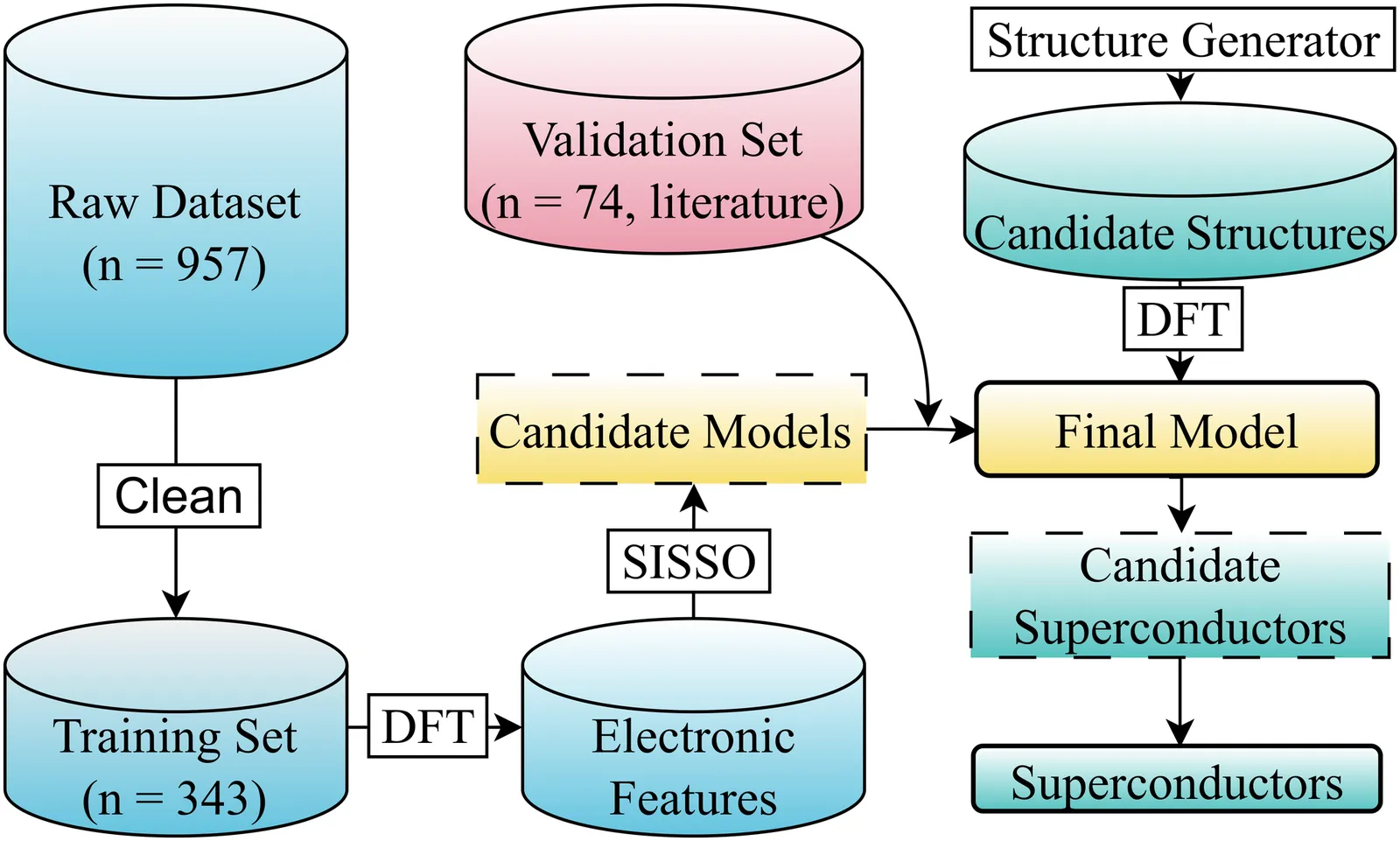
Room temperature superconductivity remains elusive, and hydrogen-base compounds despite remarkable transition temperatures(Tc) typically require extreme pressures that hinder application. To accelerate discovery under moderate pressures, an interpretable framework based on symbolic regression is developed to predict Tc in hydrogen-based superconductors. A key descriptor is an integrated density of states (IDOS) within 1 eV of the Fermi level (EF), which exhibits greater robustness than conventional single-point DOS features. The resulting analytic model links electronic-structure characteristics to superconducting performance, achieves high accuracy (RMSEtrain = 20.15 K), and generalizes well to external datasets. By relying solely on electronic structure calculations, the approach greatly accelerates materials screening. Guided by this model, four hydrogen-based candidates are identified and validated via calculation: Na2GaCuH6 with Tc =42.04 K at ambient pressure (exceeding MgB2), and NaCaH12, NaSrH12, and KSrH12 with Tc up to 162.35 K, 86.32 K, and 55.13 K at 100 GPa, 25 GPa, and 25 GPa, respectively. Beyond rapid screening, the interpretable form clarifies how hydrogen-projected electronic weight near EF and related features govern Tc in hydrides, offering a mechanism-aware route to stabilize high-Tc phases at reduced pressures.
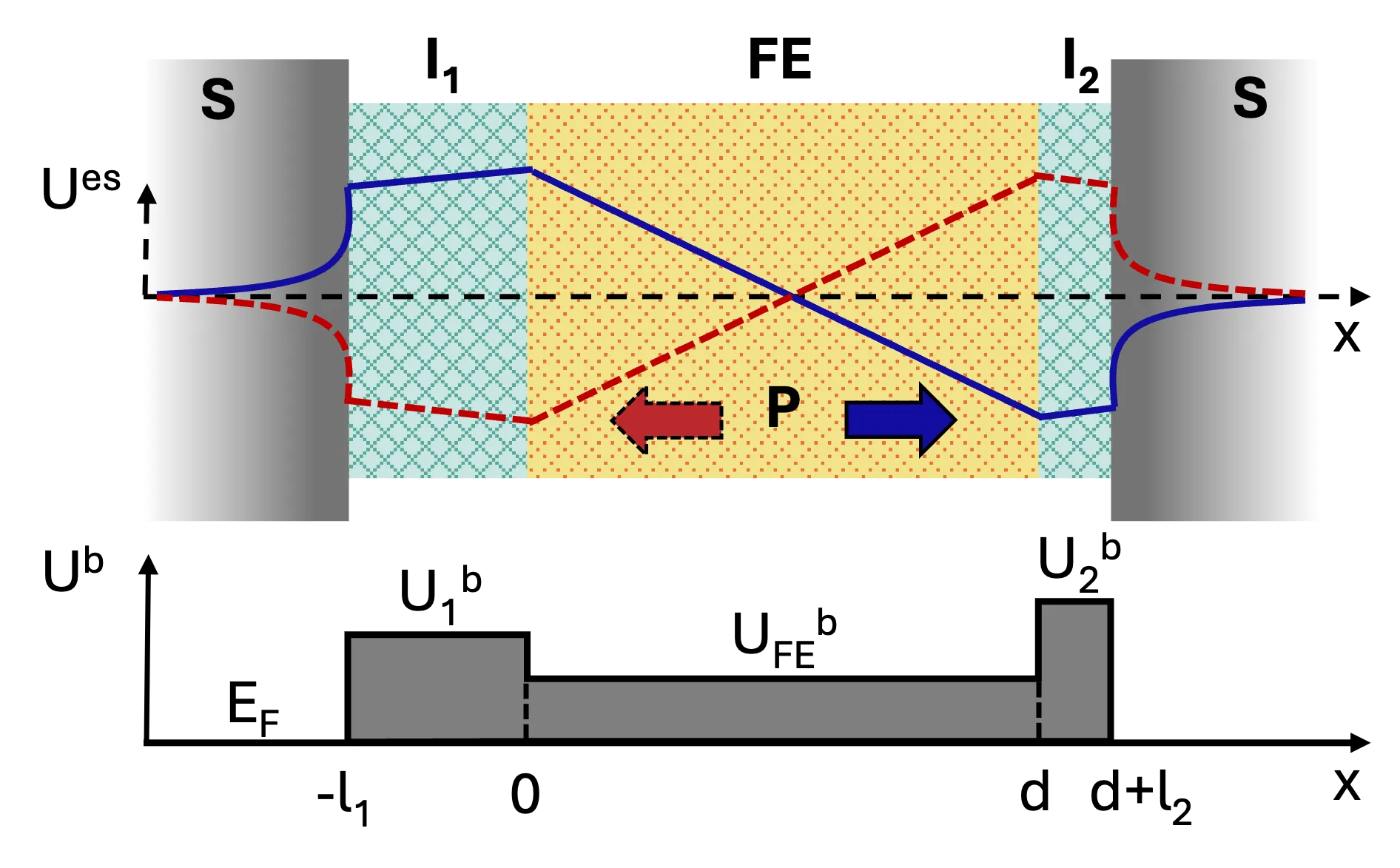
Josephson junctions are essential devices in superconducting electronics and quantum computing hardware. Here we predict electrical control of the supercurrent in composite superconductor-insulator-ferroelectric-insulator-superconductor (S-I-FE-I-S) Josephson junctions. Inversion symmetry broken by unequal dielectric barrier thicknesses and/or potentials converts ferroelectric polarization reversal into a substantial change of the critical current. With a WKB tunneling model we obtain non-volatile switching of the critical current with on-off efficiency up to 0.9 for physically realistic parameters. This can be achieved by optimizing the thicknesses and potential barriers of the insulating layers, as well as the thickness and dielectric constant of the ferroelectric layer. We also derive a compact linear expression for the critical current valid for small polarizations. Our results identify ferroelectric Josephson junctions as electrically programmable superconducting current switches for cryogenic memory and logic applications.
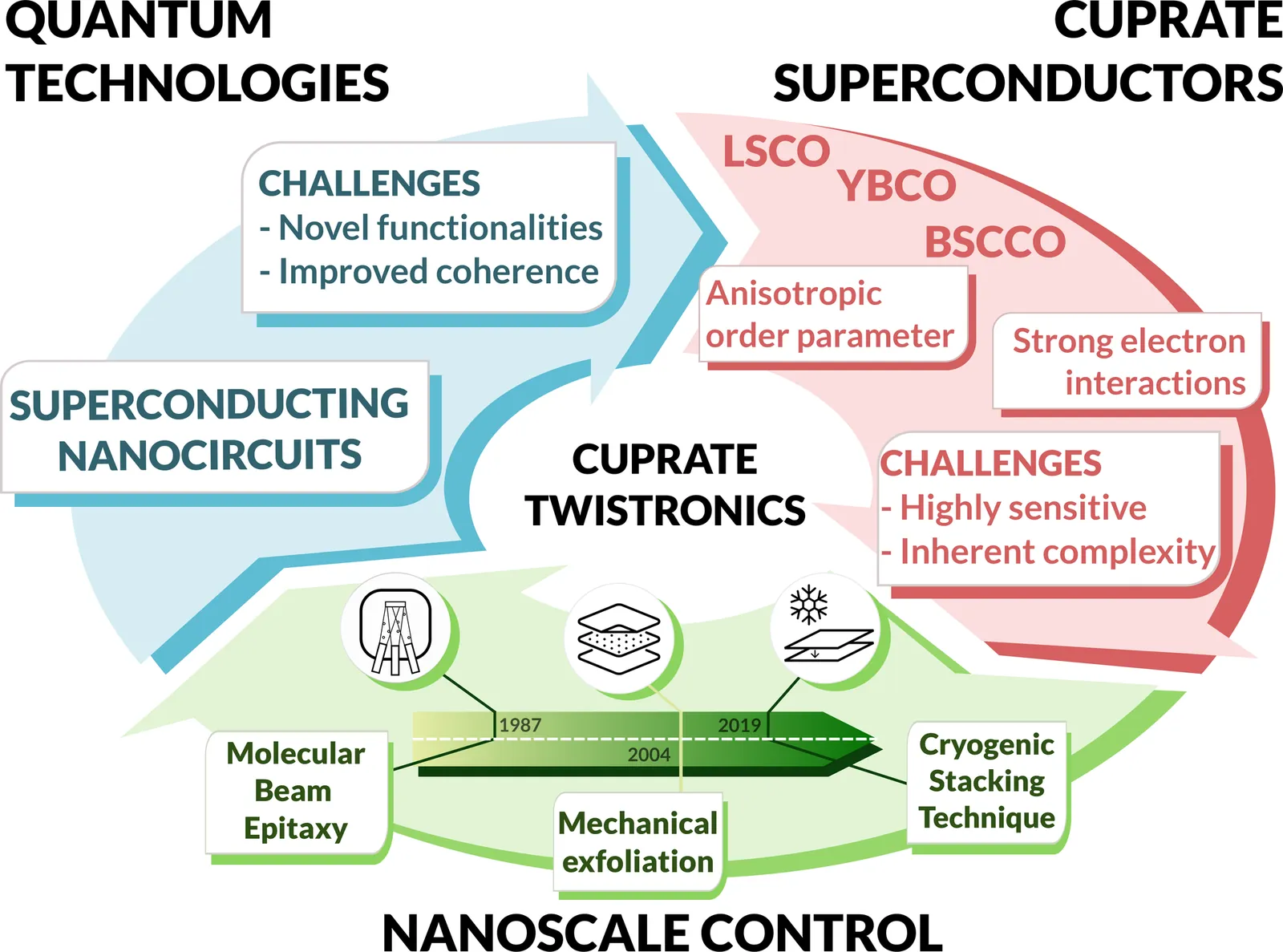
Recent advances in the manipulation of complex oxide layers, particularly the fabrication of atomically thin cuprate superconducting films via molecular beam epitaxy, have revealed new ways in which nanoscale engineering can govern superconductivity and its interwoven electronic orders. In parallel, the creation of twisted cuprate heterostructures through cryogenic stacking techniques marks a pivotal step forward, exploiting cuprate superconductors to deepen our understanding of exotic quantum states and propel next-generation quantum technologies. This review explores over three decades of research in the emerging field of cuprate twistronics, examining both experimental breakthroughs and theoretical progress. It also highlights the methodologies poised to surmount the outstanding challenges in leveraging these complex quantum materials, underscoring their potential to expand the frontiers of quantum science and technology.
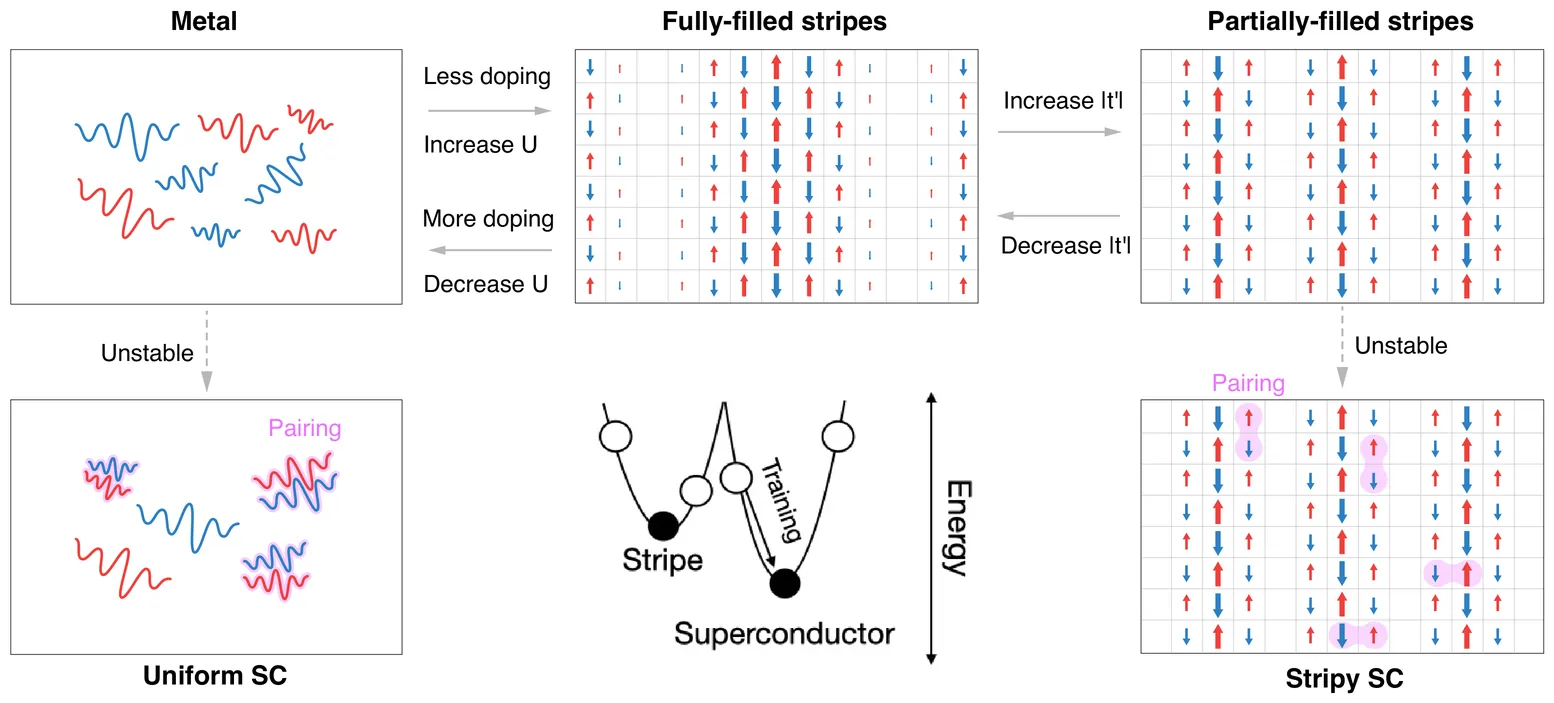
Whether the ground state of the square lattice Hubbard model exhibits superconductivity remains a major open question, central to understanding high temperature cuprate superconductors and ultra-cold fermions in optical lattices. Numerical studies have found evidence for stripe-ordered states and superconductivity at strong coupling but the phase diagram remains controversial. Here, we show that one can resolve the subtle energetics of metallic, superconducting, and stripe phases using a new class of neural quantum state (NQS) wavefunctions that extend hidden fermion determinant states to Pfaffians. We simulate several hundred electrons using fast Pfaffian algorithms allowing us to measure off-diagonal long range order. At strong coupling and low hole-doping, we find that a non-superconducting filled stripe phase prevails, while superconductivity coexisting with partially-filled stripes is stabilized by a negative next neighbor hopping t-prime, with |t-prime| > 0.1. At larger doping levels, we introduce momentum-space correlation functions to mitigate finite size effects that arise from weakly-bound pairs. These provide evidence for uniform d-wave superconductivity at U = 4, even when t-prime = 0. Our results highlight the potential of NQS approaches, and provide a fresh perspective on superconductivity in the square lattice Hubbard model.
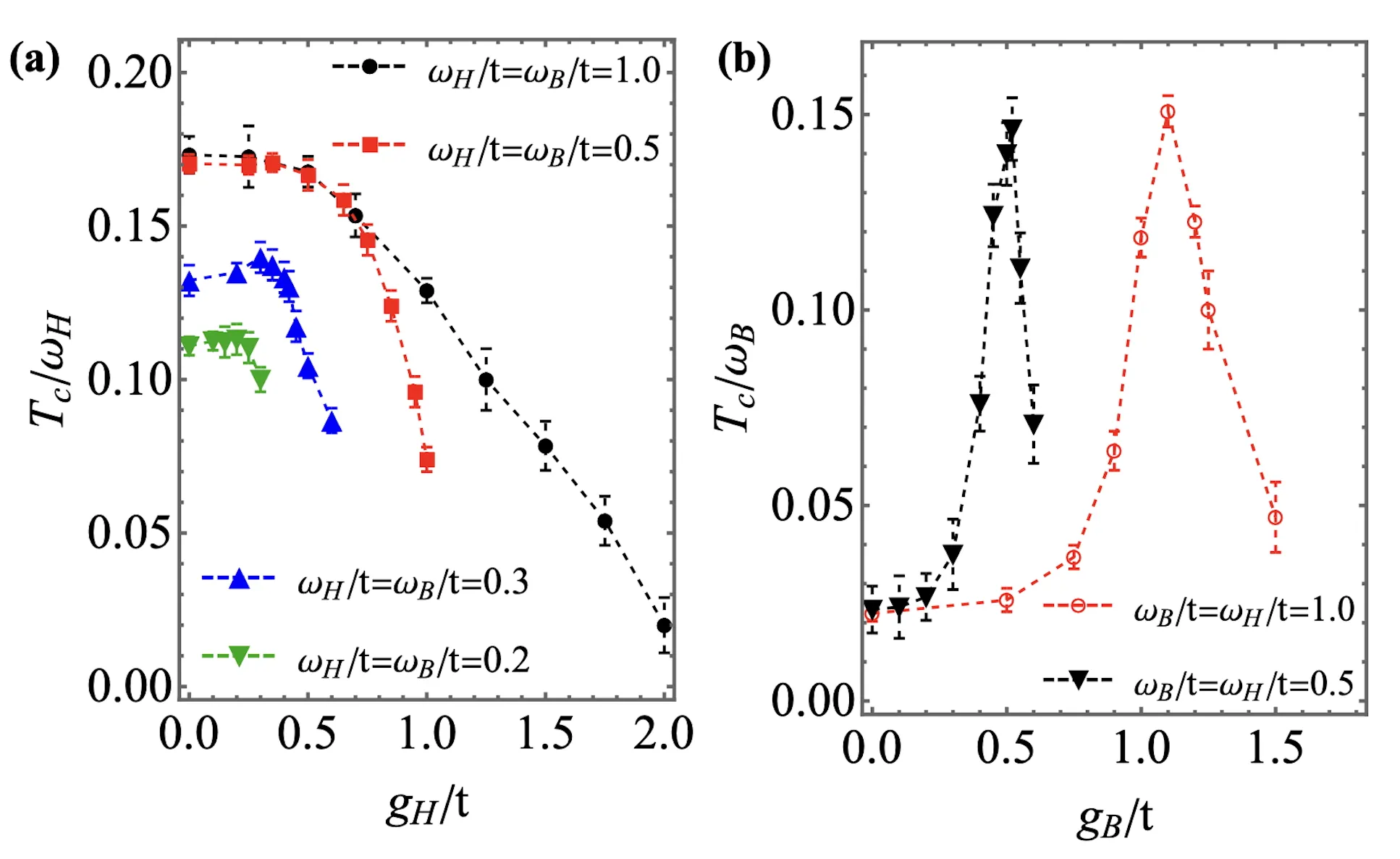
We study bipolaron formation and bipolaronic superconductivity on a square lattice, where electrons couple to both local Holstein phonons via on-site charge density and nonlocal bond Su-Schrieffer-Heeger phonons via modulation of hopping amplitudes. Using an unbiased Diagrammatic Monte Carlo method, we investigate how the interplay between these two types of electron-phonon coupling affects the bipolaron binding energy, effective mass, spatial extent (quantified by the mean-squared radius), and the superconducting transition temperature $T_c$. We find that, in some parameter space, the moderate Holstein coupling, though detrimental to $T_c$ when acting alone, can enhance superconductivity when combined with the bond SSH coupling by further compressing the bipolaron without significantly increasing its mass. Similarly, introducing bond SSH coupling into a Holstein bipolaron reduces its size while keeping the effective mass nearly unchanged, leading a higher $T_c$. These effects give rise to nonmonotonic behavior and reveal a cooperative regime in which both couplings work together to enhance superconductivity. We further examine phonon frequency asymmetry, particularly the case $ω_H/t = 2ω_B/t$, and show that in the deep adiabatic regime, adding Holstein coupling can even raise $T_c$ when combined with bond SSH coupling. These results highlight the distinct and complementary roles of local Holstein and non-local bond SSH electron-phonon couplings, and suggest strategies for optimizing high-$T_c$ superconductivity in systems with multiple phonon modes.
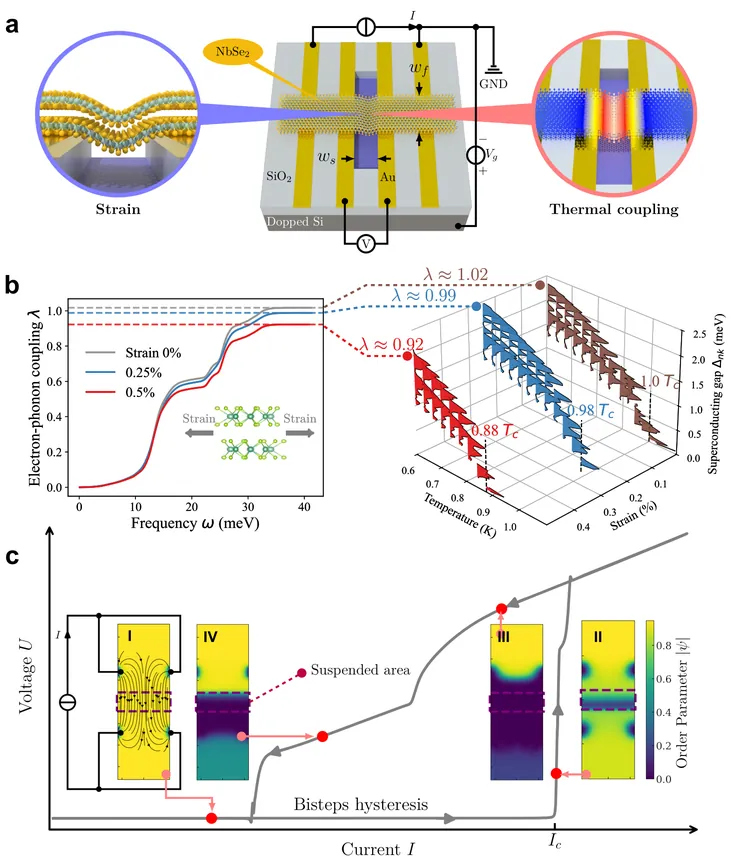
Tunable superconductors provide a versatile platform for advancing next-generation quantum technologies. Here, we demonstrate controllable superconductivity in suspended NbSe2 thin layers, achieved through local strain and thermal modulation of the superconducting state. Our results show that suspended NbSe2 structures enable strain modulation of the critical temperature by up to approximately 0.92 K (about 12.5% of the critical temperature) and allow the realization of gate-tunable superconducting critical currents. We further demonstrate configurable hysteretic transport characteristics exhibiting multistability and negative differential resistance, providing easily reconfigurable, spatially dependent superconducting states. These phenomena are well explained by calculations of electron-phonon coupling using density functional theory, together with time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau dynamics coupled to the thermal diffusion equation. Our work provides profound insight into strain and thermal modulation of van der Waals superconductors and opens new opportunities for tunable on-chip superconductor devices, integrated superconducting circuits, and quantum simulators.
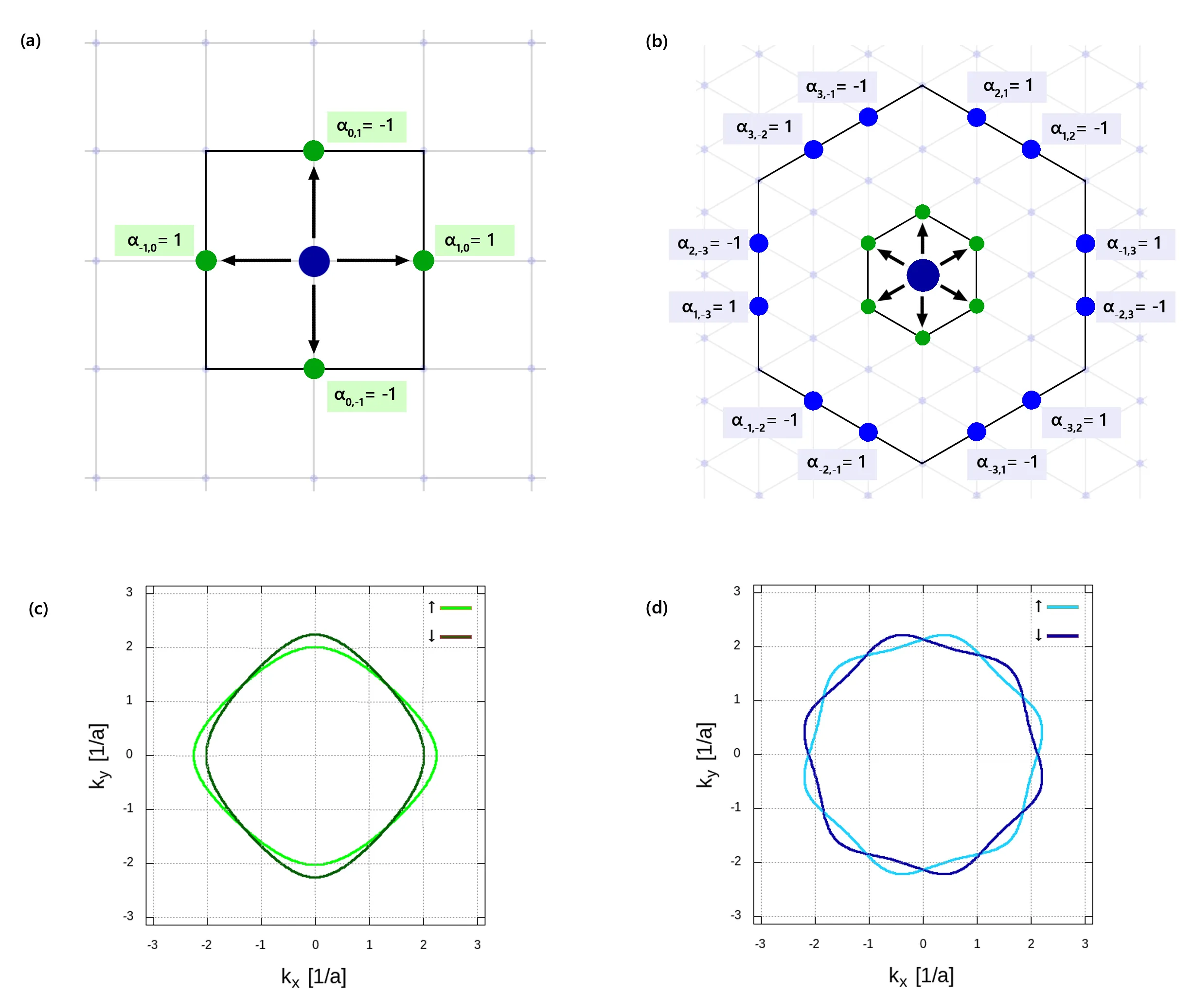
We study the interplay between altermagnetism and unconventional superconductivity for the case of two-dimensional square- and triangular-lattice systems. Our approach is based on an effective single particle Hamiltonian which mimics the alternating spin splitting characteristic for the $d$-$wave$ and $i$-$wave$ altermagnetic state. By supplementing the model with intersite pairing term we characterize the principal features of the coexistent altermagnetic-superconducting state as well as the possibility of inducing the Fulde-Ferrell-Larkin-Ovchinnikov (FFLO) phase. Our calculations show that the subtle interplay between the symmetries of the superconducting and altermagnetic order parameters as well as the shape/size of the Fermi surface lead to various types of anisotropic behaviors of the resultant non-zero momentum pairing, which has not been possible in the originally proposed FFLO state. Moreover, in the considered systems additional pairing symmetries appear leading to an exotic multi-component order parameter with singlet-triplet mixing. To interpret the obtained data we analyze the Cooper pair density in the momentum space and the corresponding Fermi wave vector mismatch resulting from the altermagnetic spin splitting. We discuss our result in the context of possible applications like, e.g., the superconducting diode.
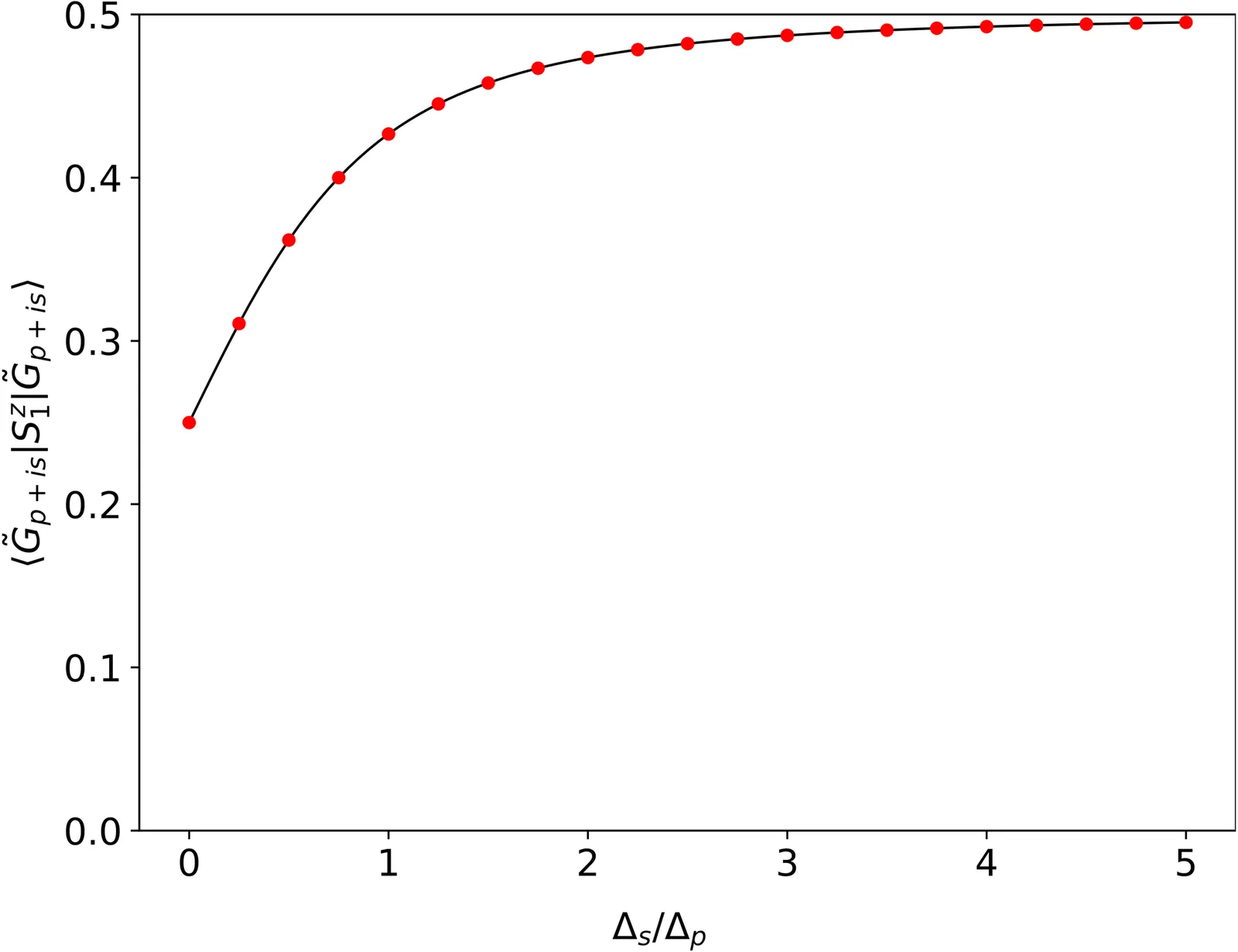
Although BCS wave function for superconductors under periodic boundary conditions are well-established, obtaining an explicit form of the many-body BCS wave function under open boundary condition is usually a nontrivial problem. In this work, we construct the exact BCS ground state wave function of a one-dimensional spin-1/2 superconductor with $p+ is$ pairing symmetry under open boundary conditions for special sets of parameters. The spin magnetization on the edges are calculated explicitly using the obtained wave function. Approximate expression of the wave function is also discussed based on degenerate perturbation theory when the $s$-wave component is much smaller than the $p$-wave one, which provides more intuitive understanding for the system. Our work is useful for obtaining deeper understandings of open $p+ is$ superconducting chains on a wave function level.
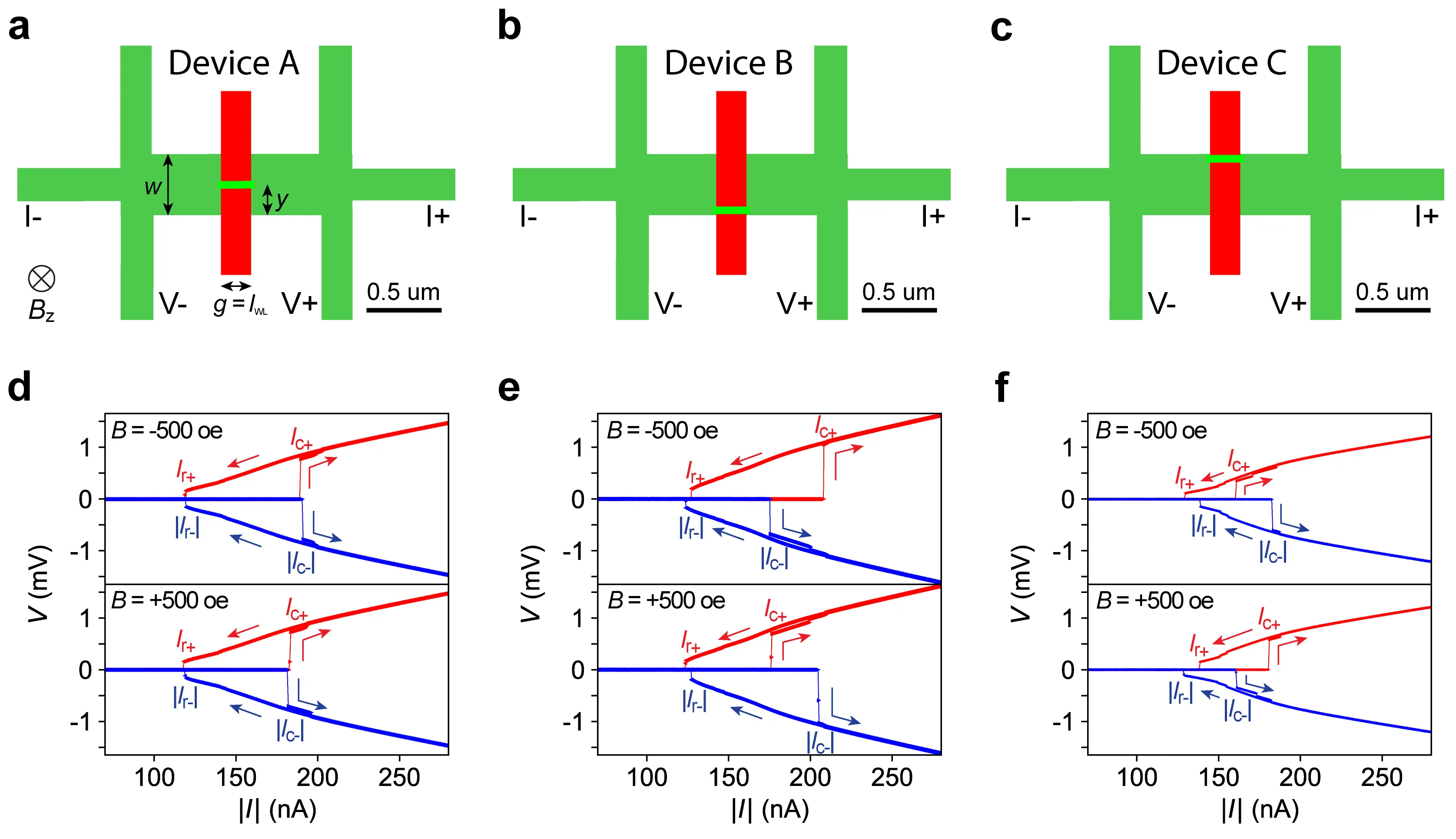
The supercurrent diode effect (SDE), characterized by nonreciprocal critical currents, represents a promising building block for future dissipationless electronics and quantum circuits. Realizing SDE requires breaking both time-reversal and inversion symmetry in the device. Here we use conductive atomic force microscopy (c-AFM) lithography to pattern reconfigurable superconducting weak links (WLs) at the LaAlO3/KTaO3 (LAO/KTO) interface. By deliberately engineering the WL geometry at the nanoscale, we realize SDE in these devices in the presence of modest out-of-plane magnetic fields. The SDE polarity can be reversed by simply changing the WL position, and the rectification efficiency reaches up to 13% under optimal magnetic field conditions. Time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau simulations reveal that the observed SDE originates from asymmetric vortex motion in the inversion-symmetry-breaking device geometry. This demonstration of SDE in the LAO/KTO system establishes a versatile platform for investigating and engineering vortex dynamics, forming the basis for engineered quantum circuit elements.
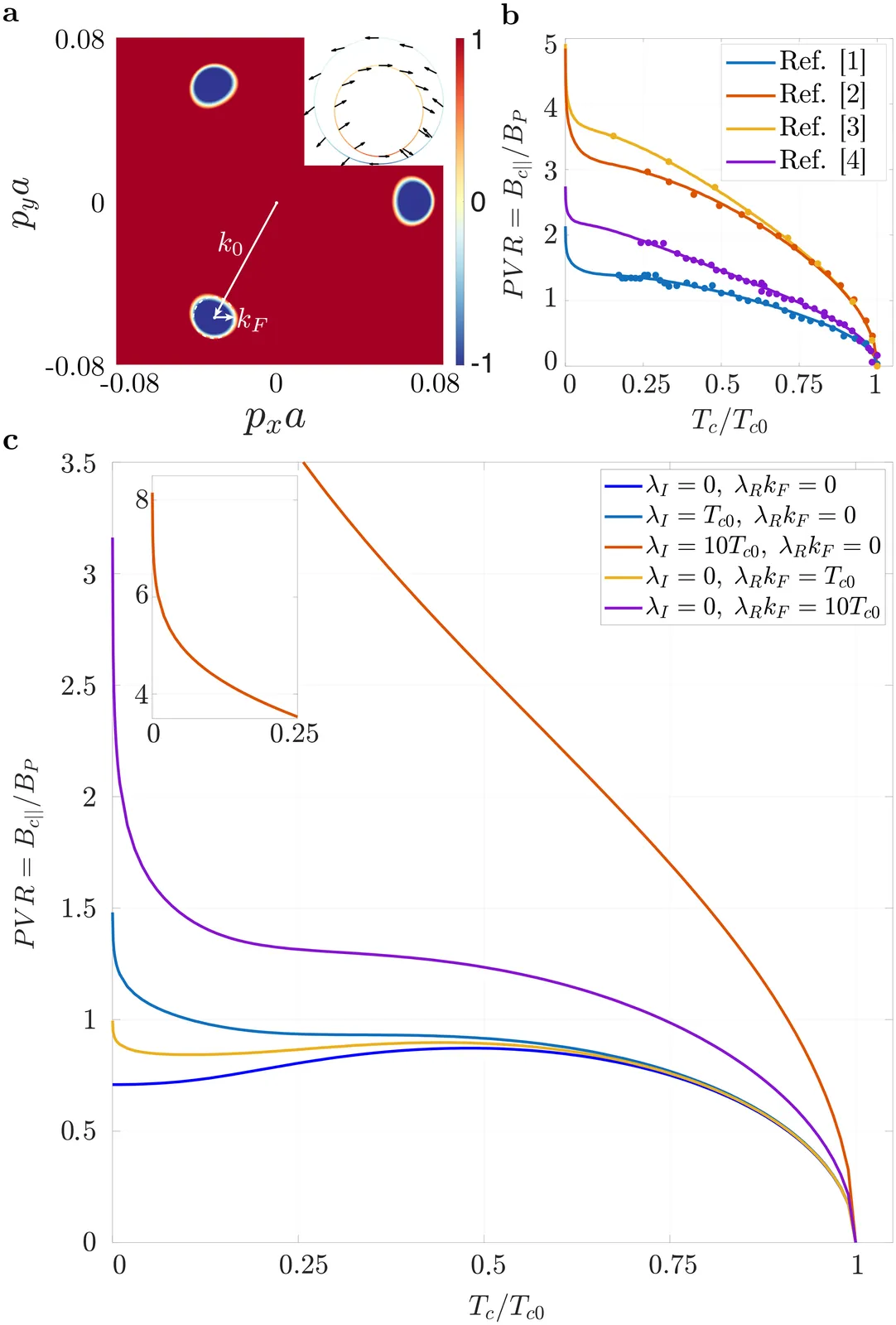
The study of the interplay of applied external magnetic field and superconductivity has been invigorated by recent works on Bernal bilayer and rhombohedral multilayer graphene. These studies, with and without proximitized spin-orbit coupling, have opened up a new frontier in the exploration of unconventional superconductors as they offer a unique platform to investigate superconductivity with high degree of in-plane magnetic field resilience and even magnetic field-induced superconductivity. Here, we present a framework for analyzing the upper critical in-plane magnetic field data in multilayer superconductors. Our framework relies on an analytically tractable superconducting pairing model that captures the normal state phenomenology of these systems and applies it to calculate the relationship between the upper critical field $H_{c2}$ and the corresponding critical temperature $T_{c}$. We study the $H_{c2}-T_{c}$ critical curve as a function of experimental parameters (Ising and Rashba spin-orbit coupling) and depairing mechanisms (Zeeman and orbital coupling) for both spin-singlet and spin-triplet pairing. By applying our framework to analyze four recent Bernal bilayer graphene-WSe$_2$ experiments [1-4], we identify an apparent discrepancy between fitted and measured spin-orbit parameters, which we propose can be explained by an enhancement of the Landé g factor in the Bernal bilayer graphene experiments.