Condensed Matter
Materials science, superconductivity, mesoscale physics, and quantum materials
Materials science, superconductivity, mesoscale physics, and quantum materials
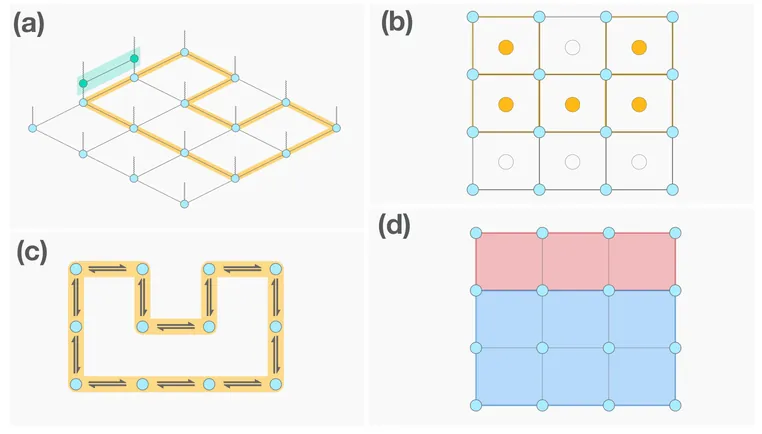
We develop a new approach to compress cyclic tensor networks called stochastic path compression (SPC) that uses an iterative importance sampling procedure to target edges with large bond-dimensions. Closed random walks in SPC form compression pathways that spatially localize large bond-dimensions in the tensor network. Analogous to the phase separation of two immiscible liquids, SPC separates the graph of bond-dimensions into spatially distinct high and low density regions. When combined with our integral decimation algorithm, SPC facilitates the accurate compression of cyclic tensor networks with continuous degrees of freedom. To benchmark and illustrate the methods, we compute the absolute thermodynamics of $q$-state clock models on two-dimensional square lattices and an XY model on a Watts-Strogatz graph, which is a small-world network with random connectivity between spins.
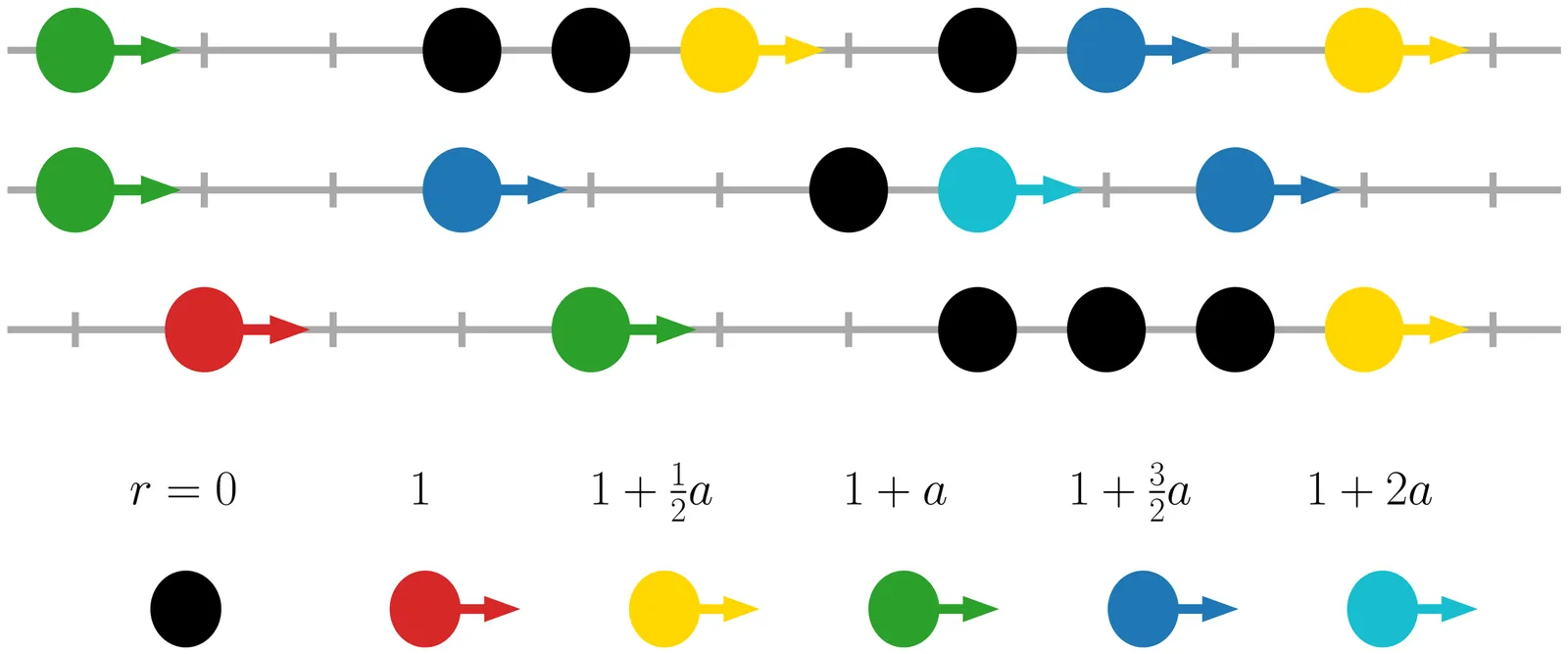
We investigate a driven particle system, a multilane asymmetric exclusion process, where the particle number in every lane is conserved, and stationary state is fully uncorrelated. The phase space has, starting from three lanes and more, an umbilic manifold where characteristic velocities of all the modes but one coincide, thus allowing us to study a weakly hyperbolic system with arbitrarily large degeneracy. We then study space-time fluctuations in the steady state, at the umbilic manifold, which are expected to exhibit universal scaling features. We formulate an effective mode-coupling theory (MCT) for the multilane model within the umbilic subspace and test its predictions. Unlike in the bidirectional two-lane model with an umbilic point studied earlier, here we find a robust $z=3/2$ dynamical exponent for the umbilic mode. The umbilic scaling function, obtained from Monte-Carlo simulations, for the simplest 3-lane scenario, appears to have an universal shape for a range of interaction parameters. Remarkably, the shape and dynamic exponent of the non-degenerate mode can be analytically predicted on the base of effective MCT, up to non-universal scaling factor. Our findings suggest the existence of novel universality classes with dynamical exponent $3/2$, appearing in long-lived hydrodynamic modes with equal characteristic velocities.
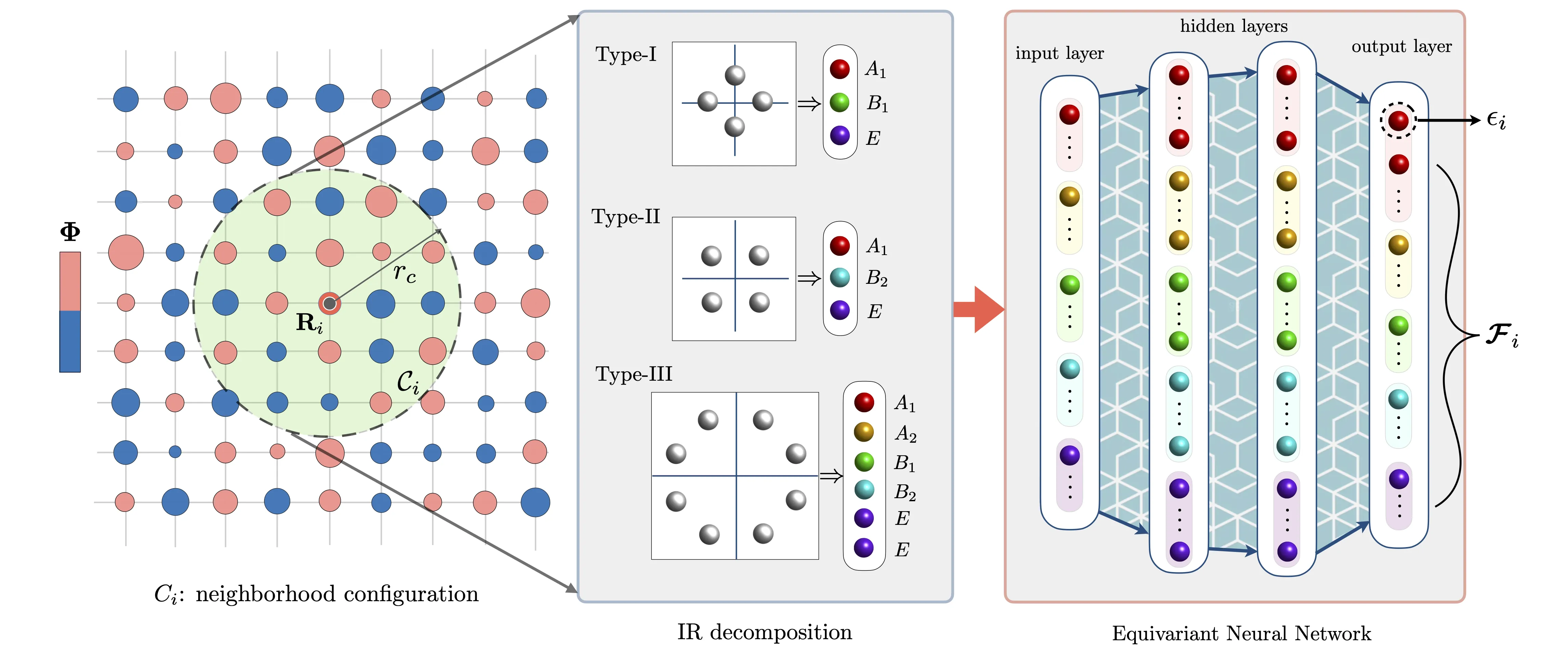
Machine-learning (ML) force fields enable large-scale simulations with near-first-principles accuracy at substantially reduced computational cost. Recent work has extended ML force-field approaches to adiabatic dynamical simulations of condensed-matter lattice models with coupled electronic and structural or magnetic degrees of freedom. However, most existing formulations rely on hand-crafted, symmetry-aware descriptors, whose construction is often system-specific and can hinder generality and transferability across different lattice Hamiltonians. Here we introduce a symmetry-preserving framework based on equivariant neural networks (ENNs) that provides a general, data-driven mapping from local configurations of dynamical variables to the associated on-site forces in a lattice Hamiltonian. In contrast to ENN architectures developed for molecular systems -- where continuous Euclidean symmetries dominate -- our approach aims to embed the discrete point-group and internal symmetries intrinsic to lattice models directly into the neural-network representation of the force field. As a proof of principle, we construct an ENN-based force-field model for the adiabatic dynamics of the Holstein Hamiltonian on a square lattice, a canonical system for electron-lattice physics. The resulting ML-enabled large-scale dynamical simulations faithfully capture mesoscale evolution of the symmetry-breaking phase, illustrating the utility of lattice-equivariant architectures for linking microscopic electronic processes to emergent dynamical behavior in condensed-matter lattice systems.
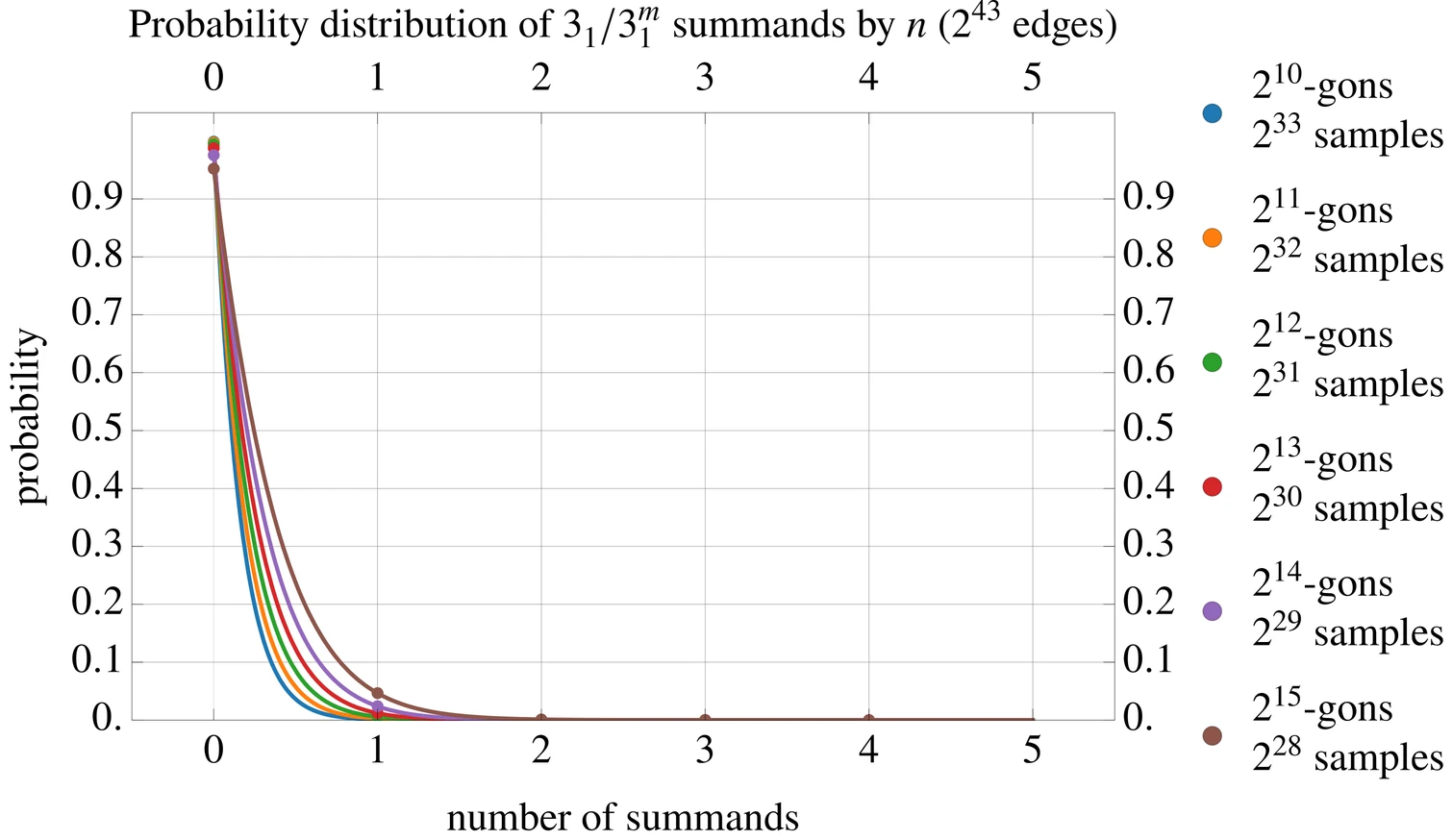
We present experimental results on knotting in off-lattice self-avoiding polygons in the bead-chain model. Using Clisby's tree data structure and the scale-free pivot algorithm, for each $k$ between $10$ and $27$ we generated $2^{43-k}$ polygons of size $n=2^k$. Using a new knot diagram simplification and invariant-free knot classification code, we were able to determine the precise knot type of each polygon. The results show that the number of prime summands of knot type $K$ in a random $n$-gon is very well described by a Poisson distribution. We estimate the characteristic length of knotting as $656500 \pm 2500$. We use the count of summands for large $n$ to measure knotting rates and amplitude ratios of knot probabilities more accurately than previous experiments. Our calculations agree quite well with previous on-lattice computations, and support both knot localization and the knot entropy conjecture.
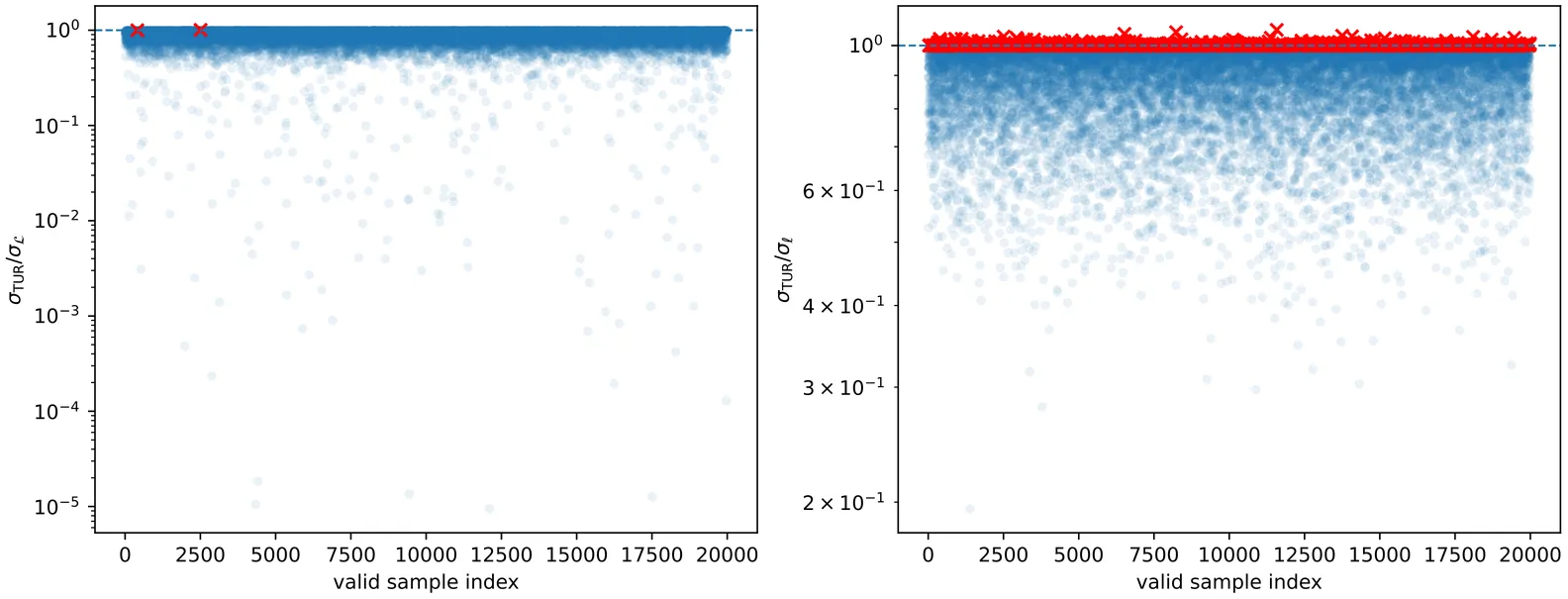
Two widely used model-free lower bounds on the steady-state entropy production rate of a continuous-time Markov jump process are the thermodynamic uncertainty relation (TUR) bound $σ_\text{TUR}$, derived from the mean and variance of a current, and the waiting-time distribution (WTD) bound $σ_\mathcal{L}$, derived from the irreversibility of partially observed transition sequences together with their waiting times. It has been conjectured that $σ_{\mathcal L}$ is always at least as tight as $σ_{\mathrm{TUR}}$ when both are constructed from the same partially observed link. Here we provide four-state counterexamples in a nonequilibrium steady state where $σ_{\mathcal L}<σ_{\mathrm{TUR}}$. This result shows that no universal ordering exists between these two inference bounds under partial observation.
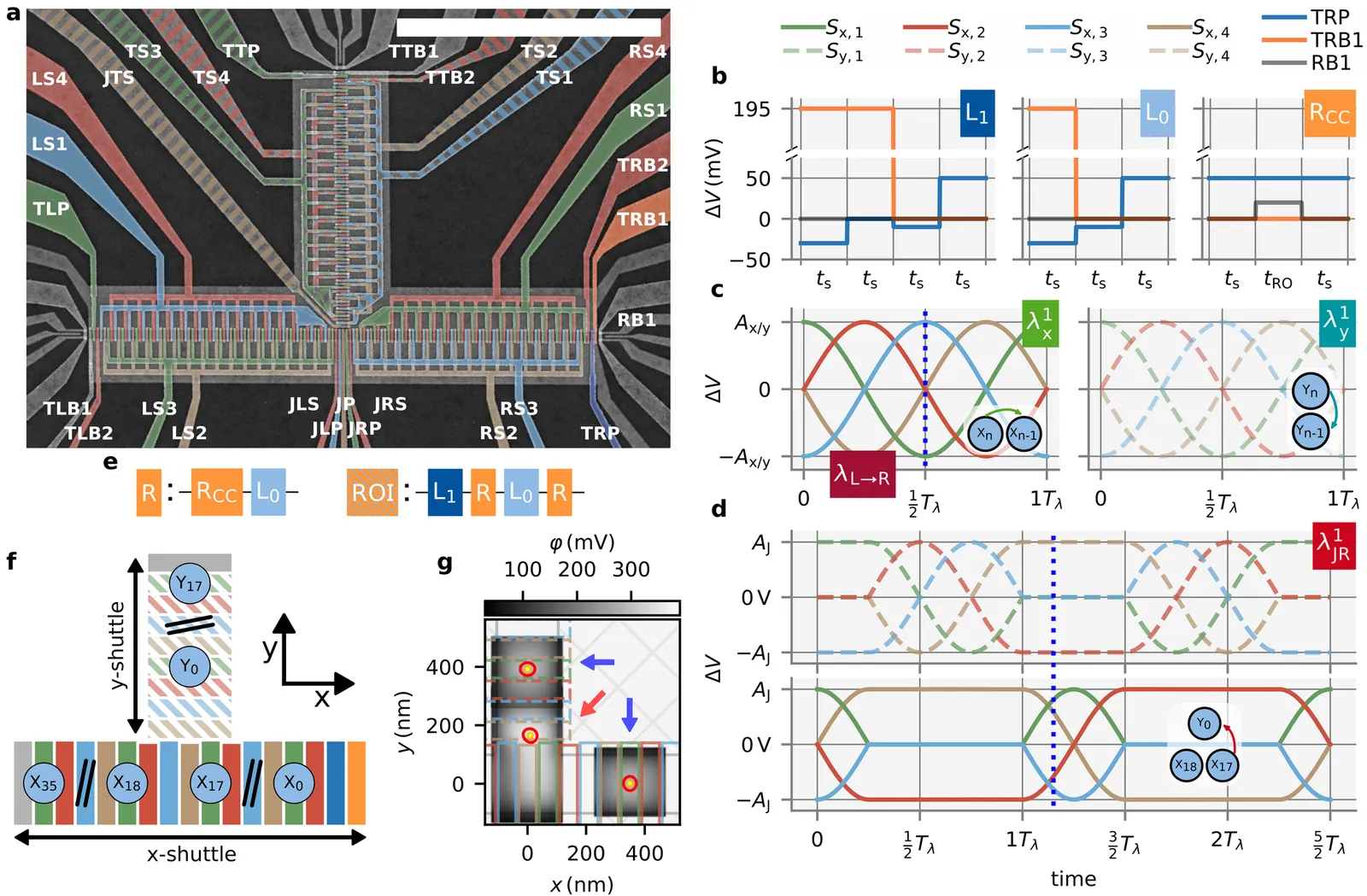
Conveyor-mode shuttling in gated Si/SiGe devices enables adiabatic transfer of single electrons, electron patterns and spin qubits confined in quantum dots across several microns with a scalable number of signal lines. To realize their full potential, linear shuttle lanes must connect into a two-dimensional grid with controllable routing. We introduce a T-junction device linking two independently driven shuttle lanes. Electron routing across the junction requires no extra control lines beyond the four channels per conveyor belt. We measure an inter-lane charge transfer fidelity of $F = 100.0000000^{+0}_{-9\times 10^{-7}}\,\%$ at an instantaneous electron velocity of $270\,\mathrm{mm}\,\mathrm{s}^{-1}$. The filling of 54 quantum dots is controlled by simple atomic pulses, allowing us to swap electron patterns, laying the groundwork for a native spin-qubit SWAP gate. This T-junction establishes a path towards scalable, two-dimensional quantum computing architectures with flexible spin qubit routing for quantum error correction.
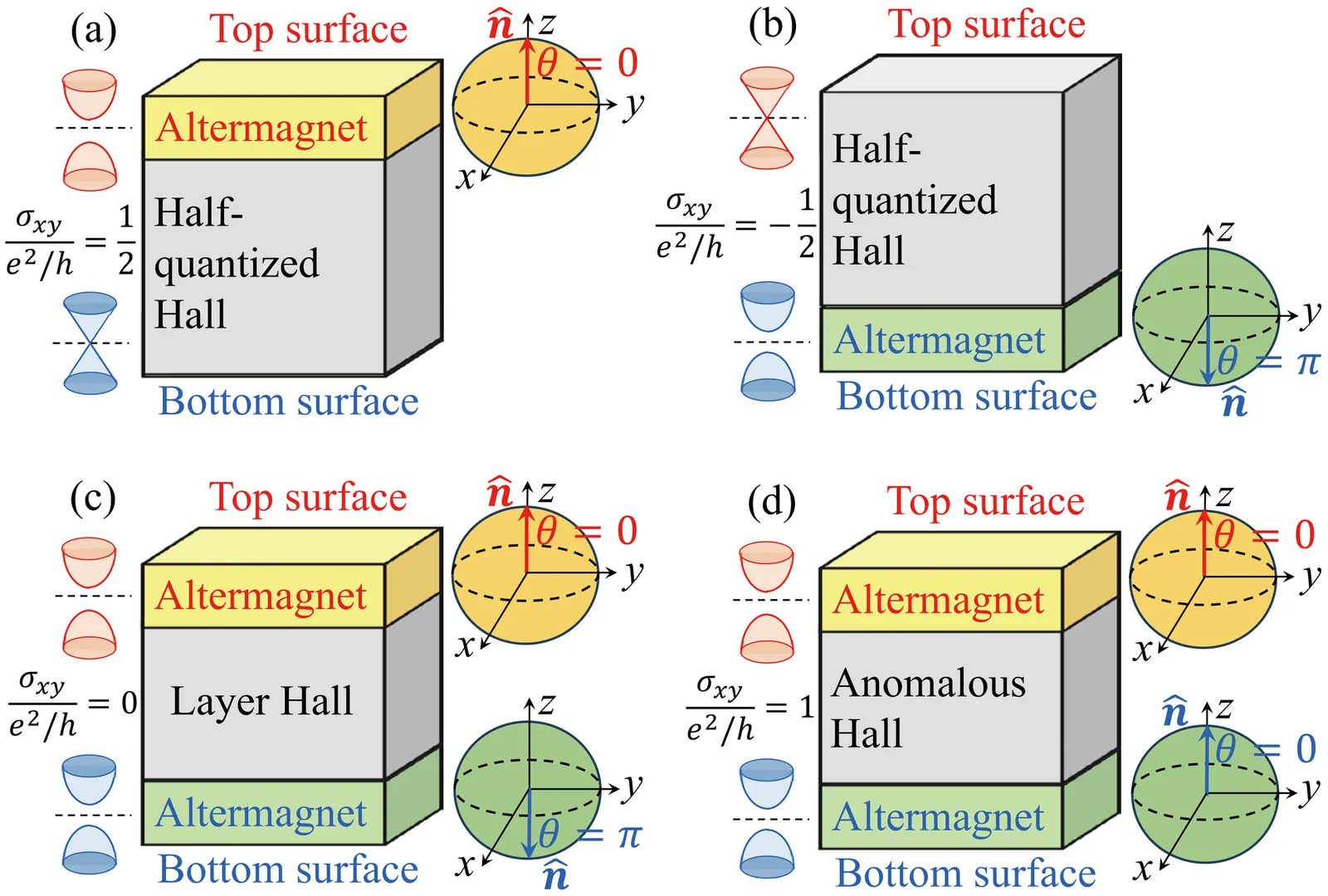
In this work, we propose a scheme to realize the layer Hall effect in the ferromagnetic topological insulator Bi$_2$Se$_3$ via proximity to $d$-wave altermagnets. We show that an altermagnet and an in-plane magnetic field applied near one surface gap the corresponding Dirac cone, yielding an altermagnet-induced half-quantized Hall effect. When altermagnets with antiparallel Néel vectors are placed near the top and bottom surfaces, giving rise to the layer Hall effect with vanishing net Hall conductance, i.e., the altermagnet-induced layer Hall effect. In contrast, altermagnets with parallel Néel vectors lead to a quantized Chern insulating state, i.e., the altermagnet-induced anomalous Hall effect. We further analyze the dependence of the Hall conductance on the orientation of the in-plane magnetic field and demonstrate that the layer Hall effect becomes observable under a perpendicular electric field. Our results establish a route to engineer altermagnet-induced topological phases in ferromagnetic topological insulators.
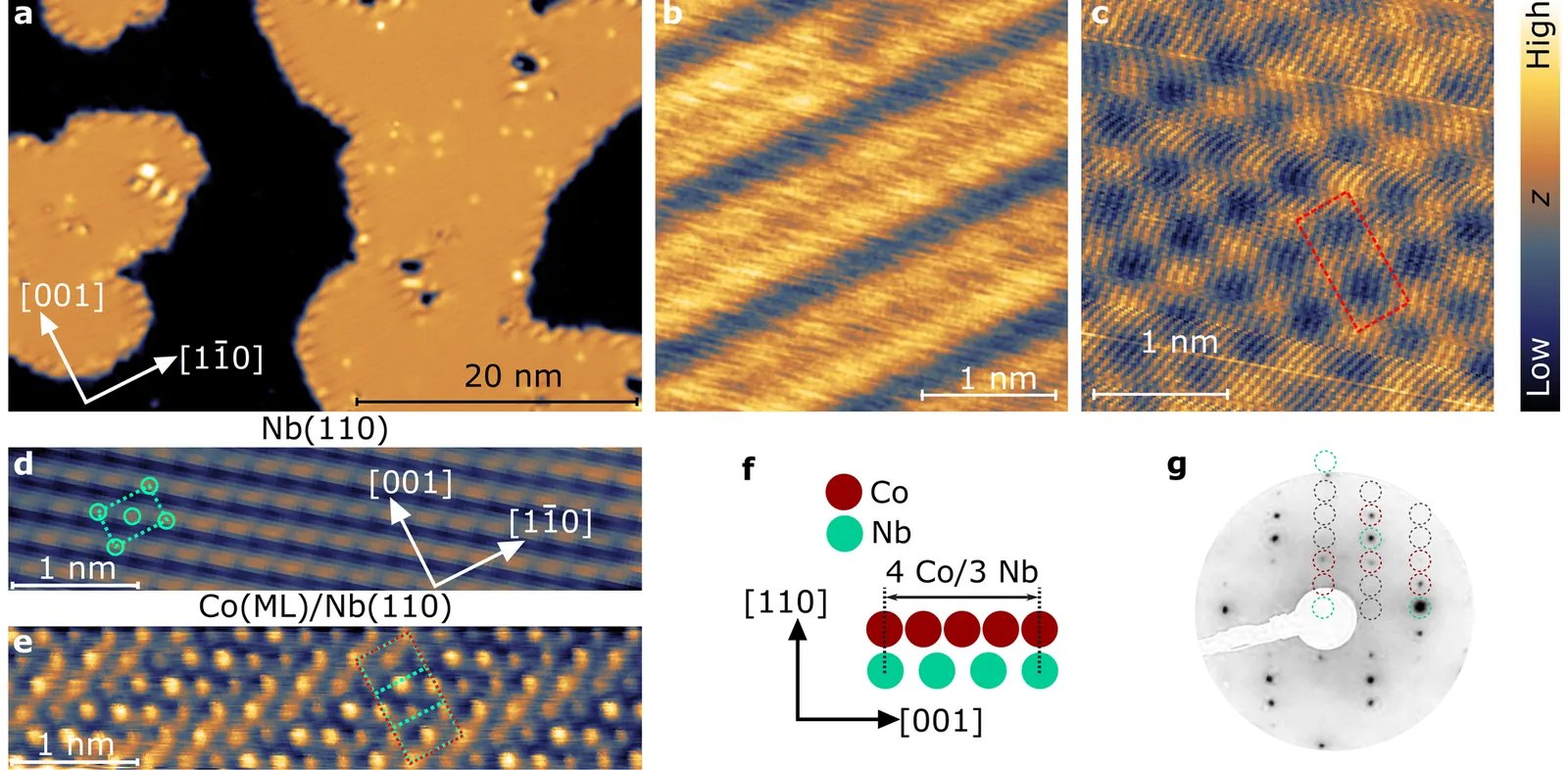
The potential application of topological superconductivity in quantum transport and quantum information has fueled an intense investigation of hybrid materials with emergent electronic properties, including magnet-superconductor heterostructures. Here, we report evidence of a topological nodal-point superconducting phase in a one-atom-thick in-plane ferromagnet in direct proximity to a conventional $s$-wave superconductor. Low-temperature scanning tunneling spectroscopy data reveal the presence of a double-peak low-energy feature in the local density of states of the hybrid system, which is rationalized via model calculations to be an emergent topological nodal-point superconducting phase with tilted Weyl cones. Our results further establish the combination of in-plane ferromagnetism and conventional superconductivity as a route to design two-dimensional topological quantum phases.
Although the measurement of current is now defined with respect to the electronic charge, producing a current standard based on a single-electron source remains challenging. The error rate of a source must be below 0.01 ppm, and many such sources must be operated in parallel to provide practically useful values of current in the nanoampere range. Achieving a single electron source using an industrial grade 300 mm wafer silicon metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) process could offer a powerful route for scaling, combined with the ability for integration with control and measurement electronics. Here, we present measurements of such a single-electron source indicating an error rate of 0.008 ppm, below the error threshold to satisfy the SI Ampere, and one of the lowest error rates reported, implemented using a gate-defined quantum dot device fabricated on an industry-grade silicon MOS process. Further evidence supporting the accuracy of the device is obtained by comparing the device performance to established models of quantum tunnelling, which reveal the mechanism of operation of our source at the single particle level. The low error rate observed in this device motivates the development of scaled arrays of parallel sources utilising Si MOS devices to realise a new generation of metrologically accurate current standards.

We study the performance of Kitaev-Heisenberg (KH) clusters as working media realizing a quantum Otto engine (QOE). An external Zeeman field with linear time dependency is used as the driving mechanism. The efficiency strongly depends on Kitaev ($κ$) and Heisenberg ($J$) exchange interaction. Interestingly, efficiency is comparable when the relative magnitude of $κ$ and $J$ is the same but of opposite signs. The above results are explained due to a subtle interplay of frustration, quantum fluctuation, and duality of eigen-spectra for the KH system when both the signs of $κ$ and $J$ are reversed. The maximum efficiency is shown to be dynamically related to eigen-spectra forming discrete narrow bands, where total spin angular momentum becomes a good quantum number. We relate this optimum efficiency to the realization of weakly interacting magnons, where the system reduces to an approximate eigen-system of the external drive. Finally, we extend our study to the large spin Kitaev model and find a quantum advantage in efficiency for $S=1/2$. The results could be of practical interest for materials with KH interactions as a platform for QOE.
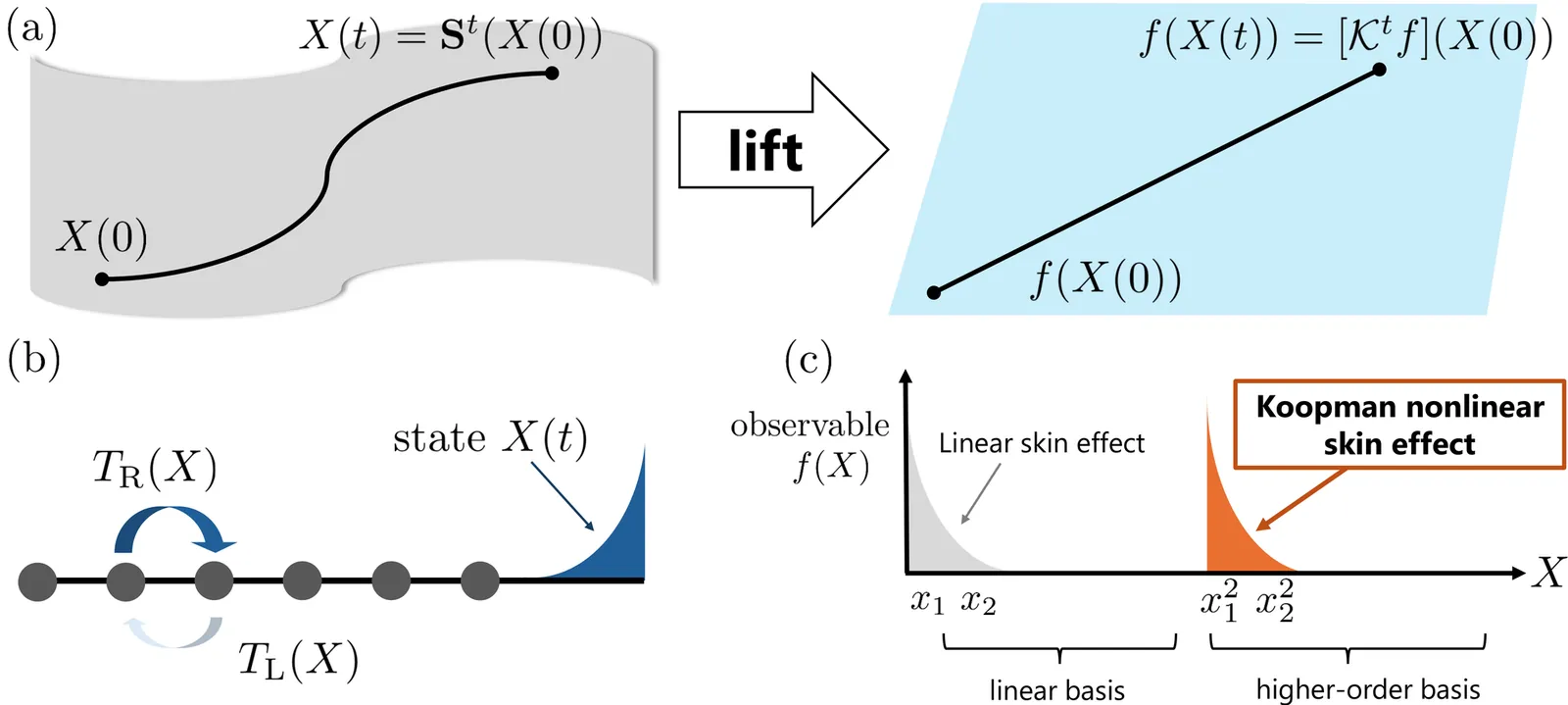
Non-Hermitian skin effects are conventionally manifested as boundary localization of eigenstates in linear systems. In nonlinear settings, however, where eigenstates are no longer well defined, it becomes unclear how skin effects should be faithfully characterized. Here, we propose a Koopman-based characterization of nonlinear skin effects, in which localization is defined in terms of Koopman eigenfunctions in a lifted observable space, rather than physical states. Using a minimal nonlinear extension of the Hatano-Nelson model, we show that dominant Koopman eigenfunctions localize sharply on higher-order observables, in stark contrast to linear skin effects confined to linear observables. This lifted-space localization governs the sensitivity to boundary amplitude perturbations, providing a distinct dynamical signature of the nonlinear skin effect. Our results establish the Koopman framework as a natural setting in which skin effects unique to nonlinear non-Hermitian systems can be identified.
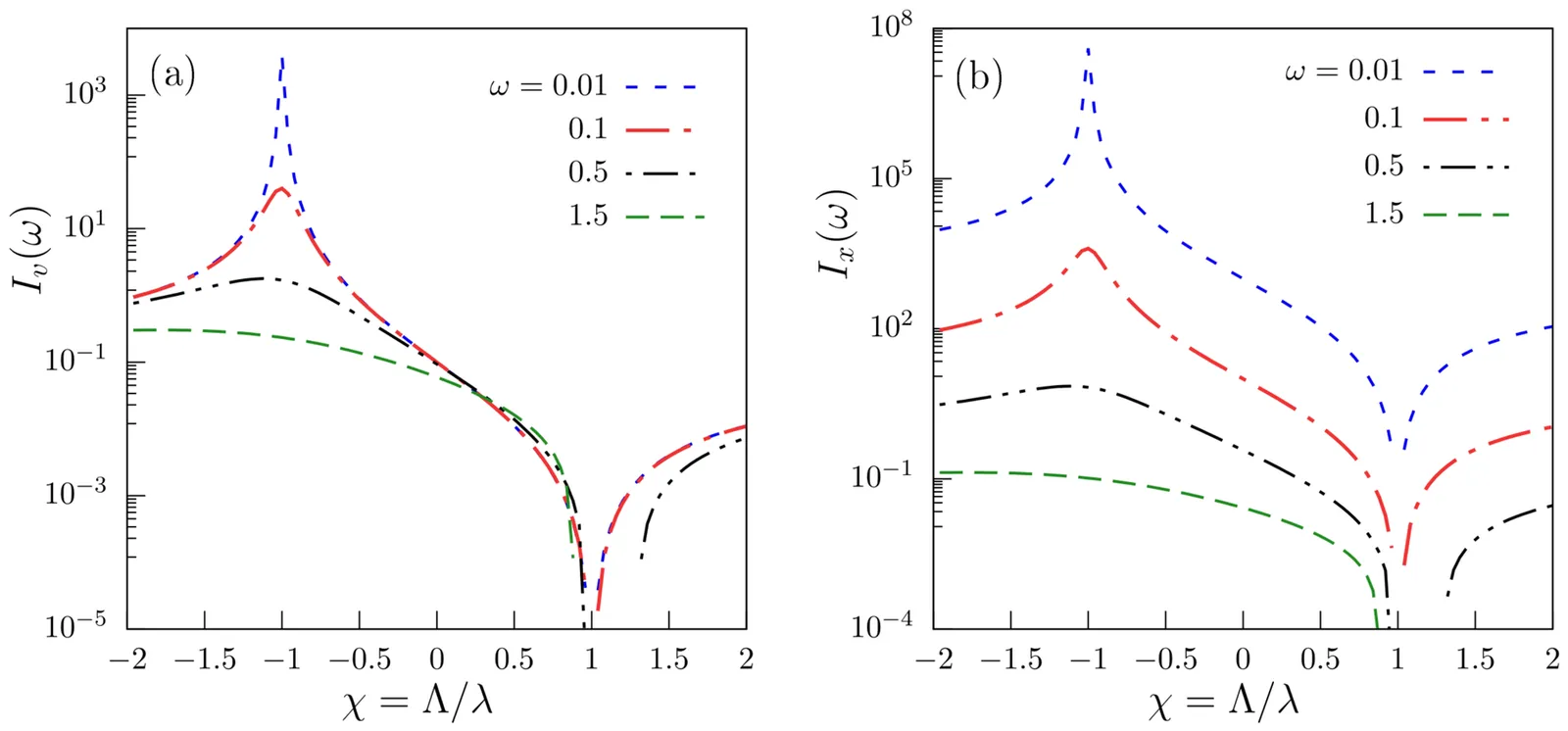
Non-reciprocal interactions play a key role in shaping transport in active and passive systems, giving rise to striking nonequilibrium behavior. Here, we study the dynamics of a tracer -- active or passive -- embedded in a bath of active or passive particles, coupled through non-reciprocal interactions. Starting from the microscopic stochastic dynamics of the full system, we derive an overdamped generalized Langevin equation for the tracer, incorporating a non-Markovian memory kernel that captures bath-mediated correlations. This framework enables us to compute the tracer's velocity and displacement response, derive a generalized nonequilibrium fluctuation-dissipation relation that quantifies deviations from equilibrium behavior, and determine the mean-squared displacement (MSD). We find that while the MSD becomes asymptotically diffusive, the effective diffusivity depends non-monotonically on the degree of non-reciprocity and diverges at an intermediate value. This regime of giant diffusivity provides a generic mechanism for enhanced transport in active soft matter and has direct implications for biological systems exhibiting chase-and-run or predator-prey interactions. Our analytical predictions are supported by numerical simulations of active Brownian particles, highlighting experimentally accessible signatures of non-reciprocal interactions in soft matter.
 2601.03583
2601.03583We examine the formulas commonly used to estimate current-induced spin-orbit torques from harmonic Hall voltage measurements. In particular, we focus on the factor of two discrepancy among expressions employed to fit harmonic Hall signals measured under an in-plane rotating magnetic field. By explicitly deriving the relevant relations, we clarify the origin of this discrepancy and present the correct form of the fitting formula. We further discuss the determination of the sign of the field-like torque from harmonic Hall voltage measurements, which depends on the assumed form of the current-induced torques.
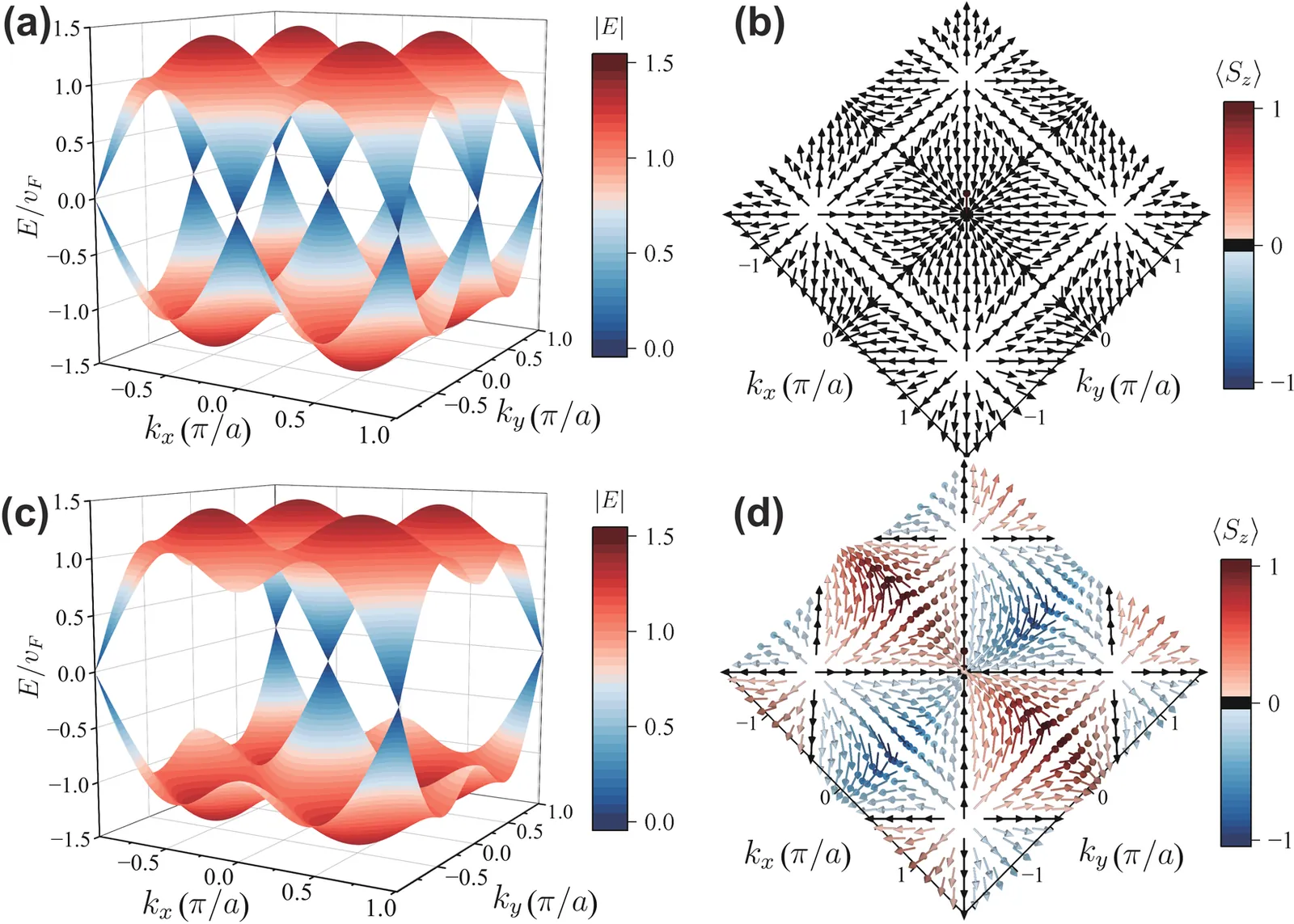
In two-dimensional lattice systems, massless Dirac fermions undergo doubling, leading to the cancellation of net chirality. We demonstrate that the recently discovered altermagnetism can induce a unique mass term, the altermagnetic mass term, which gaps out Dirac cones with one chirality while maintaining the other gapless, leading to the emergence of net chirality. The surviving gapless Dirac cones retain identical winding numbers and exhibit the quantum anomalous Hall effect in the presence of the trivial constant mass term. When subjected to an external magnetic field, the altermagnetic mass induces Landau level asymmetry in Dirac fermions, resulting in fully valley-polarized quantum Hall edge states. Our findings reveal that Dirac fermions with the altermagnetic mass harbor rich physical phenomena warranting further exploration.
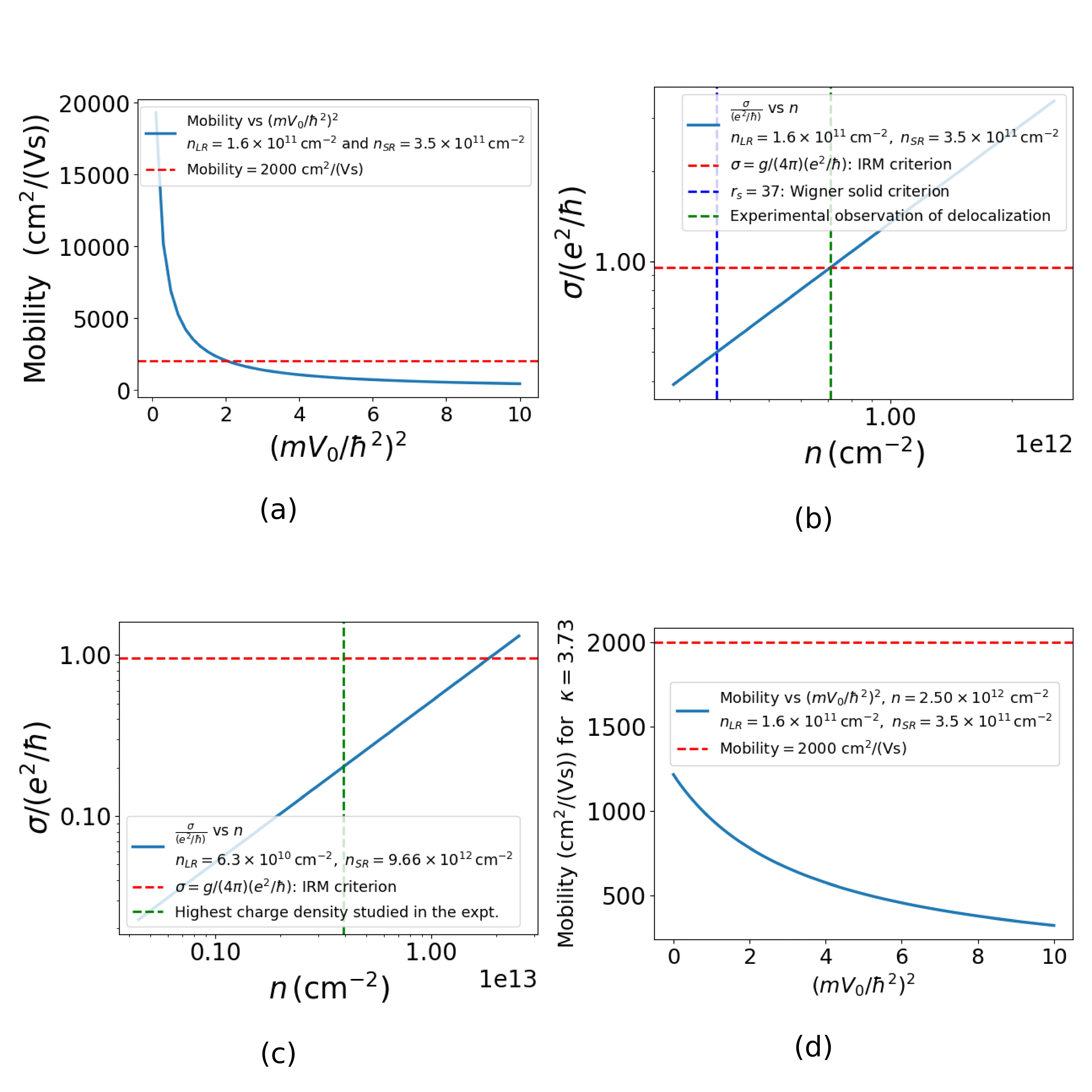
Critically analyzing recent STM and transport experiments [Z. Ge, et al, arXiv:2510.12009] on 2D electron systems in the presence of random quenched impurities, we argue that the resulting low-density putative "solid" phase reported experimentally is better described as an Anderson solid with the carriers randomly spatially localized by impurities than as a Wigner solid where the carriers form a crystal due to an interaction-induced spontaneous breaking of the translational symmetry. In strongly disordered systems, the resulting solid is amorphous, which is adiabatically connected to the infinite disorder Anderson fixed point rather than the zero disorder Wigner crystal fixed point.
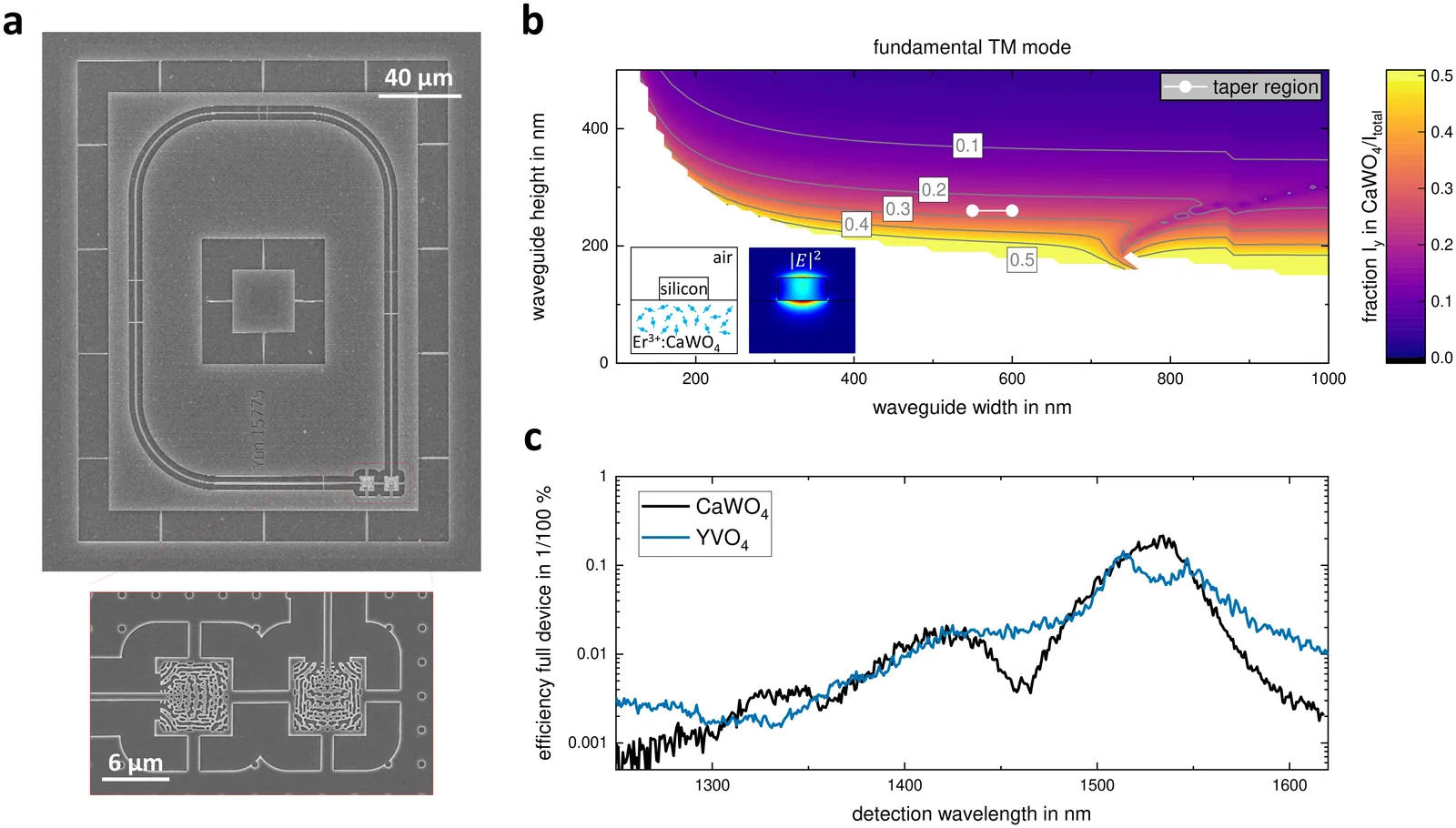
We present an optical study of near-surface Er$^{3+}$ ensembles in waveguide-integrated CaWO$_4$ and YVO$_4$, investigating how nanophotonic coupling modifies rare-earth spectroscopy. In particular, we compare bulk excitation with evanescently coupled TE and TM waveguide modes. In Er$^{3+}$:CaWO$_4$, we observe a pronounced polarization-dependent surface effect. TE-coupled spectra closely reproduce bulk behavior. In contrast, TM coupling induces strong inhomogeneous broadening and an asymmetric low-energy shoulder of the site S1 Y1Z1 transition, with linewidths exceeding those of the bulk by more than a factor of four. Temperature-dependent measurements and surface termination studies indicate that surface charges are the dominant mechanism. Er$^{3+}$:YVO$_4$ remains largely unaffected by mode polarization, and surface termination leads only to minor spectral shifts. These observations suggest that non-charge-neutral rare-earth systems are more susceptible to surface-induced decoherence sources than charge-neutral hosts.
These lecture notes present a comprehensive and powerful many-body technique pioneered in 1960 by D. N. Zubarev. The technique, known as the Zubarev Double Time Greens Function method, was used extensively by leading solid state physicists such as John Hubbard and Laura Roth in the 1960s. We present the technique and apply it to the non-interacting electron and boson gas. We next consider the (many-body) Hubbard model and show how it yields the Stoner criterion for ferromagnetism. It is easily extendable to superconductivity and related problems. Our treatment is pedagogical and understandable to those with just an elementary understanding of second quantization.
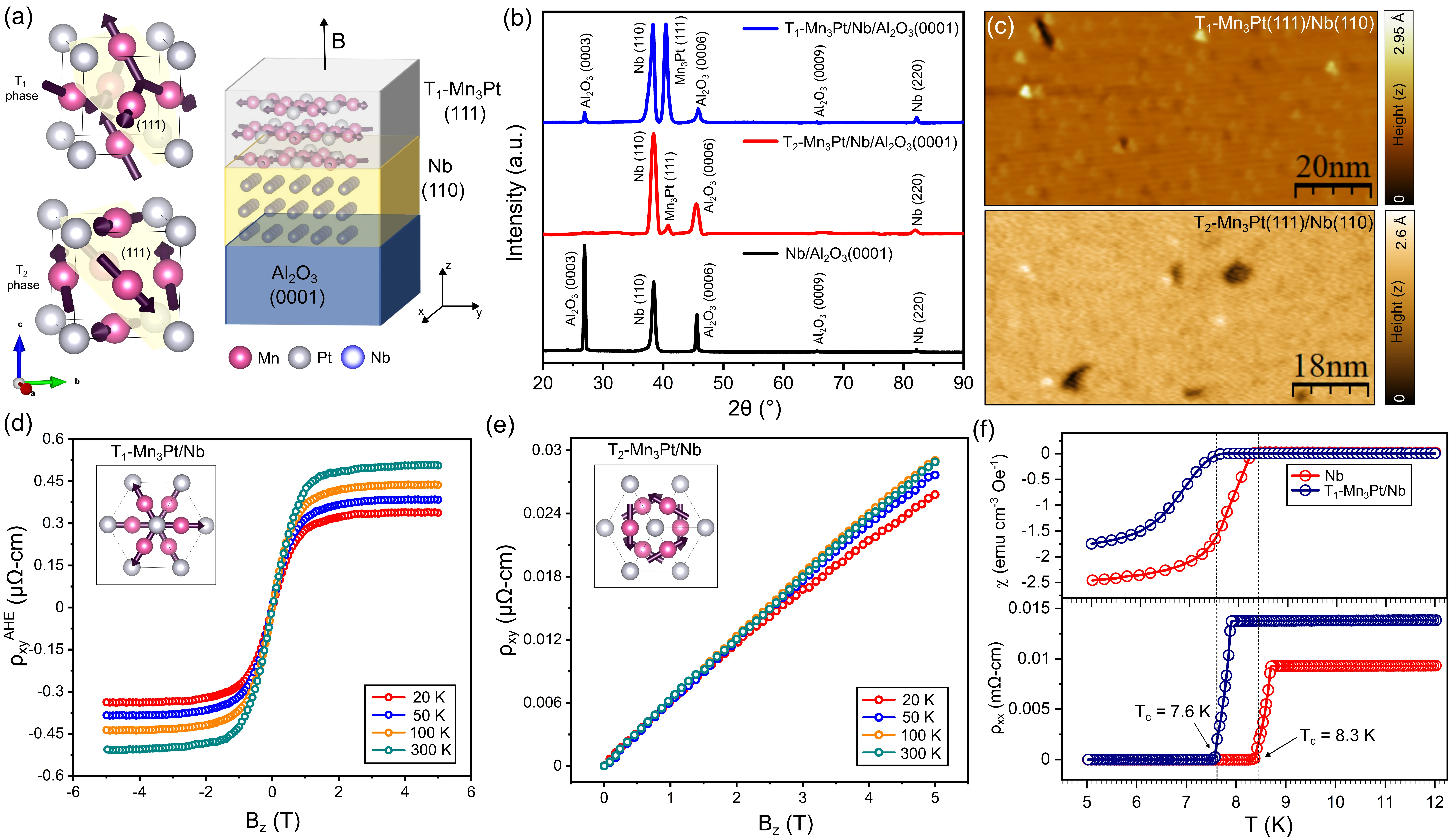
Compensated magnetic orders that can split the spin-degeneracy of electronic bands have become a very active field of research. As opposed to spin-orbit coupling, the splitting resulting from these "altermagnets" is not a small relativistic correction and, in contrast to ferromagnets, not accompanied by a net magnetization and large stray fields. In particular, the theoretical analysis of the interplay of altermagnetism and superconductivity has taken center stage, while experimental investigations of their coexistence remain in their infancy. We here study heterostructures consisting of Nb thins films interfaced with the $T_1$ and $T_2$ phases of Mn$_3$Pt. These non-collinear magnetic states can be thought of as descendants from the same altermagnetic order in the absence of spin-orbit coupling. We demonstrate the non-trivial impact on the superconducting state of Nb, which exhibits a zero-field superconducting diode effect, despite the compensated ($T_2$) and nearly-compensated ($T_1$) magnetic order; the diode efficiencies can reach large values (up to 50$\%$). The diode effect is found to be highly sensitive to the form of the magnetic order, illustrating its potential as a symmetry probe. The complex magnetic field and temperature dependence hint at a rich interplay of multiple contributing mechanisms. Our results define a new materials paradigm for dissipationless spintronics and magnetization-free diode functionality, while motivating further exploration of non-collinear altermagnetic superconductors.
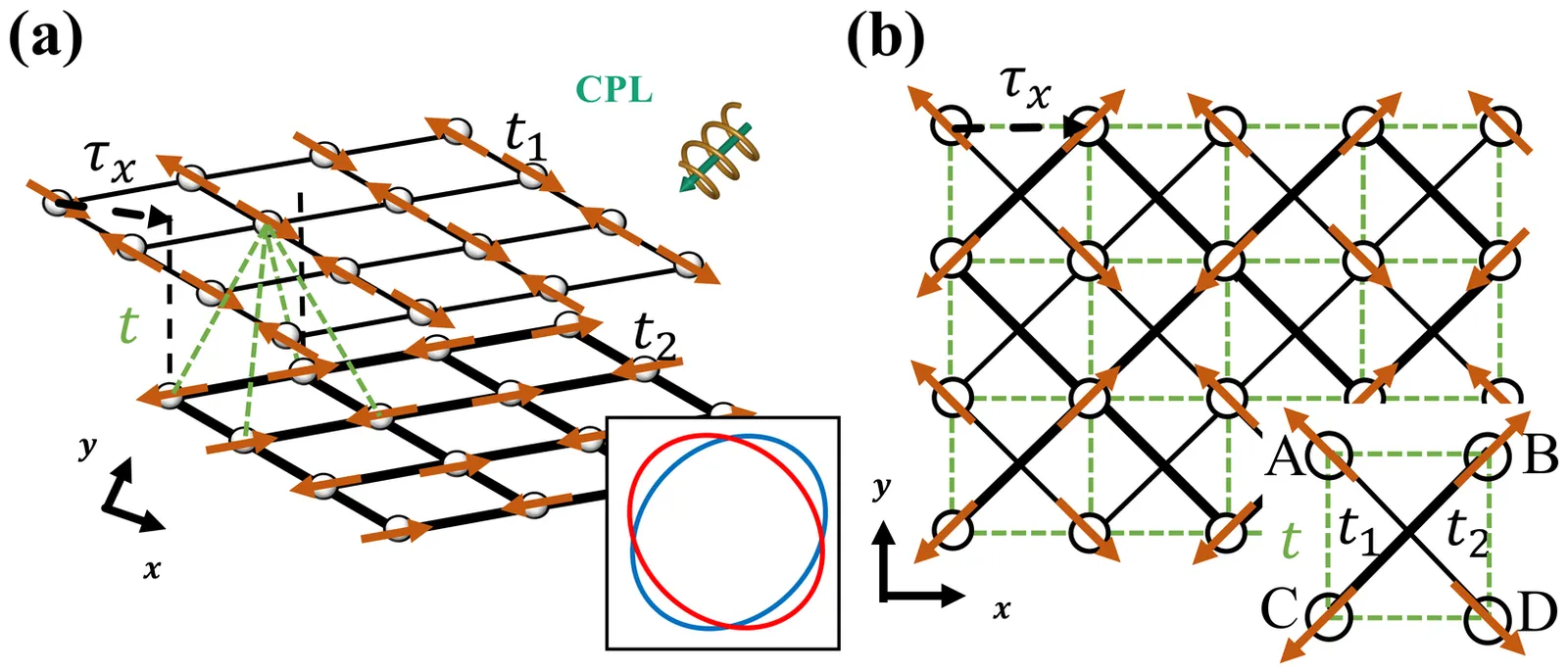
When a coplanar antiferromagnet (AFM) with $xy$-plane magnetic moments exhibits a spin-split band structure and unidirectional spin polarization along $z$, the spin polarization is forced to be an odd function of momentum by the fundamental symmetry $[\bar{C}_{2z}\|\mathcal{T}]$. Coplanar AFMs displaying such odd-parity unidirectional spin splittings are known as odd-parity magnets. In this work, we propose the realization of their missing even-parity counterparts. We begin by deriving the symmetry conditions required for an even-parity, out-of-plane spin splitting. We then show that irradiating a spin-degenerate coplanar AFM with circularly polarized light lifts the $[\bar{C}_{2z}|\mathcal{T}]$ constraint, dynamically generating this even-parity state. Specifically, the light-induced unidirectional spin splitting exhibits a $d$-wave texture in momentum space, akin to that of a $d$-wave altermagnet. We prove this texture's robustness against spin canting and show it yields a unique clover-like angular dependence in the Drude spin conductivity. Our work demonstrates that optical driving can generate novel spin-split phases in coplanar AFMs, thereby diversifying the landscape of materials exhibiting distinct spin splittings.
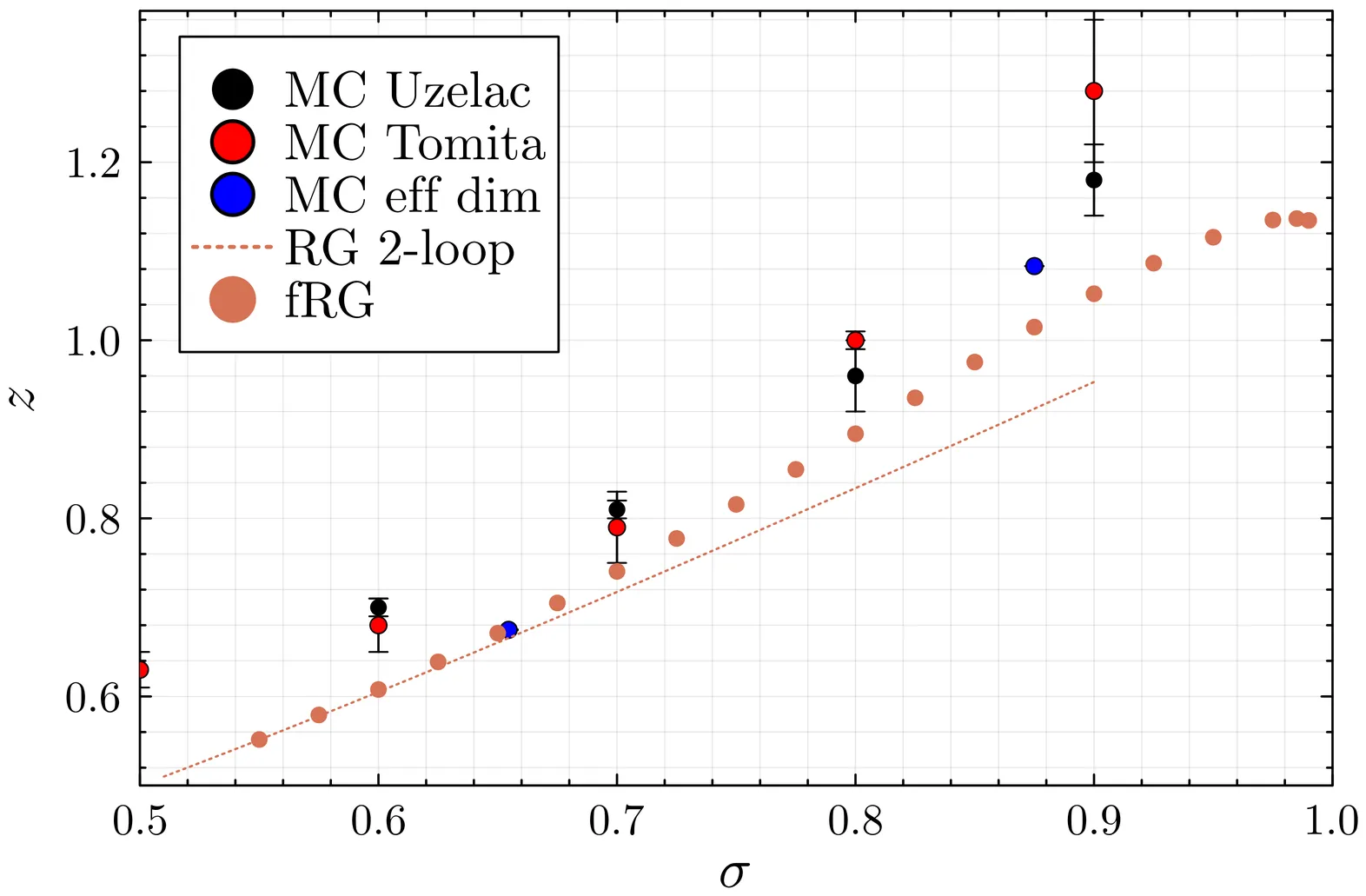
We study the dynamical scaling of long-range $\mathrm{O}(N)$ models after a sudden quench to the critical temperature, using the functional renormalization group approach. We characterize both short-time aging and long-time relaxation as a function of the symmetry index $N$, the interaction range decay exponent $σ$ and the dimension $d$. Our results substantially improve on perturbative predictions, as demonstrated by benchmarks against Monte Carlo simulations and the large-$N$ limit. Finally, we demonstrate that long-range systems increase the performance of critical heat engines with respect to a local active medium.