Dynamical Systems
Dynamics of differential equations and flows, mechanics, classical few-body problems, iterations, complex dynamics, delayed differential equations.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Dynamics of differential equations and flows, mechanics, classical few-body problems, iterations, complex dynamics, delayed differential equations.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
 2601.03999
2601.03999We prove quantitative polynomial Wiener-Wintner theorems in a very general setup, including measure-preserving actions of nilpotent Lie groups. Our results apply both to ergodic averages and to averages with singular integral weights. The proof relies on the generalized polynomial Carleson theorem developed in the companion paper by van Doorn, Srivastava, and the authors.
 2601.03501
2601.03501We prove that if a recursively presented group admits a (nonempty) subshift of finite type with nonzero Medvedev degree then it fails to have the strong topological Rokhlin property. This result simplifies a known criterion and provides new examples of recursively presented groups without this property.
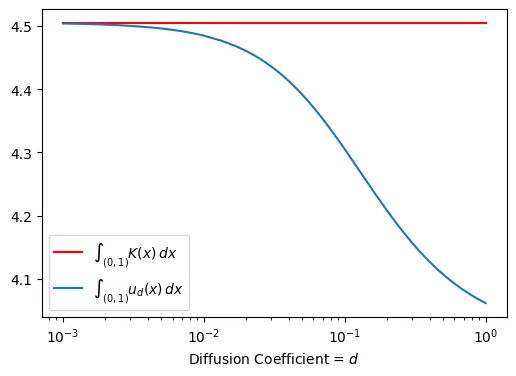
In 2006 (J. Differential Equ.), Lou proved that, once the intrinsic growth rate $r$ in the logistic model is proportional to the spatially heterogeneous carrying capacity $K$ ($r=K^1$), the total population under the regular diffusion exceeds the total of the carrying capacity. He also conjectured that the dependency of the total population on the diffusion coefficient is unimodal, increasing to its maximum and then decreasing to the asymptote which is the total of the carrying capacity. DeAngelis et al (J. Math. Biol. 2016) argued that the prevalence of the population over the carrying capacity is only observed when the growth rate and the carrying capacity are positively correlated, at least for slow dispersal. Guo et al (J. Math. Biol. 2020) justified that, once $r$ is constant ($r=K^0$), the total population is less than the cumulative carrying capacity. Our paper fills up the gap for when $r=K^λ$ for any real $λ$, disproving an assumption that there is a critical $λ^{\ast} \in (0,1)$ at which the tendency of the prevalence of the carrying capacity over the total population size changes, demonstrating instead that the relationship is more complicated. In addition, we explore the dependency of the total population size on the diffusion coefficient when the third parameter of the dispersal strategy $P$ is involved: the diffusion term is $d Δ(u/P)$, not just $d Δu$, for any $λ$. We outline some differences from the random diffusion case, in particular, concerning the profile of the total population as a function of the diffusion coefficient.

Artificial muscles are essential for compliant musculoskeletal robotics but complicate control due to nonlinear multiphysics dynamics. Hydraulically amplified electrostatic (HASEL) actuators, a class of soft artificial muscles, offer high performance but exhibit memory effects and hysteresis. Here we present a data-driven reduction and control strategy grounded in spectral submanifold (SSM) theory. In the adiabatic regime, where inputs vary slowly relative to intrinsic transients, trajectories rapidly converge to a low-dimensional slow manifold. We learn an explicit input-to-output map on this manifold from forced-response trajectories alone, avoiding decay experiments that can trigger hysteresis. We deploy the SSM-based model for real-time control of an antagonistic HASEL-clutch joint. This approach yields a substantial reduction in tracking error compared to feedback-only and feedforward-only baselines under identical settings. This record-and-control workflow enables rapid characterization and high-performance control of soft muscles and muscle-driven joints without detailed physics-based modeling.
How can we build surrogate solvers that train on small domains but scale to larger ones without intrusive access to PDE operators? Inspired by the Data-Driven Finite Element Method (DD-FEM) framework for modular data-driven solvers, we propose the Latent Space Element Method (LSEM), an element-based latent surrogate assembly approach in which a learned subdomain ("element") model can be tiled and coupled to form a larger computational domain. Each element is a LaSDI latent ODE surrogate trained from snapshots on a local patch, and neighboring elements are coupled through learned directional interaction terms in latent space, avoiding Schwarz iterations and interface residual evaluations. A smooth window-based blending reconstructs a global field from overlapping element predictions, yielding a scalable assembled latent dynamical system. Experiments on the 1D Burgers and Korteweg-de Vries equations show that LSEM maintains predictive accuracy while scaling to spatial domains larger than those seen in training. LSEM offers an interpretable and extensible route toward foundation-model surrogate solvers built from reusable local models.
In this paper we develop Host--Kra and inverse Gowers theory for abelian groups of bounded exponent. We show that the Host--Kra factors $Z^{\leq k}(\mathrm{X})$ associated with actions of such groups admit extensions with the structure of \emph{polynomial towers}. This new notion is a system obtained as a finite iteration of abelian extensions of the trivial system by polynomial cocycles; crucially, the intermediate extensions in this system are not required to agree with the Host--Kra factors. We prove that all such extensions are Abramov (generalizing a recent result of Candela, González-Sánchez, and Szegedy), but not necessarily Weyl, and have the structure of k-step translational systems. Combining this structure theorem with a correspondence principle due to the first and third authors, we derive an inverse theorem for the Gowers norms on finite abelian groups of bounded exponent: large $U^{k+1}$-norm implies large correlation with a polynomial of degree $\le k$ (on the same group), even when the exponent is not square-free or is divisible by small primes. This resolves a conjecture of the first and third authors for such groups, and also answers a question of Candela, González-Sánchez, and Szegedy.
 2601.00233
2601.00233We introduce the mean Assouad dimension of a dynamical system, motivated by the Assouad dimension in fractal geometry. Using dimension interpolation, we further define the mean Assouad spectrum. This provides a new family of bi-Lipschitz invariants of dynamical systems. We study its basic properties and calculate it for several classes of dynamical systems. As an application, we determine explicit formulae for the mean Assouad dimension and spectrum of infinite-dimensional Bedford--McMullen carpet systems, contributing to the program of studying infinite dimensional fractals, initiated recently by Tsukamoto.
We provide a notion of group cross-correlations, where the associated filter is not as tightly constrained as in the previous literature. This resolves an incompatibility previous constraints have for group actions with non-compact stabilizers. Moreover, we generalize previous results to group actions that are not necessarily transitive, and we weaken the common assumption of unimodularity.
 2512.24741
2512.24741We study locally countable acyclic measure-class-preserving (mcp) Borel graphs by analyzing their "topography" -- the interaction between the geometry and the associated Radon--Nikodym cocycle. We identify three notions of topographic significance for ends in such graphs and show that the number of nonvanishing ends governs both amenability and smoothness. More precisely, we extend the Adams dichotomy from the pmp to the mcp setting, replacing the number of ends with the number of nonvanishing ends: an acyclic mcp graph is amenable if and only if a.e. component has at most two nonvanishing ends, while it is nowhere amenable exactly when a.e. component has a nonempty perfect (closed) set of nonvanishing ends. We also characterize smoothness: an acyclic mcp graph is essentially smooth if and only if a.e. component has no nonvanishing ends. Furthermore, we show that the notion of nonvanishing ends depends only on the measure class and not on the specific measure. At the heart of our analysis lies the study of acyclic countable-to-one Borel functions. Our critical result is that, outside of the essentially two-ended setting, all back ends in a.e. orbit are vanishing and admit cocycle-finite geodesics. We also show that the number of barytropic ends controls the essential number of ends for such functions. This leads to a surprising topographic characterization of when such functions are essentially one-ended. Our proofs utilize mass transport, end selection, and the notion of the Radon--Nikodym core for acyclic mcp graphs, a new concept that serves as a guiding framework for our topographic analysis.
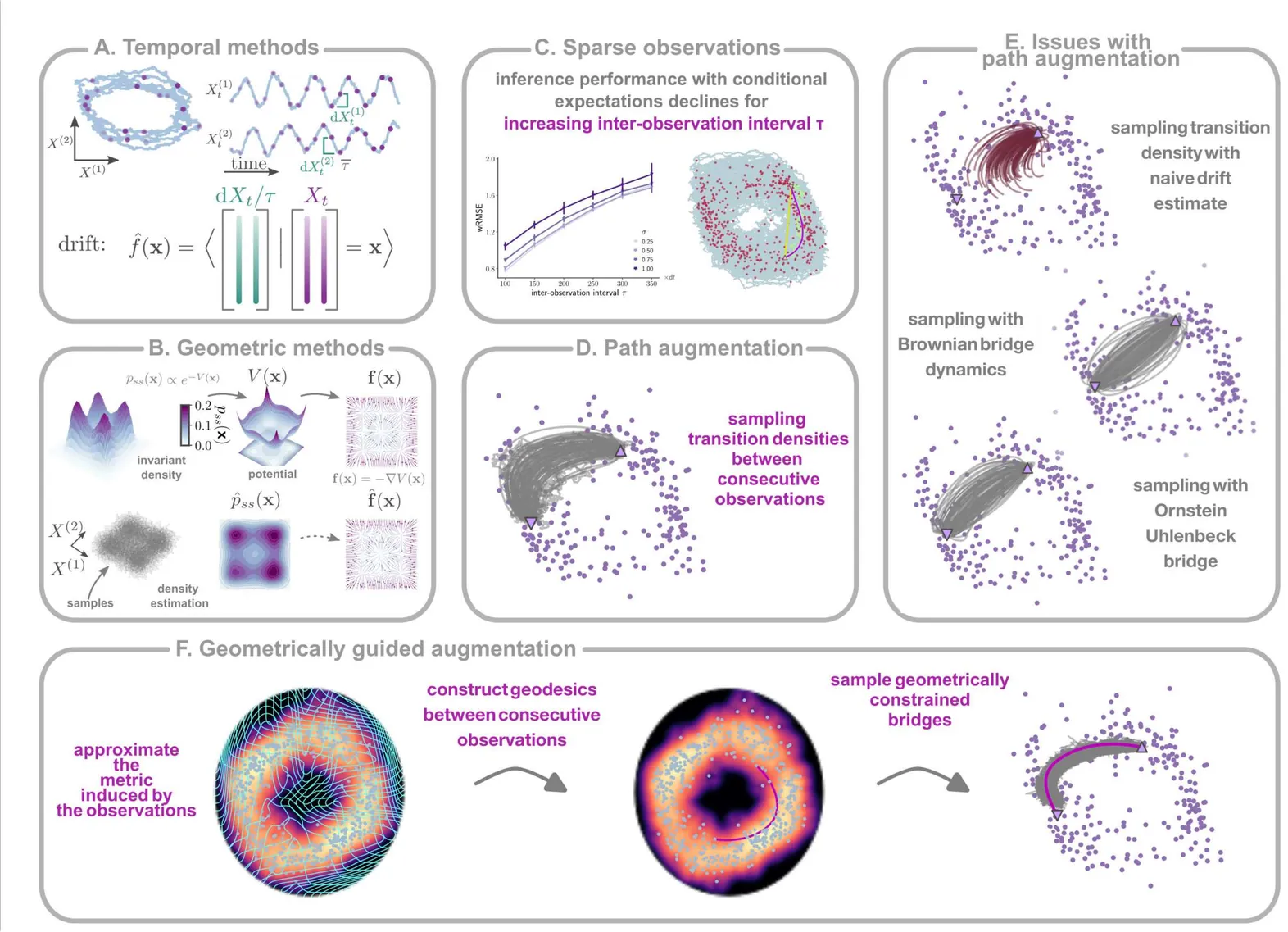
How can we learn the laws underlying the dynamics of stochastic systems when their trajectories are sampled sparsely in time? Existing methods either require temporally resolved high-frequency observations, or rely on geometric arguments that apply only to conservative systems, limiting the range of dynamics they can recover. Here, we present a new framework that reconciles these two perspectives by reformulating inference as a stochastic control problem. Our method uses geometry-driven path augmentation, guided by the geometry in the system's invariant density to reconstruct likely trajectories and infer the underlying dynamics without assuming specific parametric models. Applied to overdamped Langevin systems, our approach accurately recovers stochastic dynamics even from extremely undersampled data, outperforming existing methods in synthetic benchmarks. This work demonstrates the effectiveness of incorporating geometric inductive biases into stochastic system identification methods.

The α-Kakutani substitution rule splits the unit interval into two subintervals of lengths alpha and 1 - α, for a fixed α in (0,1). A simple inflation-substitution procedure produces tilings of the real line and their associated Delone sets. We show that there are precisely five distinct values of min(α, 1 - α) for which these sets are uniformly spread, meaning that they are a bounded displacement of a lattice. The proof of this surprising fact combines the construction and analysis of a related family of primitive substitution tilings, Solomon's criterion for uniform spreadness, and a classification of Pisot-Vijayaraghavan polynomials.
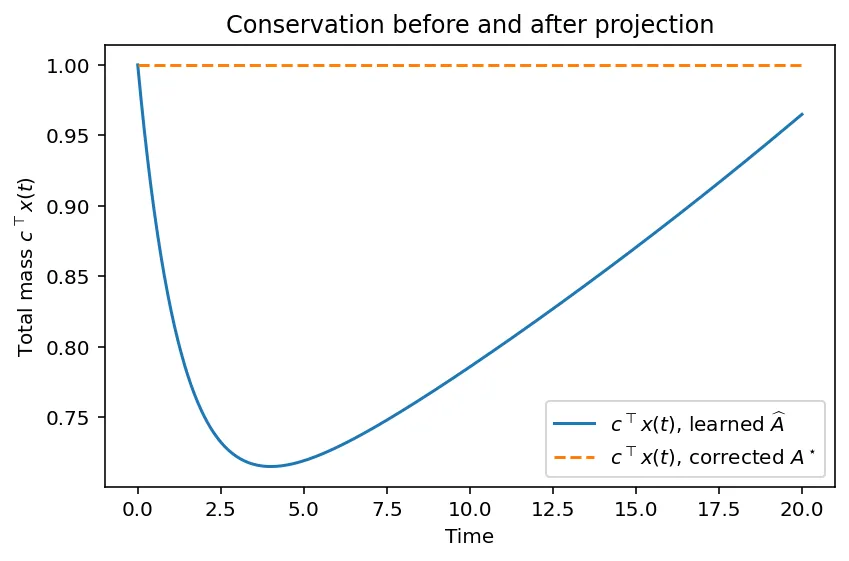
We consider the problem of restoring linear conservation laws in data-driven linear dynamical models. Given a learned operator $\widehat{A}$ and a full-rank constraint matrix $C$ encoding one or more invariants, we show that the matrix closest to $\widehat{A}$ in the Frobenius norm and satisfying $C^\top A = 0$ is the orthogonal projection $A^\star = \widehat{A} - C(C^\top C)^{-1}C^\top \widehat{A}$. This correction is uniquely defined, low rank and fully determined by the violation $C^\top \widehat{A}$. In the single-invariant case it reduces to a rank-one update. We prove that $A^\star$ enforces exact conservation while minimally perturbing the dynamics, and we verify these properties numerically on a Markov-type example. The projection provides an elementary and general mechanism for embedding exact invariants into any learned linear model.
 2512.19628
2512.19628In this article, we study a class of invariant measures generated by a random homogeneous self-similar iterated function system. Unlike the deterministic setting, the random quantization problem requires controlling distortion errors across non-uniform scales. For $r>0$, under a suitable separation condition, we precisely determine the almost sure quantization dimension $κ_r$ of this class, by utilizing the ergodic theory of the shift map on the symbolic space. By imposing an additional separation condition, we establish almost sure positivity of the $κ_r$-dimensional lower quantization coefficient. Furthermore, without assuming any separation condition, we provide a sufficient condition that guarantees almost sure finiteness of the $κ_r$-dimensional upper quantization coefficient. We also include some illustrative examples.
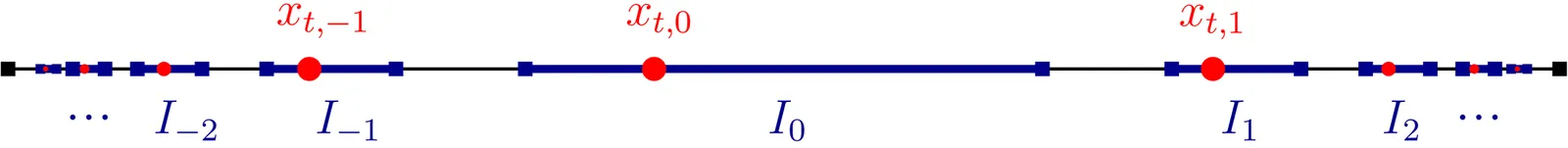
We show that two-dimensional billiard systems are Turing complete by encoding their dynamics within the framework of Topological Kleene Field Theory. Billiards serve as idealized models of particle motion with elastic reflections and arise naturally as limits of smooth Hamiltonian systems under steep confining potentials. Our results establish the existence of undecidable trajectories in physically natural billiard-type models, including billiard-type models arising in hard-sphere gases and in collision-chain limits of celestial mechanics.
 2512.18861
2512.18861We study the dynamical properties of a Hopf algebra Markov chain with state space the binary rooted forests with labelled leaves. This Markovian dynamical system describes the core computational process of structure formation and transformation in syntax via the Merge operation, according to Chomsky's Minimalism model of generative linguistics. The dynamics decomposes into an ergodic dynamical system with uniform stationary distribution, given by the action of Internal Merge, while the contributions of External Merge and (a minimal form of) Sideward Merge reduce to a simpler Markov chain with state space the set of partitions and with combinatorial weights. The Sideward Merge part of the dynamics prevents convergence to fully formed connected structures (trees), unless the different forms of Merge are weighted by a cost function, as predicted by linguistic theory. Results on the asymptotic behavior of the Perron-Frobenius eigenvalue and eigenvector in this weighted case, obtained in terms of an associated Perron-Frobenius problem in the tropical semiring, show that the usual cost functions (Minimal Search and Resource Restrictions) proposed in the linguistic literature do not suffice to obtain convergence to the tree structures, while an additional optimization property based on the Shannon entropy achieves the expected result for the dynamics. We also comment on the introduction of continuous parameters related to semantic embedding and other computational models, and also on some filtering of the dynamics by coloring rules that model the linguistic filtering by theta roles and phase structure, and on parametric variation and the process of parameter setting in Externalization.
 2512.18278
2512.18278In this paper, we derive several criteria for (weak) synchronization by noise without the global swift transitivity property. Our sufficient conditions for (weak) synchronization are necessary and can be applied to scenarios involving degenerate or non-Gaussian noise. These results partially answer the open question posed by Flandoli et al. (Probab Theory Relat Fields 168:511-556, 2017). As an application, we prove that the weak attractor for stochastic Lorenz 63 systems driven by degenerate noise consists of a single random point provided the noise intensity is small, and there is no weak synchronization if the noise intensity is large. This indicates that a bifurcation occurs in relation to the intensity of the noise.
We prove a first inverse theorem for Gowers norms on all finite abelian groups that uses only nilmanifolds (rather than possibly more general nilspaces). This makes progress toward confirming the Jamneshan--Tao conjecture. The correlating function in our theorem is a projected nilsequence, obtained as the fiber-wise average of a nilsequence defined on a boundedly-larger abelian group extending the original abelian group. This result is tight in the following sense: we prove also that $k$-step projected nilsequences of bounded complexity are genuine obstructions to having small Gowers $U^{k+1}$-norm. This inverse theorem relies on a new result concerning compact finite-rank (CFR) nilspaces, which is the main contribution in this paper: every $k$-step CFR nilspace is a factor of a $k$-step nilmanifold. This new connection between the classical theory of nilmanifolds and the more recent theory of nilspaces has applications beyond arithmetic combinatorics. We illustrate this with an application in topological dynamics, by proving the following result making progress on a question of Jamneshan, Shalom and Tao: every minimal $\mathbb{Z}^ω$-system of order $k$ is a factor of an inverse limit of $\mathbb{Z}^ω$-polynomial orbit systems of order $k$, these being natural generalizations of nilsystems alternative to translational systems.
We analyze a generalization of the self-affine carpets of Bedford and McMullen where the defining iterated function system includes coordinate reflections. We show that the Hausdorff dimension is invariant under such reflections. The upper bound follows from the standard covering argument using approximate squares, while the lower bound is established by constructing a dimension-maximizing Bernoulli measure and applying the Ledrappier-Young formula. The key to the proof is the observation that the fiber entropies determining the dimension are invariant under the action of the reflection group.
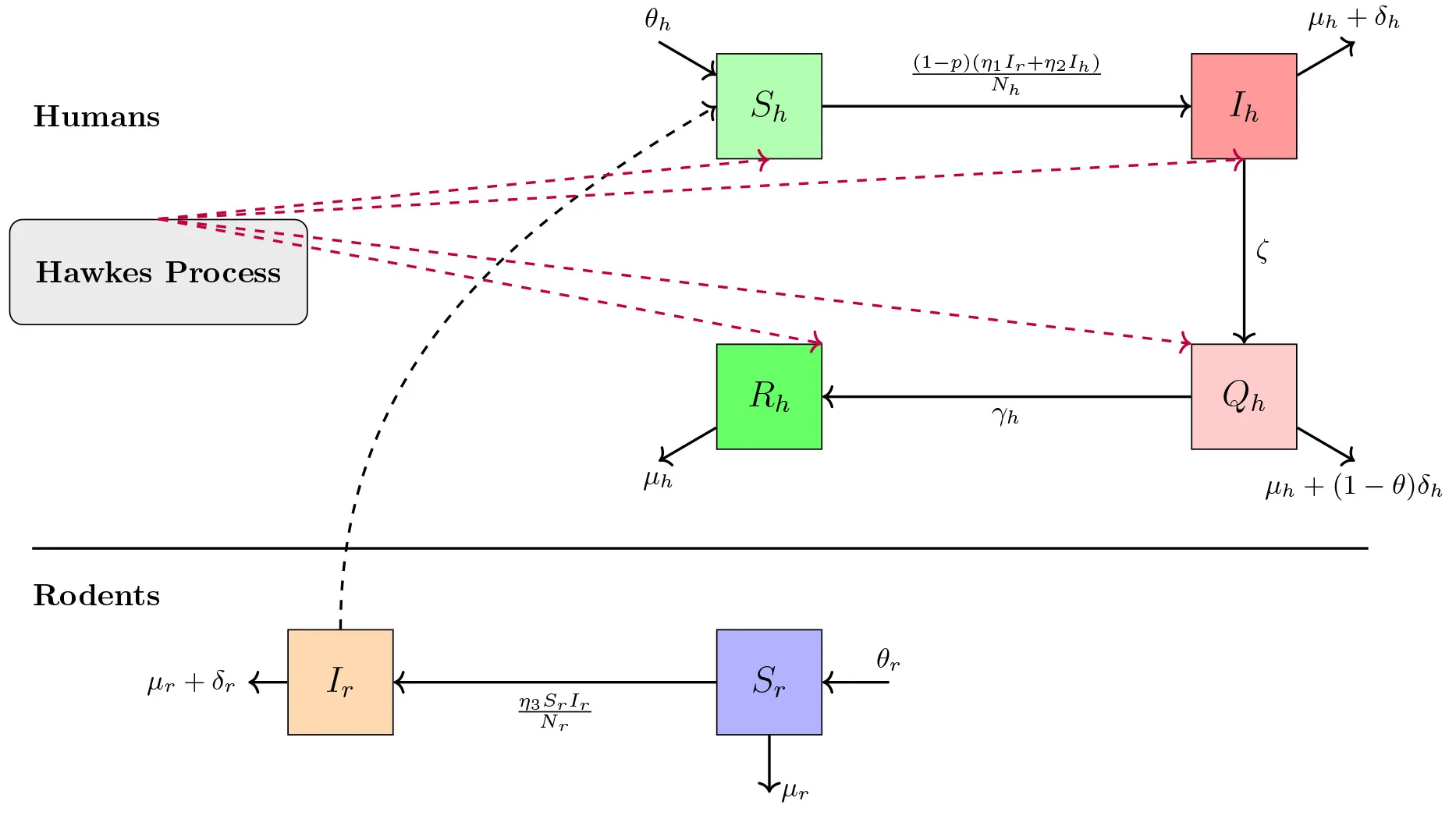
We develop a stochastic human-rodent compartment model for Mpox transmission that combines diffusion noise with Hawkes self-exciting jumps in the human infection dynamics. Including Hawkes processes allows, for instance, to model the short but significant spikes in transmission happening after crowded events. For the coupled human-rodent system, we prove global existence, uniqueness and positivity of solutions, derive a basic reproduction number R_0 that guarantees almost sure extinction when R_0 < 1, and obtain explicit persistence-in-the-mean conditions for both infected rodents and humans, which define persistence thresholds for the joint dynamics. Numerical experiments show how clustered human transmission events, environmental variability and control measures shift these thresholds and shape the frequency and size of Mpox outbreaks.
 2512.14940
2512.14940In this note we unify the results of A.C. Lazer and P.O. Frederickson [3], A.C. Lazer [6], A.C. Lazer and D.E. Leach [7], J.M. Alonso and R. Ortega [1], and P. Korman and Y. Li [4] on periodic oscillations and unbounded solutions of nonlinear equations with linear part at resonance and periodic forcing. We give conditions for the existence and non-existence of periodic solutions, and obtain a rather detailed description of the dynamics for nonlinear oscillations at resonance, in case periodic solutions do not exist.