Classical Analysis and ODEs
Special functions, orthogonal polynomials, harmonic analysis, ODEs, differential relations, calculus of variations, approximations, expansions.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Special functions, orthogonal polynomials, harmonic analysis, ODEs, differential relations, calculus of variations, approximations, expansions.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
 2601.03987
2601.03987We define a nonlinear Fourier transform which maps sequences of contractive $n \times n$ matrices to $SU(2n)$-valued functions on the circle $\mathbb{T}$. We characterize the image of finitely supported sequences and square-summable sequences on the half-line, and construct an inverse for $SU(2n)$-valued functions whose diagonal $n \times n$ blocks are outer matrix functions. As an application, we relate this nonlinear Fourier transform with quantum signal processing over $U(2n)$ and multivariate quantum signal processing.
We study a family of fractional integral operators whose kernels satisfying an non-isotropic dilation have singularity on a coordinate subspace. A characterization is given for these operators bounded from the classical, atom decomposable $H^1$-Hardy space to $L^q$-spaces.
We construct a class of homogeneous Cantor-Moran measures with all contraction ratios being reciprocal of integers, and prove that they are pointwise absolutely normal. Our approach relies on methods developed by Davenport, Erd{ő}s, and LeVeque \cite{DEL1963} and properties of the order of integers in the multiplicative groups. The construction of these measures differs from the class of pointwise absolutely normal self-similar measures introduced by Hochman and Shmerkin \cite{Hochman2015}, in which dynamical approaches were used. As an application, for all gauge functions $\varphi(r)$ with $r/\varphi(r)\to 0$ as $r\to 0$, we obtain a set of uniqueness $K$ with ${\mathcal H}^{\varphi}(K)>0$. Moreover, we show that there exists a pointwise absolutely normal measure $ μ$ of dimension one fully supported on $K$. The result demonstrates that having a lot of absolutely normal numbers in a Cantor set, even with dimension one, cannot guarantee that it supports a measure with Fourier decay. It also shows that the ${\mathsf{DEL}}$ criterion being satisfied for all integers does not guarantee any Fourier decay nor the supporting set is a set of multiplicity.
 2601.02866
2601.02866We exhibit new biorthogonal sequences generated by index integrals of the squares of the modified Bessel functions and gamma functions. The composition orthogonality, involving differential operators is employed. Generalized Wilson polynomials are introduced. Some properties are investigated.
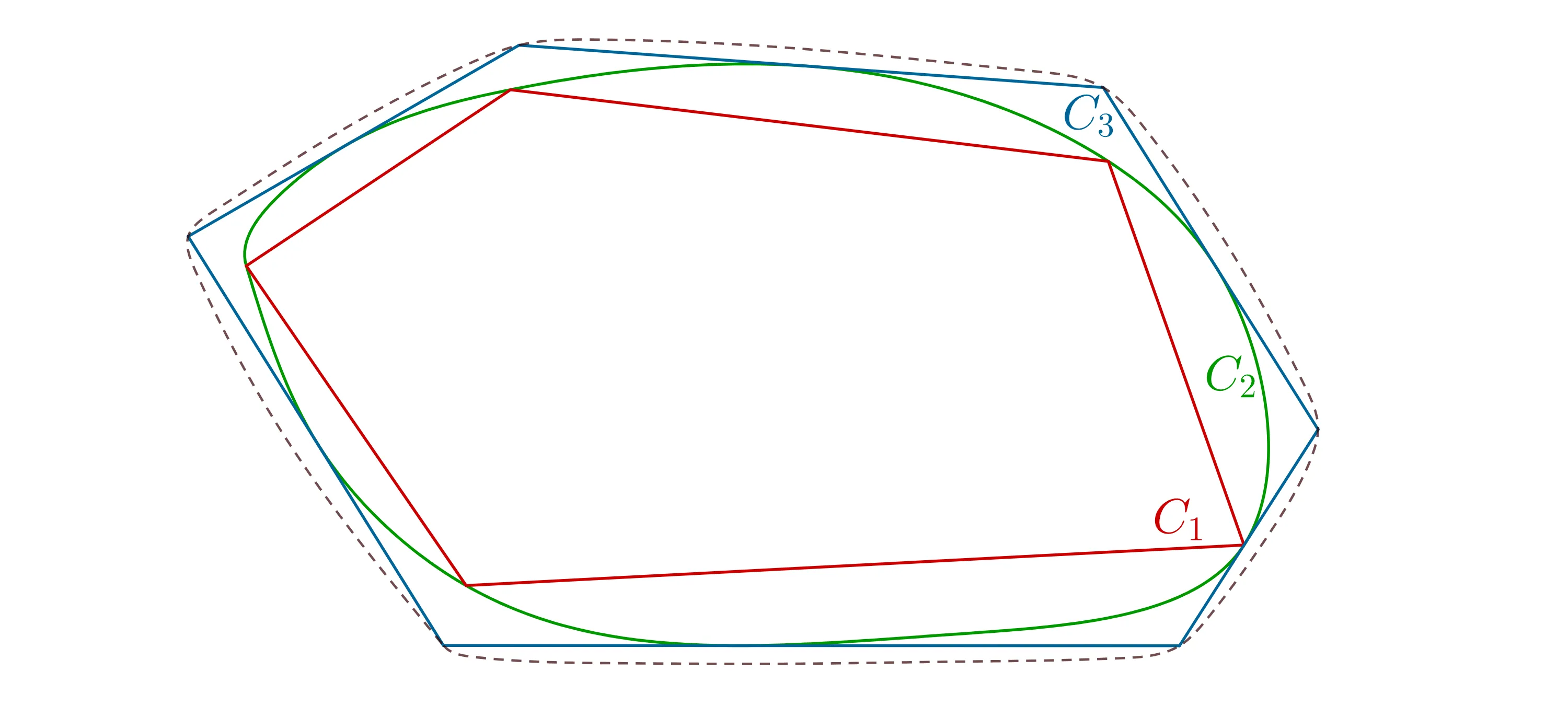
Let $C\subset\mathbb{R}^2$ be a convex body, and let $\mathcal{P}\subset[0,1)^2$ be a set of $N$ points. The discrepancy of $\mathcal{P}$ with respect to $C$ is defined as \begin{equation*} \mathcal{D}(\mathcal{P},\, C)=\sum_{\mathbf{p}\in\mathcal{P}}\sum_{\mathbf{n}\in\mathbb{Z}^2}\mathds{1}_C(\mathbf{p}+\mathbf{n})-N|C|. \end{equation*} A standard approach for estimating how a point distribution deviates from uniformity is to average the latter quantity over a family of sets; in particular, when considering quadratic averages over translations and dilations, one obtains \begin{equation*} \mathcal{D}_2(\mathcal{P},\, C)=\int_{0}^{1}\int_{[0,1)^2}\left|\mathcal{D}( \mathcal{P},\,\boldsymbolτ+δC)\right|^2\,{\rm d}\boldsymbolτ\,{\rm d} δ. \end{equation*} This paper concerns the behaviour of optimal \textit{homothetic quadratic discrepancy} \begin{equation*} \inf_{\# \mathcal{P}=N} \mathcal{D}_2(\mathcal{P},\, C)\quad\text{as}\quad N\to+\infty. \end{equation*} Beck and Chen \cite{MR1489133} showed that the optimal \textit{h.q.d.} of convex polygons has an order of growth of $\log N$. More recently, Brandolini and Travaglini \cite{MR4358540} showed that the optimal \textit{h.q.d.} of planar convex bodies has an order of growth of $N^{1/2}$ if their boundary is $\mathcal{C}^2$, and of $N^{2/5}$ if their boundary is only piecewise-$\mathcal{C}^2$ and not polygonal. We show that, in general, no order of growth is required. First, by an implicit geometric construction, we show that one can obtain prescribed oscillations from a logarithmic order of $\log N$ to polynomial orders of $N^{2/5}$ and $N^{1/2}$, and vice versa. Secondly, by using Fourier-analytic methods, we show that prescribed polynomial-order oscillations in the range $N^α$ with $α\in(2/5,1/2)$ are achievable.
 2601.01880
2601.01880We investigate the $L^p$ mapping properties of maximal functions associated with analytic hypersurfaces in $\mathbb R^d$, with a particular emphasis on the role of transversality. Around points that are not transversal, we show that the associated maximal function is bounded on $L^p(\mathbb R^d)$ for all $p>2$, regardless of the decay of the Fourier transform of surface measures. In contrast, away from non-transversal points, we prove that $L^p$ bounds for the maximal operator imply that the Fourier transform of the surface measure decays at rate $1/q$ for $q>p$. Combining these two regimes, we demonstrate that the conjecture of Stein and Iosevich-Sawyer on maximal functions could be re-formulated, in the analytic setting, by restricting attention to transversal points. Moreover, our result completely settles the refined form of the conjecture for certain cases.
 2601.01821
2601.01821This paper investigates the stability of wavelet frames within anisotropic function spaces. By replacing classical integral estimates with a matrix algebra approach, we establish the boundedness of frame operators and derive optimal dual wavelets via variational principles. Our analysis reveals fundamental geometric obstructions, identified here as an anisotropic Balian-Low phenomenon, which preclude the existence of tight frames for isotropic generators in high-shear regimes. Furthermore, we apply these results to determine sharp constants for Sobolev embeddings, explicitly quantifying the impact of dilation geometry on analytic stability.
 2601.01203
2601.01203We show that for the standard sinusoidal Winfree model, a coupling strength exceeding twice the maximal magnitude of the intrinsic frequencies guarantees the convergence of the system for Lebesgue almost every initial data. This is proven by first showing, via an order parameter bootstrapping argument, that the pathwise critical coupling strength is upper bounded by a function of the order parameter, and then showing by a volumetric argument that for Lebesgue almost every data the order parameter cannot stay below and be bounded away from 1 for all time; this is a Winfree model counterpart of the analysis of Ha and the author (2020) performed for the Kuramoto model. Using concentration of measure and the aforementioned volumetric argument, we show that, except possibly on a set of very small measure, oscillator death is observed in finite time; this rigorously demonstrates the existence of the oscillator death regime numerically observed by Ariaratnam and Strogatz (2001). These results are robust under many other choices of interaction functions often considered for the Winfree model. We demonstrate that the asymptotic dynamics described in this paper are sharp by analyzing the equilibria of the Winfree model, and we bound the total number of equilibria using a polynomial description. The sequel to this paper will deal with the Winfree model on higher-dimensional manifolds, such as the Euclidean spheres and the unitary groups.
 2601.01182
2601.01182The paper presents new and known results on estimates of important linear and nonlinear approximation characteristics of generalized Wiener classes of functions of several variables in different metrics.
 2601.01032
2601.01032We study optimal multiple weight assumptions in the weighted theory of multilinear Fourier multipliers and multilinear pseudo-differential operators. For multilinear Fourier multipliers, we revisit the weighted Hörmander-type theorem of Li and Sun, as a multilinear version of Kurtz and Wheeden, and show that their multiple weight condition is sharp. This provides the sharp necessary condition in the multilinear setting and simultaneously improves the classical linear necessity established by Kurtz and Wheeden. In the pseudo-differential setting, we consider recent weighted estimates of the authors for symbols in the multilinear Hörmander class and prove that their multiple weight hypothesis is also best possible. As a corollary, we can obtain the optimality of sharp maximal function estimates for multilinear pseudo-differential operators in the papers of the authors which originated from the results of Chanillo and Torchinsky.
 2601.00721
2601.00721This paper focuses on symbolic integration of differential forms, with a particular emphasis on historical and modern developments, from Abel's addition theorems for Abelian integrals to Zeilberger's creative telescoping for parameterized integrals. It explores closed rational $p$-forms and provides algorithmic approaches for their integration, extending classical results like Hermite reduction and Liouville's theorem. The integration of closed differential forms with parameters is further examined through telescopers, offering a unified framework for handling both algebraic and transcendental cases.
 2601.00201
2601.00201We establish characterization of $H^1$ Sobolev spaces by certain square functions, improving previous results.
 2601.00902
2601.00902We study the fractional Hardy inequality on the integer lattice. We prove null-criticality of the Hardy weight and hence optimality of the constant. More specifically, we present a family of Hardy weights with respect to a parameter and show that below a certain threshold the Hardy weight is positive critical while above the threshold it is subcritical. In particular, the Hardy weight at the threshold is optimal in the sense that any larger weight would fail to be a Hardy weight and the Hardy inequality does not allow for a minimizer. A crucial ingredient in our proof is an asymptotic expansion of the fractional discrete Riesz kernel.
 2512.24990
2512.24990We give a proof of Fourier extension conjecture on the paraboloid in all dimensions bigger than 2 that begins with a decomposition suggested in Sawyer [Saw8] of writing a smooth Alpert projection as a sum of pieces whose Fourier extensions are localized. This is then used in the case d=3 to establish the trilinear equivalence of the Fourier extension conjecture given in C. Rios and E. Sawyer [RiSa1] and [RiSa3]. A key aspect of the proof is that the trilinear equivalence only requires an averaging over grids, which converts a difficult exponential sum into an oscillatory integral with periodic amplitude, that is then used to prove the localization on the Fourier side. Finally, we extend this argument to all dimensions bigger than 2 using bilinear analogues of the smooth Alpert trilinear inequalities, which generalize those in Tao, Vargas and Vega [TaVaVe].
Motivated by the work of Cheng--Fang--Wang--Yu on the hypersingular Bergman projection, we develop a real-variable and dyadic framework for hypersingular operators in regimes where strong-type estimates fail at the critical line. The main new input is a hypersingular sparse domination principle combined with Bourgain's interpolation method, which provides a flexible mechanism to establish critical-line (and endpoint) estimates. In the unit disc setting with $1<t<3/2$, we obtain a full characterization of the $(p,q)$ mapping theory for the dyadic hypersingular maximal operator $\mathcal M_t^{\mathcal D}$, in particular including estimates on the critical line $1/q-1/p=2t-2$ and a weighted endpoint criterion in the radial setting. We also prove endpoint estimates for the hypersingular Bergman projection \[ K_{2t}f(z)=\int_{\mathbb D}\frac{f(w)}{(1-z\overline w)^{2t}}\,dA(w), \] including a restricted weak-type bound at $(p,q)=\bigl(\tfrac{1}{3-2t},1\bigr)$. Finally, we introduce a class of hypersingular cousin of sparse operators in $\mathbb R^n$ associated with \emph{graded} sparse families, quantified by the sparseness $η$ and a new structural parameter (the \emph{degree}) $K_{\mathcal S}$, and we characterize the corresponding strong/weak/restricted weak-type regimes in terms of $(n,t,η,K_{\mathcal S})$. Our real-variable perspective addresses to an inquiry raised by Cheng--Fang--Wang--Yu on developing effective real-analytic tools in the hypersingular regime for $K_{2t}$, and it also provides a new route toward the critical-line analysis of Forelli--Rudin type operators and related hypersingular operators in both real and complex settings.
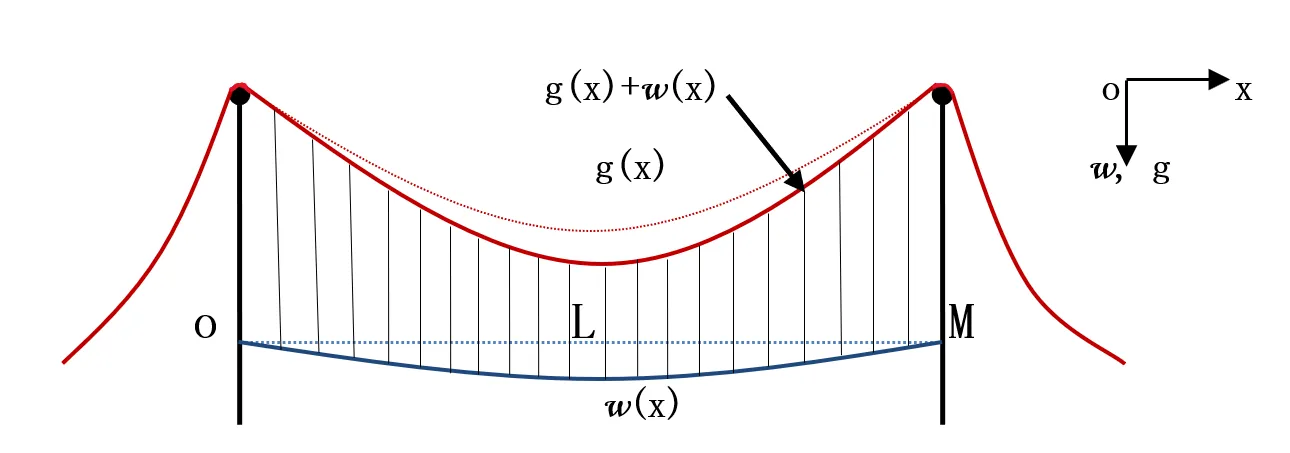
The classical Melan equation modeling suspension bridges is considered. We first study the explicit expression and the uniform positivity of the analytical solution for the simplified ``less stiff'' model, based on which we develop a monotone iterative technique of lower and upper solutions to investigate the existence, uniqueness and approximability of the solution for the original classical Melan equation.The applicability and the efficiency of the monotone iterative technique for engineering design calculations are discussed by verifying some examples of actual bridges. Some open problems are suggested.
 2512.24348
2512.24348We explicitly construct a heat kernel as a Neumann series for certain function spaces, such as $L^{1}$, $L^{2}$, and Hilbert spaces, associated to a locally compact Hausdorff space $\mathfrak{X}$ with Borel $σ$-algebra $\mathcal{B}$, and endowed with additional measure-theoretic data. Our approach is an adaptation of classical work due to Minakshishundaram and Pleijel, and it requires as input a parametrix or small time approximation to the heat kernel. The methodology developed in this article applies to yield new instances of heat kernel constructions, including normalized Laplacians on finite and infinite graphs as well as Hilbert spaces with reproducing kernels.
 2512.24283
2512.24283The aim of this note is to present the simple observation that a slight refinement of the Contraction Mapping Principle allows one to recover the precise convergence rate in the Picard-Lindelöf Theorem.
 2512.23949
2512.23949A theorem of Hoischen states that given a positive continuous function $\varepsilon:\mathbb{R}\to\mathbb{R}$, an integer $n\geq 0$, and a closed discrete set $E\subseteq\mathbb{R}$, any $C^n$ function $f:\mathbb{R}\to\mathbb{R}$ can be approximated by an entire function $g$ so that for $k=0,\dots,n$, and $x\in\mathbb{R}$, $|D^{k}g(x)-D^{k}f(x)|<\varepsilon(x)$, and if $x\in E$ then $D^{k}g(x)=D^{k}f(x)$. The approximating function $g$ is entire and hence piecewise monotone. Building on earlier work, for $n\leq 3$, we determine conditions under which when $f$ is piecewise monotone we can choose $g$ to be comonotone with $f$ (increasing and decreasing on the same intervals), and under which the derivatives of $g$ can be taken to be comonotone with the corresponding derivatives of $f$ if the latter are piecewise monotone. The proof for $n\leq 3$ establishes the theorem for all $n$, assuming a conjecture (shown in previous work with Haris and Madhavendra to hold for $n\leq 3$) regarding the set of $2(n+1)$-tuples $(f(0),Df(0),\dots,D^nf(0),f(1),Df(1),\dots,D^nf(1))$ of the values at the endpoints of the derivatives of a $C^n$ function $f$ on $[0,1]$ for which $D^nf$ is increasing and not constant.
 2512.23876
2512.23876We study the existence of positive eigenvalues with associated nonnegative mild eigenfunctions for a class of abstract initial value problems in Banach spaces with functional, possibly nonlocal, initial conditions. The framework includes periodic, multipoint, and integral average conditions. Our approach relies on nonlinear analysis, topological methods, and the theory of strongly continuous semigroups, yielding results applicable to a wide range of models. As an illustration, we apply the abstract theory to a reaction-diffusion equation with a nonlocal initial condition arising from a heat flow problem.