Analysis of PDEs
Existence and uniqueness, boundary conditions, linear and nonlinear operators, stability, soliton theory, integrable PDEs.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Existence and uniqueness, boundary conditions, linear and nonlinear operators, stability, soliton theory, integrable PDEs.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
 2601.04173
2601.04173We present results on the trace regularity of the stress vector on the boundary of an elastic solid satisfying the time-dependent, displacement-traction problem for the Navier equations of linear elasticity in a bounded domain of $\mathbb{R}^3$. Specifically, the solid's displacement is subject to Dirichlet- and Neumann-type conditions on different portions of its boundary and possibly non-zero body forces and initial data. Our regularity results are reminiscent of the so-called "hidden trace regularity" results for solutions to the scalar wave equation obtained in [12].
We prove energy, Morawetz and $r^p$-weighted estimates for solutions to the Teukolsky equation set on a slowly-rotating Kerr-de Sitter background. The main feature of our estimates is their uniformity with respect to the cosmological constant $Λ>0$ (thus allowed to tend to $0$), while they hold on the whole domain of outer communications, extending up to $r\sim Λ^{-\frac{1}{2}}$. As an application of our result, we recover well-known corresponding estimates for solutions to Teukolsky on a slowly-rotating Kerr background in the limit $Λ\to 0$.
 2601.04105
2601.04105Conformable derivatives provide a fractional-looking calculus that remains local and admits a simple representation through classical derivatives with explicit weights. In this paper we develop a systematic operator-theoretic perspective showing that conformable time evolution is, in essence, a classical $C_0$-semigroup observed through a nonlinear clock. We introduce the conformable time map $ψ(t)=t^α/α$ and prove that every $C_0$--$α$-semigroup $\{T_α(t)\}_{t\ge0}$ can be written as $T_α(t)=T(ψ(t))$ for a uniquely determined classical $C_0$-semigroup $\{T(s)\}_{s\ge0}$, with generators agreeing on a common domain. This correspondence yields a one-to-one transfer of mild solutions and shows that orbit-based linear dynamics are invariant under conformable reparametrization. In particular, $α$-hypercyclicity and $α$--chaos coincide with the usual notions for the associated classical semigroup. As a consequence, we obtain a conformable version of the Desch--Schappacher--Webb spectral criterion for chaos. We also place the analysis in the natural functional setting provided by conformable Lebesgue spaces $L^{p,α}$ and their explicit isometric identification with standard $L^p$ spaces, which allows one to transport estimates and spectral arguments without loss. The results clarify which dynamical phenomena in conformable models are genuinely new and which are inherited from classical semigroup dynamics via a nonlinear change of time.
 2601.04088
2601.04088We propose a novel approach for studying small-time asymptotics of the fractional heat content of $C^2$ non-characteristic domains in Carnot groups. Denoting the sub-Laplacian operator by $\mathcal{L}$, the fractional heat content of a bounded domain $Ω$ is defined as $Q^{(α)}_Ω(t)=\int_Ω u_α(t,x)dx$, where $u_α$ is the solution to the heat equation corresponding to the fractional sub-Laplacian $\mathcal{L}_α:=\mathcal{L}^{α/2}$ with Dirichlet boundary condition on $Ω$. We prove that for $1\leα\le 2$, there exists explict rate function $μ_α: (0,\infty)\to (0,\infty)$ such that \[ \lim_{t\to 0}\frac{|Ω|-Q^{(α)}_Ω(t)}{μ_α(t)}=|\partialΩ|_H, \] where $|\partialΩ|_H$ is the horizontal perimeter of $Ω$. Moreover, the rate function $μ_α$ coincides with the same for the Euclidean case.
 2601.04018
2601.04018We consider the three-dimensional relativistic Vlasov-Maxwell-Boltzmann system, where the speed of light $c$ is an arbitrary constant no less than 1, and we establish global existence and nonlinear stability of the vacuum for small initial data, with bounds that are uniform in $c$. The analysis is based on the vector field method combined with the Glassey-Strauss decomposition of the electromagnetic field, and does not require any compact support assumption on the initial data. A key ingredient of the proof is the derivation of a chain rule for the relativistic Boltzmann collision operator that is compatible with the commutation properties of the vector fields. These tools allow us to control the coupled kinetic and electromagnetic equations and to obtain global stability near vacuum.
 2601.03968
2601.03968The paper is concerned with a nonlinear system of two coupled fractional Schrödinger equations with both attractive intraspecies and attractive interspecies interactions in $\mathbb{R}$. By analyzing an associated $L^2$-constrained minimization problem, the uniqueness of solutions to this system is proved via the implicit function theorem. Under a certain type of trapping potential, by establishing some delicate energy estimates, we present a detailed analysis on the concentration behavior of the solutions as the total strength of intraspecies and interspecies interactions tends to a critical value, where each component of the solutions blows up and concentrates at a flattest common minimum point of the associated trapping potentials. An optimal blow-up rate of solutions to the system is also given.
 2601.03865
2601.03865In this paper, we investigate the Fučík spectrum $Σ_L$ associated with the logarithmic Laplacian. This spectrum is defined as the set of all pairs $(α,β) \in \mathbb{R}^2$ for which the problem \[ L_Δu = αu^+-βu^- ~\text{in} ~ Ω\quad \text{and} \quad u=0 ~\text{in} ~\mathbb{R}^N\setminus Ω\] admits a nontrivial solution $u$. Here, $Ω\subset \mathbb{R}^N$ is a bounded domain with $C^{1,1}$ boundary, $u^\pm = \max\{\pm u,0\}$, and $u = u^+ - u^-$. We show that the lines $λ_1^L \times \mathbb{R}$ and $\mathbb{R} \times λ_1^L$, where $λ_1^L$ denotes the first eigenvalue of $L_Δ$, lies in the spectrum $Σ_L$ and are isolated within the spectrum. Furthermore, we establish the existence of the first nontrivial curve in $Σ_L$ and analyze its qualitative properties, including Lipschitz continuity, strict monotonicity, and asymptotic behavior. In addition, we obtain a variational characterization of the second eigenvalue of the logarithmic Laplacian and show that all eigenfunctions corresponding to eigenvalues $λ> λ_1^L$ are sign-changing. Finally, we address a nonresonance problem with respect to the Fučík spectrum $Σ_L$, employing variational methods and carefully overcoming the difficulties arising from the contrasting features of the first eigenvalue $λ_1^L$.
 2601.03833
2601.03833We establish the global existence of forward self-similar solutions to the two-dimensional incompressible Navier-Stokes equations for any divergence-free initial velocity $u_0$ that is homogeneous of degree $-1$ and locally Hölder continuous. This result requires no smallness assumption on the initial data. In sharp contrast to the three-dimensional case, where $(-1)$-homogeneous vector fields are locally square-integrable, the 2D problem is critical in the sense that the initial kinetic energy is locally infinite at the origin, and the initial vorticity fails to be locally integrable. Consequently, the classical local energy estimates are not available. To overcome this, we decompose the solution into a linear part solving the heat equation and a finite-energy perturbation part. By exploiting a kind of inherent cancellation relation between the linear part and the perturbation part, we can control interaction terms and establish the $H^1$-estimates for the perturbation part. Further investigating the corresponding Leray system in weighted Sobolev space, we can derive an optimal pointwise estimate. This gives the faster decay of the perturbation part at infinity and enables us to construct global-in-time self-similar solutions.
 2601.03755
2601.03755In the present work, we establish space Bounded Variation $(BV)$ regularity of the solution for a non-linear parabolic partial differential equations involving a linear drift term. We study the problem in a bounded domain with mixed Dirichlet-Neumann boundary conditions, a general non-linearity and reasonable assumptions on the data. Our results also cover, as a particular case, the linear transport equation in a bounded domain with an outward-pointing drift vector field on the boundary.
 2601.03742
2601.03742We study the large-population limit of interacting particle systems evolving on adaptive dynamical networks, motivated in particular by models of opinion dynamics. In such systems, agents interact through weighted graphs whose structure evolves over time in a coupled manner with the agents' states, leading to non-exchangeable dynamics. In the dense-graph regime, we show that the asymptotic behavior is described by a Vlasov-type equation posed on an extended phase space that includes both the agents' states and identities and the evolving interaction weights. We establish this limiting equation through two complementary approaches. The first follows the mean-field methodology in the spirit of Sznitman [28]. In this framework, we impose the additional assumption that the weight dynamics is independent of one of the agent's states, an assumption that remains well motivated from a modeling perspective and allows for a direct derivation of the mean-field limit. The second approach is based on the graph limit framework and is formulated in a deterministic setting. This perspective makes it possible to remove the aforementioned restriction on the weight dynamics and to handle more general interaction structures. Our analysis includes wellposedness and stability results for the limiting Vlasov-type equation, as well as quantitative estimates ensuring the propagation of independence. We further clarify the relationship between the continuum (graph limit) formulation and the mean-field limit, thereby providing a unified description of the asymptotic dynamics of interacting particle systems on adaptive dynamical networks.
 2601.03739
2601.03739In this paper, we first investigate quasi-entropy solutions to scalar conservation laws in several space dimensions. In this setting, we introduce a suitable Lagrangian representation for such solutions. Next, we prove that, in one space dimension and for fluxes $f$ satisfying a general non-degeneracy condition, the entropy dissipation measures of quasi-entropy solutions are concentrated on a 1-rectifiable set. The same result is obtained for the isentropic Euler system with $γ= 3$, for which we also slightly improve the available fractional regularity by exploiting the sign of the kinetic measures.
 2601.03721
2601.03721In this paper we establish gradient estimates for positive solutions to the nonlinear elliptic equation $$Δ_{V}u^{m}+μ(x)u+p(x)u^α=0 , \quad m>1$$on any smooth metric measure space whose $k$-Bakry-Émery curvature is bounded from below by $-(k-1)K$ with $K \geq 0$. Additionally, we obtain related Liouville theorems and Harnack inequalities. We partially extend conclusions of Wang, when $V=0$, $μ=0$ the equation becomes $Δu^{m}+p(x)u^α=0$. And $V=f$, $μ=c, p=0 $, the equation becomes $Δ_{f}u^{m}+cu=0 $.
 2601.03576
2601.03576We consider the Cauchy problem for the hyperbolic-elliptic Ishimori system with general decoupling constant $κ\in \mathbb{R}$ and prove global well-posedness in the critical Sobolev space. The proof relies primarily on new bilinear estimates, which are established via a novel div-curl lemma first introduced by the second author in \cite{zhou_1+2dimensional_2022}. Our approach combines the caloric gauge technique with $U^p$-$V^p$ type Strichartz estimates to handle the hyperbolic structure of the equation. The results extend previous work on the integrable case $κ= 1$ to general $κ$ and provide a unified framework that also applies to hyperbolic and elliptic Schrödinger maps in dimensions $d \ge 2$.
Existence, uniqueness and classification is established for plane waves supported by an irreversible reaction which is a smooth function of local reactant and product concentrations (or prey and predator populations). Rudimentary analytic techniques are used to guarantee a unique plane wave at every wavespeed $V>V_*$ above some threshold. The result readily extends to cutoff reactions, which are zero below some threshold product concentration. These results are not novel, but the method of proof is.
 2601.03188
2601.03188Here we explore, in a series of articles, semiclassical quasimodes u(h,b), approximative solutions P(h)u(h,b)\sim 0, depending on $0<h<1$, and on b, the subprincipal symbol. We study a pseudodifferential operator with transversal intersections of bicharacteristics, where the principal symbol has double multiplicity, $p=dp=0$, in a small neigborhood $Ω$. Because of this fact, we instead study the subprincipal symbol b, and we can conclude that we get transport equations depending on b where sign changes for the imaginary part of b give approximative solutions with small support. These modes are used to estimate spectral instability, or the pseudospectrum. We also investigate the possibility that we can factorize the model operator as $P(h)=h^2P_1P_2,$ in this way actually annihilating the subprincipal symbol, thus there is no condition for the imaginary part of b. In a follow-up article, we examine different cases for more complex operators with tangential intersections of bicharacteristics, thereby generalizing the findings here.
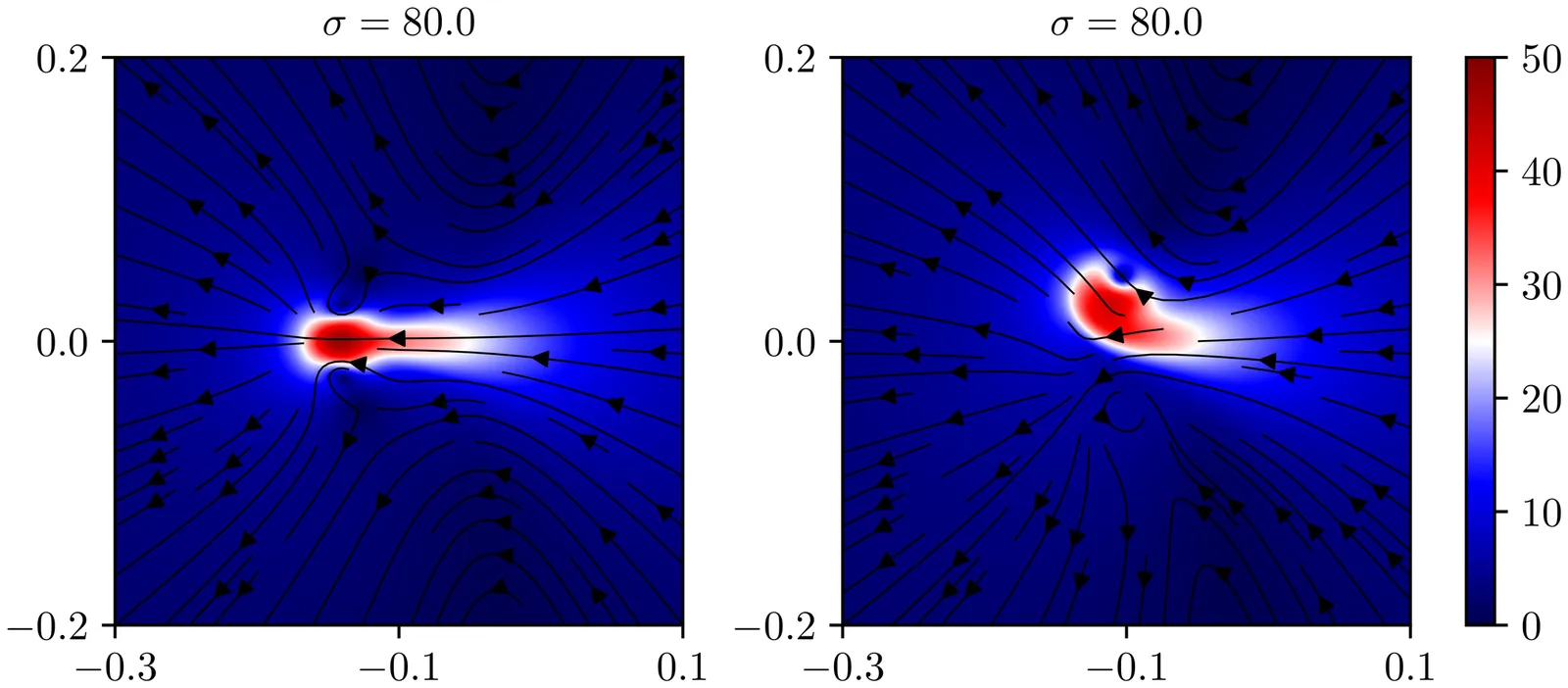
We construct self-similar solutions to the 2D Navier--Stokes equations evolving from arbitrarily large $-1$--homogeneous initial data and present numerical evidence for their non-uniqueness.
This paper deals with the interactions of waves governed by a non-linear dispersive Boussinesq type system with the vertical displacement of a cylindrical floating structure in an axisymmetric without swirl situation. The Boussinesq regime is a good approximation of free surface Euler's equations when the non-linear parameter and the shallowness parameter are small. The vertical motion of the floating body is governed by the Newton equation. The full coupled wave-structure interaction problem under consideration is reduced to a boundary problem. The boundary condition satisfied by the discharge is given in terms of the vertical displacement of the floating cylinder. The latter is calculated using an ODE, which requires knowledge of the trace of the surface elevation and its second-time derivative. We use the dispersion in order to exhibit a hidden second order ODE on the trace of the surface elevation. This finally allows us to rewrite the waves-structure interaction problem as a system of non-local conservative PDEs plus bounded radial terms with a dispersive boundary layer, combined with an ODE at the boundary. This is what we call the Augmented formulation. Afterwards we showed that this formulation is well-posed with two different methods. Finally, we study the return to equilibrium situation in the linear regime. In particular, we improved previous results on the explicit time decay. We showed that the center mass of the floating body cannot converge to its equilibrium faster than $\mathcal{O}(t^{-1/2})$ in 2D without viscosity and faster than $\mathcal{O}(t^{-3/2})$ with viscosity.
 2601.03107
2601.03107We study the homogeneous Landau equation with Maxwell molecules and prove that the entropy production is non-increasing provided the directional temperatures are well-distributed and the solution admits a moment of order $\ell$, for some $\ell$ arbitrarily close to $2$. It implies that for an initial condition with finite moment of order $\ell$, the entropy production is guaranteed to be non-increasing after a certain time, that we explicitly compute. This is the first partial answer to a conjecture made by Henry P. McKean in 1966 on the sign of the time-derivatives of the entropy. We also obtain algebraic decay estimates for the entropy production for large time; as well as a short-time estimate without moment assumptions.
 2601.03095
2601.03095We show here that the quasilinear Kirchhoff-Pokhozhaev equation $$u_{tt}-\big(a\int_{\mathbb{R}^n} |\nabla u |^2 dx + b \big)^{-2} Δu = 0,$$ with $a\neq0$, admits conservation laws of all orders.
 2601.03078
2601.03078We consider Lipschitz solutions to the possibly highly degenerate elliptic equation $ {\rm div} G(\nabla u)=0$ in $B_1\subset\mathbb{R}^2 $, for any continuous strictly monotone vector field $G \colon \mathbb{R}^2 \to \mathbb{R}^2$. We show that $u$ is either $C^1$ at $0$, or any blowup limit $v(x)=\lim \frac{u(δx)-u(0)}δ $ along a sequence $δ\to 0$ satisfies $ \nabla v\in \mathcal{D}\cap \mathcal{S} \text{ a.e} $. Here, $ \mathcal{D}$ and $\mathcal{S}$ can be roughly interpreted as the sets where ellipticity degenerates from below and above, that is, the symmetric parts of $ \nabla G$ and $(\nabla G)^{-1}$ have a zero eigenvalue. This is a strong indication in favor of the expected continuity of $H(\nabla u)$ for any continuous $H$ vanishing on $\mathcal{D}\cap \mathcal{S}$. In contrast with previous results in the same spirit, we do not make any assumption on the structure of $G$ besides its continuity and strict monotony.