Digital Libraries
Covers all aspects of the digital library design and document and text creation.
Covers all aspects of the digital library design and document and text creation.

We introduce LongDA, a data analysis benchmark for evaluating LLM-based agents under documentation-intensive analytical workflows. In contrast to existing benchmarks that assume well-specified schemas and inputs, LongDA targets real-world settings in which navigating long documentation and complex data is the primary bottleneck. To this end, we manually curate raw data files, long and heterogeneous documentation, and expert-written publications from 17 publicly available U.S. national surveys, from which we extract 505 analytical queries grounded in real analytical practice. Solving these queries requires agents to first retrieve and integrate key information from multiple unstructured documents, before performing multi-step computations and writing executable code, which remains challenging for existing data analysis agents. To support the systematic evaluation under this setting, we develop LongTA, a tool-augmented agent framework that enables document access, retrieval, and code execution, and evaluate a range of proprietary and open-source models. Our experiments reveal substantial performance gaps even among state-of-the-art models, highlighting the challenges researchers should consider before applying LLM agents for decision support in real-world, high-stakes analytical settings.

The adoption of artificial intelligence in dermatology promises democratized access to healthcare, but model reliability depends on the quality and comprehensiveness of the data fueling these models. Despite rapid growth in publicly available dermatology images, the field lacks quantitative key performance indicators to measure whether new datasets expand clinical coverage or merely replicate what is already known. Here we present SkinMap, a multi-modal framework for the first comprehensive audit of the field's entire data basis. We unify the publicly available dermatology datasets into a single, queryable semantic atlas comprising more than 1.1 million images of skin conditions and quantify (i) informational novelty over time, (ii) dataset redundancy, and (iii) representation gaps across demographics and diagnoses. Despite exponential growth in dataset sizes, informational novelty across time has somewhat plateaued: Some clusters, such as common neoplasms on fair skin, are densely populated, while underrepresented skin types and many rare diseases remain unaddressed. We further identify structural gaps in coverage: Darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick V-VI) constitute only 5.8% of images and pediatric patients only 3.0%, while many rare diseases and phenotype combinations remain sparsely represented. SkinMap provides infrastructure to measure blind spots and steer strategic data acquisition toward undercovered regions of clinical space.
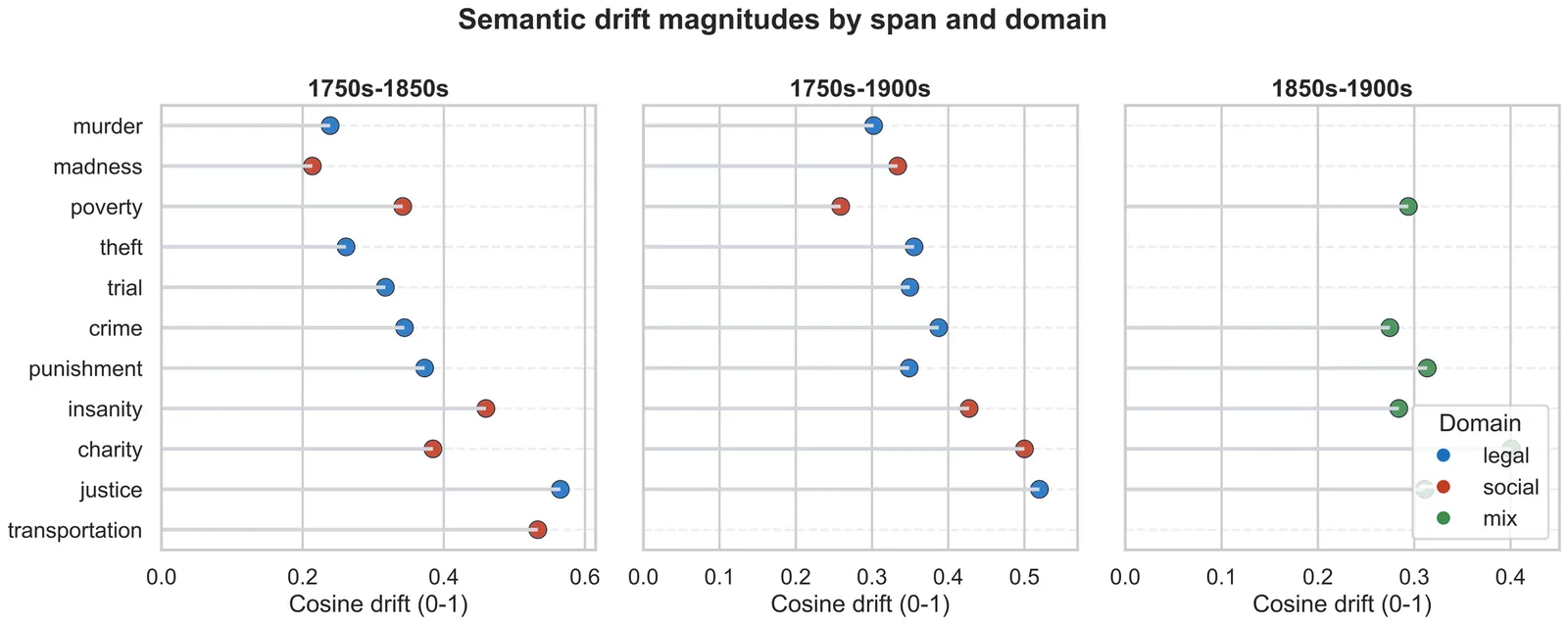
Digital-humanities work on semantic shift often alternates between handcrafted close readings and opaque embedding machinery. We present a reproducible expert-system style pipeline that quantifies and visualises lexical drift in the Old Bailey Corpus (1720--1913), coupling interpretable trajectories with legally meaningful axes. We bin proceedings by decade with dynamic merging for low-resource slices, train skip-gram embeddings, align spaces through orthogonal Procrustes, and measure both geometric displacement and neighborhood turnover. Three visual analytics outputs, which are drift magnitudes, semantic trajectories, and movement along a mercy-versus-retribution axis, expose how justice, crime, poverty, and insanity evolve with penal reforms, transportation debates, and Victorian moral politics. The pipeline is implemented as auditable scripts so results can be reproduced in other historical corpora.
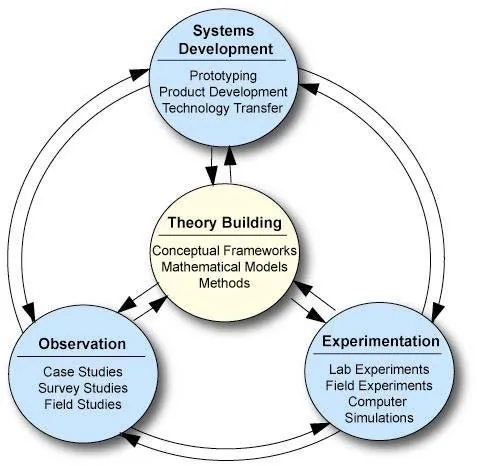
The unprecedented proliferation of digital data presents significant challenges in access, integration, and value creation across all data-intensive sectors. Valuable information is frequently encapsulated within disparate systems, unstructured documents, and heterogeneous formats, creating silos that impede efficient utilization and collaborative decision-making. This paper introduces the Intelligent Knowledge Mining Framework (IKMF), a comprehensive conceptual model designed to bridge the critical gap between dynamic AI-driven analysis and trustworthy long-term preservation. The framework proposes a dual-stream architecture: a horizontal Mining Process that systematically transforms raw data into semantically rich, machine-actionable knowledge, and a parallel Trustworthy Archiving Stream that ensures the integrity, provenance, and computational reproducibility of these assets. By defining a blueprint for this symbiotic relationship, the paper provides a foundational model for transforming static repositories into living ecosystems that facilitate the flow of actionable intelligence from producers to consumers. This paper outlines the motivation, problem statement, and key research questions guiding the research and development of the framework, presents the underlying scientific methodology, and details its conceptual design and modeling.
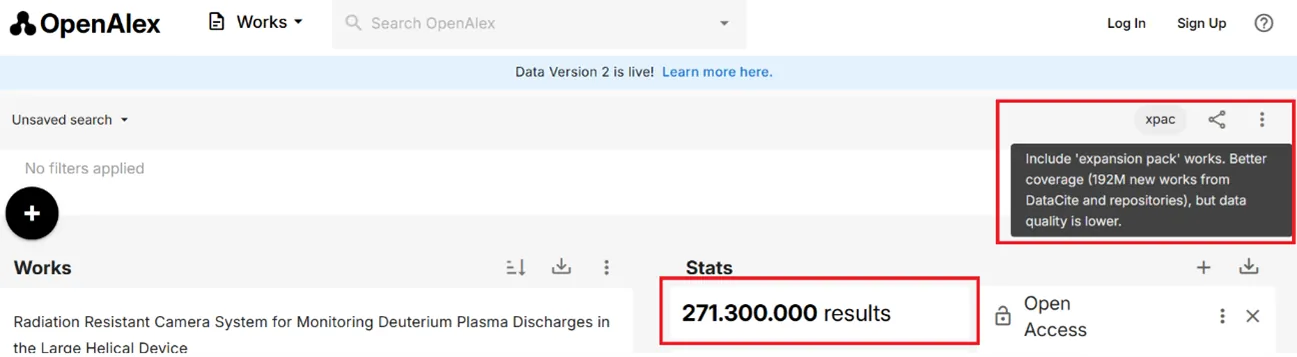
OpenAlex is an open bibliographic database that has been proposed as an alternative to commercial platforms in a context defined by the aim of transforming science evaluation systems into more transparent sources based on open data. This paper analyses its features, information sources, entities, advantages and limitations. The results reveal numerous records lacking abstracts, affiliations and references; deficiencies in identifying document types and languages; and issues with authority control and versioning. Although OpenAlex has been adopted in important initiatives and has yielded results comparable to those obtained with commercial databases, gaps in its metadata and a lack of consistency point to a need for intensive data cleaning, suggesting it should be used with caution. The study concludes by identifying three lines of action to improve data quality: increasing publishers' commitment to completing metadata in primary sources; creating coordination structures to channel the contributions of institutional users; and endowing the project with sufficient human resources and reliable procedures to address internal quality control tasks and user support requests.
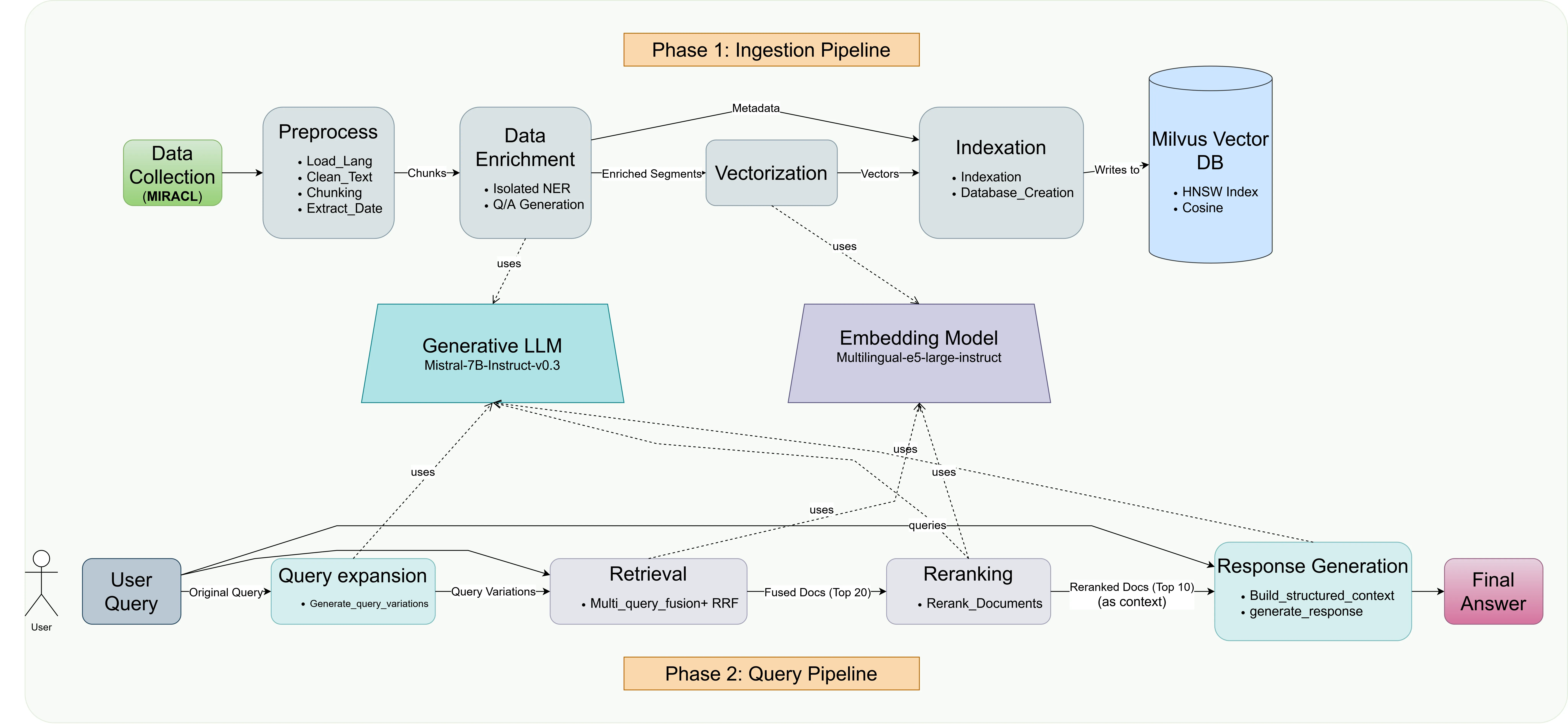
Large-scale digitization initiatives have unlocked massive collections of historical newspapers, yet effective computational access remains hindered by OCR corruption, multilingual orthographic variation, and temporal language drift. We develop and evaluate a multilingual Retrieval-Augmented Generation pipeline specifically designed for question answering on noisy historical documents. Our approach integrates: (i) semantic query expansion and multi-query fusion using Reciprocal Rank Fusion to improve retrieval robustness against vocabulary mismatch; (ii) a carefully engineered generation prompt that enforces strict grounding in retrieved evidence and explicit abstention when evidence is insufficient; and (iii) a modular architecture enabling systematic component evaluation. We conduct comprehensive ablation studies on Named Entity Recognition and embedding model selection, demonstrating the importance of syntactic coherence in entity extraction and balanced performance-efficiency trade-offs in dense retrieval. Our end-to-end evaluation framework shows that the pipeline generates faithful answers for well-supported queries while correctly abstaining from unanswerable questions. The hybrid retrieval strategy improves recall stability, particularly benefiting from RRF's ability to smooth performance variance across query formulations. We release our code and configurations at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/RAGs-C5AE/, providing a reproducible foundation for robust historical document question answering.
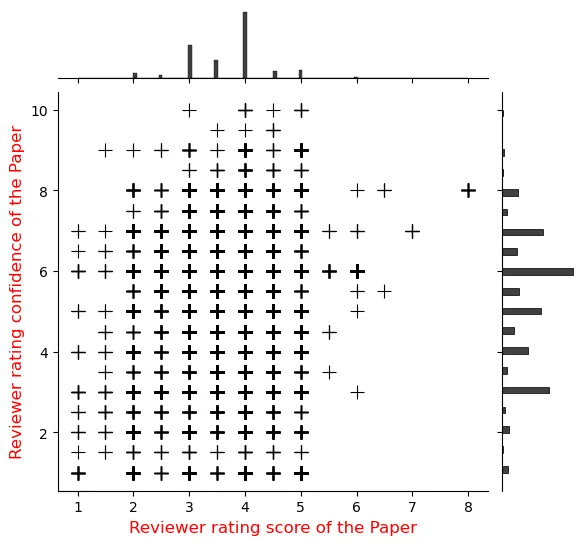
Large Language Models are versatile general-task solvers, and their capabilities can truly assist people with scholarly peer review as \textit{pre-review} agents, if not as fully autonomous \textit{peer-review} agents. While incredibly beneficial, automating academic peer-review, as a concept, raises concerns surrounding safety, research integrity, and the validity of the academic peer-review process. The majority of the studies performing a systematic evaluation of frontier LLMs generating reviews across science disciplines miss the mark on addressing the alignment/misalignment of reviews along with the utility of LLM generated reviews when compared against publication outcomes such as \textbf{Citations}, \textbf{Hit-papers}, \textbf{Novelty}, and \textbf{Disruption}. This paper presents an experimental study in which we gathered ground-truth reviewer ratings from OpenReview and used various frontier open-weight LLMs to generate reviews of papers to gauge the safety and reliability of incorporating LLMs into the scientific review pipeline. Our findings demonstrate the utility of frontier open-weight LLMs as pre-review screening agents despite highlighting fundamental misalignment risks when deployed as autonomous reviewers. Our results show that all models exhibit weak correlation with human peer reviewers (0.15), with systematic overestimation bias of 3-5 points and uniformly high confidence scores (8.0-9.0/10) despite prediction errors. However, we also observed that LLM reviews correlate more strongly with post-publication metrics than with human scores, suggesting potential utility as pre-review screening tools. Our findings highlight the potential and address the pitfalls of automating peer reviews with language models. We open-sourced our dataset $D_{LMRSD}$ to help the research community expand the safety framework of automating scientific reviews.
For scientific knowledge to be findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable, it needs to be machine-readable. Moving forward from post-publication extraction of knowledge, we adopted a pre-publication approach to write research findings in a machine-readable format at early stages of data analysis. For this purpose, we developed the package dtreg in Python and R. Registered and persistently identified data types, aka schemata, which dtreg applies to describe data analysis in a machine-readable format, cover the most widely used statistical tests and machine learning methods. The package supports (i) downloading a relevant schema as a mutable instance of a Python or R class, (ii) populating the instance object with metadata about data analysis, and (iii) converting the object into a lightweight Linked Data format. This paper outlines the background of our approach, explains the code architecture, and illustrates the functionality of dtreg with a machine-readable description of a t-test on Iris Data. We suggest that the dtreg package can enhance the methodological repertoire of researchers aiming to adhere to the FAIR principles.

We present BookReconciler, an open-source tool for enhancing and clustering book data. BookReconciler allows users to take spreadsheets with minimal metadata, such as book title and author, and automatically 1) add authoritative, persistent identifiers like ISBNs 2) and cluster related Expressions and Manifestations of the same Work, e.g., different translations or editions. This enhancement makes it easier to combine related collections and analyze books at scale. The tool is currently designed as an extension for OpenRefine -- a popular software application -- and connects to major bibliographic services including the Library of Congress, VIAF, OCLC, HathiTrust, Google Books, and Wikidata. Our approach prioritizes human judgment. Through an interactive interface, users can manually evaluate matches and define the contours of a Work (e.g., to include translations or not). We evaluate reconciliation performance on datasets of U.S. prize-winning books and contemporary world fiction. BookReconciler achieves near-perfect accuracy for U.S. works but lower performance for global texts, reflecting structural weaknesses in bibliographic infrastructures for non-English and global literature. Overall, BookReconciler supports the reuse of bibliographic data across domains and applications, contributing to ongoing work in digital libraries and digital humanities.
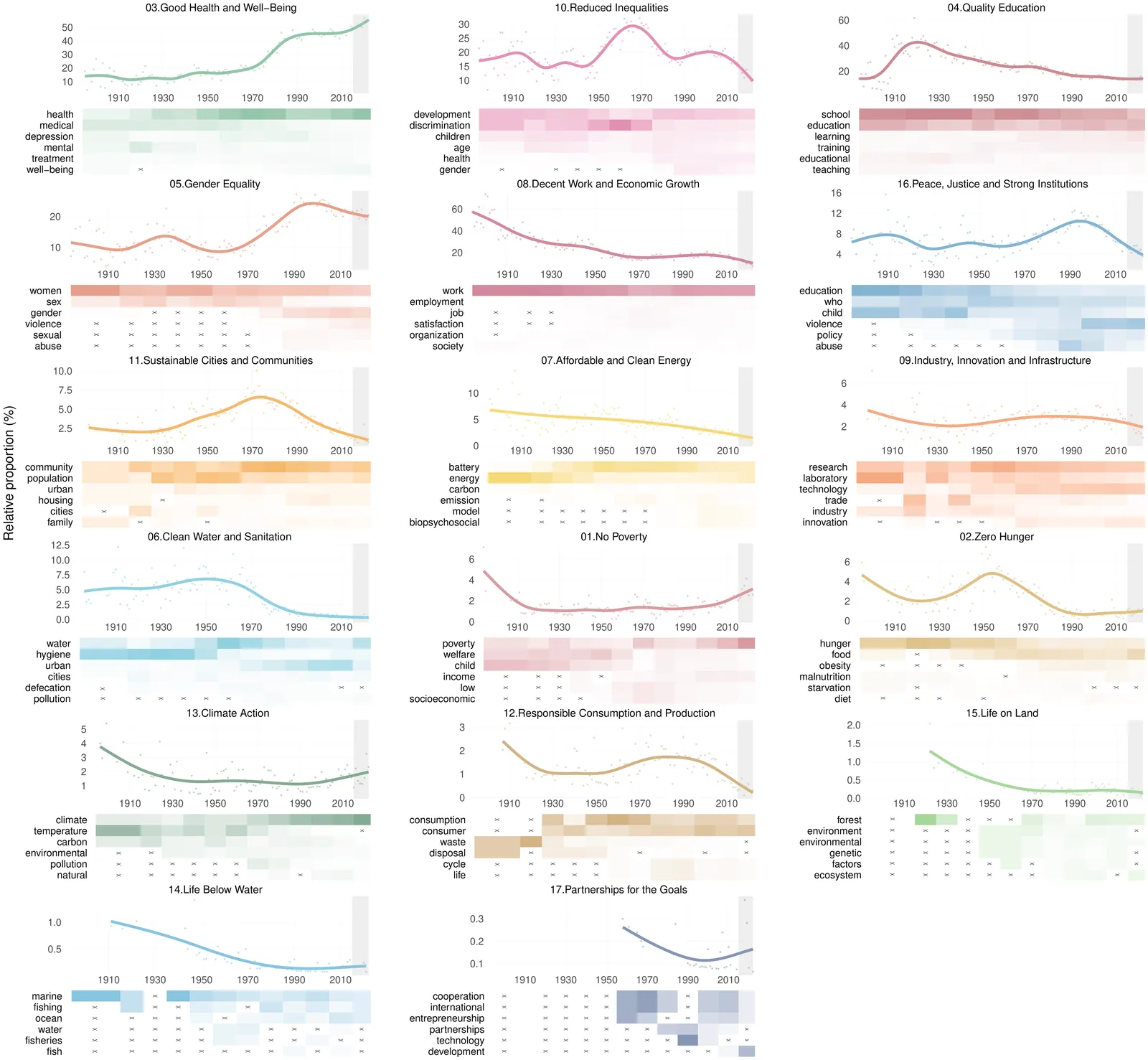
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) offer a lens for tracking societal change, yet contributions from the social and behavioral sciences have rarely been integrated into policy agendas. To take stock and create a baseline and benchmark for the future, we assemble 233,061 psychology publications (1894 -- 2022) and tag them to the 17 SDGs using a query-based classifier. Health, education, work, inequality, and gender dominate the study of SDGs in psychology, shifting from an early focus on work to education and inequality, and since the 1960s, health. United States-based research leads across most goals. Other countries set distinct priorities (e.g., China: education and work; Australia: health). Women comprise about one-third of authors, concentrated in social and health goals, but have been underrepresented in STEM-oriented goals. The 2015 launch of the SDGs marked a turning point: SDG-tagged publications have been receiving more citations than comparable non-SDG work, reversing a pre-2015 deficit. Tracking the SDGs through psychology clarifies long-run engagement with social priorities, identifies evidence gaps, and guides priorities to accelerate the field's contribution to the SDG agenda.
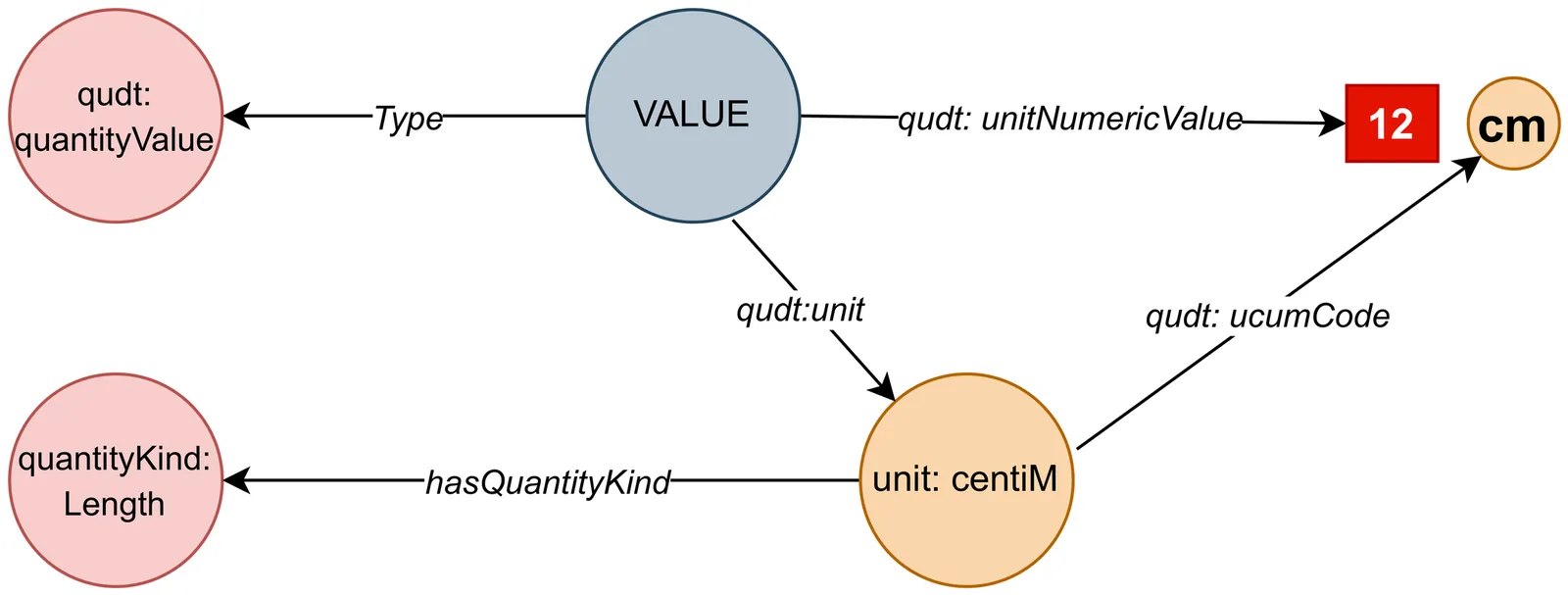
Scientists have always used the studies and research of other researchers to achieve new objectives and perspectives. In particular, employing and operating the measured data in previous studies is so practical. Searching the content of other scientists' articles is a challenge that researchers have always struggled with. Nowadays, the use of knowledge graphs as a semantic database has helped a lot in saving and retrieving scholarly knowledge. Such technologies are crucial to upgrading traditional search systems to smart knowledge retrieval, which is crucial to getting the most relevant answers for a user query, especially in information and knowledge management. However, in most cases, only the metadata of a paper is searchable, and it is still cumbersome for scientists to have access to the content of the papers. In this paper, we present a novel method of faceted search \emph{structured content} for comparing and filtering measured data in scholarly knowledge graphs while different units of measurement are used in different studies. This search system proposes applicable units as facets to the user and would dynamically integrate content from further remote knowledge graphs to materialize the scholarly knowledge graph and achieve a higher order of exploration usability on scholarly content, which can be filtered to better satisfy the user's information needs. The state of the art is that, by using our faceted search system, users can not only search the contents of scientific articles, but also compare and filter heterogeneous data.
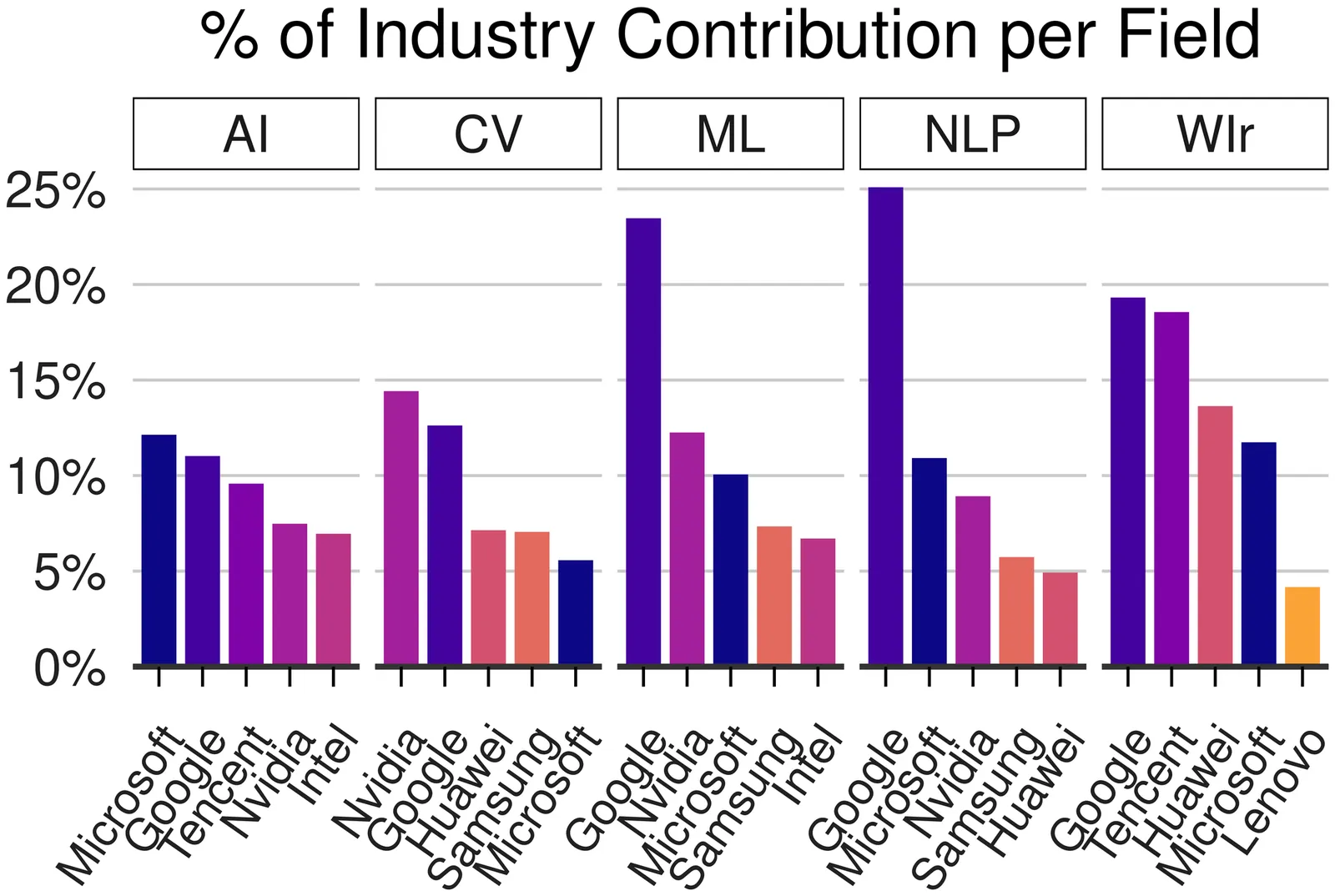
Over the past four decades, artificial intelligence (AI) research has flourished at the nexus of academia and industry. However, Big Tech companies have increasingly acquired the edge in computational resources, big data, and talent. So far, it has been largely unclear how many papers the industry funds, how their citation impact compares to non-funded papers, and what drives industry interest. This study fills that gap by quantifying the number of industry-funded papers at 10 top AI conferences (e.g., ICLR, CVPR, AAAI, ACL) and their citation influence. We analyze about 49.8K papers, about 1.8M citations from AI papers to other papers, and about 2.3M citations from other papers to AI papers from 1998-2022 in Scopus. Through seven research questions, we examine the volume and evolution of industry funding in AI research, the citation impact of funded papers, the diversity and temporal range of their citations, and the subfields in which industry predominantly acts. Our findings reveal that industry presence has grown markedly since 2015, from less than 2 percent to more than 11 percent in 2020. Between 2018 and 2022, 12 percent of industry-funded papers achieved high citation rates as measured by the h5-index, compared to 4 percent of non-industry-funded papers and 2 percent of non-funded papers. Top AI conferences engage more with industry-funded research than non-funded research, as measured by our newly proposed metric, the Citation Preference Ratio (CPR). We show that industry-funded research is increasingly insular, citing predominantly other industry-funded papers while referencing fewer non-funded papers. These findings reveal new trends in AI research funding, including a shift towards more industry-funded papers and their growing citation impact, greater insularity of industry-funded work than non-funded work, and a preference of industry-funded research to cite recent work.
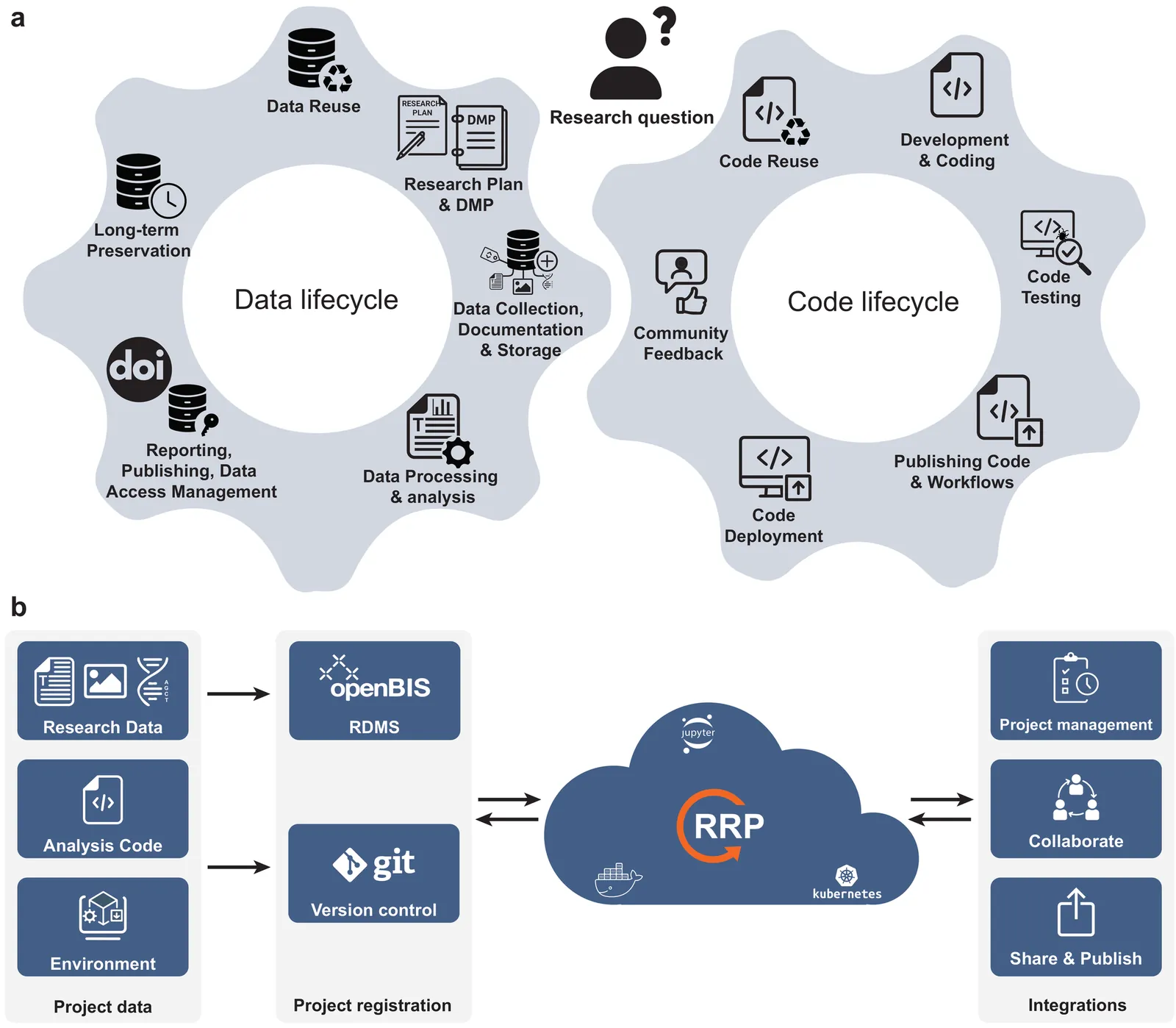
Many research groups aspire to make data and code FAIR and reproducible, yet struggle because the data and code life cycles are disconnected, executable environments are often missing from published work, and technical skill requirements hinder adoption. Existing approaches rarely enable researchers to keep using their preferred tools or support seamless execution across domains. To close this gap, we developed the open-source Reproducible Research Platform (RRP), which unifies research data management with version-controlled, containerized computational environments in modular, shareable projects. RRP enables anyone to execute, reuse, and publish fully documented, FAIR research workflows without manual retrieval or platform-specific setup. We demonstrate RRP's impact by reproducing results from diverse published studies, including work over a decade old, showing sustained reproducibility and usability. With a minimal graphical interface focused on core tasks, modular tool installation, and compatibility with institutional servers or local computers, RRP makes reproducible science broadly accessible across scientific domains.
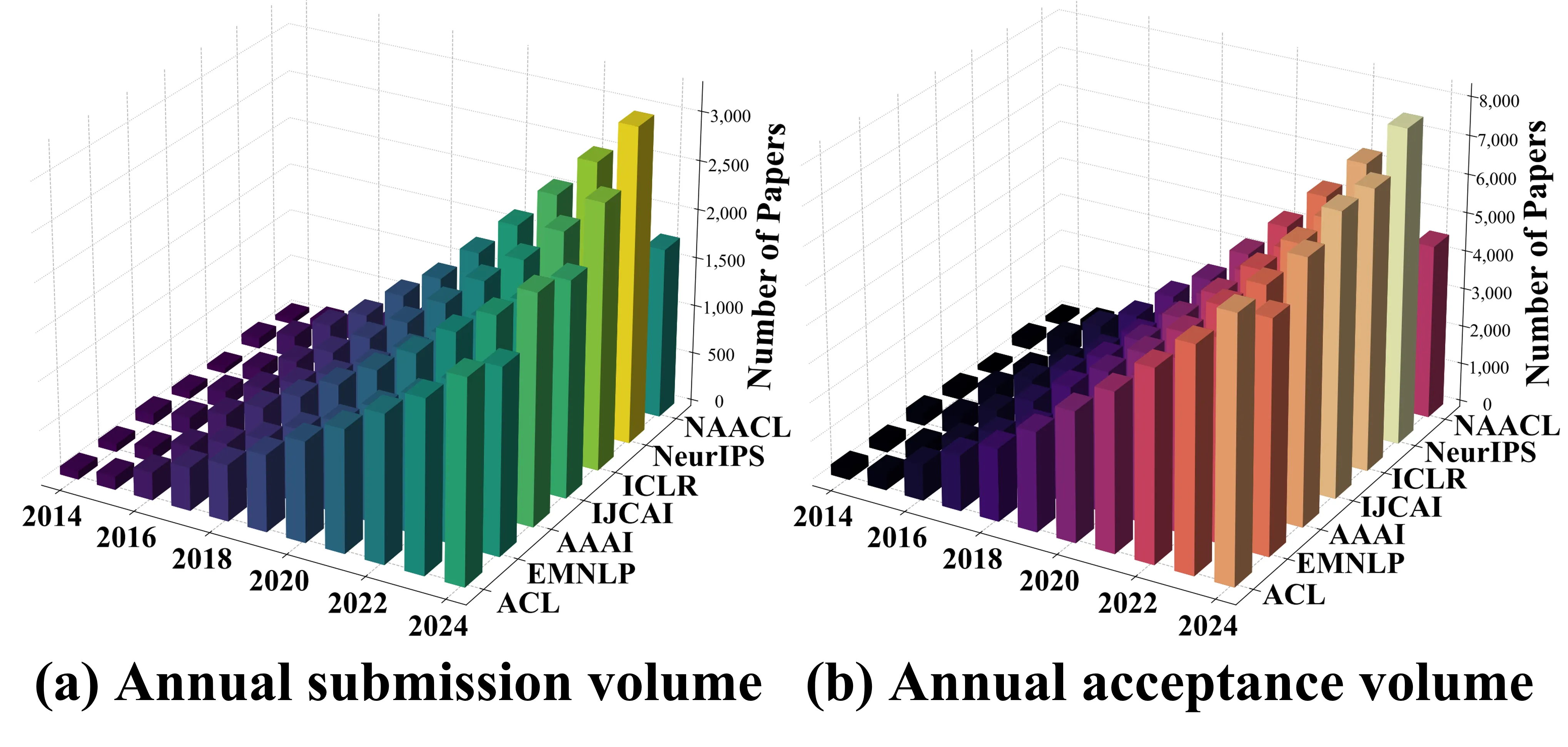
The recent surge of language models has rapidly expanded NLP research, driving an exponential rise in submissions and acceptances at major conferences. Yet this growth has been shadowed by escalating concerns over conference quality, e.g., plagiarism, reviewer inexperience and collusive bidding. However, existing studies rely largely on qualitative accounts (e.g., expert interviews, social media discussions, etc.), lacking longitudinal empirical evidence. To fill this gap, we conduct a ten year empirical study spanning seven leading conferences. We build a four dimensional bibliometric framework covering conference scale, core citation statistics,impact dispersion, cross venue and journal influence, etc. Notably, we further propose a metric Quality Quantity Elasticity, which measures the elasticity of citation growth relative to acceptance growth. Our findings show that ML venues sustain dominant and stable impact, NLP venues undergo widening stratification with mixed expansion efficiency, and AI venues exhibit structural decline. This study provides the first decade-long, cross-venue empirical evidence on the evolution of major conferences.
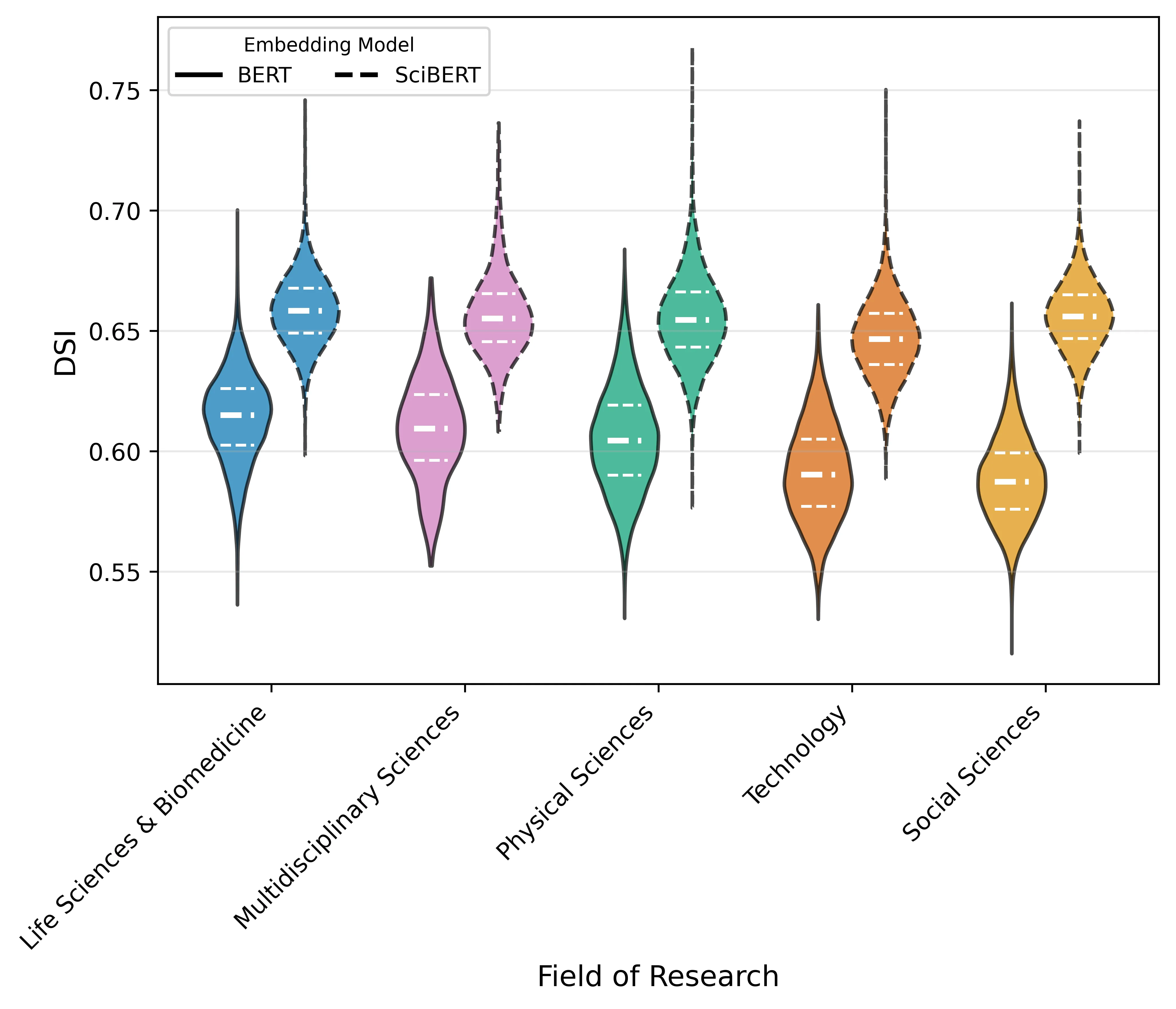
The study of creativity in science has long sought quantitative metrics capable of capturing the originality of the scientific insights contained within articles and other scientific works. In recent years, the field has witnessed a substantial expansion of research activity, enabled by advances in natural language processing and network analysis, and has utilised both macro- and micro-scale approaches with success. However, they often do not examine the text itself for evidence of originality. In this paper, we apply a computational measure correlating with originality from creativity science, Divergent Semantic Integration (DSI), to a set of 51,200 scientific abstracts and titles sourced from the Web of Science. To adapt DSI for application to scientific texts, we advance the original BERT method by incorporating SciBERT (a model trained on scientific corpora) into the computation of DSI. In our study, we observe that DSI plays a more pronounced role in the accrual of early citations for papers with fewer authors, varies substantially across subjects and research fields, and exhibits a declining correlation with citation counts over time. Furthermore, by modelling SciBERT- and BERT-DSI as predictors of the logarithm of 5-year citation counts alongside field, publication year, and the logarithm of author count, we find statistically significant relationships, with adjusted R-squared of 0.103 and 0.101 for BERT-DSI and SciBERT-DSI. Because existing scientometric measures rarely assess the originality expressed in textual content, DSI provides a valuable means of directly quantifying the conceptual originality embedded in scientific writing.
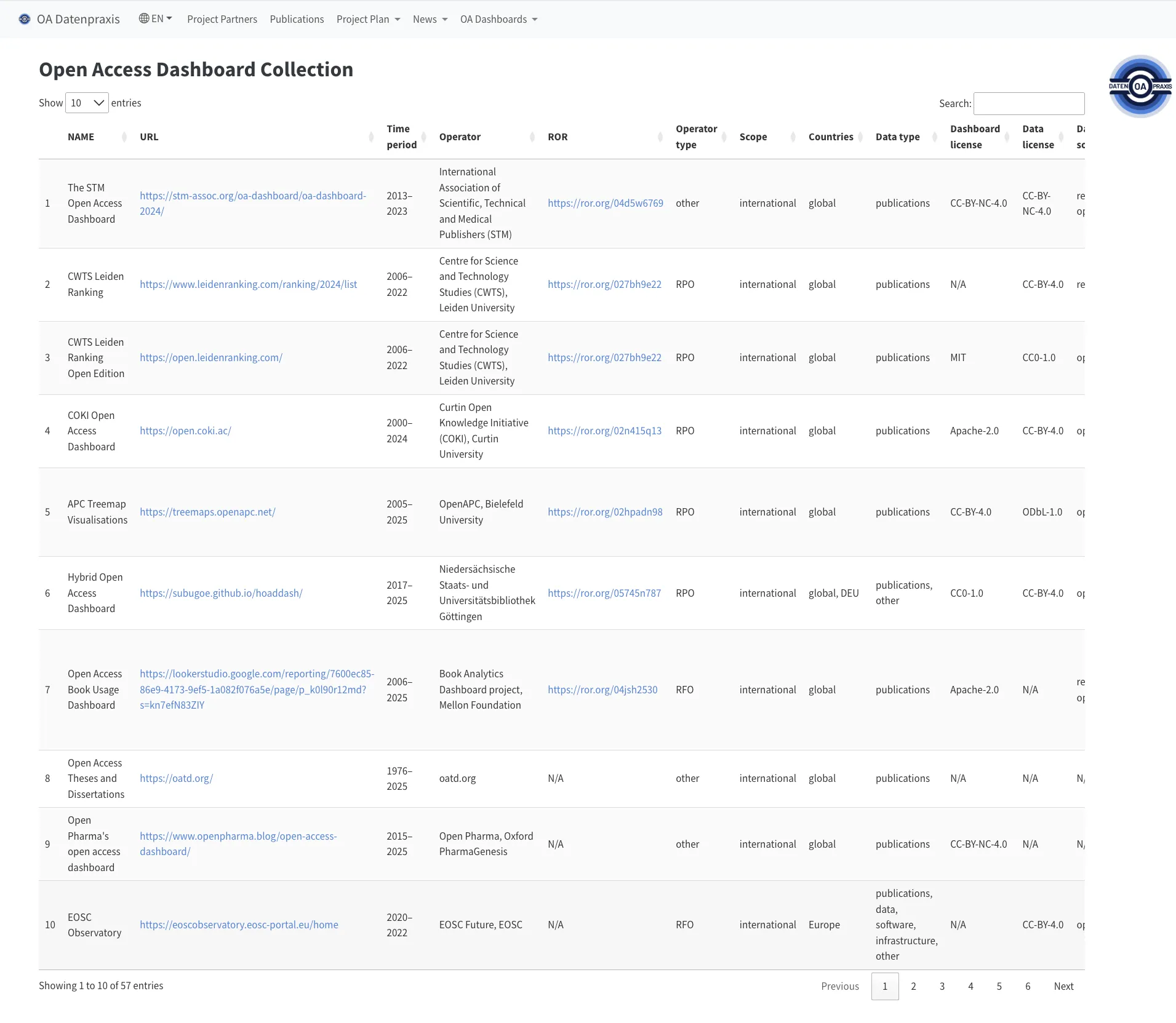
As Open Access continues to gain importance in science policy, understanding the proportion of Open Access publications relative to the total research output of research-performing organizations, individual countries, or even globally has become increasingly relevant. In response, dashboards are being developed to capture and communicate progress in this area. To provide an overview of these dashboards and their characteristics, an extensive survey was conducted, resulting in the identification of nearly 60 dashboards. To support a detailed and structured description, a dedicated metadata schema was developed, and the identified dashboards were systematically indexed accordingly. To foster community engagement and ensure ongoing development, a participatory process was launched, allowing interested stakeholders to contribute to the dataset. The dataset is particularly relevant for researchers in Library and Information Science (LIS) and Science and Technology Studies (STS), supporting both empirical analyses of Open Access and the methodological refinement of indicators and policy instruments in the context of Open Science.
Peer-review venues have increasingly adopted open reviewing policies that publicly release anonymized reviews and permit public commenting. Venues have adopted a variety of policies, and there is still ongoing debate about the benefits and drawbacks of decisions. To inform this debate, we surveyed 2,385 reviewers, authors, and other peer-review participants in machine learning to understand their experiences and opinions. Our key findings are: (a) Preferences: Over 80% of respondents support releasing reviews for accepted papers and allowing public comments. However, only 27.1% support releasing rejected manuscripts. (b) Benefits: Respondents cite improved public understanding (75.3%) and reviewer education (57.8%), increased fairness (56.6%), and stronger incentives for high-quality reviews (48.0%). (c) Challenges: The top concern is resubmission bias, where rejection history biases future reviewers (ranked top impact of open reviewing by 41% of respondents, and mentioned in over 50% of free responses). Other challenges include fear of reviewer de-anonymization (33.2%) and potential commenting abuse. (d) AI and open peer review: Participants believe open policies deter "AI slop" submissions (71.9%) and AI-generated reviews (38.9%). Respondents are split regarding peer-review venues generating official AI reviews, with 56.0% opposed and 44.0% supportive. Finally, we use AI to annotate 4,244 reviews from ICLR (fully open) and NeurIPS (partially open). We find that the fully open venue (ICLR) has higher levels of correctness and completeness than the partially open venue (NeurIPS). The effect size is small for correctness and very small for completeness, and both are statistically significant. We also find that there is no statistically significant difference in the level of substantiation. We release the full dataset at https://github.com/justinpayan/OpenReviewAnalysis.
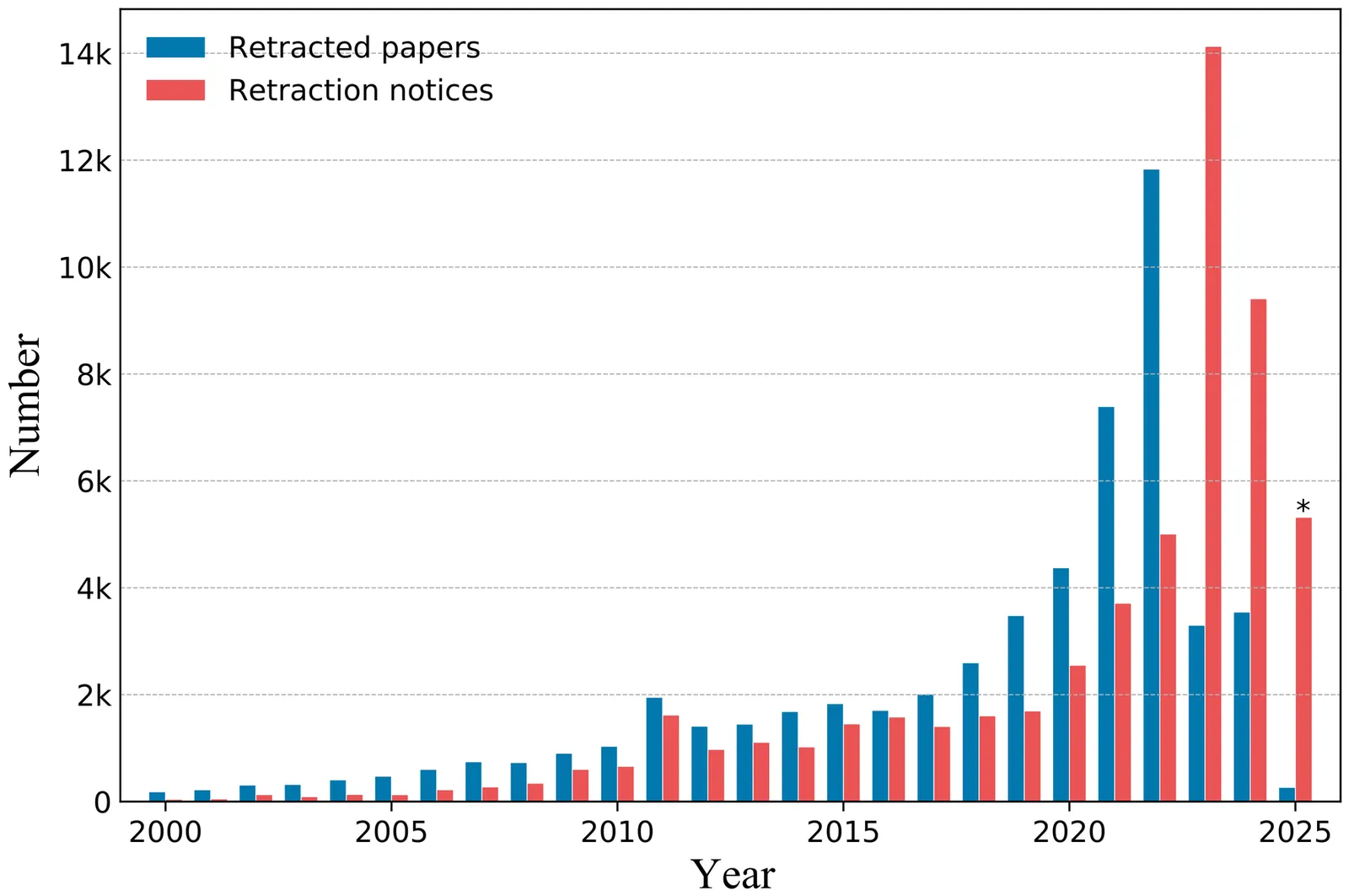
Scientific publications form the cornerstone of innovation and have maintained a stable growth trend over the years. However, in recent years, there has been a significant surge in retractions, driven largely by the proliferation of low-quality and fraudulent papers. This study aims to examine retractions and their evolving trends through a topic lens. Our analysis of global retraction data reveals that the numbers of retraction have remained alarmingly high in recent years, with the growth rate of retracted papers significantly outpacing that of overall global publications. While retractions are observed across various fields, their distribution is not uniform. In disciplines characterized by high retraction rates, certain topics may only encounter minor issues, whereas in fields with lower retraction rates, some topics can experience substantial challenges. Moreover, an unexpected surge in publications has been observed in specific topics that also display abnormally high retraction rates. This study underscores several indicators that can assist the scientific community in pinpointing key fields that require rigorous scrutiny for potential low-quality and fraudulent research. Ultimately, our findings could serve as a benchmark for examining scientific integrity across diverse topics and offer crucial insights for developing tailored governance policies to enhance research integrity in each field.
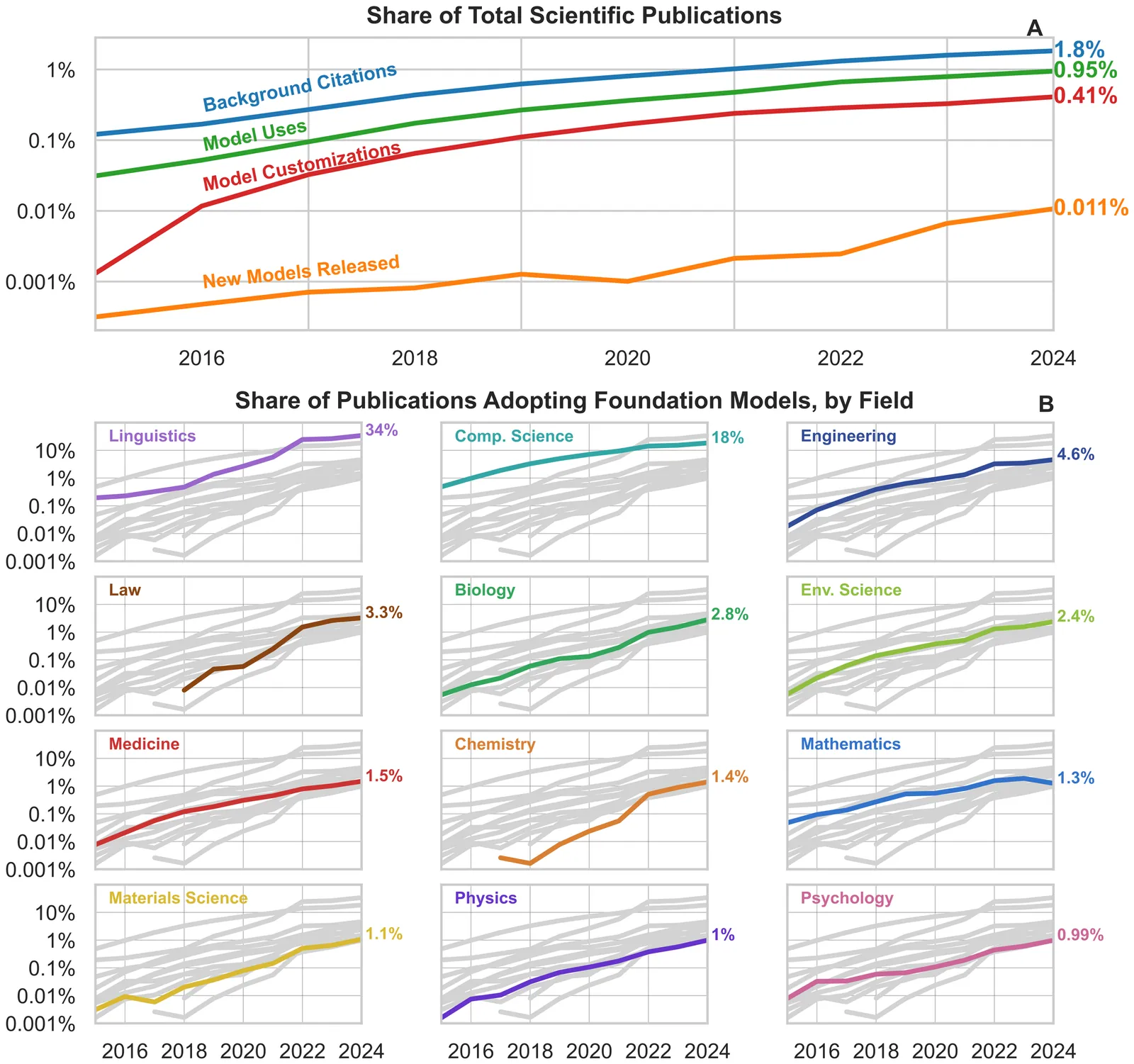
We present the first large-scale analysis of AI foundation model usage in science - not just citations or keywords. We find that adoption has grown rapidly, at nearly-exponential rates, with the highest uptake in Linguistics, Computer Science, and Engineering. Vision models are the most used foundation models in science, although language models' share is growing. Open-weight models dominate. As AI builders increase the parameter counts of their models, scientists have followed suit but at a much slower rate: in 2013, the median foundation model built was 7.7x larger than the median one adopted in science, by 2024 this had jumped to 26x. We also present suggestive evidence that scientists' use of these smaller models may be limiting them from getting the full benefits of AI-enabled science, as papers that use larger models appear in higher-impact journals and accrue more citations.
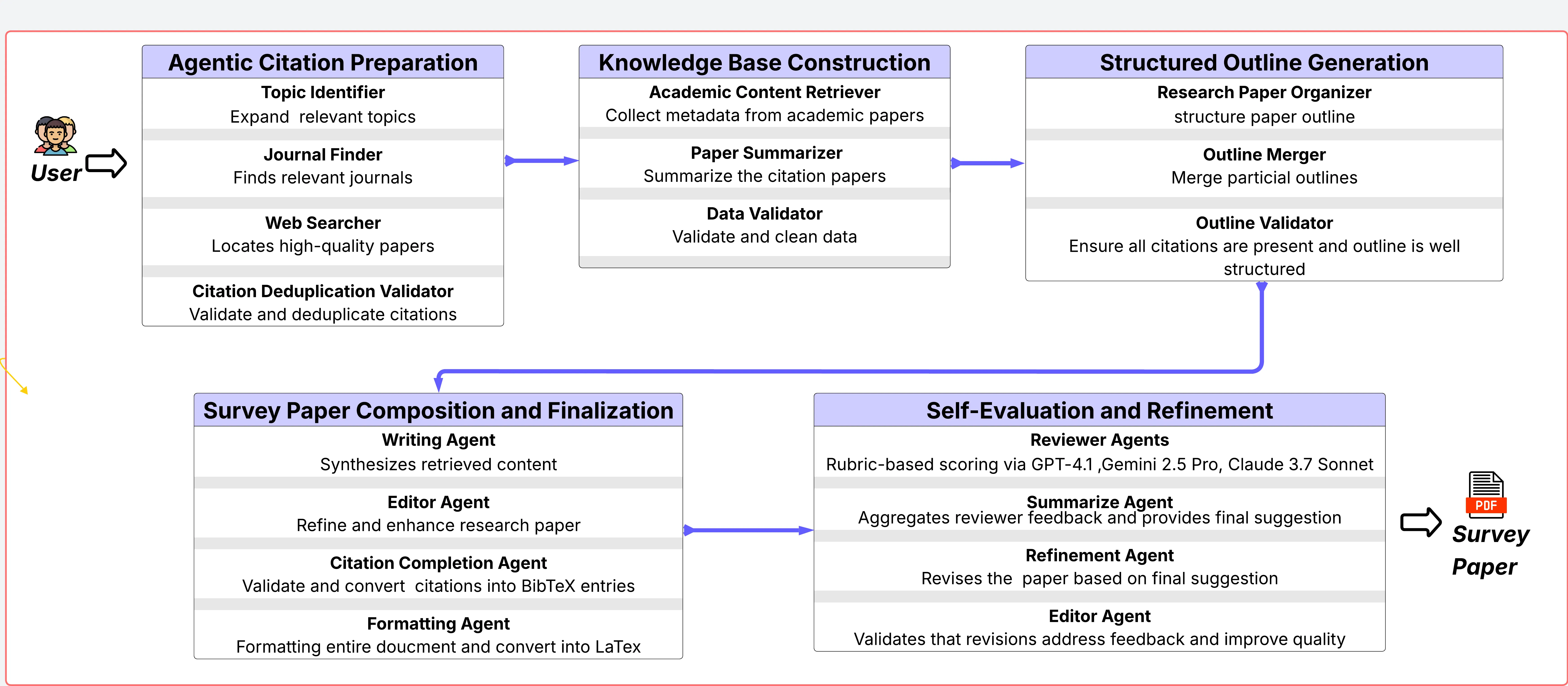
The rapid expansion of scholarly literature presents significant challenges in synthesizing comprehensive, high-quality academic surveys. Recent advancements in agentic systems offer considerable promise for automating tasks that traditionally require human expertise, including literature review, synthesis, and iterative refinement. However, existing automated survey-generation solutions often suffer from inadequate quality control, poor formatting, and limited adaptability to iterative feedback, which are core elements intrinsic to scholarly writing. To address these limitations, we introduce ARISE, an Agentic Rubric-guided Iterative Survey Engine designed for automated generation and continuous refinement of academic survey papers. ARISE employs a modular architecture composed of specialized large language model agents, each mirroring distinct scholarly roles such as topic expansion, citation curation, literature summarization, manuscript drafting, and peer-review-based evaluation. Central to ARISE is a rubric-guided iterative refinement loop in which multiple reviewer agents independently assess manuscript drafts using a structured, behaviorally anchored rubric, systematically enhancing the content through synthesized feedback. Evaluating ARISE against state-of-the-art automated systems and recent human-written surveys, our experimental results demonstrate superior performance, achieving an average rubric-aligned quality score of 92.48. ARISE consistently surpasses baseline methods across metrics of comprehensiveness, accuracy, formatting, and overall scholarly rigor. All code, evaluation rubrics, and generated outputs are provided openly at https://github.com/ziwang11112/ARISE