Genomics
DNA/RNA sequencing and analysis, gene finding, genome assembly and annotation, transcriptomics.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
DNA/RNA sequencing and analysis, gene finding, genome assembly and annotation, transcriptomics.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
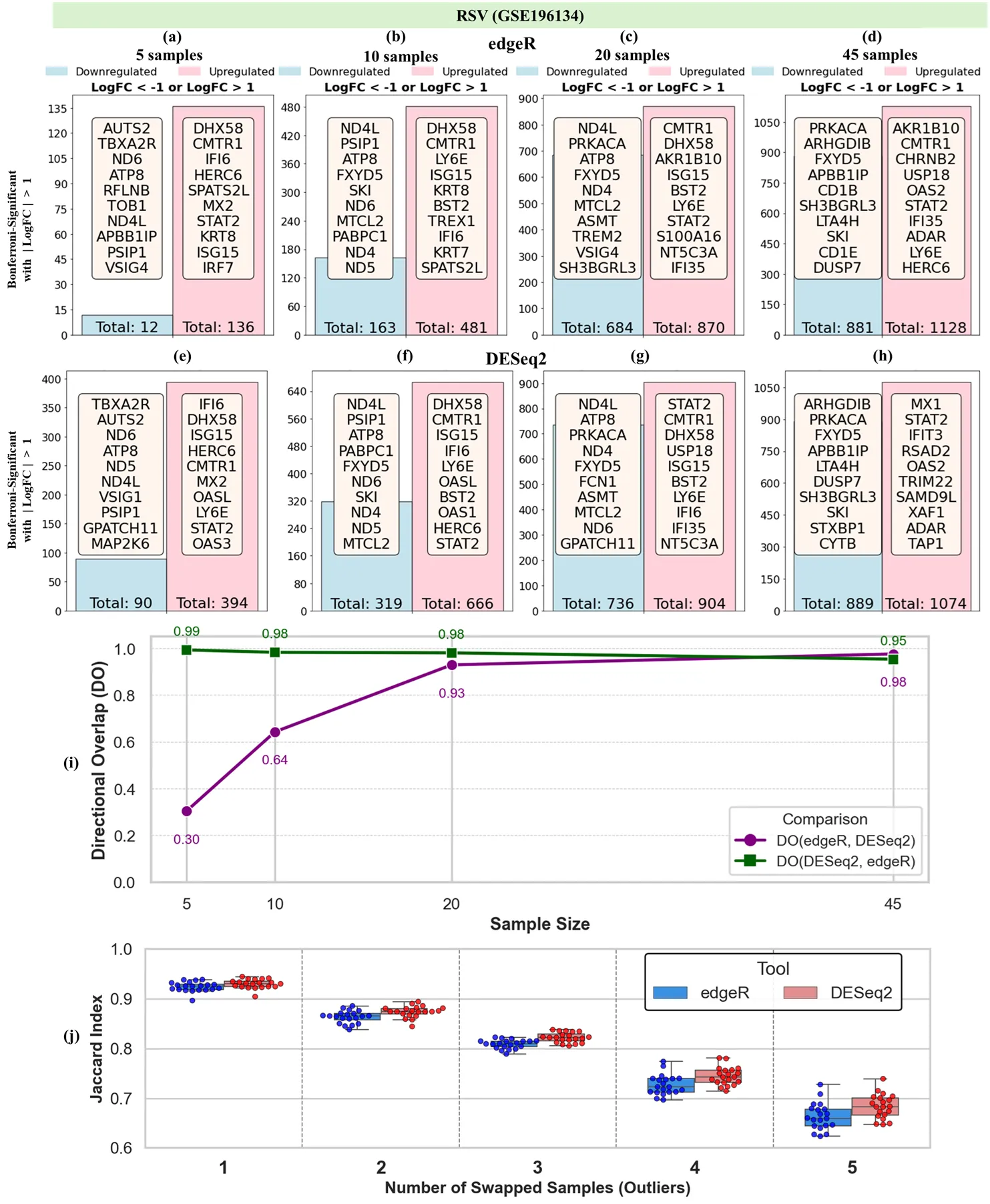
Differential gene expression (DGE) analysis is foundational to transcriptomic research, yet tool selection can substantially influence results. This study presents a comprehensive comparison of two widely used DGE tools, edgeR and DESeq2, using real and semi-simulated bulk RNA-Seq datasets spanning viral, bacterial, and fibrotic conditions. We evaluated tool performance across three key dimensions: (1) sensitivity to sample size and robustness to outliers; (2) classification performance of uniquely identified gene sets within the discovery dataset; and (3) generalizability of tool-specific gene sets across independent studies. First, both tools showed similar responses to simulated outliers, with Jaccard similarity between the DEG sets from perturbed and original (unperturbed) data decreasing as more outliers were added. Second, classification models trained on tool-specific genes showed that edgeR achieved higher F1 scores in 9 of 13 contrasts and more frequently reached perfect or near-perfect precision. Dolan-More performance profiles further indicated that edgeR maintained performance closer to optimal across a greater proportion of datasets. Third, in cross-study validation using four independent SARS-CoV-2 datasets, gene sets uniquely identified by edgeR yielded higher AUC, precision, and recall in classifying samples from held-out datasets. This pattern was consistent across folds, with some test cases achieving perfect separation using edgeR-specific genes. In contrast, DESeq2-specific genes showed lower and more variable performance across studies. Overall, our findings highlight that while DESeq2 may identify more DEGs even under stringent significance conditions, edgeR yields more robust and generalizable gene sets for downstream classification and cross-study replication, which underscores key trade-offs in tool selection for transcriptomic analyses.
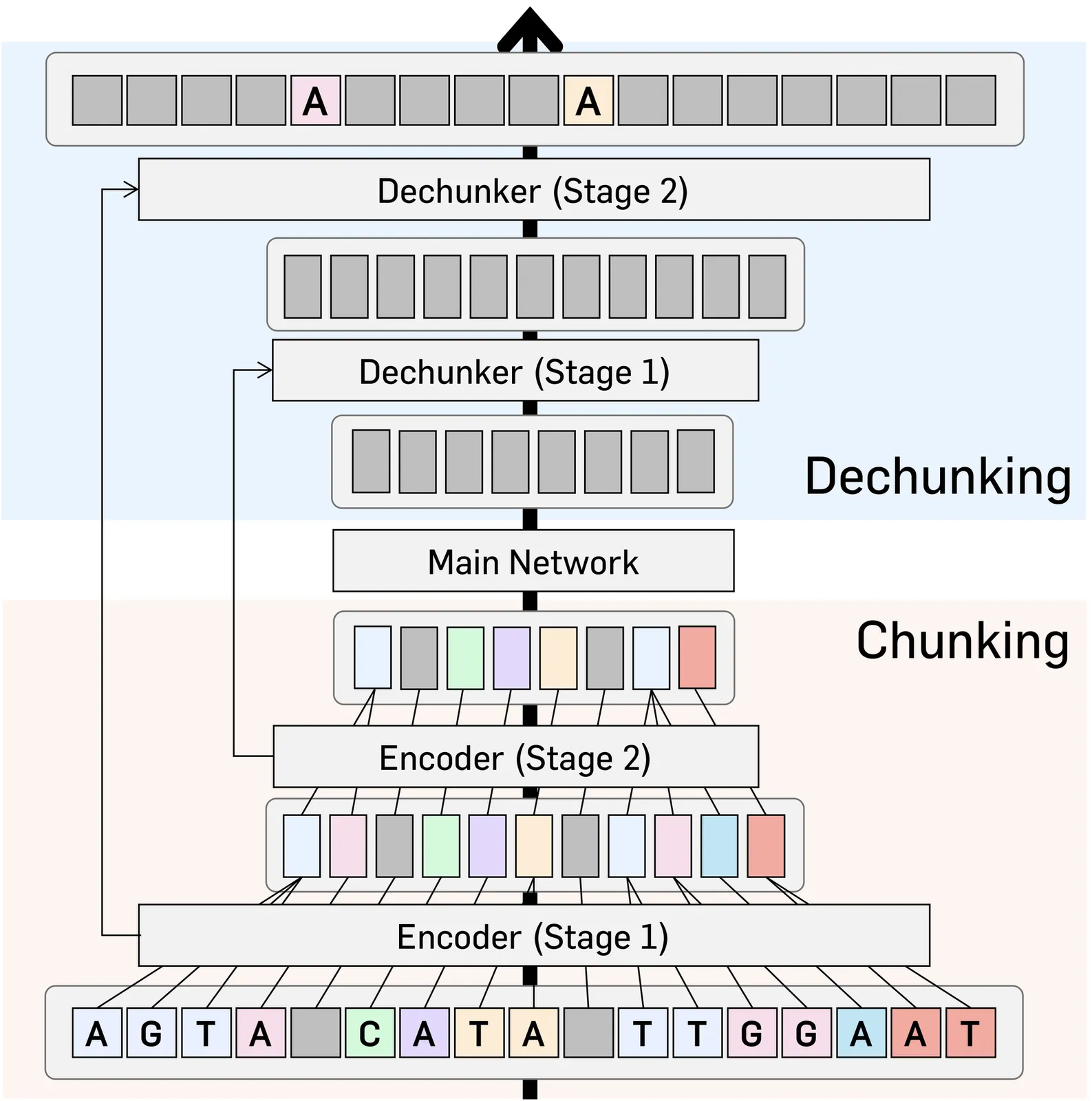
DNA language models have emerged as powerful tools for decoding the complex language of DNA sequences. However, the performance of these models is heavily affected by their tokenization strategy, i.e., a method used to parse DNA sequences into a shorter sequence of chunks. In this work, we propose DNACHUNKER, which integrates a learnable dynamic DNA tokenization mechanism and is trained as a masked language model. Adopting the dynamic chunking procedure proposed by H-Net, our model learns to segment sequences into variable-length chunks. This dynamic chunking offers two key advantages: it's resilient to shifts and mutations in the DNA, and it allocates more detail to important functional areas. We demonstrate the performance of DNACHUNKER by training it on the human reference genome (HG38) and testing it on the Nucleotide Transformer and Genomic benchmarks. Further ablative experiments reveal that DNACHUNKER learns tokenization that grasps biological grammar and uses smaller chunks to preserve detail in important functional elements such as promoters and exons, while using larger chunks for repetitive, redundant regions.
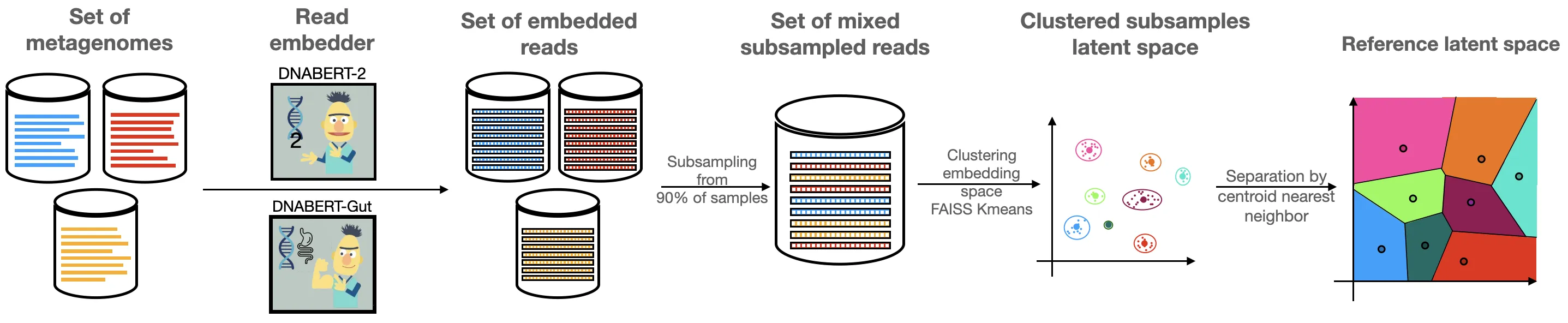
Metagenomic disease prediction commonly relies on species abundance tables derived from large, incomplete reference catalogs, constraining resolution and discarding valuable information contained in DNA reads. To overcome these limitations, we introduce MetagenBERT, a Transformer based framework that produces end to end metagenome embeddings directly from raw DNA sequences, without taxonomic or functional annotations. Reads are embedded using foundational genomic language models (DNABERT2 and the microbiome specialized DNABERTMS), then aggregated through a scalable clustering strategy based on FAISS accelerated KMeans. Each metagenome is represented as a cluster abundance vector summarizing the distribution of its embedded reads. We evaluate this approach on five benchmark gut microbiome datasets (Cirrhosis, T2D, Obesity, IBD, CRC). MetagenBERT achieves competitive or superior AUC performance relative to species abundance baselines across most tasks. Concatenating both representations further improves prediction, demonstrating complementarity between taxonomic and embedding derived signals. Clustering remains robust when applied to as little as 10% of reads, highlighting substantial redundancy in metagenomes and enabling major computational gains. We additionally introduce MetagenBERT Glob Mcardis, a cross cohort variant trained on the large, phenotypically diverse MetaCardis cohort and transferred to other datasets, retaining predictive signal including for unseen phenotypes, indicating the feasibility of a foundation model for metagenome representation. Robustness analyses (PERMANOVA, PERMDISP, entropy) show consistent separation of different states across subsamples. Overall, MetagenBERT provides a scalable, annotation free representation of metagenomes pointing toward future phenotype aware generalization across heterogeneous cohorts and sequencing technologies.
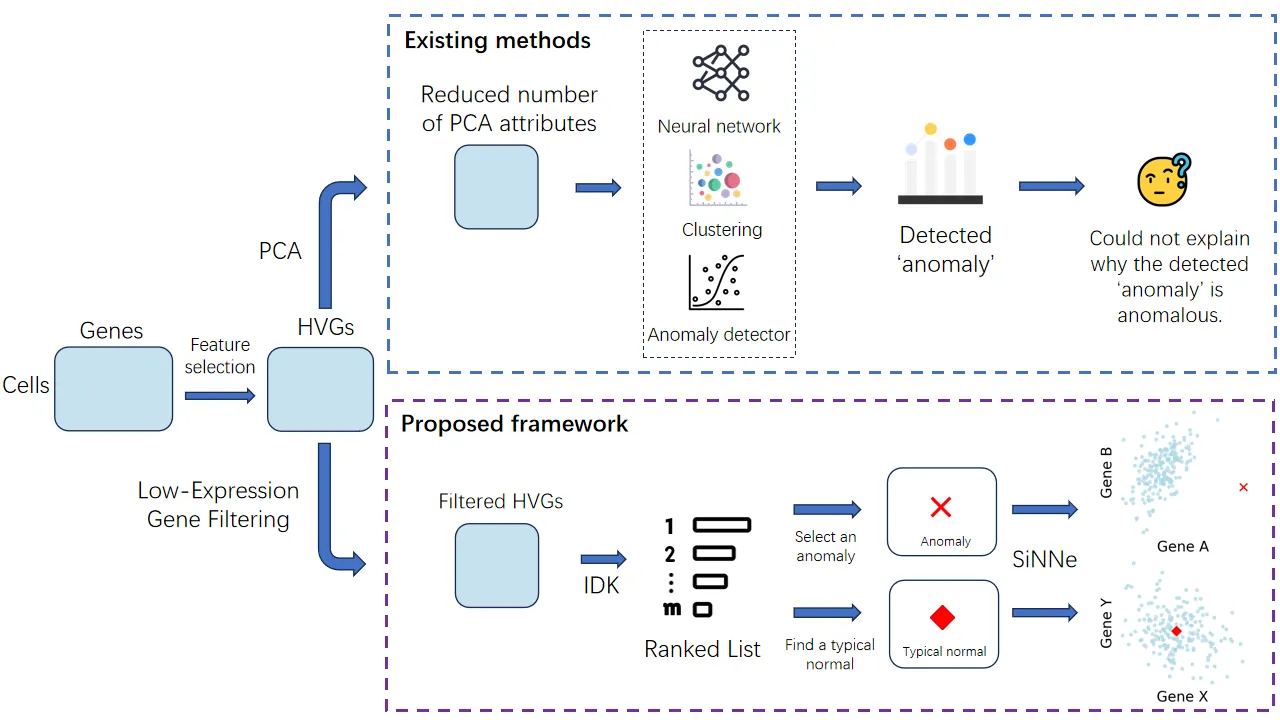
The detection of rare cell types in single-cell transcriptomics data is crucial for elucidating disease pathogenesis and tissue development dynamics. However, a critical gap that persists in current methods is their inability to provide an explanation based on genes for each cell they have detected as rare. We identify three primary sources of this deficiency. First, the anomaly detectors often function as "black boxes", designed to detect anomalies but unable to explain why a cell is anomalous. Second, the standard analytical framework hinders interpretability by relying on dimensionality reduction techniques, such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA), which transform meaningful gene expression data into abstract, uninterpretable features. Finally, existing explanation algorithms cannot be readily applied to this domain, as single-cell data is characterized by high dimensionality, noise, and substantial sparsity. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a framework for explainable anomaly detection in single-cell transcriptomics data which not only identifies individual anomalies, but also provides a visual explanation based on genes that makes an instance anomalous. This framework has two key ingredients that are not existed in current methods applied in this domain. First, it eliminates the PCA step which is deemed to be an essential component in previous studies. Second, it employs the state-of-art anomaly detector and explainer as the efficient and effective means to find each rare cell and the relevant gene subspace in order to provide explanations for each rare cell as well as the typical normal cell associated with the rare cell's closest normal cells.
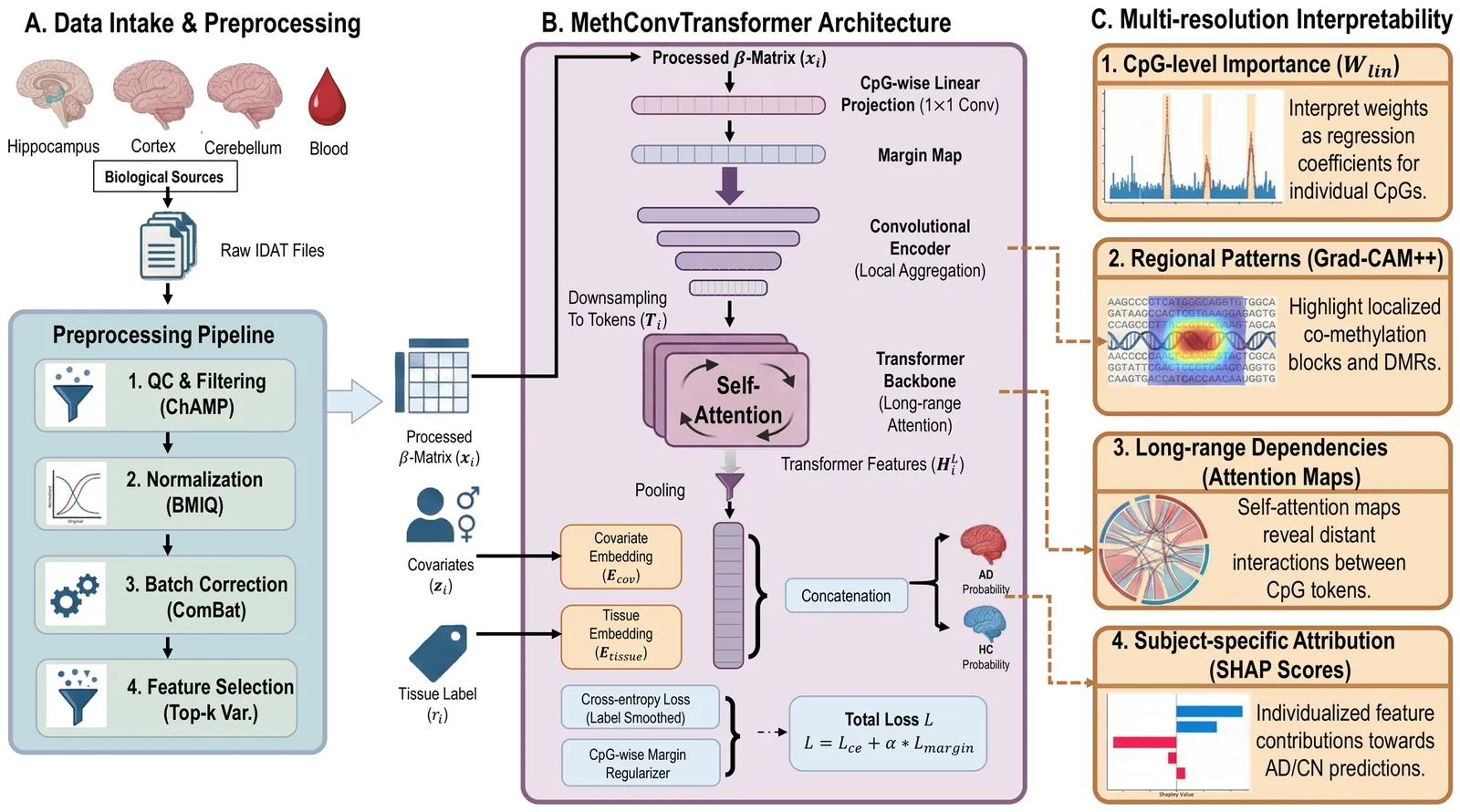
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive cognitive decline and widespread epigenetic dysregulation in the brain. DNA methylation, as a stable yet dynamic epigenetic modification, holds promise as a noninvasive biomarker for early AD detection. However, methylation signatures vary substantially across tissues and studies, limiting reproducibility and translational utility. To address these challenges, we develop MethConvTransformer, a transformer-based deep learning framework that integrates DNA methylation profiles from both brain and peripheral tissues to enable biomarker discovery. The model couples a CpG-wise linear projection with convolutional and self-attention layers to capture local and long-range dependencies among CpG sites, while incorporating subject-level covariates and tissue embeddings to disentangle shared and region-specific methylation effects. In experiments across six GEO datasets and an independent ADNI validation cohort, our model consistently outperforms conventional machine-learning baselines, achieving superior discrimination and generalization. Moreover, interpretability analyses using linear projection, SHAP, and Grad-CAM++ reveal biologically meaningful methylation patterns aligned with AD-associated pathways, including immune receptor signaling, glycosylation, lipid metabolism, and endomembrane (ER/Golgi) organization. Together, these results indicate that MethConvTransformer delivers robust, cross-tissue epigenetic biomarkers for AD while providing multi-resolution interpretability, thereby advancing reproducible methylation-based diagnostics and offering testable hypotheses on disease mechanisms.
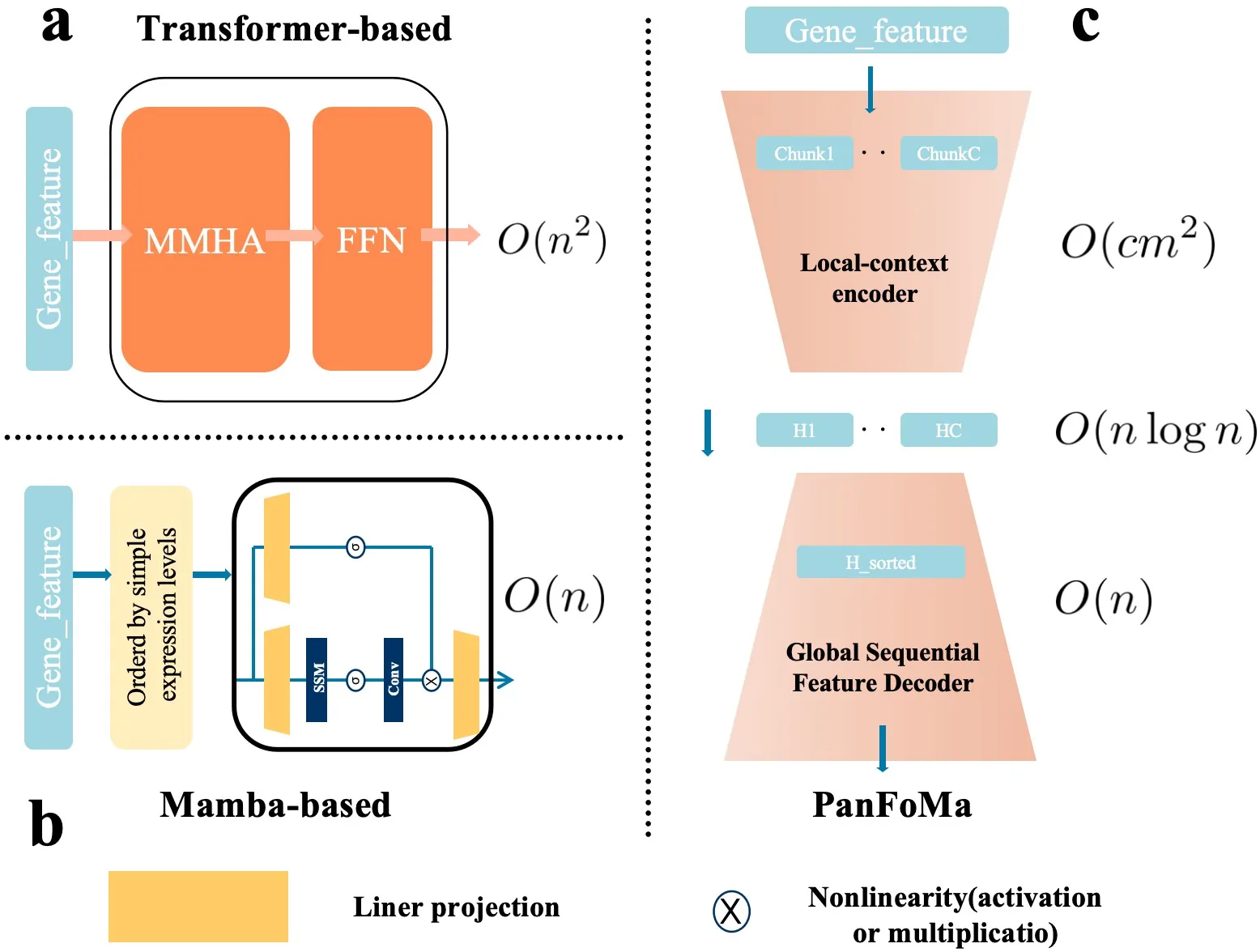
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is essential for decoding tumor heterogeneity. However, pan-cancer research still faces two key challenges: learning discriminative and efficient single-cell representations, and establishing a comprehensive evaluation benchmark. In this paper, we introduce PanFoMa, a lightweight hybrid neural network that combines the strengths of Transformers and state-space models to achieve a balance between performance and efficiency. PanFoMa consists of a front-end local-context encoder with shared self-attention layers to capture complex, order-independent gene interactions; and a back-end global sequential feature decoder that efficiently integrates global context using a linear-time state-space model. This modular design preserves the expressive power of Transformers while leveraging the scalability of Mamba to enable transcriptome modeling, effectively capturing both local and global regulatory signals. To enable robust evaluation, we also construct a large-scale pan-cancer single-cell benchmark, PanFoMaBench, containing over 3.5 million high-quality cells across 33 cancer subtypes, curated through a rigorous preprocessing pipeline. Experimental results show that PanFoMa outperforms state-of-the-art models on our pan-cancer benchmark (+4.0\%) and across multiple public tasks, including cell type annotation (+7.4\%), batch integration (+4.0\%) and multi-omics integration (+3.1\%). The code is available at https://github.com/Xiaoshui-Huang/PanFoMa.
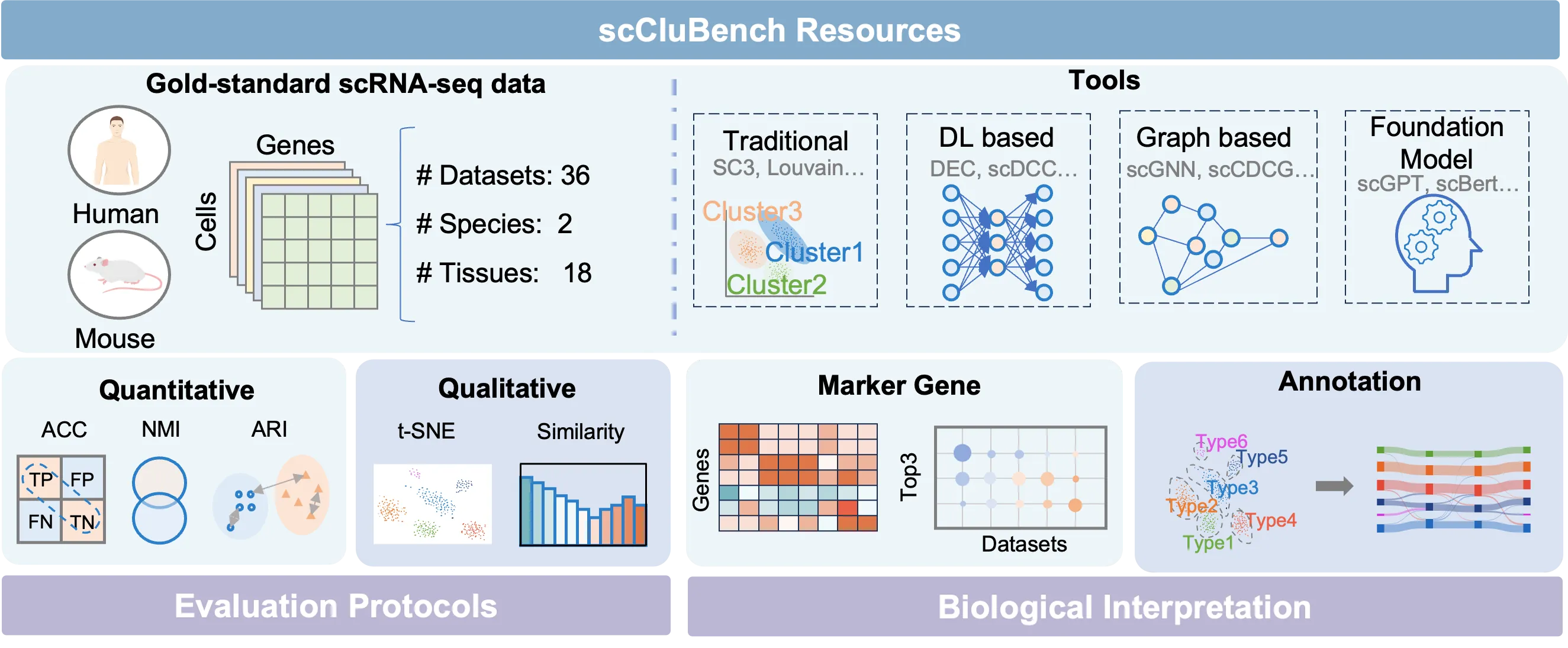
Cell clustering is crucial for uncovering cellular heterogeneity in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data by identifying cell types and marker genes. Despite its importance, benchmarks for scRNA-seq clustering methods remain fragmented, often lacking standardized protocols and failing to incorporate recent advances in artificial intelligence. To fill these gaps, we present scCluBench, a comprehensive benchmark of clustering algorithms for scRNA-seq data. First, scCluBench provides 36 scRNA-seq datasets collected from diverse public sources, covering multiple tissues, which are uniformly processed and standardized to ensure consistency for systematic evaluation and downstream analyses. To evaluate performance, we collect and reproduce a range of scRNA-seq clustering methods, including traditional, deep learning-based, graph-based, and biological foundation models. We comprehensively evaluate each method both quantitatively and qualitatively, using core performance metrics as well as visualization analyses. Furthermore, we construct representative downstream biological tasks, such as marker gene identification and cell type annotation, to further assess the practical utility. scCluBench then investigates the performance differences and applicability boundaries of various clustering models across diverse analytical tasks, systematically assessing their robustness and scalability in real-world scenarios. Overall, scCluBench offers a standardized and user-friendly benchmark for scRNA-seq clustering, with curated datasets, unified evaluation protocols, and transparent analyses, facilitating informed method selection and providing valuable insights into model generalizability and application scope.
 2511.19068
2511.19068Modern genomic analyses increasingly rely on pangenomes, that is, representations of the genome of entire populations. The simplest representation of a pangenome is a set of individual genome sequences. Compared to e.g. sequence graphs, this has the advantage that efficient exact search via indexes based on the Burrows-Wheeler Transform (BWT) is possible, that no chimeric sequences are created, and that the results are not influenced by heuristics. However, such an index may report a match in thousands of positions even if these all correspond to the same locus, making downstream analysis unnecessarily expensive. For sufficiently similar sequences (e.g. human chromosomes), a multiple sequence alignment (MSA) can be computed. Since an MSA tends to group similar strings in the same columns, it is likely that a string occurring thousands of times in the pangenome can be described by very few columns in the MSA. We describe a method to tag entries in the BWT with the corresponding column in the MSA and develop an index that can map matches in the BWT to columns in the MSA in time proportional to the output. As a by-product, we can efficiently project a match to a designated reference genome, a capability that current pangenome aligners based on the BWT lack.
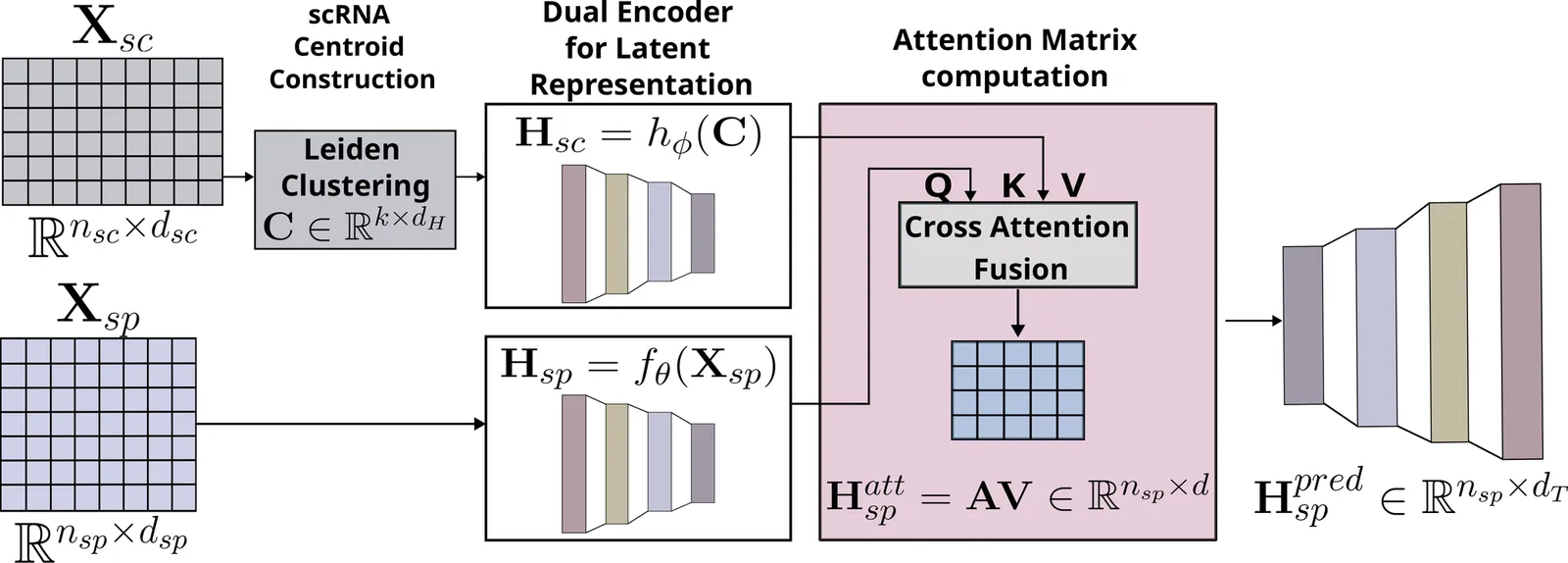
Spatial Transcriptomics enables mapping of gene expression within its native tissue context, but current platforms measure only a limited set of genes due to experimental constraints and excessive costs. To overcome this, computational models integrate Single-Cell RNA Sequencing data with Spatial Transcriptomics to predict unmeasured genes. We propose CASPER, a cross-attention based framework that predicts unmeasured gene expression in Spatial Transcriptomics by leveraging centroid-level representations from Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. We performed rigorous testing over four state-of-the-art Spatial Transcriptomics/Single-Cell RNA Sequencing dataset pairs across four existing baseline models. CASPER shows significant improvement in nine out of the twelve metrics for our experiments. This work paves the way for further work in Spatial Transcriptomics to Single-Cell RNA Sequencing modality translation. The code for CASPER is available at https://github.com/AI4Med-Lab/CASPER.
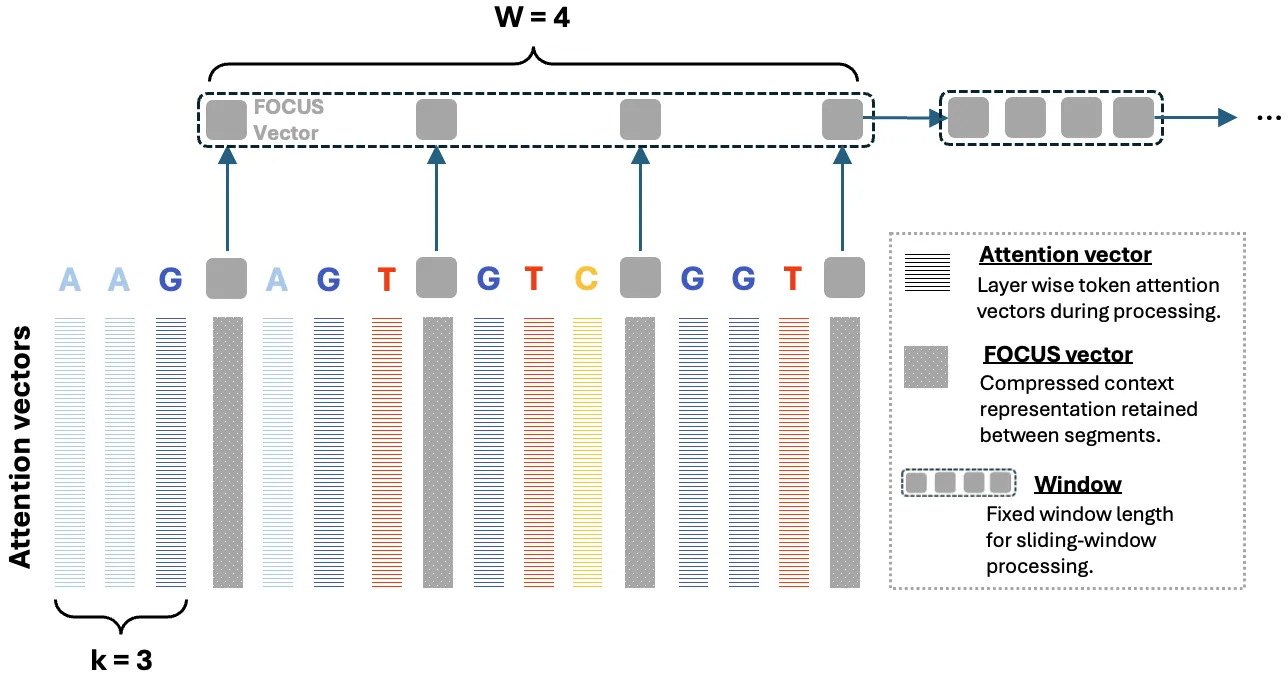
Trained on massive cross-species DNA corpora, DNA large language models (LLMs) learn the fundamental "grammar" and evolutionary patterns of genomic sequences. This makes them powerful priors for DNA sequence modeling, particularly over long ranges. However, two major constraints hinder their use in practice: the quadratic computational cost of self-attention and the growing memory required for key-value (KV) caches during autoregressive decoding. These constraints force the use of heuristics such as fixed-window truncation or sliding windows, which compromise fidelity on ultra-long sequences by discarding distant information. We introduce FOCUS (Feature-Oriented Compression for Ultra-long Self-attention), a progressive context-compression module that can be plugged into pretrained DNA LLMs. FOCUS combines the established k-mer representation in genomics with learnable hierarchical compression: it inserts summary tokens at k-mer granularity and progressively compresses attention key and value activations across multiple Transformer layers, retaining only the summary KV states across windows while discarding ordinary-token KV. A shared-boundary windowing scheme yields a stationary cross-window interface that propagates long-range information with minimal loss. We validate FOCUS on an Evo-2-based DNA LLM fine-tuned on GRCh38 chromosome 1 with self-supervised training and randomized compression schedules to promote robustness across compression ratios. On held-out human chromosomes, FOCUS achieves near-lossless fidelity: compressing a 1 kb context into only 10 summary tokens (about 100x) shifts the average per-nucleotide probability by only about 0.0004. Compared to a baseline without compression, FOCUS reduces KV-cache memory and converts effective inference scaling from O(N^2) to near-linear O(N), enabling about 100x longer inference windows on commodity GPUs with near-lossless fidelity.
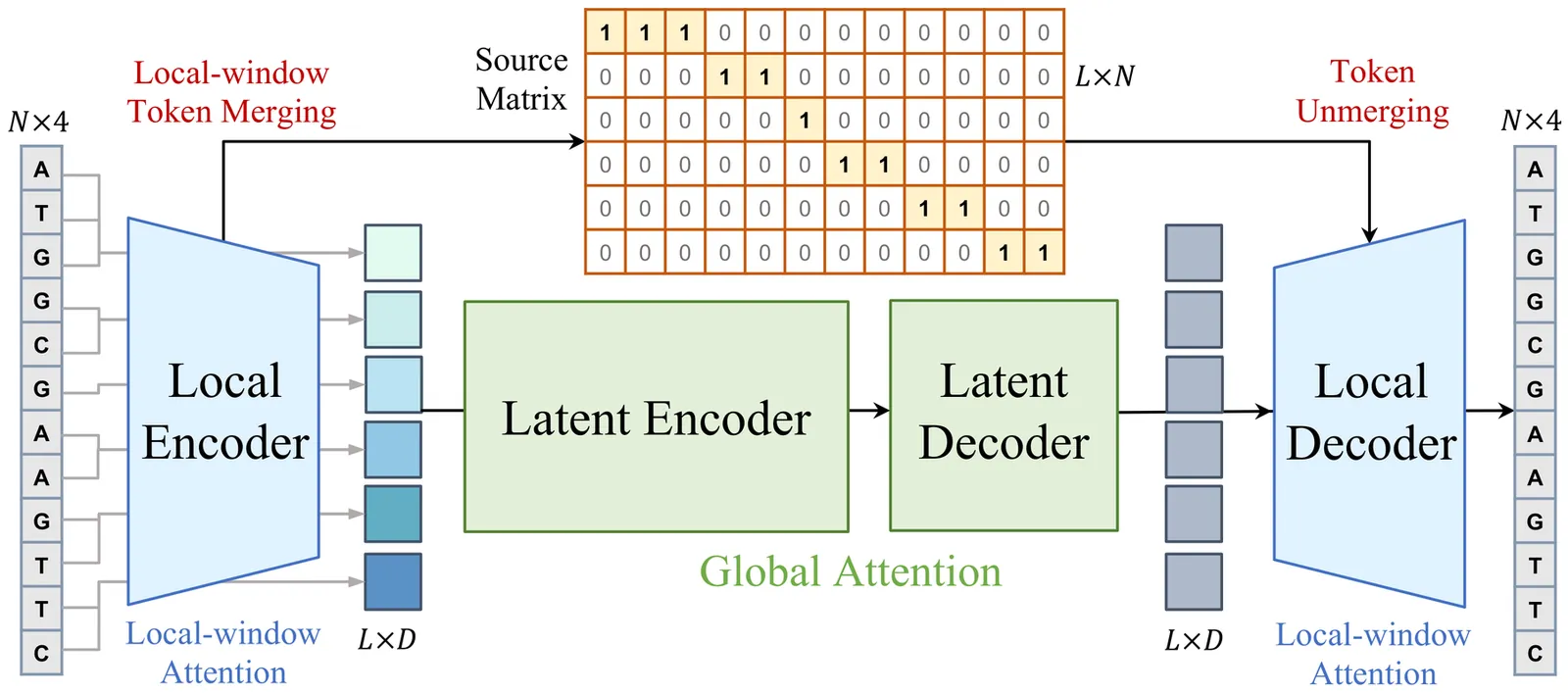
Modeling genomic sequences faces two unsolved challenges: the information density varies widely across different regions, while there is no clearly defined minimum vocabulary unit. Relying on either four primitive bases or independently designed DNA tokenizers, existing approaches with naive masked language modeling pre-training often fail to adapt to the varying complexities of genomic sequences. Leveraging Token Merging techniques, this paper introduces a hierarchical architecture that jointly optimizes a dynamic genomic tokenizer and latent Transformers with context-aware pre-training tasks. As for network structures, the tokenization module automatically chunks adjacent bases into words by stacking multiple layers of the differentiable token merging blocks with local-window constraints, then a Latent Encoder captures the global context of these merged words by full-attention blocks. Symmetrically employing a Latent Decoder and a Local Decoder, MergeDNA learns with two pre-training tasks: Merged Token Reconstruction simultaneously trains the dynamic tokenization module and adaptively filters important tokens, while Adaptive Masked Token Modeling learns to predict these filtered tokens to capture informative contents. Extensive experiments show that MergeDNA achieves superior performance on three popular DNA benchmarks and several multi-omics tasks with fine-tuning or zero-shot evaluation, outperforming typical tokenization methods and large-scale DNA foundation models.
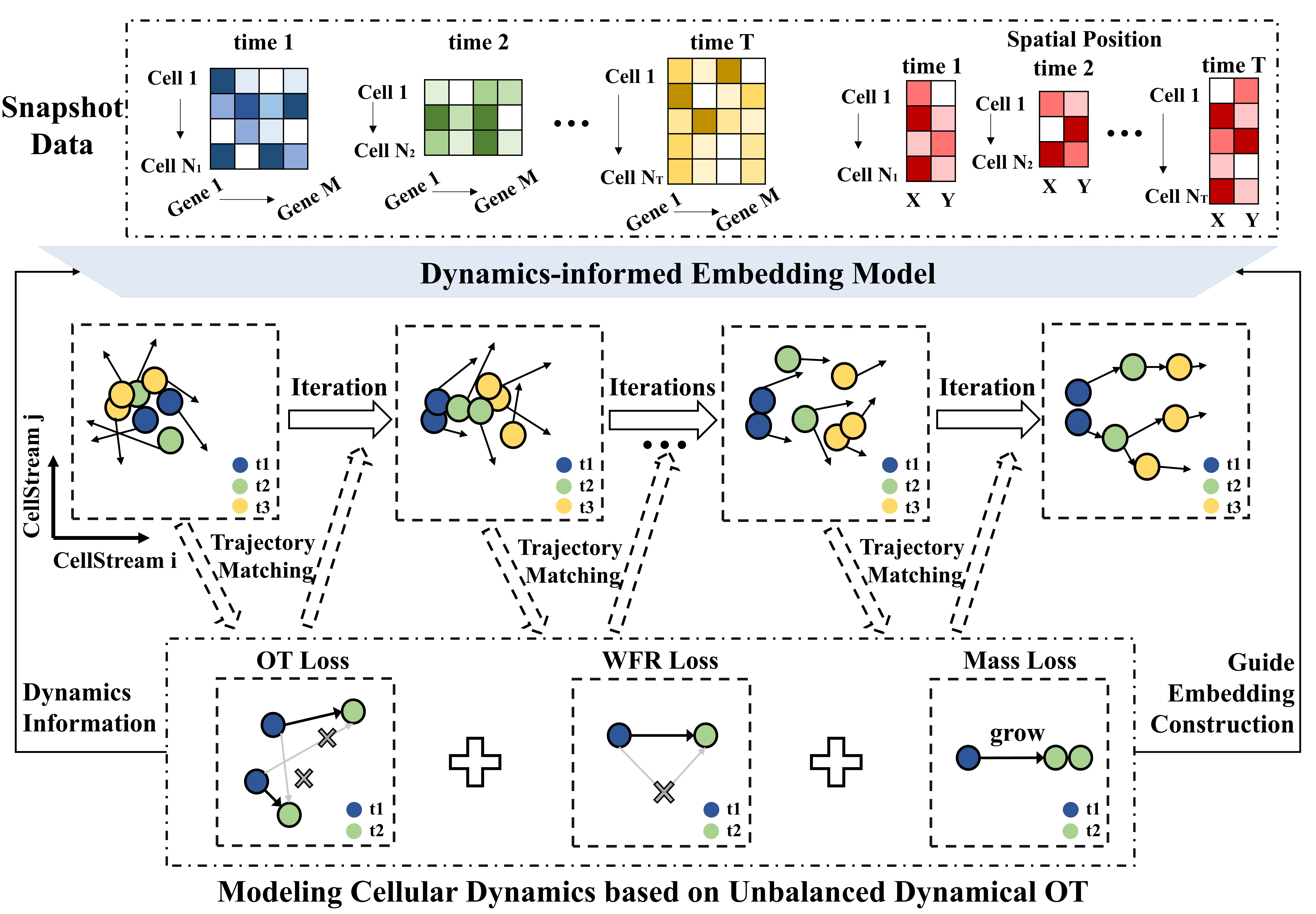
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), especially temporally resolved datasets, enables genome-wide profiling of gene expression dynamics at single-cell resolution across discrete time points. However, current technologies provide only sparse, static snapshots of cell states and are inherently influenced by technical noise, complicating the inference and representation of continuous transcriptional dynamics. Although embedding methods can reduce dimensionality and mitigate technical noise, the majority of existing approaches typically treat trajectory inference separately from embedding construction, often neglecting temporal structure. To address this challenge, here we introduce CellStream, a novel deep learning framework that jointly learns embedding and cellular dynamics from single-cell snapshot data by integrating an autoencoder with unbalanced dynamical optimal transport. Compared to existing methods, CellStream generates dynamics-informed embeddings that robustly capture temporal developmental processes while maintaining high consistency with the underlying data manifold. We demonstrate CellStream's effectiveness on both simulated datasets and real scRNA-seq data, including spatial transcriptomics. Our experiments indicate significant quantitative improvements over state-of-the-art methods in representing cellular trajectories with enhanced temporal coherence and reduced noise sensitivity. Overall, CellStream provides a new tool for learning and representing continuous streams from the noisy, static snapshots of single-cell gene expression.
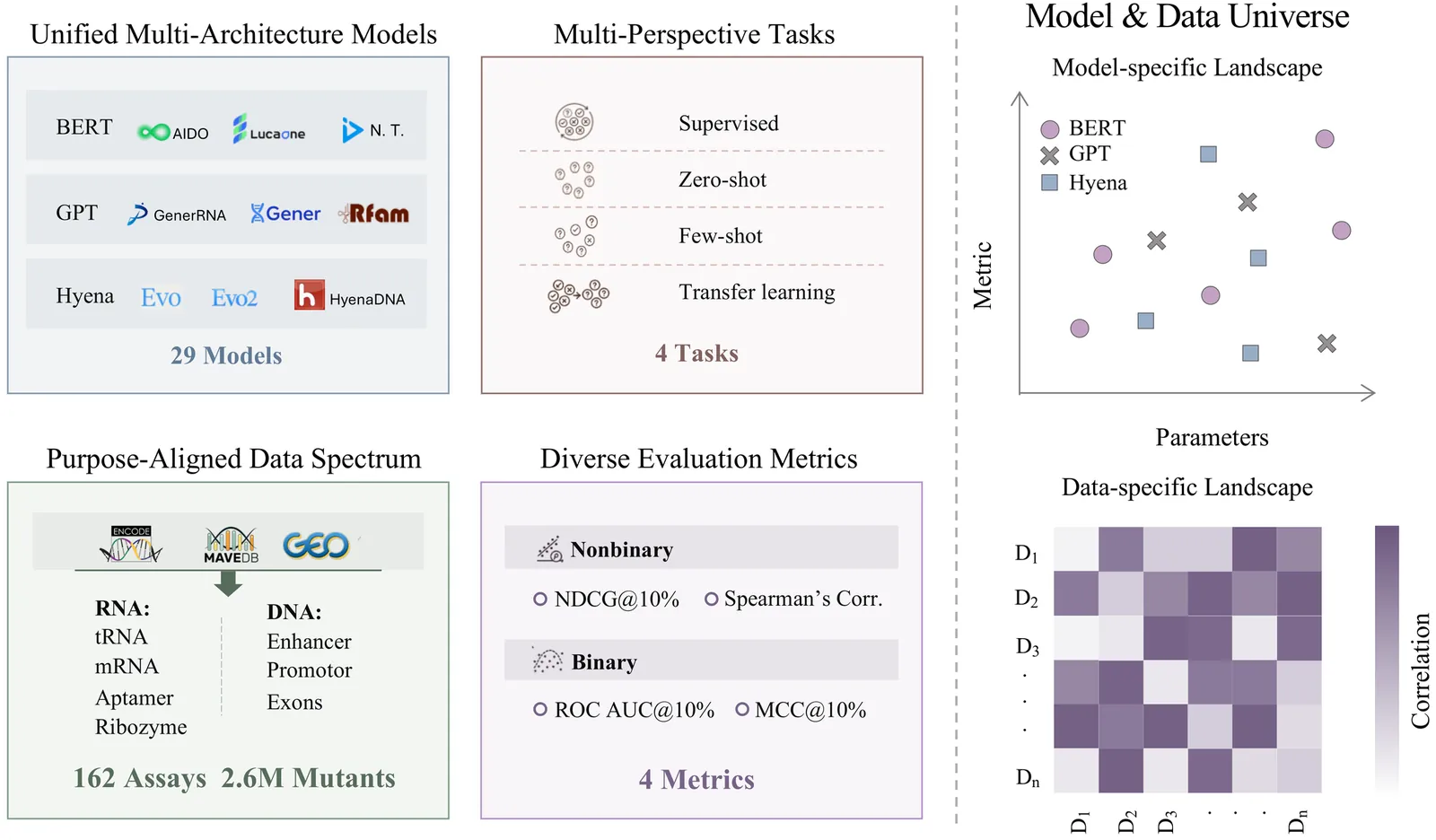
Nucleotide sequence variation can induce significant shifts in functional fitness. Recent nucleotide foundation models promise to predict such fitness effects directly from sequence, yet heterogeneous datasets and inconsistent preprocessing make it difficult to compare methods fairly across DNA and RNA families. Here we introduce NABench, a large-scale, systematic benchmark for nucleic acid fitness prediction. NABench aggregates 162 high-throughput assays and curates 2.6 million mutated sequences spanning diverse DNA and RNA families, with standardized splits and rich metadata. We show that NABench surpasses prior nucleotide fitness benchmarks in scale, diversity, and data quality. Under a unified evaluation suite, we rigorously assess 29 representative foundation models across zero-shot, few-shot prediction, transfer learning, and supervised settings. The results quantify performance heterogeneity across tasks and nucleic-acid types, demonstrating clear strengths and failure modes for different modeling choices and establishing strong, reproducible baselines. We release NABench to advance nucleic acid modeling, supporting downstream applications in RNA/DNA design, synthetic biology, and biochemistry. Our code is available at https://github.com/mrzzmrzz/NABench.
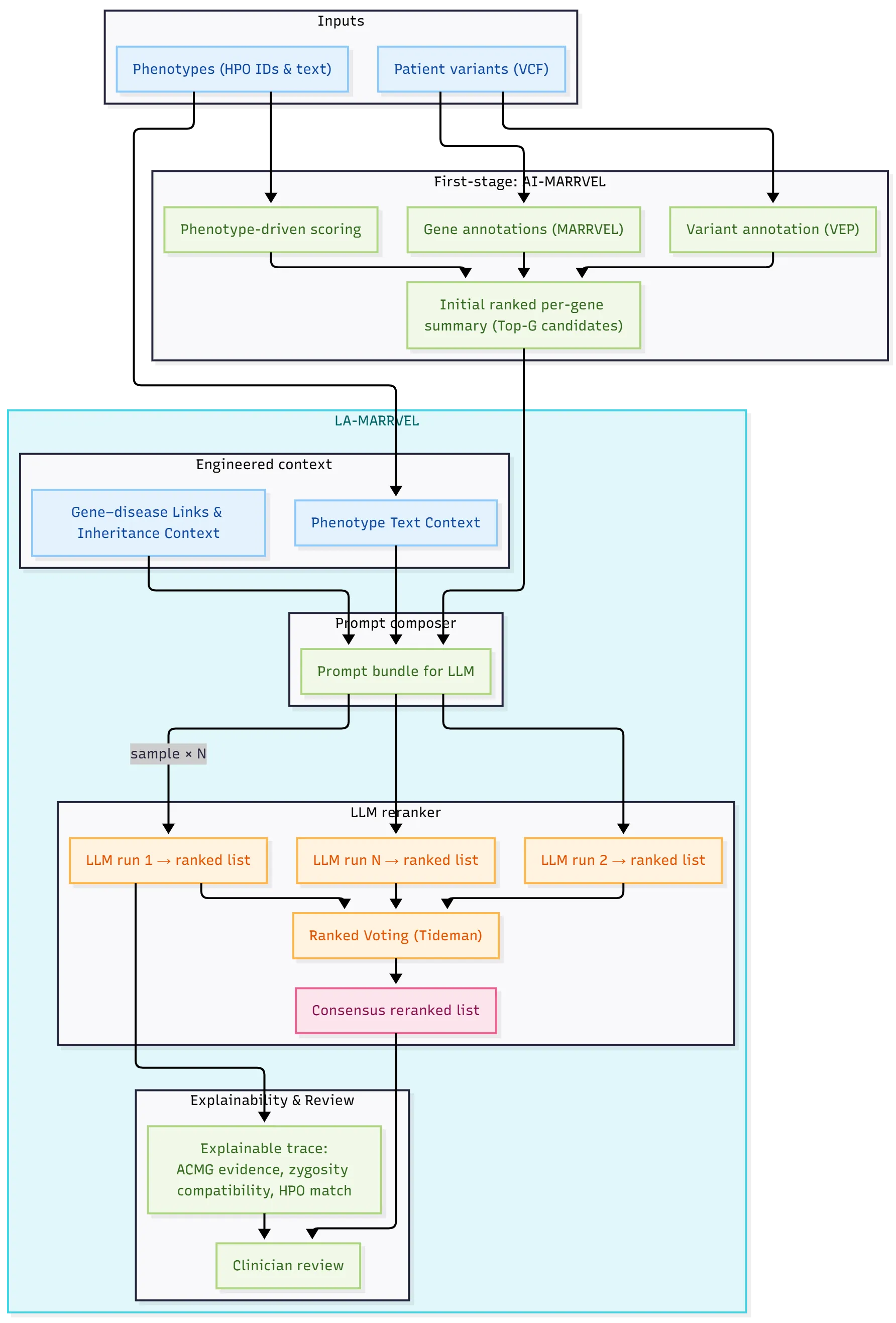
Diagnosing rare diseases requires linking gene findings with often unstructured reference text. Current pipelines collect many candidate genes, but clinicians still spend a lot of time filtering false positives and combining evidence from papers and databases. A key challenge is language: phenotype descriptions and inheritance patterns are written in prose, not fully captured by tables. Large language models (LLMs) can read such text, but clinical use needs grounding in citable knowledge and stable, repeatable behavior. We explore a knowledge-grounded and language-aware reranking layer on top of a high-recall first-stage pipeline. The goal is to improve precision and explainability, not to replace standard bioinformatics steps. We use expert-built context and a consensus method to reduce LLM variability, producing shorter, better-justified gene lists for expert review. LA-MARRVEL achieves the highest accuracy, outperforming other methods -- including traditional bioinformatics diagnostic tools (AI-MARRVEL, Exomiser, LIRICAL) and naive large language models (e.g., Anthropic Claude) -- with an average Recall@5 of 94.10%, a +3.65 percentage-point improvement over AI-MARRVEL. The LLM-generated reasoning provides clear prose on phenotype matching and inheritance patterns, making clinical review faster and easier. LA-MARRVEL has three parts: expert-engineered context that enriches phenotype and disease information; a ranked voting algorithm that combines multiple LLM runs to choose a consensus ranked gene list; and the AI-MARRVEL pipeline that provides first-stage ranks and gene annotations, already known as a state-of-the-art method in Rare Disease Diagnosis on BG, DDD, and UDN cohorts. The online AI-MARRVEL includes LA-MARRVEL as an LLM feature at https://ai.marrvel.org . We evaluate LA-MARRVEL on three datasets from independent cohorts of real-world diagnosed patients.

Introduction: Epigenomic datasets from high-throughput sequencing experiments are commonly summarized as genomic intervals. As the volume of this data grows, so does interest in analyzing it through deep learning. However, the heterogeneity of genomic interval data, where each dataset defines its own regions, creates barriers for machine learning methods that require consistent, discrete vocabularies. Methods: We introduce gtars-tokenizers, a high-performance library that maps genomic intervals to a predefined universe or vocabulary of regions, analogous to text tokenization in natural language processing. Built in Rust with bindings for Python, R, CLI, and WebAssembly, gtars-tokenizers implements two overlap methods (BITS and AIList) and integrates seamlessly with modern ML frameworks through Hugging Face-compatible APIs. Results: The gtars-tokenizers package achieves top efficiency for large-scale datasets, while enabling genomic intervals to be processed using standard ML workflows in PyTorch and TensorFlow without ad hoc preprocessing. This token-based approach bridges genomics and machine learning, supporting scalable and standardized analysis of interval data across diverse computational environments. Availability: PyPI and GitHub: https://github.com/databio/gtars.
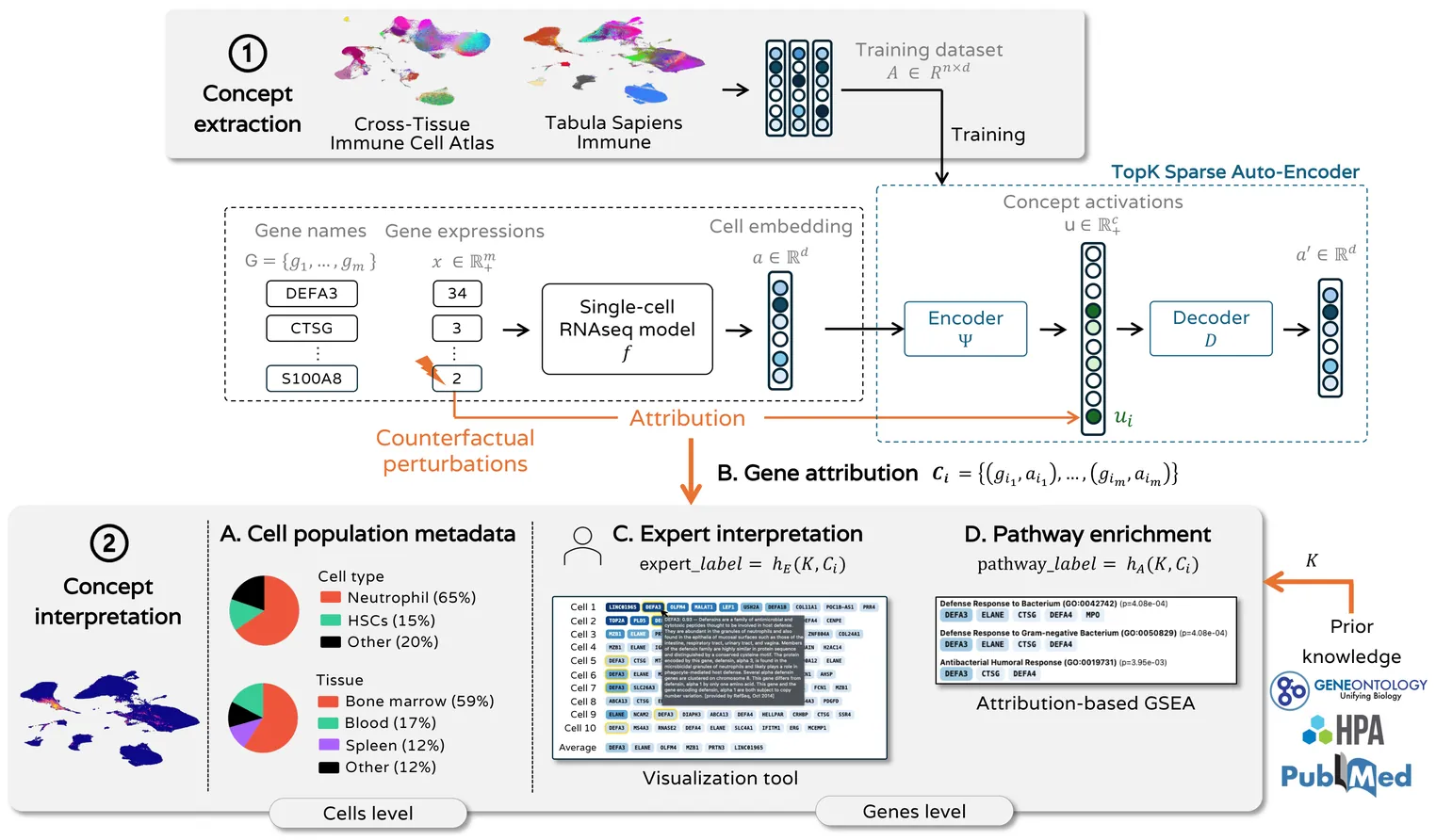
Single-cell RNA-seq foundation models achieve strong performance on downstream tasks but remain black boxes, limiting their utility for biological discovery. Recent work has shown that sparse dictionary learning can extract concepts from deep learning models, with promising applications in biomedical imaging and protein models. However, interpreting biological concepts remains challenging, as biological sequences are not inherently human-interpretable. We introduce a novel concept-based interpretability framework for single-cell RNA-seq models with a focus on concept interpretation and evaluation. We propose an attribution method with counterfactual perturbations that identifies genes that influence concept activation, moving beyond correlational approaches like differential expression analysis. We then provide two complementary interpretation approaches: an expert-driven analysis facilitated by an interactive interface and an ontology-driven method with attribution-based biological pathway enrichment. Applying our framework to two well-known single-cell RNA-seq models from the literature, we interpret concepts extracted by Top-K Sparse Auto-Encoders trained on two immune cell datasets. With a domain expert in immunology, we show that concepts improve interpretability compared to individual neurons while preserving the richness and informativeness of the latent representations. This work provides a principled framework for interpreting what biological knowledge foundation models have encoded, paving the way for their use for hypothesis generation and discovery.
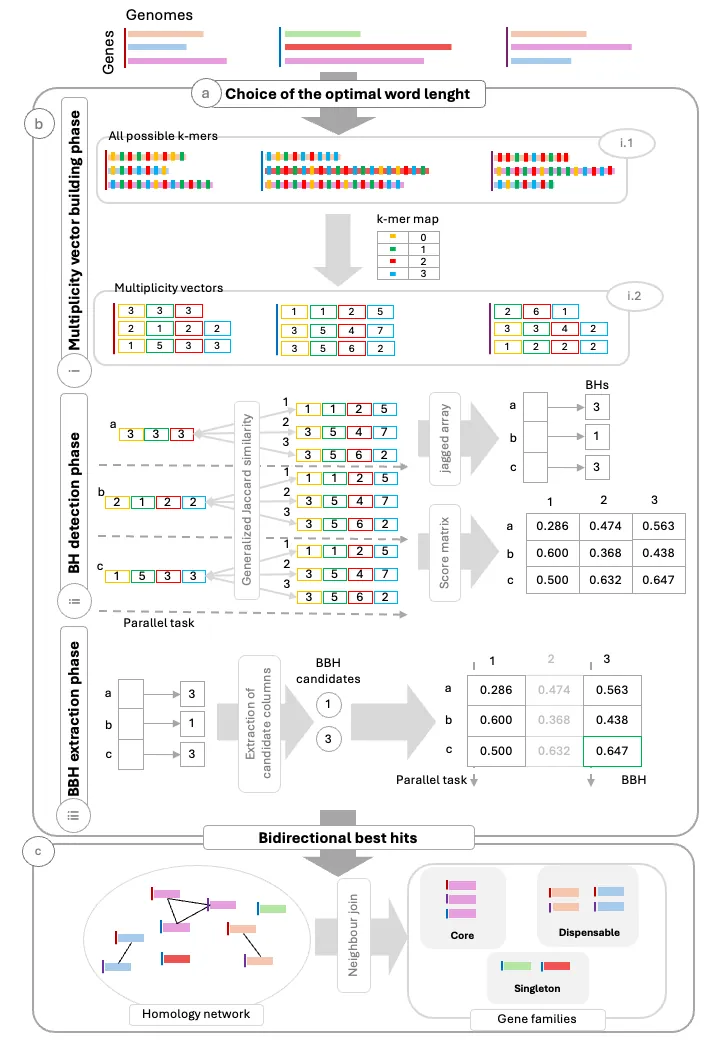
The identification of homologous gene families across multiple genomes is a central task in bacterial pangenomics traditionally requiring computationally demanding all-against-all comparisons. PanDelos addresses this challenge with an alignment-free and parameter-free approach based on k-mer profiles, combining high speed, ease of use, and competitive accuracy with state-of-the-art methods. However, the increasing availability of genomic data requires tools that can scale efficiently to larger datasets. To address this need, we present PanDelos-plus, a fully parallel, gene-centric redesign of PanDelos. The algorithm parallelizes the most computationally intensive phases (Best Hit detection and Bidirectional Best Hit extraction) through data decomposition and a thread pool strategy, while employing lightweight data structures to reduce memory usage. Benchmarks on synthetic datasets show that PanDelos-plus achieves up to 14x faster execution and reduces memory usage by up to 96%, while maintaining accuracy. These improvements enable population-scale comparative genomics to be performed on standard multicore workstations, making large-scale bacterial pangenome analysis accessible for routine use in everyday research.
Cancer exhibits diverse and complex phenotypes driven by multifaceted molecular interactions. Recent biomedical research has emphasized the comprehensive study of such diseases by integrating multi-omics datasets (genome, proteome, transcriptome, epigenome). This approach provides an efficient method for identifying genetic variants associated with cancer and offers a deeper understanding of how the disease develops and spreads. However, it is challenging to comprehend complex interactions among the features of multi-omics datasets compared to single omics. In this paper, we analyze lung cancer multi-omics datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Using four statistical methods, LIMMA, the T test, Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA), and the Wilcoxon test, we identified differentially expressed genes across gene expression, DNA methylation, and miRNA expression data. We then integrated these multi-omics data using the Kernel Machine Regression (KMR) approach. Our findings reveal significant interactions among the three omics: gene expression, miRNA expression, and DNA methylation in lung cancer. From our data analysis, we identified 38 genes significantly associated with lung cancer. From our data analysis, we identified 38 genes significantly associated with lung cancer. Among these, eight genes of highest ranking (PDGFRB, PDGFRA, SNAI1, ID1, FGF11, TNXB, ITGB1, ZIC1) were highlighted by rigorous statistical analysis. Furthermore, in silico studies identified three top-ranked potential candidate drugs (Selinexor, Orapred, and Capmatinib) that could play a crucial role in the treatment of lung cancer. These proposed drugs are also supported by the findings of other independent studies, which underscore their potential efficacy in the fight against lung cancer.
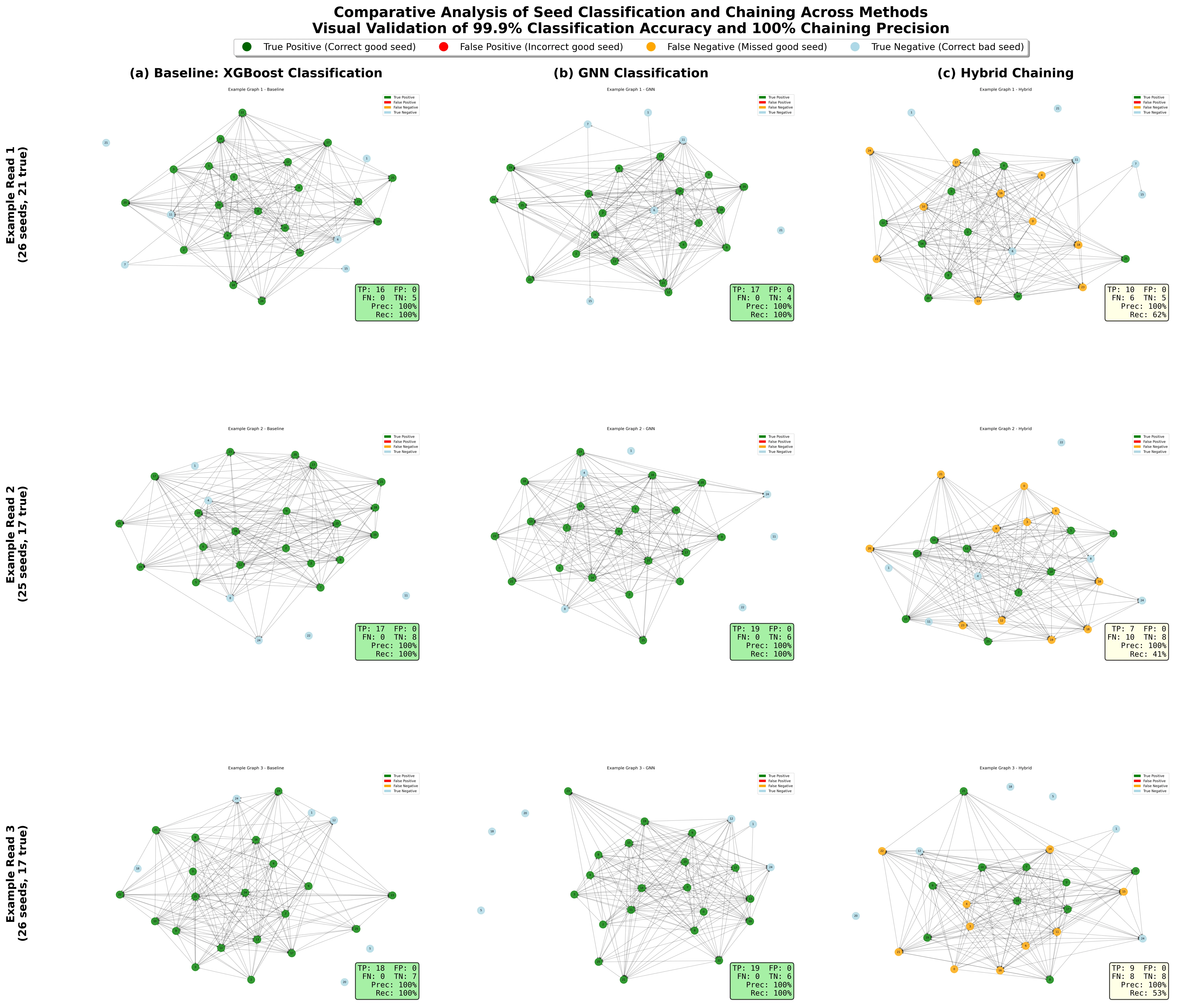
Nanopore sequencing enables real-time long-read DNA sequencing with reads exceeding 10 kilobases, but inherent error rates of 12-15 percent present significant computational challenges for read alignment. The critical seed chaining step must connect exact k-mer matches between reads and reference genomes while filtering spurious matches, yet state-of-the-art methods rely on fixed gap penalty functions unable to adapt to varying genomic contexts including tandem repeats and structural variants. This paper presents RawHash3, a hybrid framework combining graph neural networks with classical dynamic programming for adaptive seed chaining that maintains real-time performance while providing statistical guarantees. We formalize seed chaining as graph learning where seeds constitute nodes with 12-dimensional feature vectors and edges encode 8-dimensional spatial relationships including gap consistency. Our architecture employs three-layer EdgeConv GNN with confidence-based method selection that dynamically switches between learned guidance and algorithmic fallback. Comprehensive evaluation on 1,000 synthetic nanopore reads with 5,200 test seeds demonstrates RawHash3 achieves 99.94 percent precision and 40.07 percent recall, representing statistically significant 25.0 percent relative improvement over baseline with p less than 0.001. The system maintains median inference latency of 1.59ms meeting real-time constraints, while demonstrating superior robustness with 100 percent success rate under 20 percent label corruption versus baseline degradation to 30.3 percent. Cross-validation confirms stability establishing graph neural networks as viable approach for production genomics pipelines.
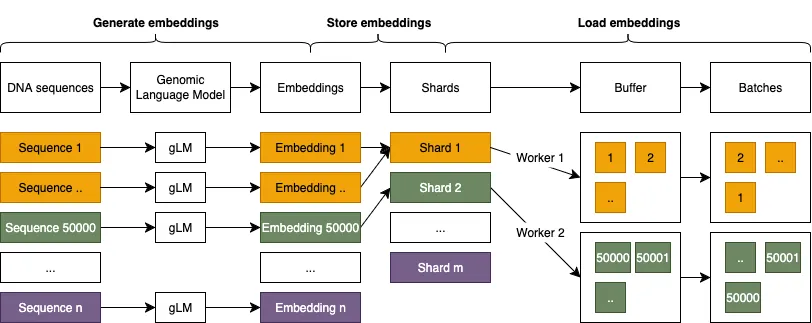
Large Language Models are increasingly popular in genomics due to their potential to decode complex biological sequences. Hence, researchers require a standardized benchmark to evaluate DNA Language Models (DNA LMs) capabilities. However, evaluating DNA LMs is a complex task that intersects genomic's domain-specific challenges and machine learning methodologies, where seemingly minor implementation details can significantly compromise benchmark validity. We demonstrate this through BEND (Benchmarking DNA Language Models), where hardware-dependent hyperparameters -- number of data loading workers and buffer sizes -- create spurious performance variations of up to 4% for identical models. The problem stems from inadequate data shuffling interacting with domain specific data characteristics. Experiments with three DNA language models (HyenaDNA, DNABERT-2, ResNet-LM) show these artifacts affect both absolute performance and relative model rankings. We propose a simple solution: pre-shuffling data before storage eliminates hardware dependencies while maintaining efficiency. This work highlights how standard ML practices can interact unexpectedly with domain-specific data characteristics, with broader implications for benchmark design in specialized domains.