General Mathematics
Mathematical material of general interest, broadly accessible to all mathematicians.
Mathematical material of general interest, broadly accessible to all mathematicians.
 2512.20686
2512.20686Divisor methods are well known to satisfy house monotonicity, which allows representative seats to be allocated sequentially. We focus on stationary divisor methods defined by a rounding cut point $c \in [0,1]$. For such methods with integer-valued votes, the resulting apportionment sequences are periodic. Restricting attention to two-party allocations, we characterize the set of possible sequences and establish a connection between the lexicographical ordering of these sequences and the parameter $c$. We then show how sequences for all pairs of parties can be systematically extended to the $n$-party setting. Further, we determine the number of distinct sequences in the $n$-party problem for all $c$. Our approach offers a refined perspective on large-party bias: rather than viewing large parties as simply receiving more seats, we show that they instead obtain their seats earlier in the apportionment sequence. Of particular interest is a new relationship we uncover between the sequences generated by the smallest divisors (Adams) and greatest divisors (d'Hondt or Jefferson) methods.
 2512.01154
2512.01154Let $θ:[0,1]\rightarrow[-\infty,+\infty]$ be a function with both $θ(x^{-})$ and $θ(x^{+})$ existing for every $x\in [0,1]$ and $\vartheta:[-\infty,+\infty]\rightarrow[-\infty,+\infty]$ be a function. In this article we completely characterize the pair $(θ,\vartheta)$ for the bivariate function $O_{θ,\vartheta}: [0,1]^{2}\rightarrow[0,1]$ given by $$O_{θ,\vartheta}(x,y)=\vartheta(θ(x)+θ(y))$$ being an overlap function. In particular, we give analytical expressions of some transformations for the pair $(θ,\vartheta)$.
 2512.03085
2512.03085We study a Fejer-type smoothing kernel on the finite cyclic group Z/NZ. For each smoothing radius we give explicit l1 and l2 norms, compute the discrete Fourier transform, and record bounds that are uniform in N. As an application we prove a smoothed discrepancy estimate with explicit constants that can be used in quantitative problems on finite cyclic groups. The arguments are elementary and the note is intended as a self contained reference.
 2511.21776
2511.21776In this work, we consider four theorems that can be used to prove the irrationality of $π$. These theorems are related to nested radicals with roots of $2$ of kind $c_k = \sqrt{2 + c_{k - 1}} $ and $c_0 = 0$. Sample computations showing how the rational approximation tend to $π$ with increasing the integer $k$ are presented.
 2511.21765
2511.21765Given l<s<m an upper bound on the s norm is given using l norm and m norm. The result is applied in bounding odd values of zeta function, binomial sums and gamma and beta functions.
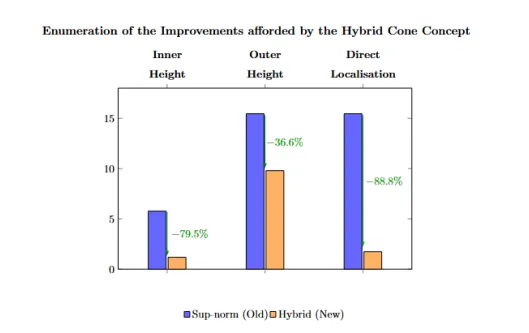
We investigate a class of variable growth nonlocal differential equations of Kirchhoff-type having the general form \(-A\!\left(\int_0^1 b(1-s)\,\big(u(s)\big)^{p(s)}\,ds\right)\,u''(t) = λ\,f(t,u(t))\) for \(t\in(0,1)\), where \(A\) is a possibly sign-changing function. Our analysis is carried out in the variable-exponent Lebesgue space \(L^{p(\cdot)}([0,1])\) under the standing hypothesis \(p(t)>1\). We demonstrate that using the Luxemburg norm allows for a much sharper localisation of the solution to the nonlocal problem. Moreover, the conditions imposed on both \(λ\) and \(f\) are appreciably weakened when the problem is analysed within the Luxemburg norm framework. An example explicitly demonstrates both the qualitative and quantitative advantages over earlier techniques.
 2512.00071
2512.00071This paper develops a Mellin-Laplace analytic framework for the fixed-shift prime correlation r_h(n) = Lambda(n) Lambda(n+h) for h not equal to 0. This sequence has no multiplicative structure, no Euler product, and no singularity at s = 1. For every compactly supported Mellin-Laplace admissible kernel W, the smoothed shifted sum S_{W,h}(N) admits an absolutely convergent Mellin representation that holds entirely in the half-plane Re(s) > 1, with no use of analytic continuation. The Mellin transform of W provides quantitative vertical decay, enabling full contour control on the boundary line Re(s) = 1 + eps. A Tauberian boundary analysis shows that both components of the boundary integral grow like N^{1+eps}, while the oscillatory part contributes an unavoidable N^{1+eps} (log N)^2 term. As a result, the boundary integral cannot be decomposed into a dominant main term plus a smaller error term, revealing a structural obstruction to main-term extraction for fixed-shift correlations. These results give a complete analytic description of shifted prime correlations in their natural domain of convergence and clarify the analytic difficulties underlying problems such as the twin prime conjecture.
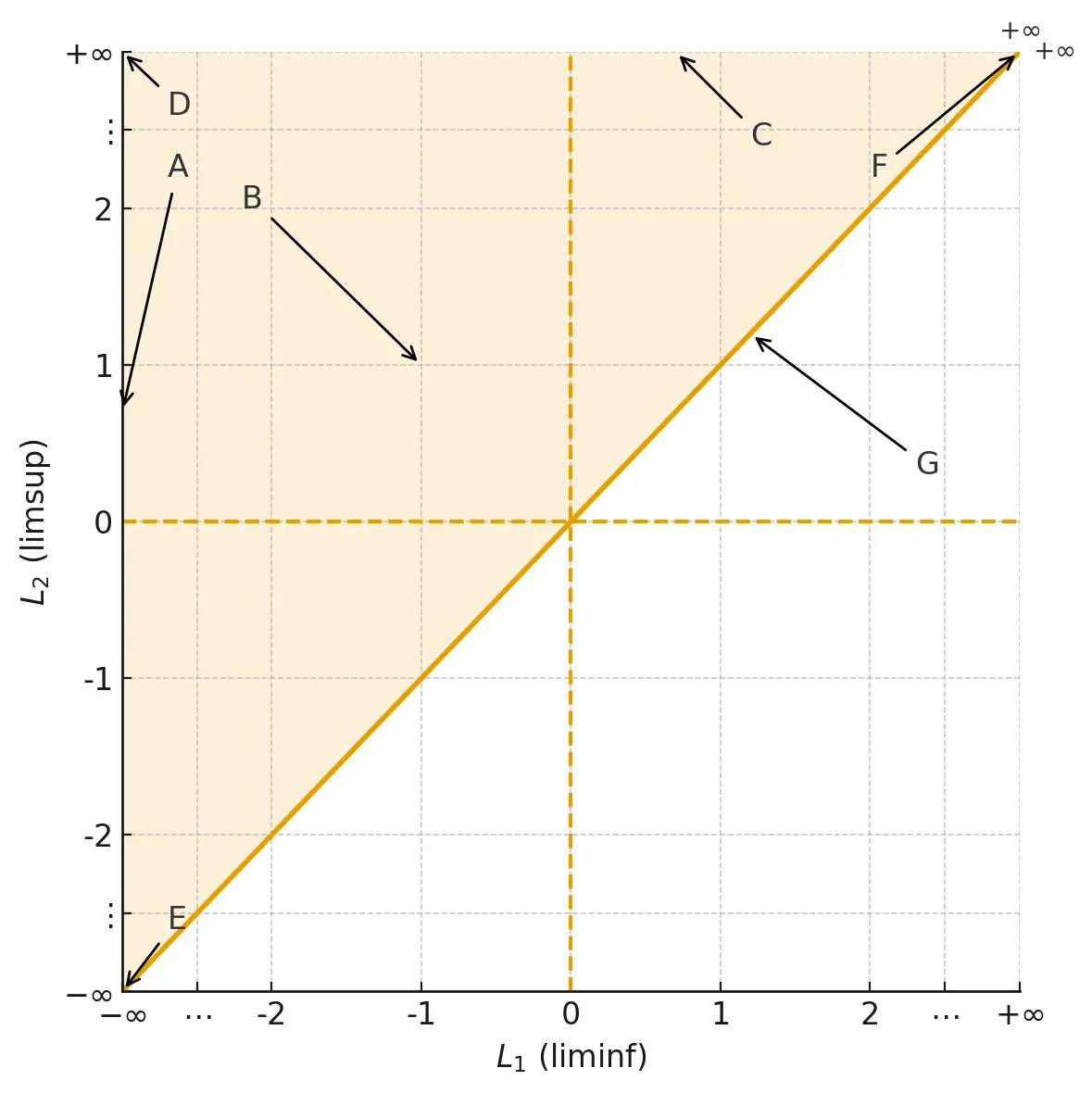
The sequence space of all real-valued sequences, denoted $Seq(\mathbb{R})$, is typically investigated through the lens of infinite-dimensional vector spaces, utilizing Banach space norms or Schauder bases. This work proposes a complementary, constructive classification based instead on the asymptotic limit profile encoded by the pair $(\liminf a_n, \limsup a_n)$. We demonstrate that this perspective naturally partitions $Seq(\mathbb{R})$ into seven mutually disjoint macroscale blocks, covering behaviors from finite convergence to bounded and unbounded oscillation. For each block, we provide explicit closed-form representative sequences and establish that every constituent class possesses the cardinality of the continuum. Furthermore, we investigate the structural relationships between these blocks at two distinct levels of granularity. At the macroscale, we employ injective mappings to define an idealized connectivity graph, while at the microscale, we introduce a connection relation governed by the Hadamard (pointwise) product. This dual analysis reveals a rich directed graph structure where the block of finite convergent sequences functions both as the only block subspace and as a global attractor with no outgoing connections. Statistical comparisons between the idealized and realized adjacency matrices indicate that the pointwise product structure realizes approximately two-thirds of the theoretically possible macroscale relations. Ultimately, this partition-based framework endows the seemingly chaotic space $Seq(\mathbb{R})$ with a transparent, geometrically interpretable internal structure.
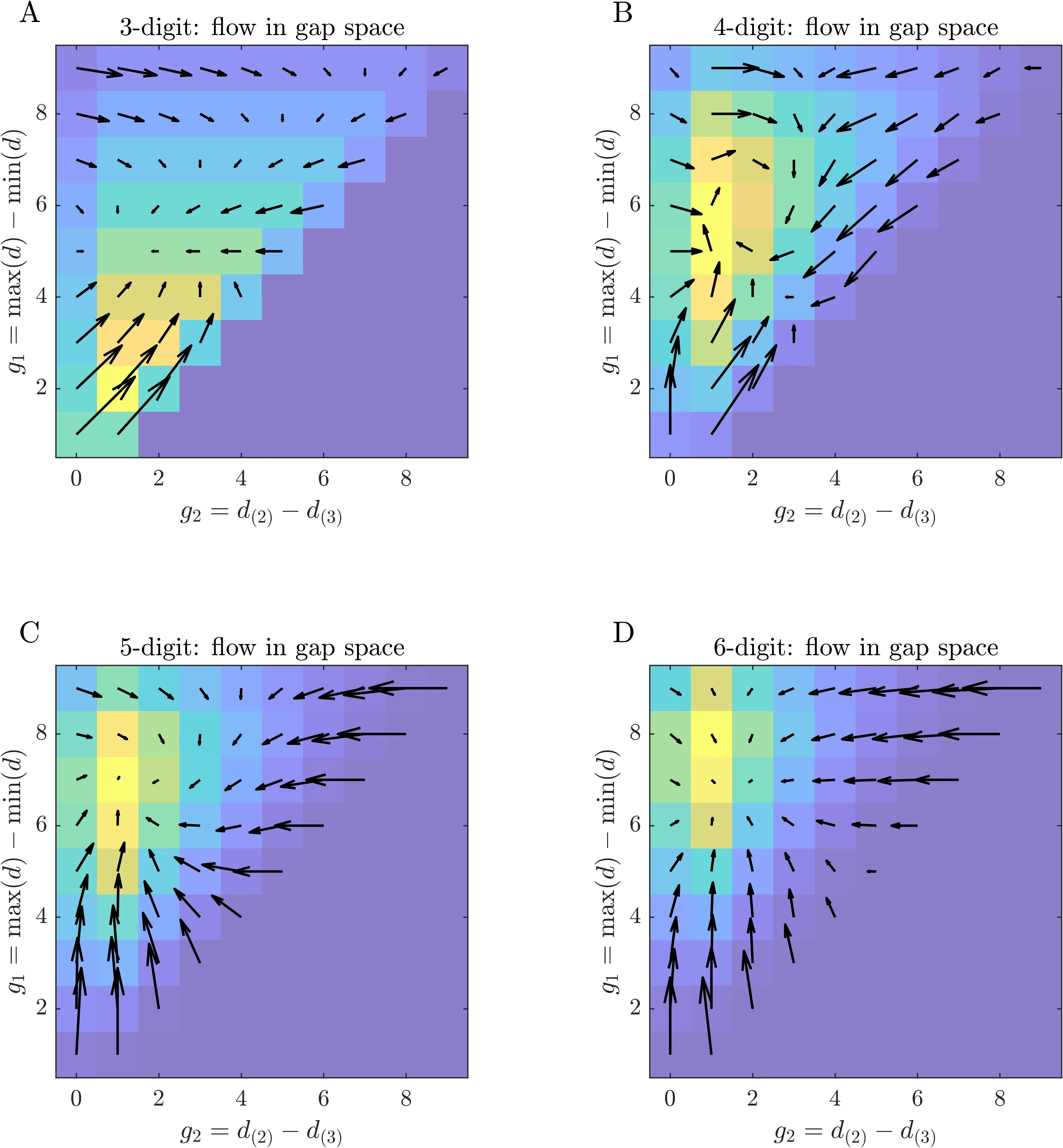
Kaprekar's routine, i.e., sorting the digits of an integer in ascending and descending order and subtracting the two, defines a finite deterministic map on the state space of fixed-length digit strings. While its attractors (such as 495 for D = 3 and 6174 for D = 4) are classical, the global information-theoretic structure of the induced dynamics and its dependence on the digit length D have received little attention. Here an exhaustive analysis is carried out for D in {3,4,5,6}. For each D, all states are enumerated, their attractors and convergence distances are obtained, and the induced distribution over attractors across iterations is used to construct "entropy funnels". Despite the combinatorial growth of the state space, average distances remain small and entropy decays rapidly before entering a slow tail. Permutation symmetry is then exploited by grouping states into digit multisets and, in a further reduction, into low-dimensional digit-gap features. On this gap space, Kaprekar's routine induces a first-order Markov approximation whose transition structure, stationary distribution and drift fields are characterised, showing that simple gap features strongly constrain the dynamics for D=3 but lose predictive power as D increases.
Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) has emerged as a powerfulparadigm for cooperative decision-making in connected autonomous vehicles(CAVs); however, existing approaches often fail to guarantee stability, optimality,and interpretability in systems characterized by nonlinear dynamics,partial observability, and complex inter-agent coupling. This study addressesthese foundational challenges by introducing MARL-CC, a unified MathematicalFramework for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Control Coordination.The proposed framework integrates differential geometric control, Bayesian inference,and Shapley-value-based credit assignment within a coherent optimizationarchitecture, ensuring bounded policy updates, decentralized belief estimation,and equitable reward distribution. Theoretical analyses establish convergence andstability guarantees under stochastic disturbances and communication delays.Empirical evaluations across simulation and real-world testbeds demonstrate upto a 40% improvement in convergence rate and enhanced cooperative efficiencyover leading baselines, including PPO, DDPG, and QMIX.These results signify a decisive advance in control-oriented reinforcement learning,bridging the gap between mathematical rigor and practical autonomy.The MARL-CC framework provides a scalable foundation for intelligent transportation,UAV coordination, and distributed robotics, paving the way toward interpretable, safe, and adaptive multi-agent systems. All codes and experimentalconfigurations are publicly available on GitHub to support reproducibilityand future research.
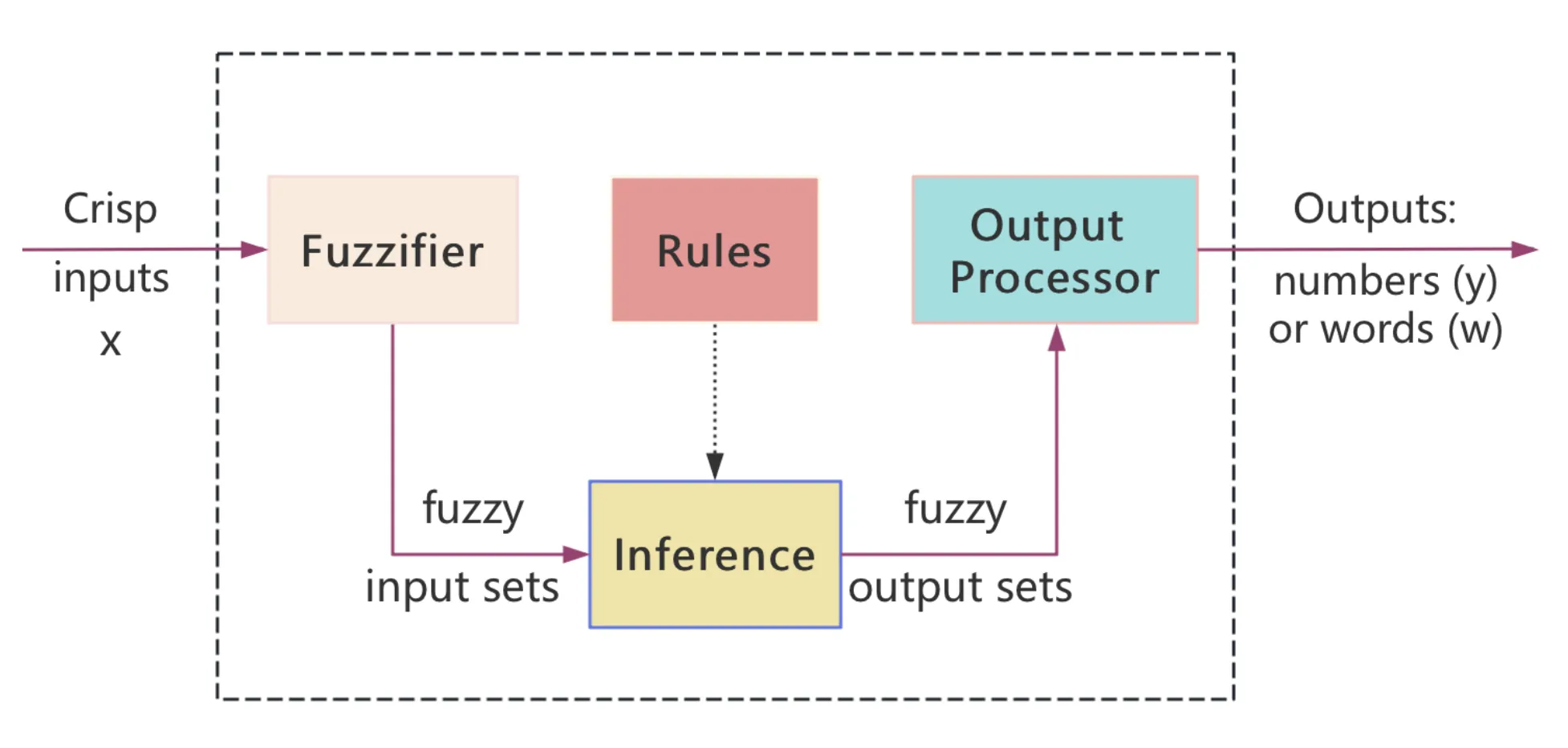
Type-2 fuzzy set (T2 FS) were introduced by Zadeh in 1965, and the membership degrees of T2 FSs are type-1 fuzzy sets (T1 FSs). Owing to the fuzziness of membership degrees, T2 FSs can better model the uncertainty of real life, and thus, type-2 rule-based fuzzy systems (T2 RFSs) become hot research topics in recent decades. In T2 RFS, the compositional rule of inference is based on triangular norms (t-norms) defined on complete lattice $(L,\sqsubseteq)$ ( L is the set of all convex normal functions from [0,1] to [0,1], and , $\sqsubseteq$ is the so-called convolution order). Hence, the choice of t-norm on $(L,\sqsubseteq)$ may influence the performance of T2 RFS. Therefore, it is significant to broad the set of t-norms among which domain experts can choose most suitable one. To construct t-norms on $(L,\sqsubseteq)$, the mainstream method is convolution which is induced by two operators on the unit interval [0,1]. A key problem appears naturally, when convolution is a t-norm on $(L,\sqsubseteq)$. This paper has solved this problem completely. Moreover, note that the computational complexity of operators prevent the application of T2 RFSs. This paper also provides one kind of convolutions which are t-norms on $(L,\sqsubseteq)$ and extremely easy to calculate.
 2511.11774
2511.11774In this paper we develop a duality theory for all finite-dimensional near-vector spaces and introduce a notion of inner product tailored to the broad and natural class of strongly regular near-vector spaces. This generalized construction extends the classical inner product beyond the classical framework, yielding rich families of examples on multiplicative near-vector spaces. Within this setting, several familiar norms-such as those that fail to produce Hilbert spaces in the classical sense-emerge naturally as genuine inner-product-type norms. A further contribution is the extension of the theory of generalized (weighted) means to arbitrary complex datasets. This extension unifies and generalizes the classical power and geometric means, carrying them beyond the domain of positive reals.
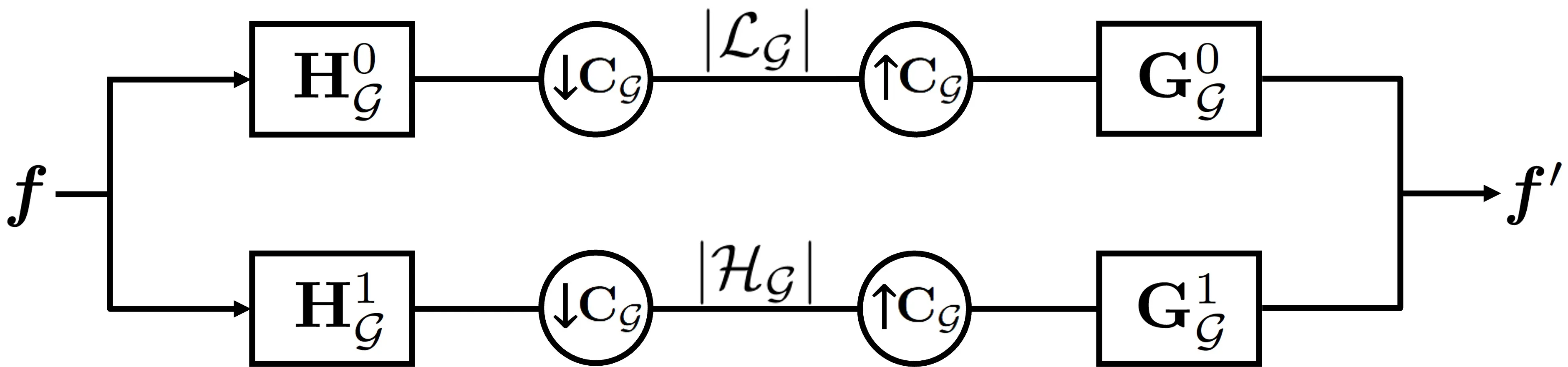
To address the limitations of conventional critically sampled graph filter banks in joint time-vertex signal processing, which require decomposing the joint graph into bipartite subgraphs and thus cannot fully exploit all temporal and spatial edges in a single-stage transform, we introduce the joint time-vertex oversampled graph Laplacian matrix. This operator enables the construction of bipartite extensions that preserve all edges of the original joint graph and supports redundant multiresolution representations. Based on this operator, we design two-channel joint time-vertex oversampled graph filter banks and develop efficient oversampling extensions using a $K$-coloring strategy. The proposed framework is applied to both graph signal and image/video denoising, modeling images as graph signals to leverage structural relationships. Extensive experiments demonstrate its effectiveness in decomposition, reconstruction, and denoising, achieving notable performance improvements over critically sampled and existing methods.
 2511.11744
2511.11744These notes aim to provide a classical approach to solving some conformable differential equations based on prior knowledge of how to solve ordinary differential equations. That is, using the methods of separation of variables, homogeneous equations, linear, Bernoulli and exact. Representative examples are presented in all cases. Emphasis is placed on the new definitions and notations.
We describe some monotone properties of solutions to second order linear difference equations with real constant coefficients. As an application, we give a characterization of the Fibonacci numbers.
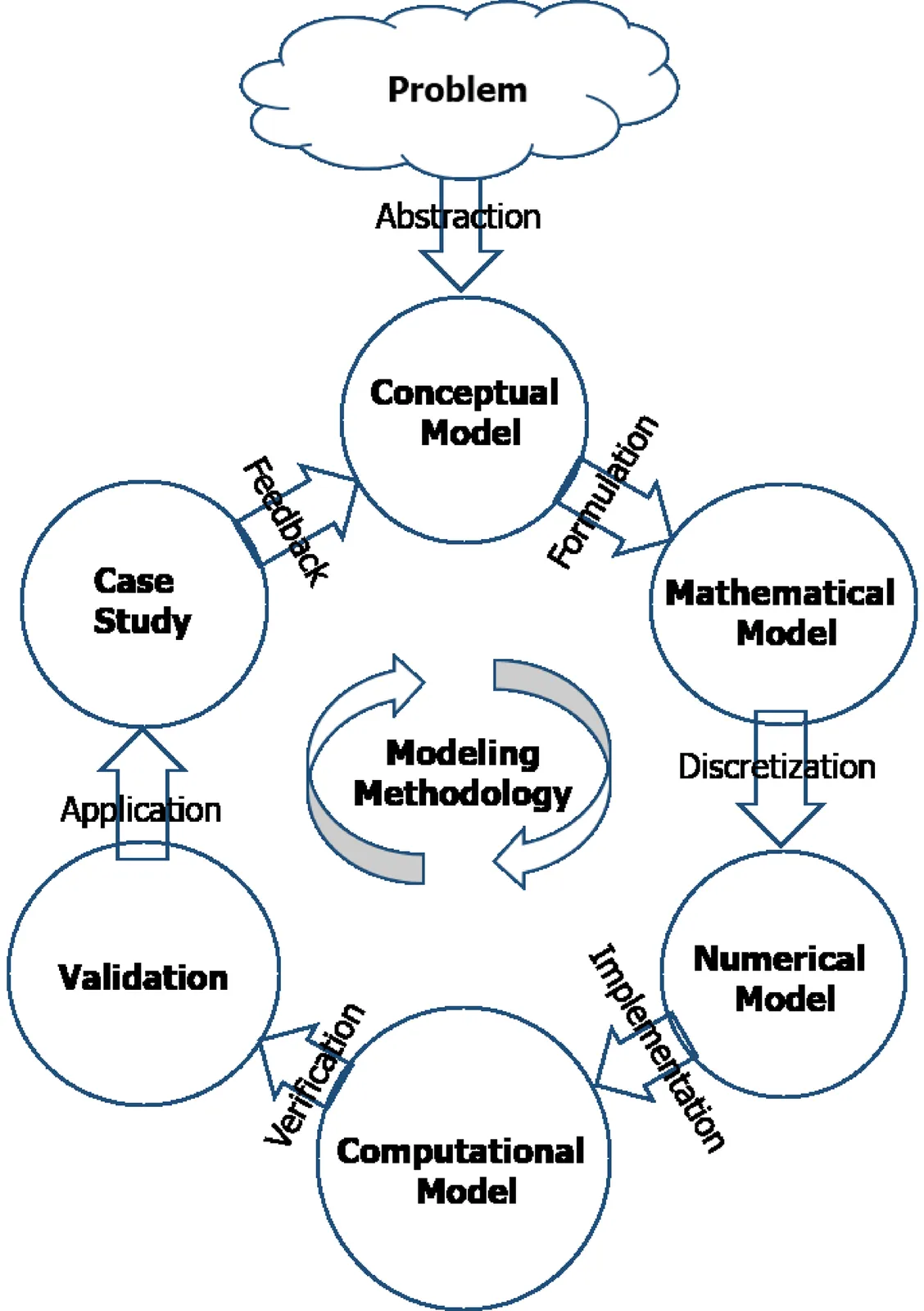
A general 3D flow-and-transport model in porous media is derived using an axiomatic continuum-mechanics approach and implemented with the finite element method to simulate microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR) at core scale under laboratory conditions. The development pipeline (conceptual -> mathematical -> numerical -> computational) is detailed. The model captures clogging/declogging from biomass, changes in interfacial tension due to biosurfactant, and the resulting impact on relative permeability, capillary pressure, and residual oil saturation via a trapping-number framework. The flow model is validated (Buckley-Leverett and coreflood benchmarks); transport (microbes/nutrients/surfactant) is validated against Hendry et al. 1997 breakthrough data. Finally, the model accurately predicts a Berea-core MEOR case study using field microbes and brine, matching recovery histories with small RMS error. Owing to its generality, the framework can be extended to other EOR scenarios and constitutive laws.
 2511.09565
2511.09565In this paper, we derive a unified generalization of Ramanujan's transformation identities for the theta function $f(a,b)$, originally appearing in Ramanujan's Notebooks, Parts~III and IV. Using an approach based on residue-class dissections and modular substitutions, we obtain a closed transformation formula for $f(ζa, ζb)$, where $ζ$ is a primitive root of unity $m$. As special cases, we recover and systematically prove Ramanujan's classical results for $m=2,3,$ and $4$, including even odd dissections, cubic transformation and the compact quartic form involving complex coefficients.
 2511.11657
2511.11657In this article, we will use elementary number theory techniques to investigate a sequence of integers defined by a sifting process called the lucky numbers. Ulam introduced lucky numbers as a sieve-based analogue of prime numbers. We derive an exact formula for the $n$th lucky number, providing a new tool for quantitative analysis. We formulate and prove a version of the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic for lucky numbers. This theorem provides an entirely new viewpoint on number theory. Building on the fundamental theorem, we introduce foundational definitions and analogues of arithmetical functions. Additionally, we prove an analogue of Bertrand's postulate for lucky numbers. Finally, we use the formula for the $n$th lucky number to prove a new result on the order of magnitude of the gaps between consecutive lucky numbers. We obtain an asymptotic bound that is much stronger than the best known bound for primes, and therefore obtain the first result that is known for lucky numbers but still conjectured to be true for primes. Together, these results establish a foundation for the arithmetic theory of lucky numbers and contribute to a broader understanding of sieve-generated sequences.
We construct a unified analytic framework connecting Bernoulli numbers, zeta-regularization, and Fredholm determinants associated with trigonometric selector kernels. Starting from the Bernoulli-Stirling algebra, Euler-Maclaurin corrections are reinterpreted as spectral traces of compact operators. This bridge transforms discrete combinatorial data into continuous spectral quantities, showing that their determinants interpolate between finite-rank projectors and the sine-kernel of random-matrix theory. In the continuum limit the Fredholm determinant becomes a Painleve-V~tau-function, revealing a hierarchy in which Bernoulli coefficients and zeta-constants jointly describe the local-global asymptotics of analytic regularization.
 2511.11642
2511.11642Relying on recent generalizations of the Fraïssé theory to a broader category-theoretic context, we study the class of abstract finite games played between two players and show the existence of an infinitetly countable game which is ultrahomogeneous and universal with respect to said class. Certain peculiarities of our game categories which clash with the usual framework found in the literature then lead us to formulate weaker category-theoretic properties which still yield a universal and ultrahomogeneous Fraïssé limit, thus further generalizing the categorical framework for a Fraïssé theory.