Other Statistics
Work in statistics not fitting other categories.
Work in statistics not fitting other categories.

Tze Leung Lai made seminal contributions to sequential analysis, particularly in sequential hypothesis testing, changepoint detection and nonlinear renewal theory. His work established fundamental optimality results for the sequential probability ratio test and its extensions, and provided a general framework for testing composite hypotheses. In changepoint detection, he introduced new optimality criteria and computationally efficient procedures that remain influential. He applied these and related tools to problems in biostatistics. In this article, we review these key results in the broader context of sequential analysis.
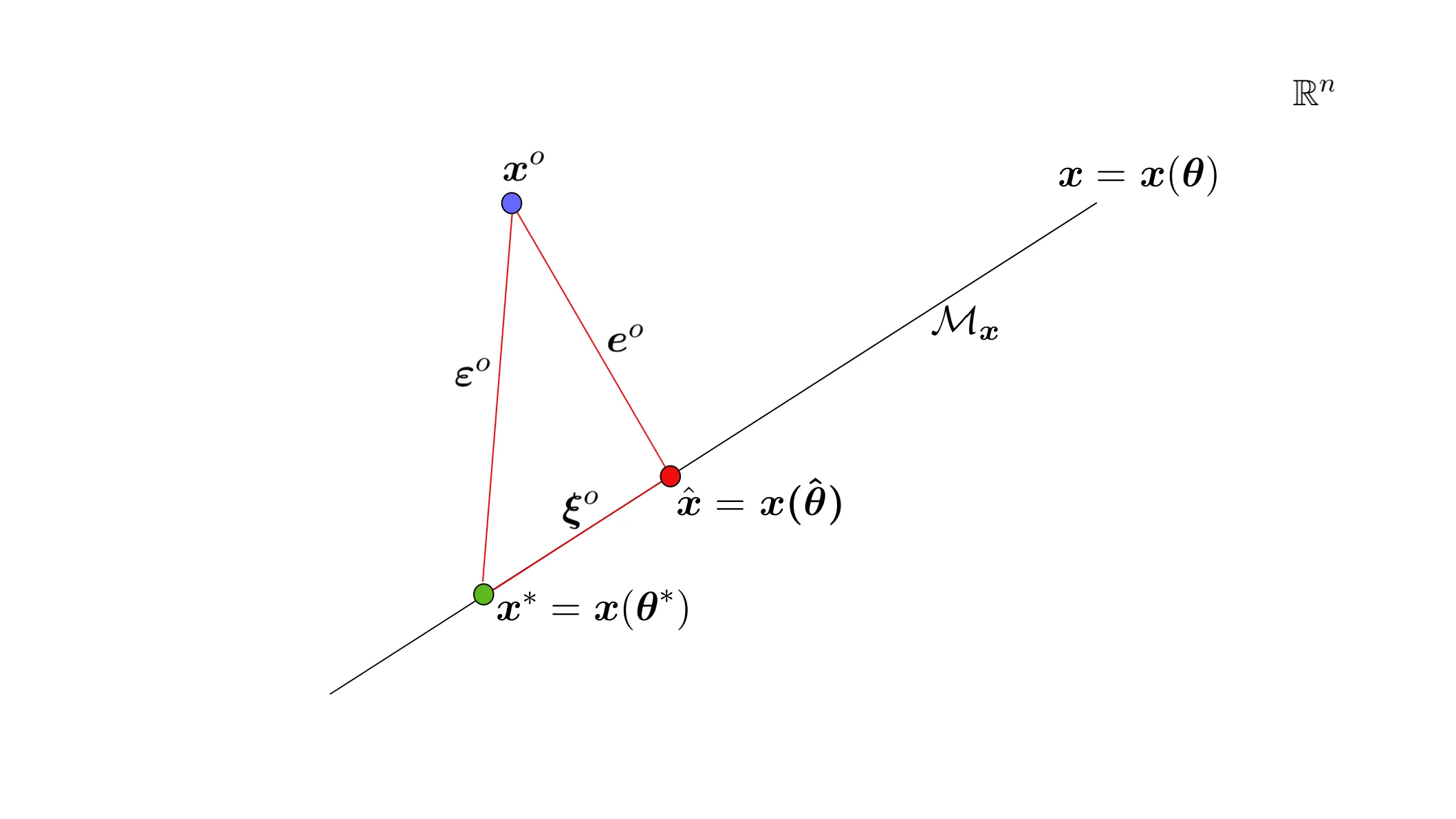
Modeling has become a widespread, useful tool in mathematics applied to diverse fields, from physics to economics to biomedicine. Practitioners of modeling may use algebraic or differential equations, to the elements of which they attribute an intuitive relationship with some relevant aspect of reality they wish to represent. More sophisticated expressions may include stochasticity, either as observation error or system noise. However, a clear, unambiguous mathematical definition of what a model is and of what is the relationship between the model and the real-life phenomena it purports to represent has so far not been formulated. The present work aims to fill this gap, motivating the definition of a mathematical model as an operator on a Hilbert space of random variables, identifying the experimental realization as the map between the theoretical space of model construction and the computational space of statistical model identification, and tracing the relationship of the geometry of the model manifold in the abstract setting with the corresponding geometry of the prediction surfaces in statistical estimation.