Cell Behavior
Cell signaling and development; cell-cell interactions and pattern formation; viral interactions.
Cell signaling and development; cell-cell interactions and pattern formation; viral interactions.
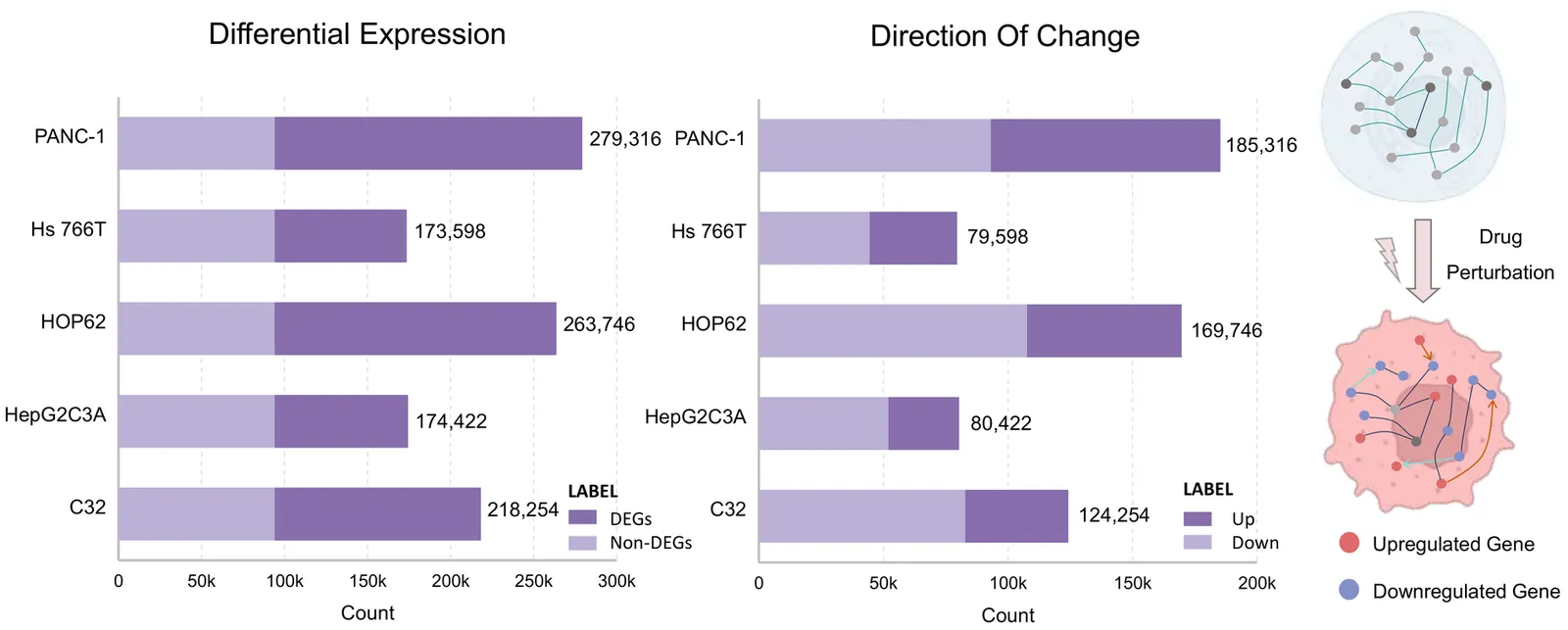
Virtual cell modeling aims to predict cellular responses to perturbations. Existing virtual cell models rely heavily on large-scale single-cell datasets, learning explicit mappings between gene expression and perturbations. Although recent models attempt to incorporate multi-source biological information, their generalization remains constrained by data quality, coverage, and batch effects. More critically, these models often function as black boxes, offering predictions without interpretability or consistency with biological principles, which undermines their credibility in scientific research. To address these challenges, we present VCWorld, a cell-level white-box simulator that integrates structured biological knowledge with the iterative reasoning capabilities of large language models to instantiate a biological world model. VCWorld operates in a data-efficient manner to reproduce perturbation-induced signaling cascades and generates interpretable, stepwise predictions alongside explicit mechanistic hypotheses. In drug perturbation benchmarks, VCWorld achieves state-of-the-art predictive performance, and the inferred mechanistic pathways are consistent with publicly available biological evidence.
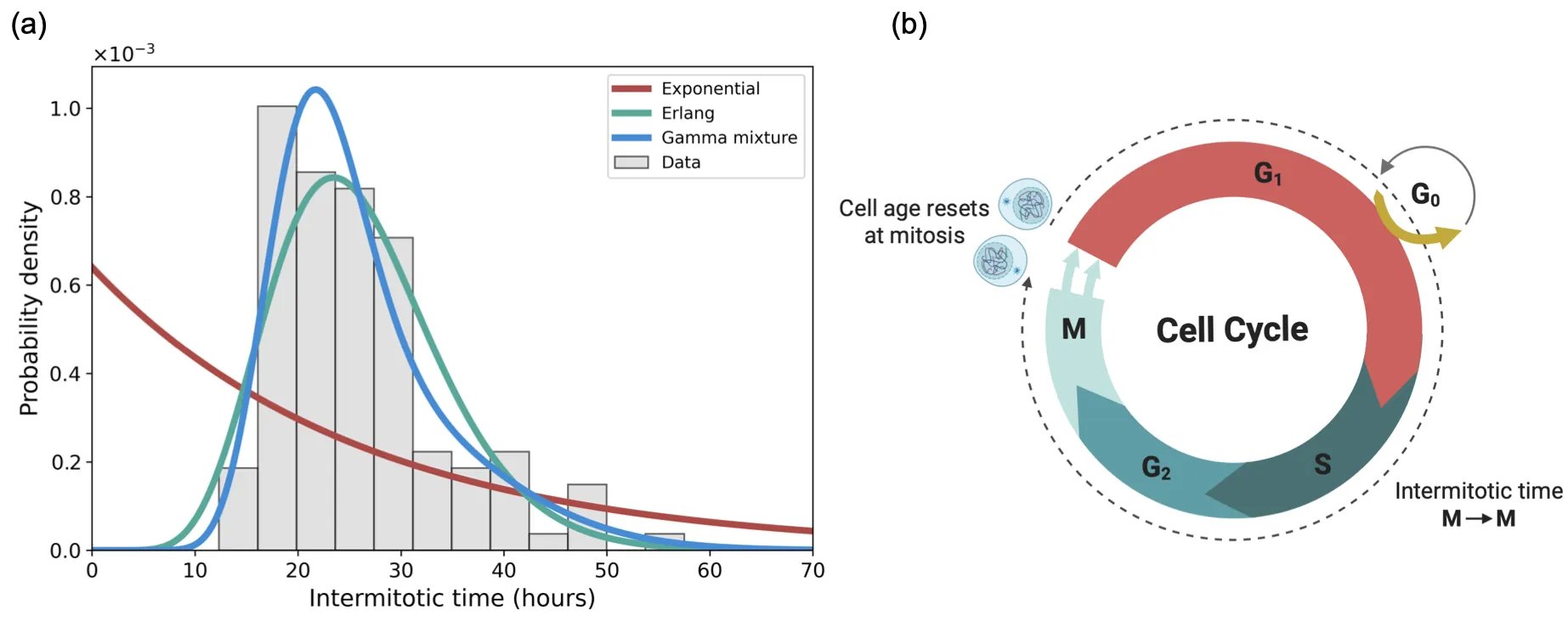
Cell populations invade through a combination of proliferation and motility. Proliferation depends on the internal timing of cell division: how long cells take to complete the cell cycle. This timing varies substantially within (and across) cell types, creating age structure where cells at different times since their last division have different propensities to divide. Classical mathematical models of cell spreading treat division as memoryless and predict exponential cell-cycle-time distributions. Lineage tracing, by contrast, reveals peaked, gamma-like distributions that indicate a maturation delay leading to a fertility window. This gap motivates a modelling framework that incorporates age-dependent cell division rates while retaining analytical tractability. We address this through a moment-hierarchy framework that tracks time since cell division, with age resetting to zero at division. The framework yields explicit formulae for steady-state age distributions, cell-cycle-time distributions, and invasion speeds. For age-independent rates, we recover classical Fisher--KPP. Three fundamental principles emerge. First, age structure systematically reduces a population's carrying capacity and narrows the viable parameter range for positive steady states. Second, classical linear theory overestimates invasion speeds; the true minimal speed is slower when division is age-dependent. Third, the parameter condition for population survival is identical to the condition for a positive invasion speed.
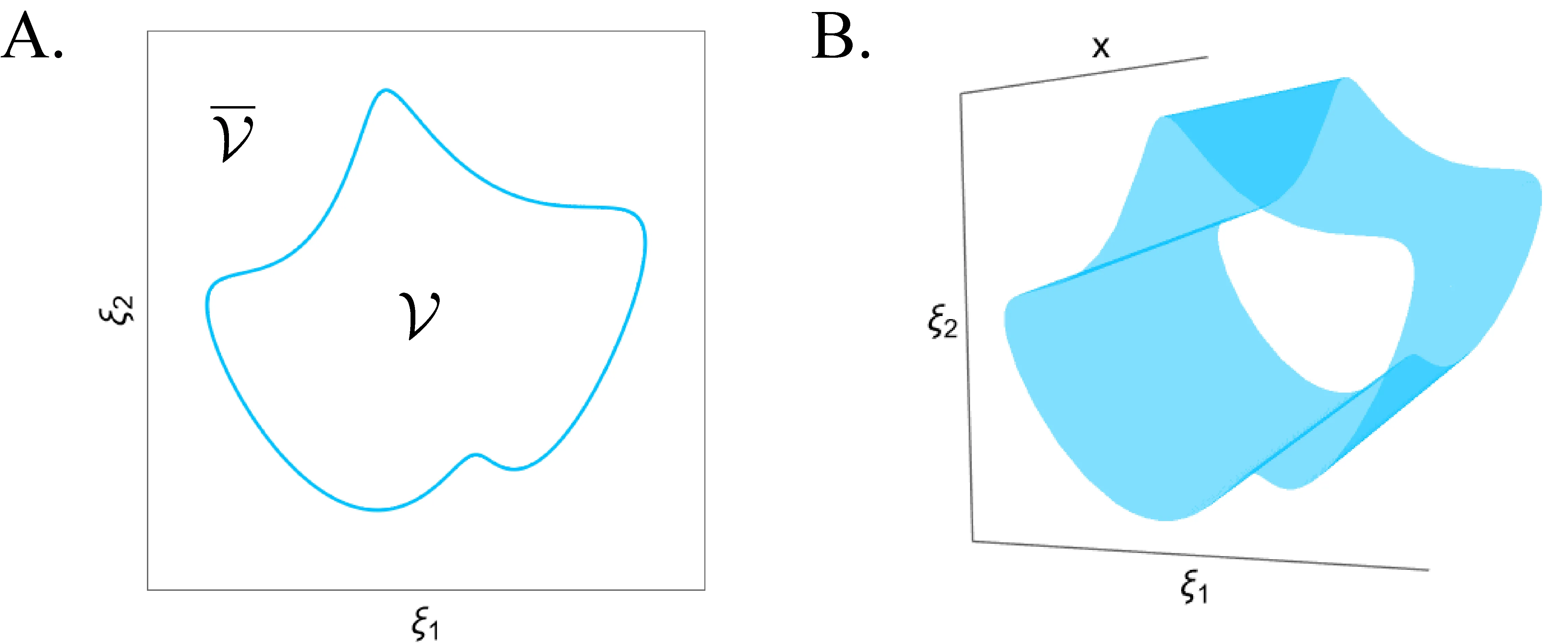
Nearly all cell models explicitly or implicitly deal with the biophysical constraints that must be respected for life to persist. Despite this, there is almost no systematicity in how these constraints are implemented, and we lack a principled understanding of how cellular dynamics interact with them and how they originate in actual biology. Computational cell biology will only overcome these concerns once it treats the life-death boundary as a central concept, creating a theory of cellular viability. We lay the foundation for such a development by demonstrating how specific geometric structures can separate regions of qualitatively similar survival outcomes in our models, offering new global organizing principles for cell fate. We also argue that idealized models of emergent individuals offer a tractable way to begin understanding life's intrinsically generated limits.
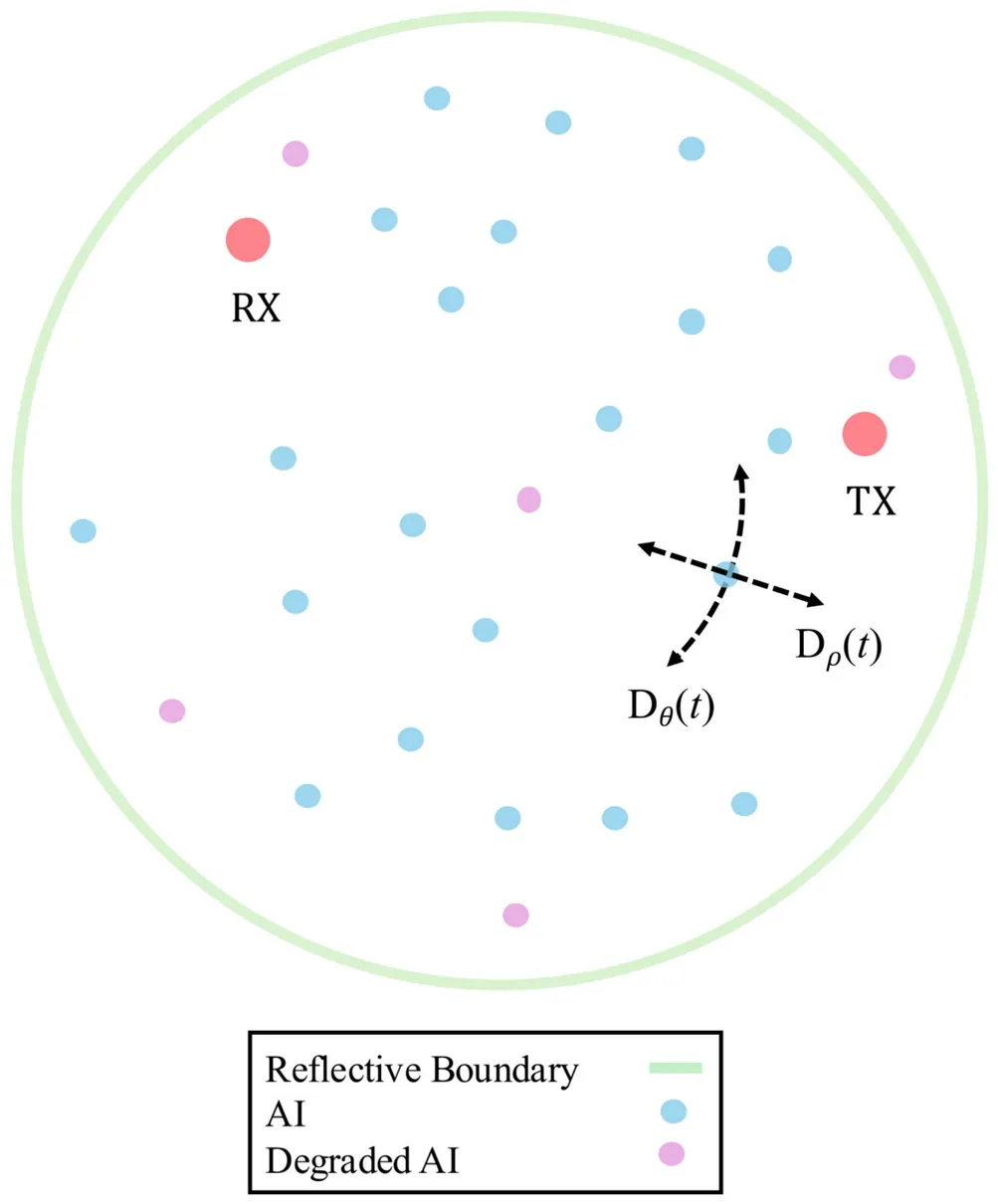
A biofilm is a self-contained community of bacteria that uses signaling molecules called autoinducers (AIs) to coordinate responses through the process of quorum sensing. Biofilms exhibit a dual role that drives interest in both combating antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and leveraging their potential in bioprocessing, since their products can have commercial potential. Previous work has demonstrated how the distinct anisotropic channel geometry in some biofilms affects AIs propagation therein. In this paper, a 2D anisotropic biofilm channel model is extended to be a time-varying channel (TVC), in order to represent the diffusion dynamics during the maturation phase when water channels develop. Since maturation is associated with the development of anisotropy, the time-varying model captures the shift from isotropic to anisotropic diffusion. Particle-based simulation results illustrate how the TVC is a hybrid scenario incorporating propagation features of both isotropic and anisotropic diffusion. This hybrid behavior aligns with biofilm maturation. Further study of the TVC includes characterization of the mutual information (MI), which reveals that an increased AI count, reduced transmitter -- receiver distance, greater degree of anisotropy, and shorter inter-symbol interference lengths increase the MI. Finally, a brief dimensional analysis demonstrates the scalability of the anisotropic channel results for larger biofilms and timescales.
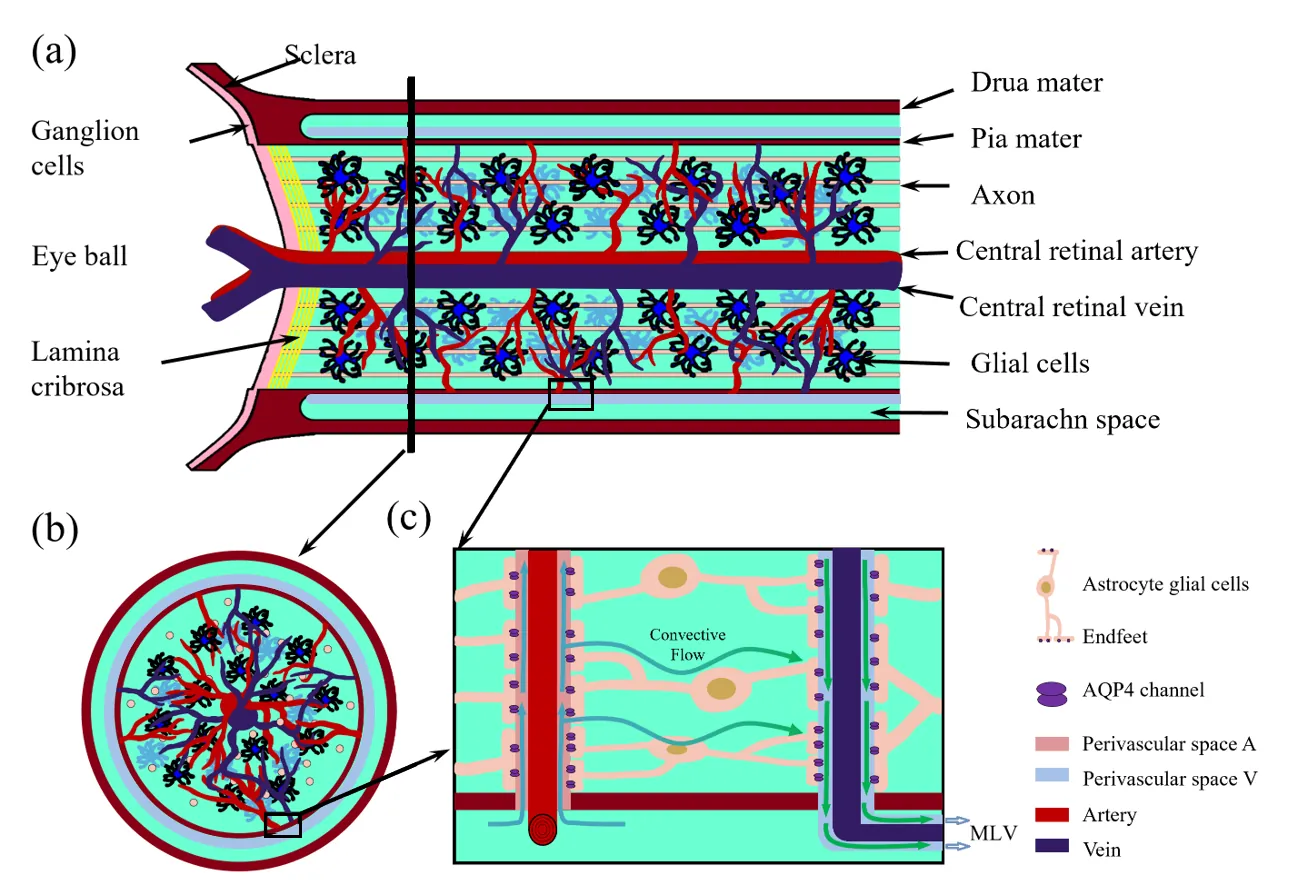
Effective metabolic waste clearance and maintaining ionic homeostasis are essential for the health and normal function of the central nervous system. To understand its mechanism and the role of fluid flow, we develop a multidomain electro-osmotic model of optic-nerve microcirculation that couples hydrostatic and osmotic fluid transport with electro-diffusive solute movement across axons, glia, the extracellular space, and arterial/venous/capillary perivascular spaces. Cerebrospinal fluid enters the optic nerve via the arterial parivascular space, passes both the glial and ECS before exiting through the venous parivascular space. Exchanges across astrocytic endfeet are essential and they occur in two distinct and coupled paths: through AQP4 on glial membranes and gaps between glial endfeet, thus establishing a mechanistic substrate for two modes of glymphatic transport, at rest and during stimulus-evoked perturbations. Parameter sweeps show that lowering AQP4-mediated fluid permeability or PVS permeability elevates pressure, suppresses radial exchange and slows clearance, effects most pronounced for solutes reliant on PVS V export. The model reproduces baseline and stimulus-evoked flow and demonstrates that PVS-mediated export is the primary clearance route for both small and moderate solutes. Small molecules clear faster because rapid ECS diffusion broadens their distribution and enhances ECS PVS exchange, whereas moderate species have low ECS diffusivity, depend on transendfoot transfer, and clear more slowly via PVS V convection. Our framework can also be used to explain the sleep-wake effect mechanistically: enlarging ECS volume or permeability increases transinterface flux and accelerates waste removal.
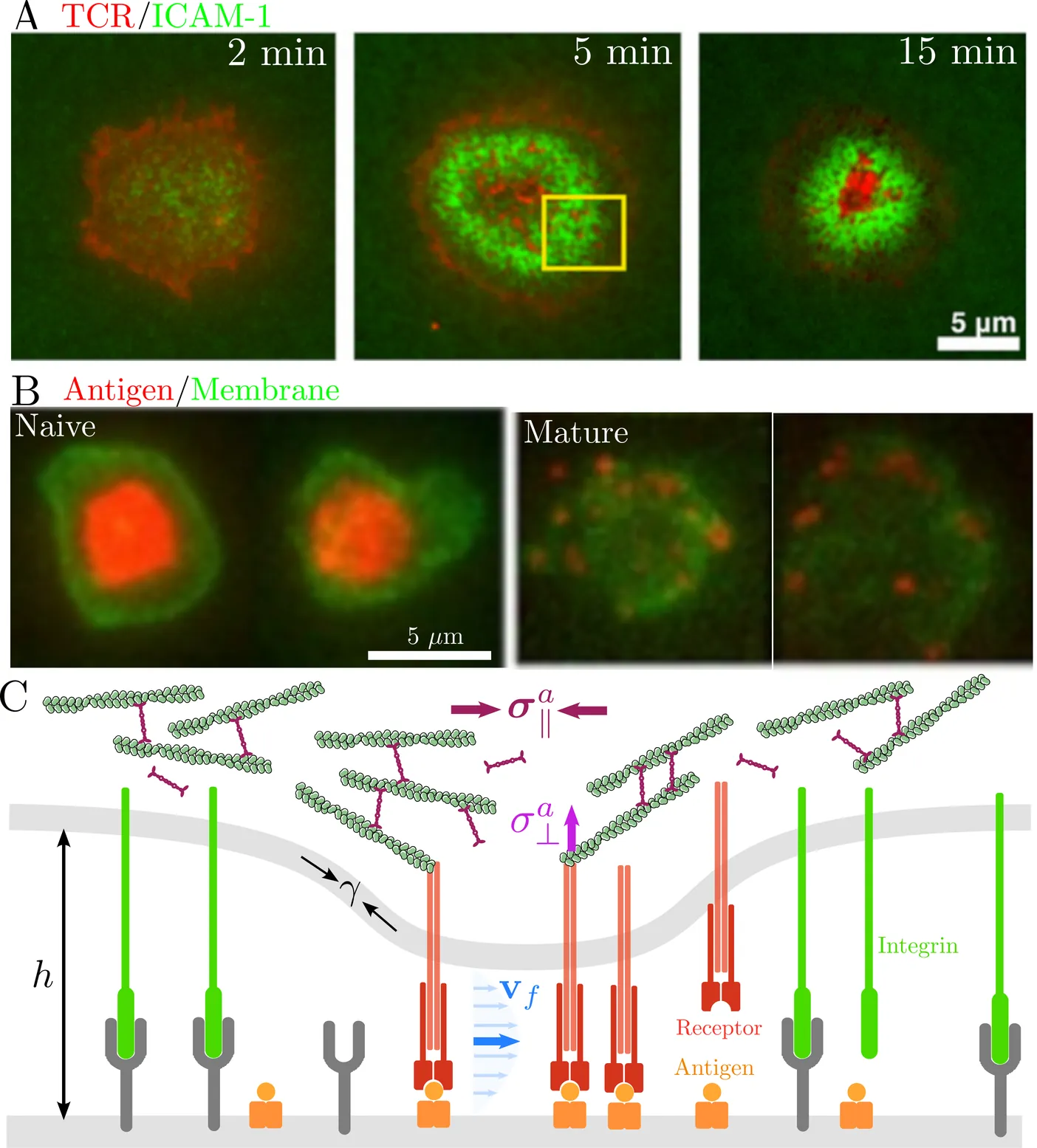
Immune cells recognize and discriminate antigens through immunological synapses - dynamic intercellular junctions exhibiting highly organized receptor-ligand patterns. While much work has focused on molecular kinetics and passive mechanisms of pattern formation, the role of active mechanical control in patterning and discrimination remains underexplored. We develop a minimal continuum model coupling receptor binding kinetics, membrane deformation, and cytoskeletal forces, with elastohydrodynamic flow in the synaptic cleft. Numerical simulations and scaling analysis reveal that contractile cortical flows arrest coarsening and stabilize long-lived multifocal clusters, whereas active pulling accelerates cluster dissolution and elevates background receptor binding. Nonequilibrium mechanical forces enable adaptive control over the speed, sensitivity, and dynamic range of affinity discrimination in a pattern-dependent manner. Our results highlight how immune cells exploit cytoskeletal remodeling to robustly regulate antigen recognition through synaptic patterning.
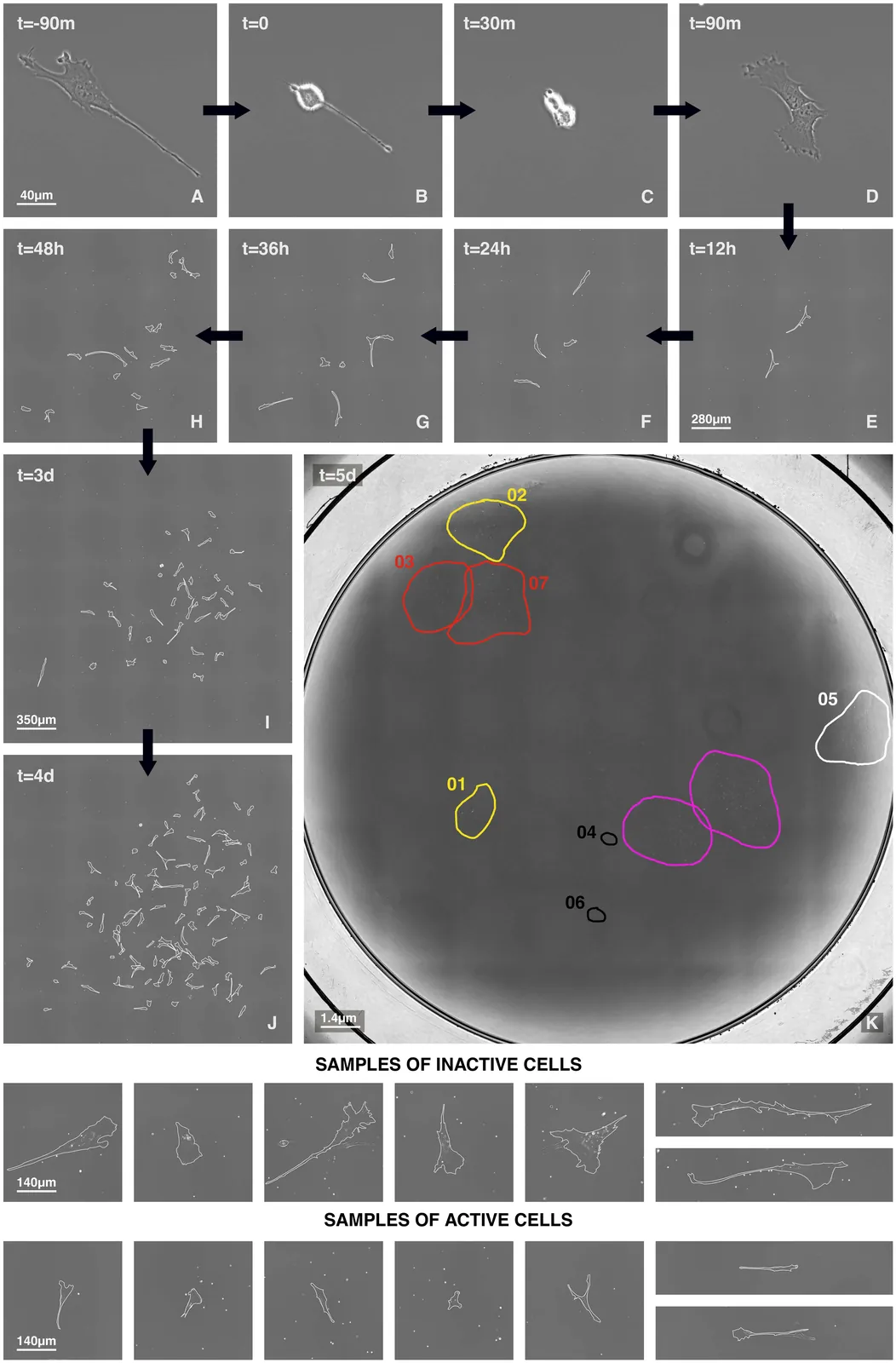
Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) -- which include skeletal stem cells -- are a promising tool in regenerative medicine. However, their heterogeneous and unpredictable in vivo behaviour remains a critical barrier preventing the development of standardized therapeutic approaches for skeletal tissue regeneration. Several studies have attempted to identify in vitro features that could correlate with the in vivo differentiation properties, yet the mechanisms ruling BMSC heterogeneity remain poorly understood. Here, using time-lapse imaging, we lineage-trace 32 single-cell-derived BMSC colonies through seven generations. We observe significant inter-colony and intra-colony heterogeneity in lineage topology (determined by the number of senescent or apoptotic cells) and in replicative kinetics (measured from proliferating cells only). Interestingly, topology and kinetics result strongly correlated, suggesting the existence of regulatory factors linking the non-dividing/apoptotic subpopulations with proliferating cells. Furthermore, BMSCs display highly synchronized cell cycles during early generations, indicating stage-specific regulatory mechanisms through which cells influence each other. By employing a non-interacting population growth model, we demonstrate that the observed synchronisation cannot be explained by an uncorrelated branching process; instead, cell-to-cell correlation of division times must exist. Our findings reveal fundamental mechanisms governing BMSC heterogeneity and growth dynamics that may inform strategies to control their regenerative potential.
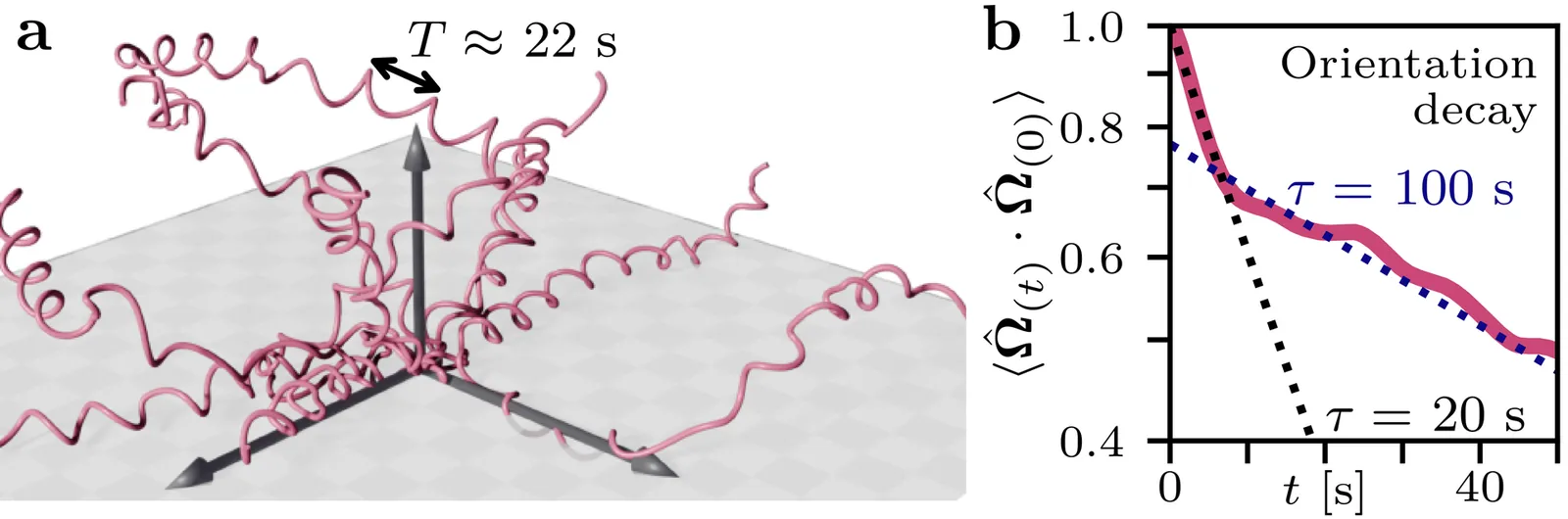
Active movement is essential for the survival of microorganisms like bacteria, algae and unicellular parasites. In three dimensions, both swimming and gliding microorganisms often exhibit helical trajectories. One such case are malaria parasites gliding through 3D hydrogels, for which we find that the internal correlation time for the stochastic process generating propulsion is similar to the time taken for one helical turn. Motivated by this experimental finding, here we theoretically analyze the case of finite internal correlation time for microorganisms with helical trajectories as chiral active particles with an Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process for torque. We present an analytical solution which is in very good agreement with computer simulations. We then show that for this type of internal noise, chirality and rotation increase the persistence of motion and results in helical trajectories that have a larger long-time mean squared displacement than straight trajectories at the same propulsion speed. Finally we provide experimental evidence for this prediction for the case of the malaria parasites.
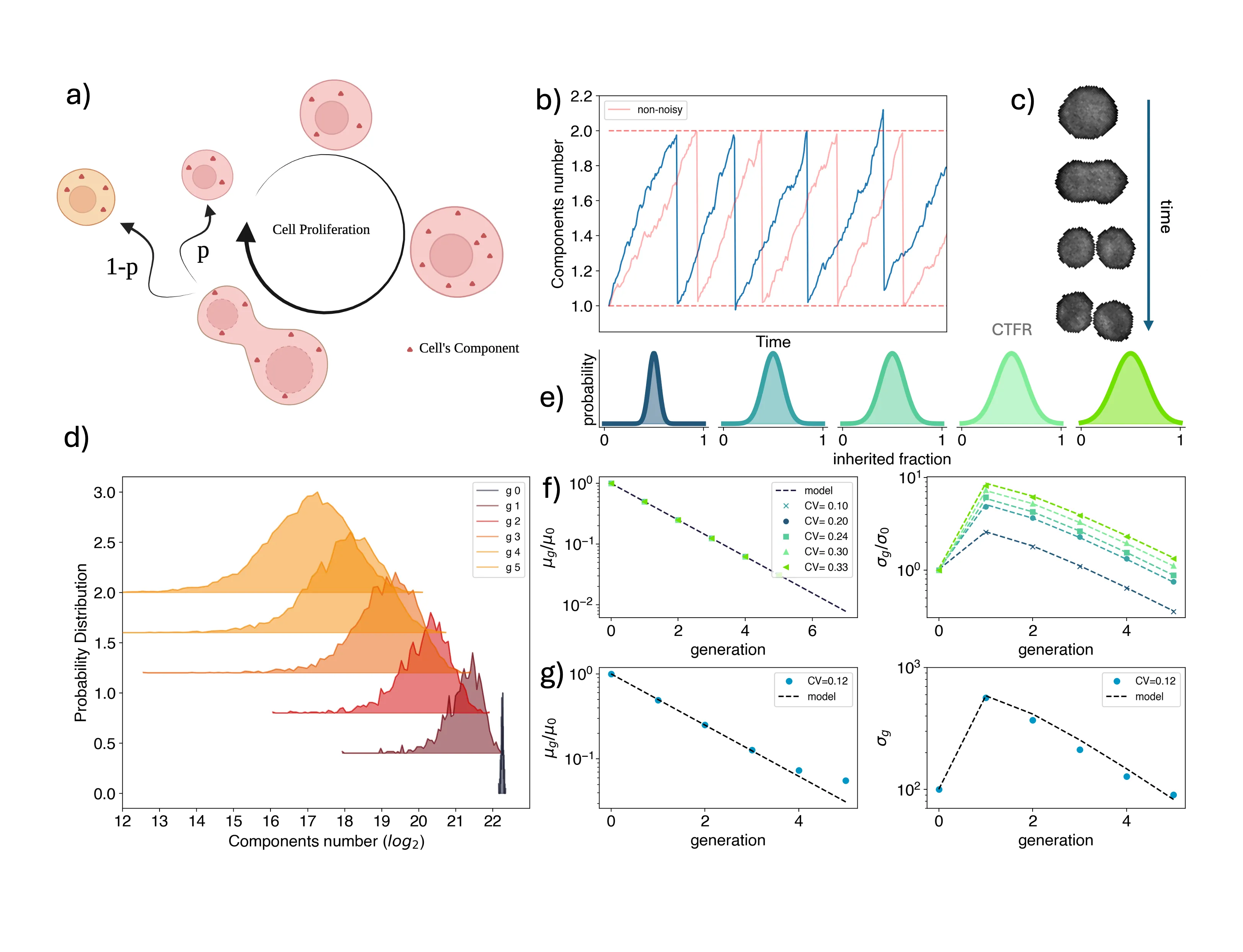
Asymmetric partition of fate determinants during cell division is a hallmark of cell differentiation. Recent work suggested that such a mechanism is hijacked by cancer cells to increase both their phenotypic heterogeneity and plasticity and in turn their fitness. To quantify fluctuations in the partitioning of cellular elements, imaging-based approaches are used, whose accuracy is limited by the difficulty of detecting cell divisions. Our work addresses this gap proposing a general method based on high-throughput flow cytometry measurements coupled with a theoretical framework. We applied our method to a panel of both normal and cancerous human colon cells, showing that different kinds of colon adenocarcinoma cells display very distinct extents of fluctuations in their cytoplasm partition, explained by an asymmetric division of their size. To test the accuracy of our population-level protocol, we directly measure the inherited fractions of cellular elements from extensive time-lapses of live-cell laser scanning microscopy, finding excellent agreement across the cell types. Ultimately, our flow cytometry-based method promises to be accurate and easily applicable to a wide range of biological systems where the quantification of partition fluctuations would help accounting for the observed phenotypic heterogeneity and plasticity