Fluid Dynamics
Turbulence, instabilities, control of fluid flows, computational fluid dynamics.
Turbulence, instabilities, control of fluid flows, computational fluid dynamics.
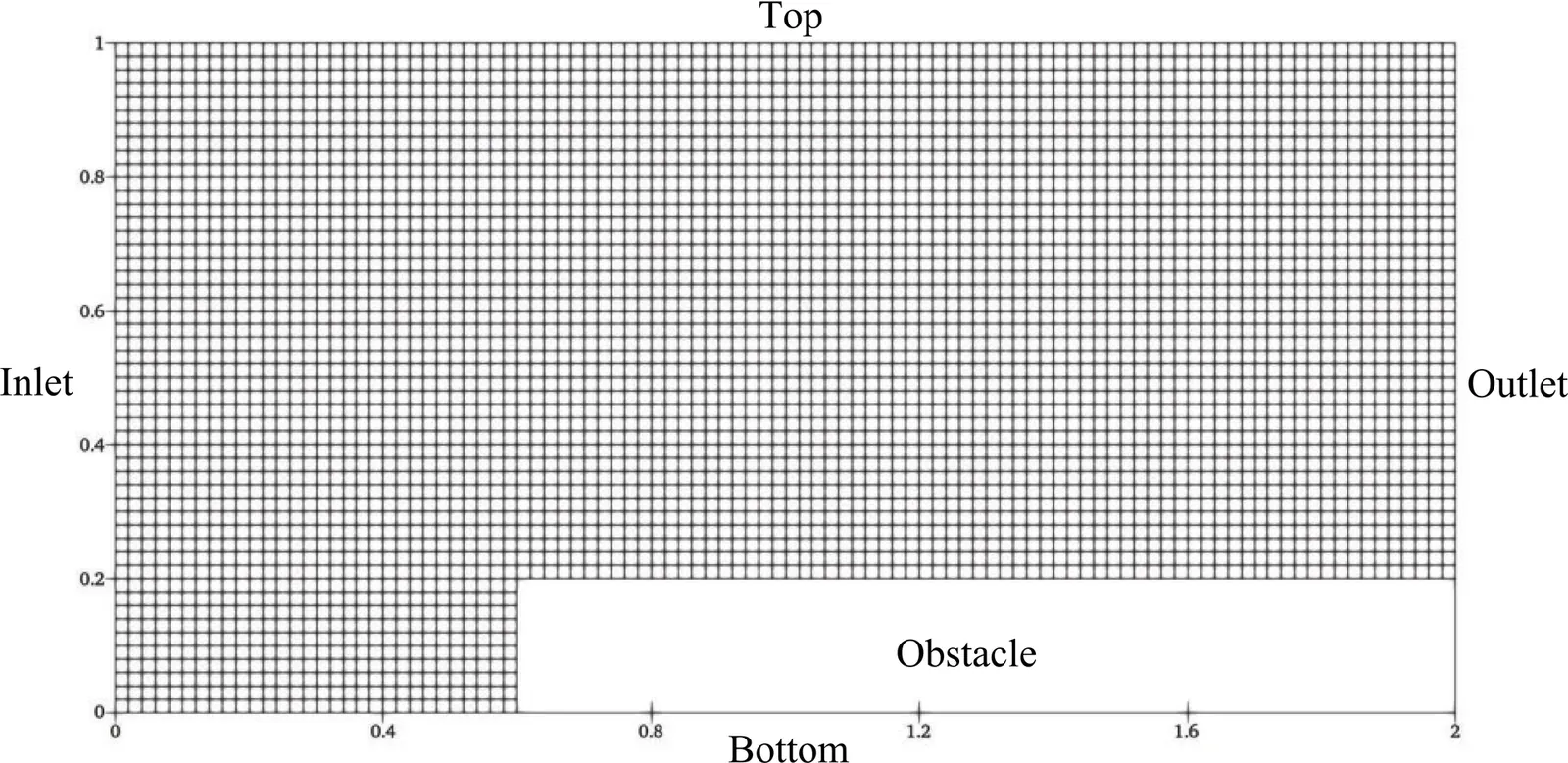
This paper investigates the temporal evolution of high-speed compressible fluids in irregular flow fields using the Fourier Neural Operator (FNO). We reconstruct the irregular flow field point set into sequential format compatible with FNO input requirements, and then embed temporal bundling technique within a recurrent neural network (RNN) for multi-step prediction. We further employ a composite loss function to balance errors across different physical quantities. Experiments are conducted on three different types of irregular flow fields, including orthogonal and non-orthogonal grid configurations. Then we comprehensively analyze the physical component loss curves, flow field visualizations, and physical profiles. Results demonstrate that our approach significantly surpasses traditional numerical methods in computational efficiency while achieving high accuracy, with maximum relative $L_2$ errors of (0.78, 0.57, 0.35)% for ($p$, $T$, $\mathbf{u}$) respectively. This verifies that the method can efficiently and accurately simulate the temporal evolution of high-speed compressible flows in irregular domains.
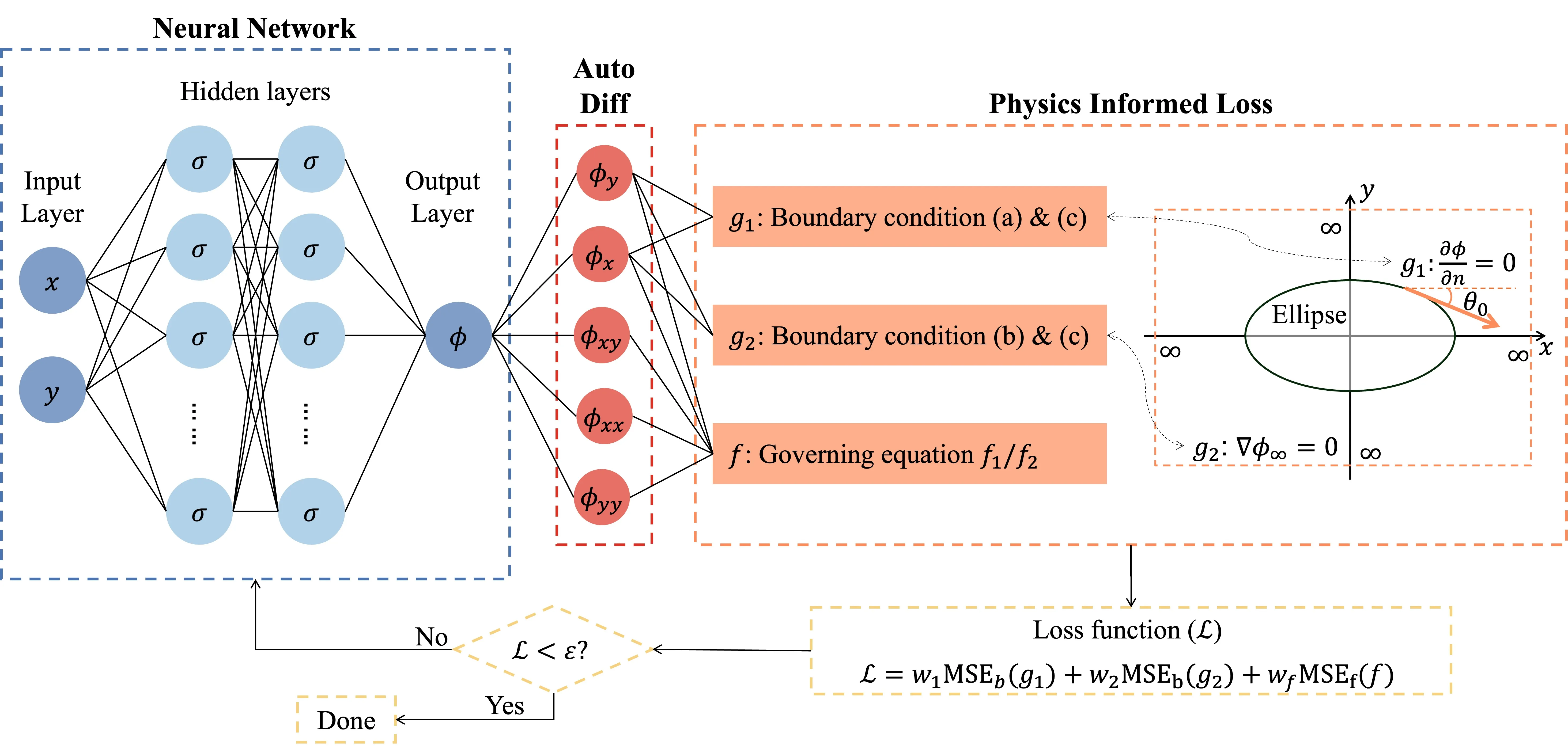
In aerodynamics, accurately modeling subsonic compressible flow over airfoils is critical for aircraft design. However, solving the governing nonlinear perturbation velocity potential equation presents computational challenges. Traditional approaches often rely on linearized equations or finite, truncated domains, which introduce non-negligible errors and limit applicability in real-world scenarios. In this study, we propose a novel framework utilizing Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) to solve the full nonlinear compressible potential equation in an unbounded (infinite) domain. We address the unbounded-domain and convergence challenges inherent in standard PINNs by incorporating a coordinate transformation and embedding physical asymptotic constraints directly into the network architecture. Furthermore, we employ a Multi-Stage PINN (MS-PINN) approach to iteratively minimize residuals, achieving solution accuracy approaching machine precision. We validate this framework by simulating flow over circular and elliptical geometries, comparing our results against traditional finite-domain and linearized solutions. Our findings quantify the noticeable discrepancies introduced by domain truncation and linearization, particularly at higher Mach numbers, and demonstrate that this new framework is a robust, high-fidelity tool for computational fluid dynamics.
We investigate the statistical accuracy of temporally interpolated spatiotemporal flow sequences between sparse, decorrelated snapshots of turbulent flow fields using conditional Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs). The developed method is presented as a proof-of-concept generative surrogate for reconstructing coherent turbulent dynamics between sparse snapshots, demonstrated on a 2D Kolmogorov Flow, and a 3D Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability (KHI). We analyse the generated flow sequences through the lens of statistical turbulence, examining the time-averaged turbulent kinetic energy spectra over generated sequences, and temporal decay of turbulent structures. For the non-stationary Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability, we assess the ability of the proposed method to capture evolving flow statistics across the most strongly time-varying flow regime. We additionally examine instantaneous fields and physically motivated metrics at key stages of the KHI flow evolution.
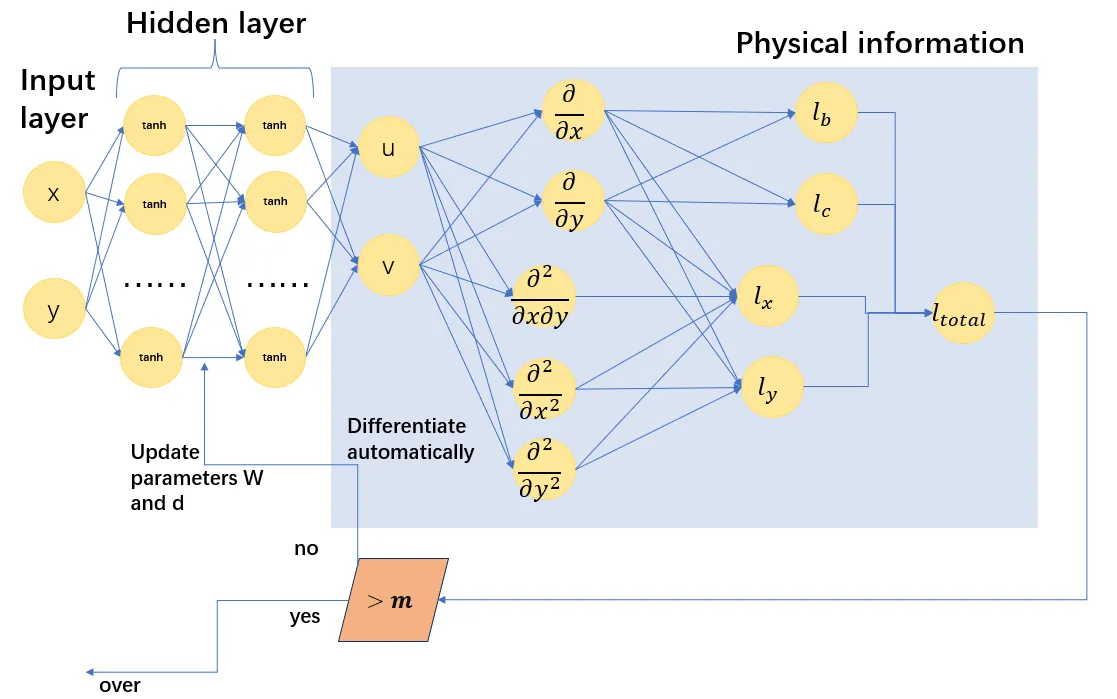
Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) have demonstrated considerable success in solving complex fluid dynamics problems. However, their performance often deteriorates in regimes characterized by steep gradients, intricate boundary conditions, and stringent physical constraints, leading to convergence failures and numerical instabilities. To overcome these limitations, we propose a hybrid framework that integrates Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks into the PINN architecture, enhancing its ability to capture spatial correlations in the steady-state velocity field of a two-dimensional charged fluid under an external electric field. Our results demonstrate that the LSTM-enhanced PINN model significantly outperforms conventional Multilayer Perceptron (MLP)-based PINNs in terms of convergence rate, numerical stability, and predictive accuracy. This innovative approach offers improved computational efficiency and reliability for modeling electrohydrodynamic flows, providing new insights and strategies for applications in microfluidics and nanofluidics.
We demonstrate that pilot-wave hydrodynamics provides a macroscopic platform for realizing band-structure physics, topological edge states, and gauge-field-induced phase shifts. We show that a submerged square lattice produces frequency-dependent transmission governed by Bloch bands. An inversion-asymmetric honeycomb lattice confines the droplet to a domain wall, revealing a hydrodynamic analog of a valley-Hall edge state. And a chiral annular structure generates an effective gauge field that produces an Aharonov-Bohm-like phase difference between clockwise and counter-clockwise orbits. Unlike conventional wave analogs, pilot-wave hydrodynamics couples a localized particle to its self-generated wave field, providing direct access to topological wave-particle behavior normally associated with quantum systems.
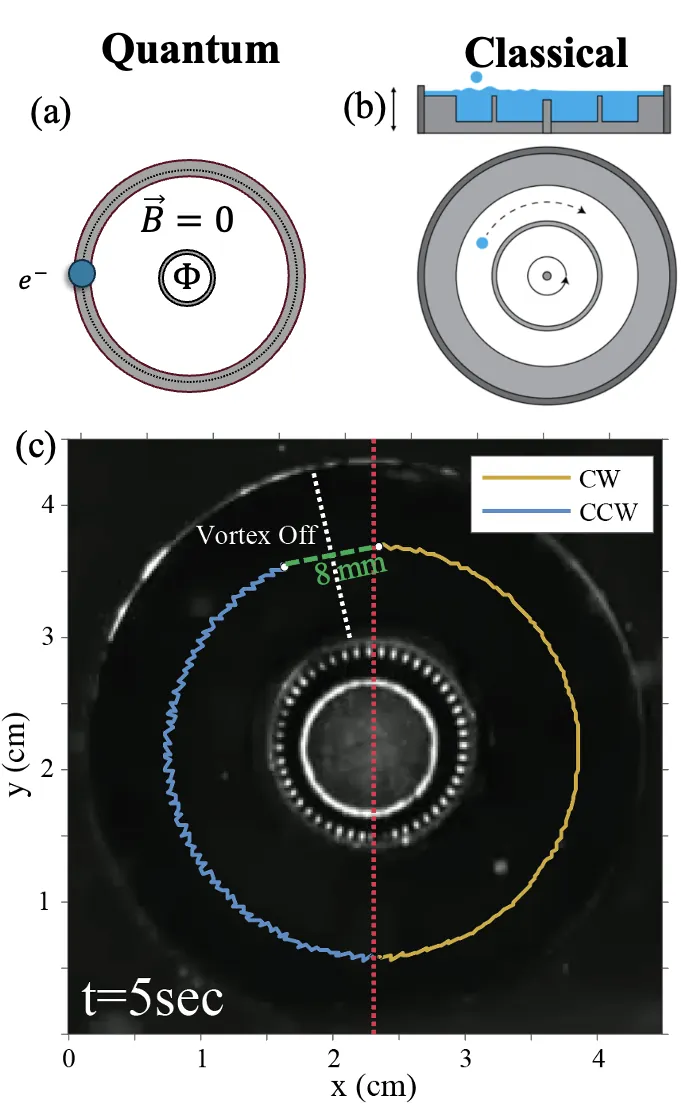
We report the results of an experimental study of an analog of the Aharonov-Bohm (AB) effect achieved with the hydrodynamic pilot-wave system. A walking droplet is confined to an annular cavity that encircles a shielded vortex, but lies outside its range of direct influence. While there is no vortex-induced flow in the immediate vicinity of the droplets, the vortex modifies the droplet's spatially extended pilot-wave field that guides its motion, producing a vortex-dependent bias in the droplet's orbital speed. High-speed tracking and delay-embedding reconstructions yield Wigner-like phase-space distributions for this hydrodynamic system that exhibits a rigid, flux-dependent translation, providing a force-free, gauge-like realization of an AB-type phase.
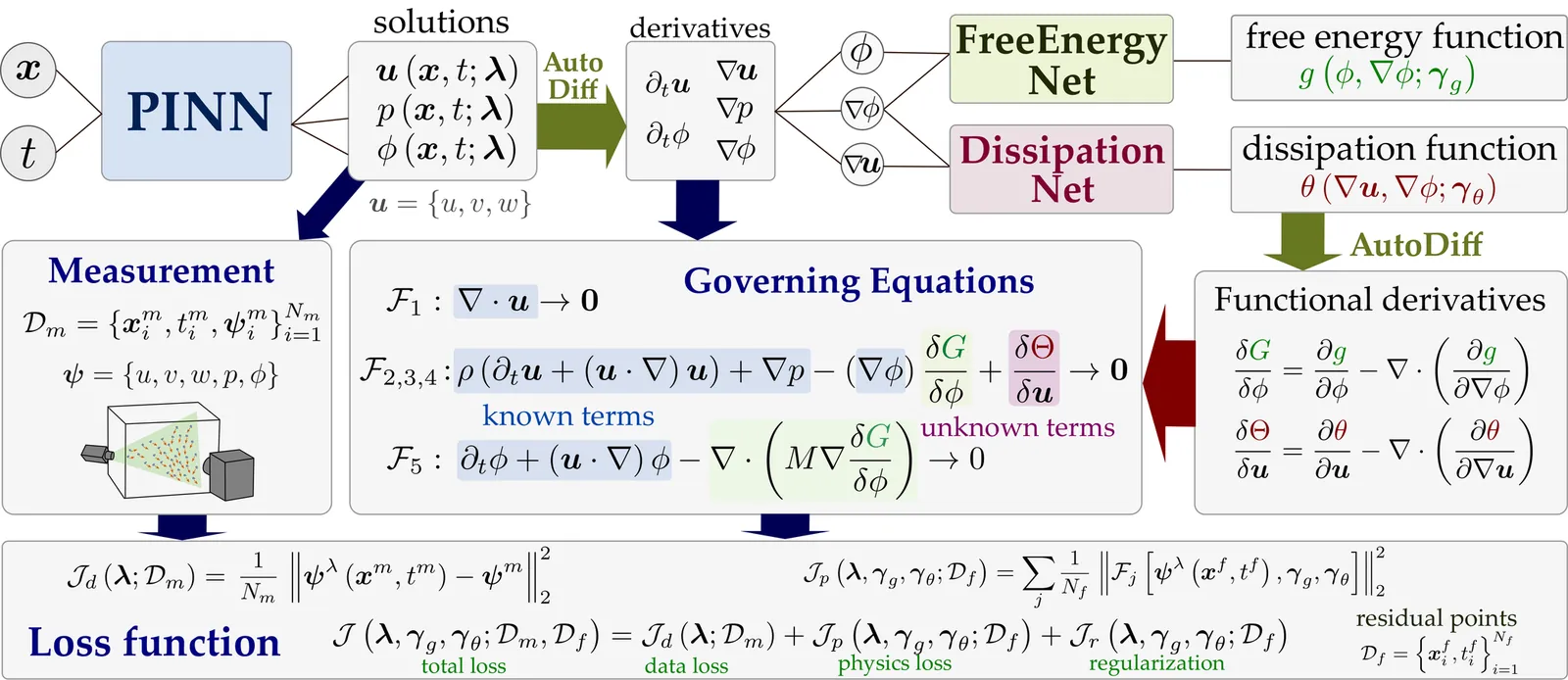
We develop a data-driven framework for discovering constitutive relations in models of fluid flow and scalar transport. Our approach infers unknown closure terms in the governing equations (gray-box discovery) under the assumption that the temporal derivative, convective transport, and pressure-gradient contributions are known. The formulation is rooted in a variational principle from nonequilibrium thermodynamics, where the dynamics is defined by a free-energy functional and a dissipation functional. The unknown constitutive terms arise as functional derivatives of these functionals with respect to the state variables. To enable a flexible and structured model discovery, the free-energy and dissipation functionals are parameterized using neural networks, while their functional derivatives are obtained via automatic differentiation. This construction enforces thermodynamic consistency by design, ensuring monotonic decay of the total free energy and non-negative entropy production. The resulting method, termed GIMLET (Generalizable and Interpretable Model Learning through Embedded Thermodynamics), avoids reliance on a predefined library of candidate functions, unlike sparse regression or symbolic identification approaches. The learned models are generalizable in that functionals identified from one dataset can be transferred to distinct datasets governed by the same underlying equations. Moreover, the inferred free-energy and dissipation functions provide direct physical interpretability of the learned dynamics. The framework is demonstrated on several benchmark systems, including the viscous Burgers equation, the Kuramoto--Sivashinsky equation, and the incompressible Navier--Stokes equations for both Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids.
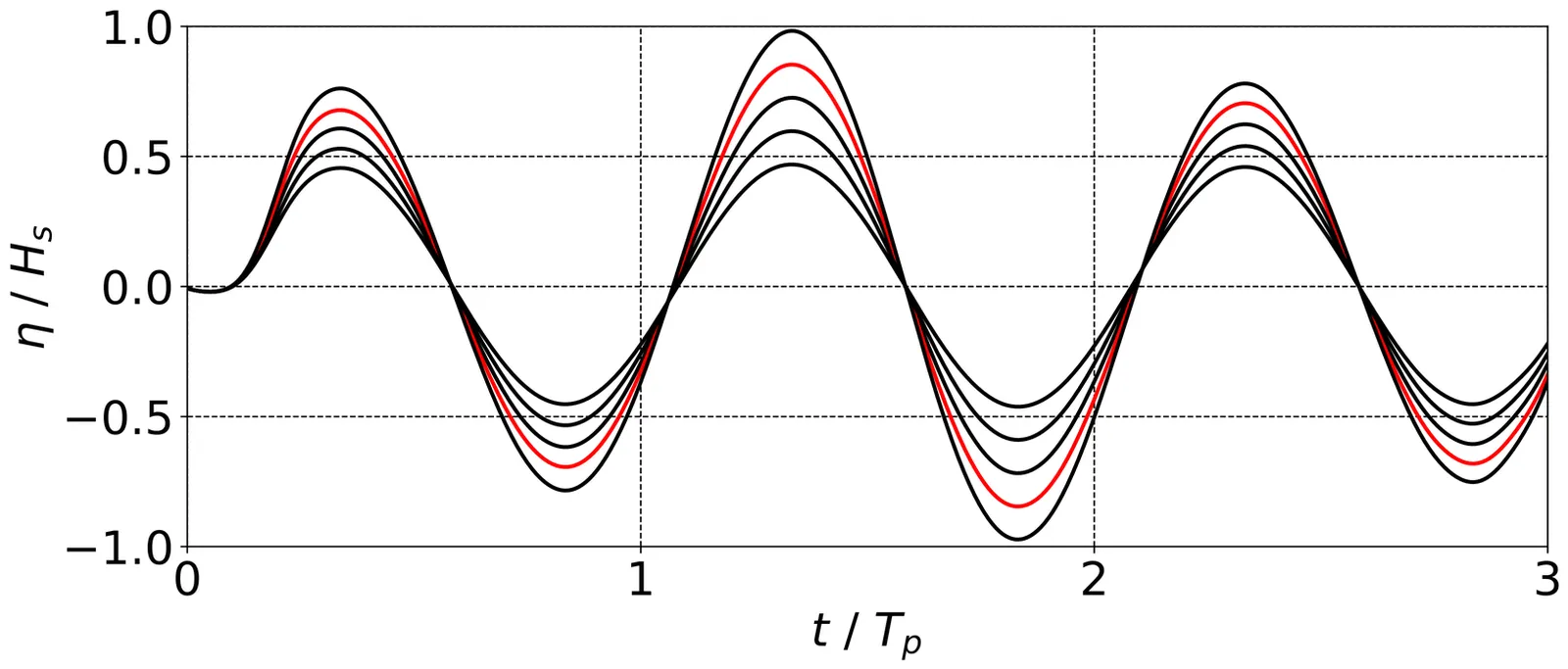
Research on the statistics of extreme events using deterministic wave group methods has largely been simplified to vessels at zero or constant speed and heading. In contrast, free-running vessels move with six degrees-of-freedom (6-DoF), leading to more complex and varied extreme response events. This paper details the extension of the Critical Wave Groups (CWG) method to free-running vessels and demonstrates that the method produces probability calculations comparable to those from a limited Monte Carlo dataset for a vessel in beam seas. This research is a critical first step in the formal validation of this free-running implementation of the CWG method.
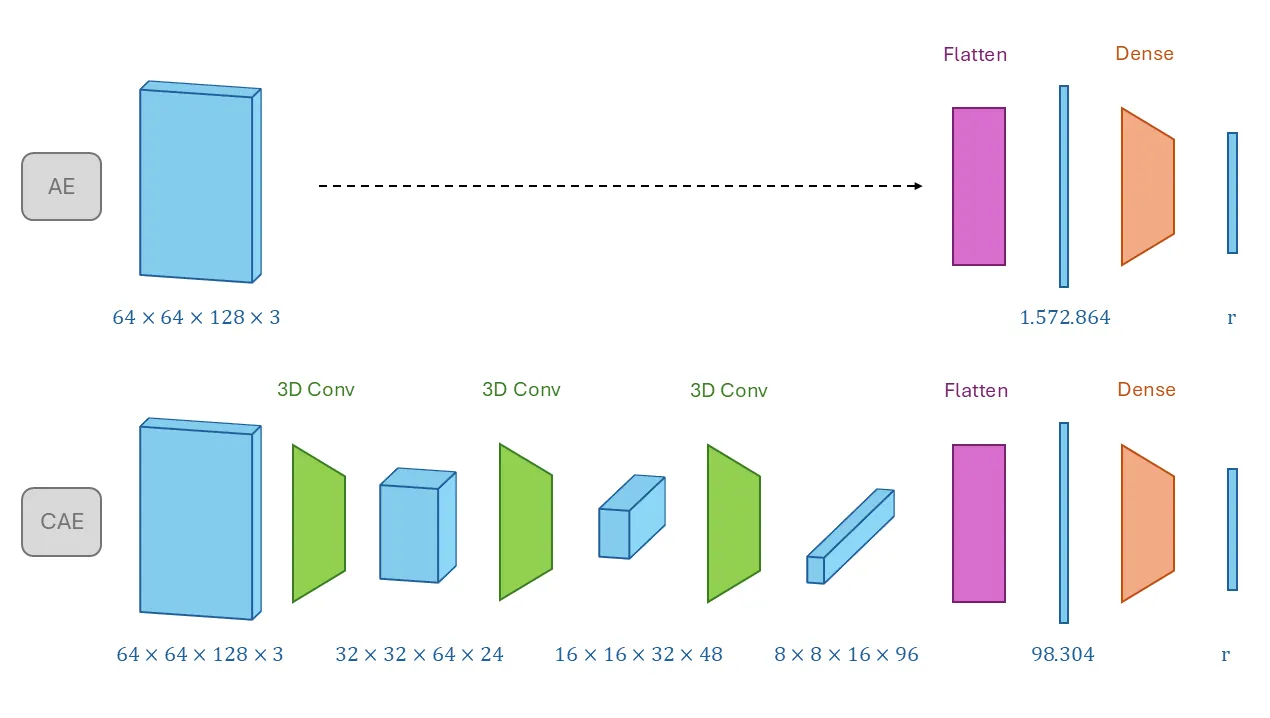
Understanding intraventricular hemodynamics requires compact and physically interpretable representations of the underlying flow structures, as characteristic flow patterns are closely associated with cardiovascular conditions and can support early detection of cardiac deterioration. Conventional visualization of velocity or pressure fields, however, provides limited insight into the coherent mechanisms driving these dynamics. Reduced-order modeling techniques, like Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) and Autoencoder (AE) architectures, offer powerful alternatives to extract dominant flow features from complex datasets. This study systematically compares POD with several AE variants (Linear, Nonlinear, Convolutional, and Variational) using left ventricular flow fields obtained from computational fluid dynamics simulations. We show that, for a suitably chosen latent dimension, AEs produce modes that become nearly orthogonal and qualitatively resemble POD modes that capture a given percentage of kinetic energy. As the number of latent modes increases, AE modes progressively lose orthogonality, leading to linear dependence, spatial redundancy, and the appearance of repeated modes with substantial high-frequency content. This degradation reduces interpretability and introduces noise-like components into AE-based reduced-order models, potentially complicating their integration with physics-based formulations or neural-network surrogates. The extent of interpretability loss varies across the AEs, with nonlinear, convolutional, and variational models exhibiting distinct behaviors in orthogonality preservation and feature localization. Overall, the results indicate that AEs can reproduce POD-like coherent structures under specific latent-space configurations, while highlighting the need for careful mode selection to ensure physically meaningful representations of cardiac flow dynamics.
 2512.17534
2512.17534Modeling and controlling fluid flows is critical for several fields of science and engineering, including transportation, energy, and medicine. Effective flow control can lead to, e.g., lift increase, drag reduction, mixing enhancement, and noise reduction. However, controlling a fluid faces several significant challenges, including high-dimensional, nonlinear, and multiscale interactions in space and time. Reinforcement learning (RL) has recently shown great success in complex domains, such as robotics and protein folding, but its application to flow control is hindered by a lack of standardized benchmark platforms and the computational demands of fluid simulations. To address these challenges, we introduce HydroGym, a solver-independent RL platform for flow control research. HydroGym integrates sophisticated flow control benchmarks, scalable runtime infrastructure, and state-of-the-art RL algorithms. Our platform includes 42 validated environments spanning from canonical laminar flows to complex three-dimensional turbulent scenarios, validated over a wide range of Reynolds numbers. We provide non-differentiable solvers for traditional RL and differentiable solvers that dramatically improve sample efficiency through gradient-enhanced optimization. Comprehensive evaluation reveals that RL agents consistently discover robust control principles across configurations, such as boundary layer manipulation, acoustic feedback disruption, and wake reorganization. Transfer learning studies demonstrate that controllers learned at one Reynolds number or geometry adapt efficiently to new conditions, requiring approximately 50% fewer training episodes. The HydroGym platform is highly extensible and scalable, providing a framework for researchers in fluid dynamics, machine learning, and control to add environments, surrogate models, and control algorithms to advance science and technology.
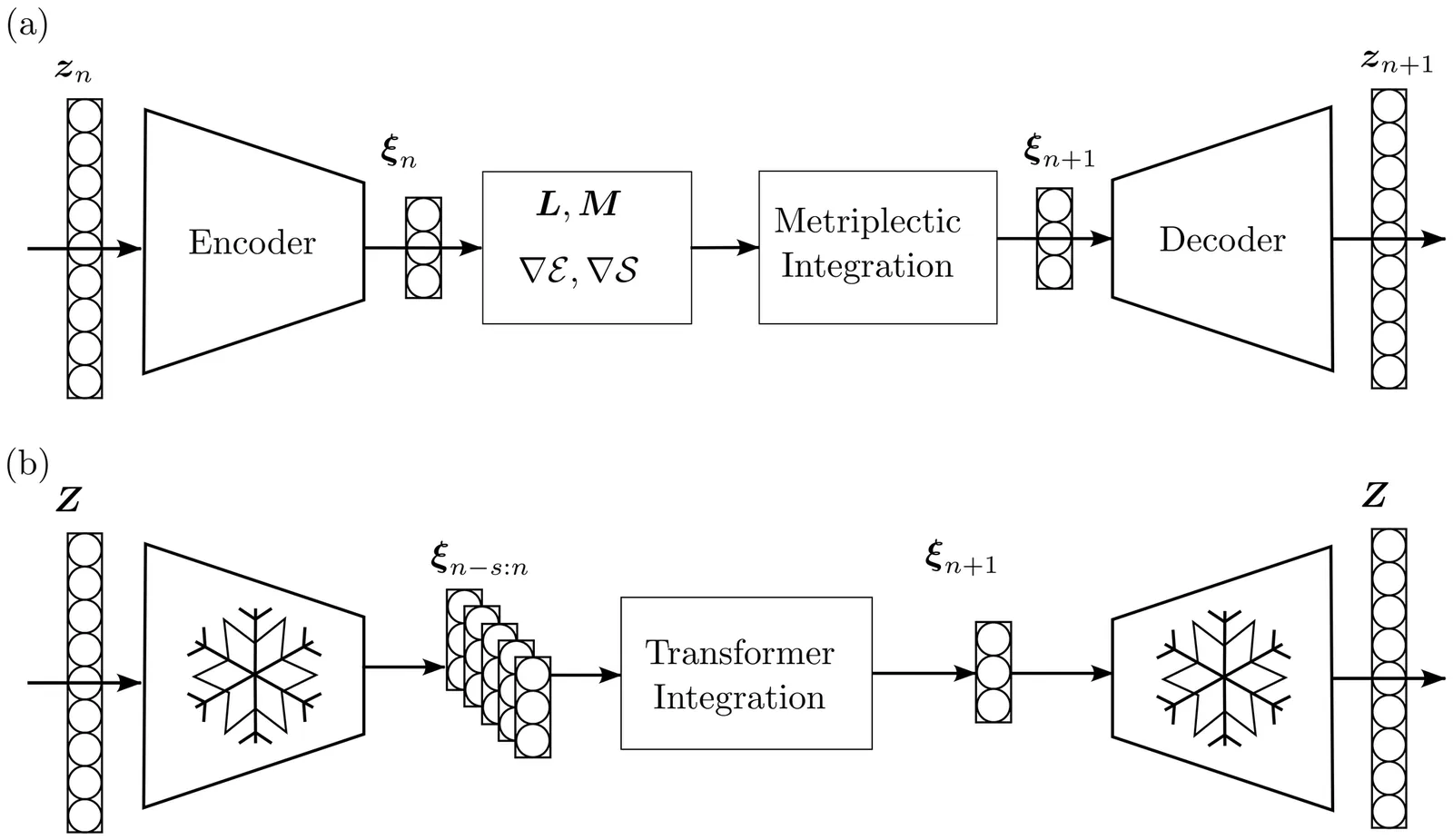
It is well known that the lack of information about certain variables necessary for the description of a dynamical system leads to the introduction of historical dependence (lack of Markovian character of the model) and noise. Traditionally, scientists have made up for these shortcomings by designing phenomenological variables that take into account this historical dependence (typically, conformational tensors in fluids). Often, these phenomenological variables are not easily measurable experimentally. In this work, we study to what extent Transformer architectures are able to cope with the lack of experimental data on these variables. The methodology is evaluated on three benchmark problems: a cylinder flow with no history dependence, a viscoelastic Couette flow modeled via the Oldroyd-B formalism, and a non-linear polymeric fluid described by the FENE model. Our results show that the Transformer outperforms a thermodynamically consistent, structure-preserving neural network with metriplectic bias in systems with missing experimental data, providing lower errors even in low-dimensional latent spaces. In contrast, for systems whose state variables can be fully known, the metriplectic model achieves superior performance.
We present a systematic numerical investigation of bifurcations in the two-dimensional incompressible Navier-Stokes flow past a confined circular cylinder. The results indicate that there is a qualitative correspondence between changes in the traction profiles of the steady Navier-Stokes equations and bifurcations of the long-time behavior of the unsteady Navier-Stokes equations. The bifurcations include the appearance of symmetry breaking, oscillations, and multiple steady solutions. The well-known planar Schäfer-Turek benchmark is considered with Reynolds numbers up to 1000. For the analysis of bifurcations and traction profiles, several numerical strategies are applied, including a duality method for computing traction profiles, deflation methods, and linear stability analysis. Long-time flow behavior is often explored through direct numerical simulation of the unsteady equations; an approach that is computationally demanding. The relations presented here indicate the possibility of a computationally inexpensive strategy to detect critical Reynolds numbers.
 2512.15188
2512.15188Mathematical estimates for the Navier-Stokes equations are traditionally expressed in terms of the Grashof number, which is a dimensionless measure of the magnitude of the forcing and hence a control parameter of the system. However, experimental measurements and statistical theories of turbulence are based on the Reynolds number. Thus, a meaningful comparison between mathematical and physical results requires a conversion of the mathematical estimates to a Reynolds-dependent form. In two dimensions, this was achieved under the assumption that the second derivative of the forcing is square integrable. Nonetheless, numerical simulations have shown that the phenomenology of turbulence is sensitive to the degree of regularity of the forcing. Therefore, we extend the available estimates for the energy and enstrophy dissipation rates as well as the attractor dimension to forcings in the Sobolev space of order $s$; i.e. forcings whose Fourier coefficients decay with the wavenumber $k$ faster than $k^{-s-1}$. We consider the range $-1\leqslant s\leqslant 2$, where $s=2$ corresponds to the known estimates, and $s=-1$ is the smallest value of $s$ for which weak solutions are known to exist. The main result is the existence of three distinct regimes as a function of the regularity of the forcing.
We develop a self-adaptive physics-informed neural network (PINN) framework that reliably solves forward Darcy flow and performs accurate permeability inversion in heterogeneous porous media. In the forward setting, the PINN predicts velocity and pressure for discontinuous, piecewise-constant permeability; in the inverse setting, it identifies spatially varying permeability directly from indirect flow observations. Both models use a region-aware permeability parameterization with binary spatial masks, which preserves sharp permeability jumps and avoids the smoothing artifacts common in standard PINNs. To stabilize training, we introduce self-learned loss weights that automatically balance PDE residuals, boundary constraints, and data mismatch, eliminating manual tuning and improving robustness, particularly for inverse problems. An interleaved AdamW-L-BFGS optimization strategy further accelerates and stabilizes convergence. Numerical results demonstrate accurate forward surrogates and reliable inverse permeability recovery, establishing the method as an effective mesh-free solver and data-driven inversion tool for porous-media systems governed by partial differential equations.
 2512.13824
2512.13824We use total energy-momentum conservation and the Bianchi identity (magnetic-flux conservation) to construct second-order relativistic magnetohydrodynamics in a Zubarev's non-equilibrium statistical operator (NESO) framework. We obtain all dissipative tensors in the medium by focusing on a relativistic magnetized plasma that preserves parity and is symmetric to charge-conjugation. We also provide Kubo formulas for all transport coefficients that arise at second order. Moreover, we extend the NESO formalism to systematically take into account for nonlocal contributions.
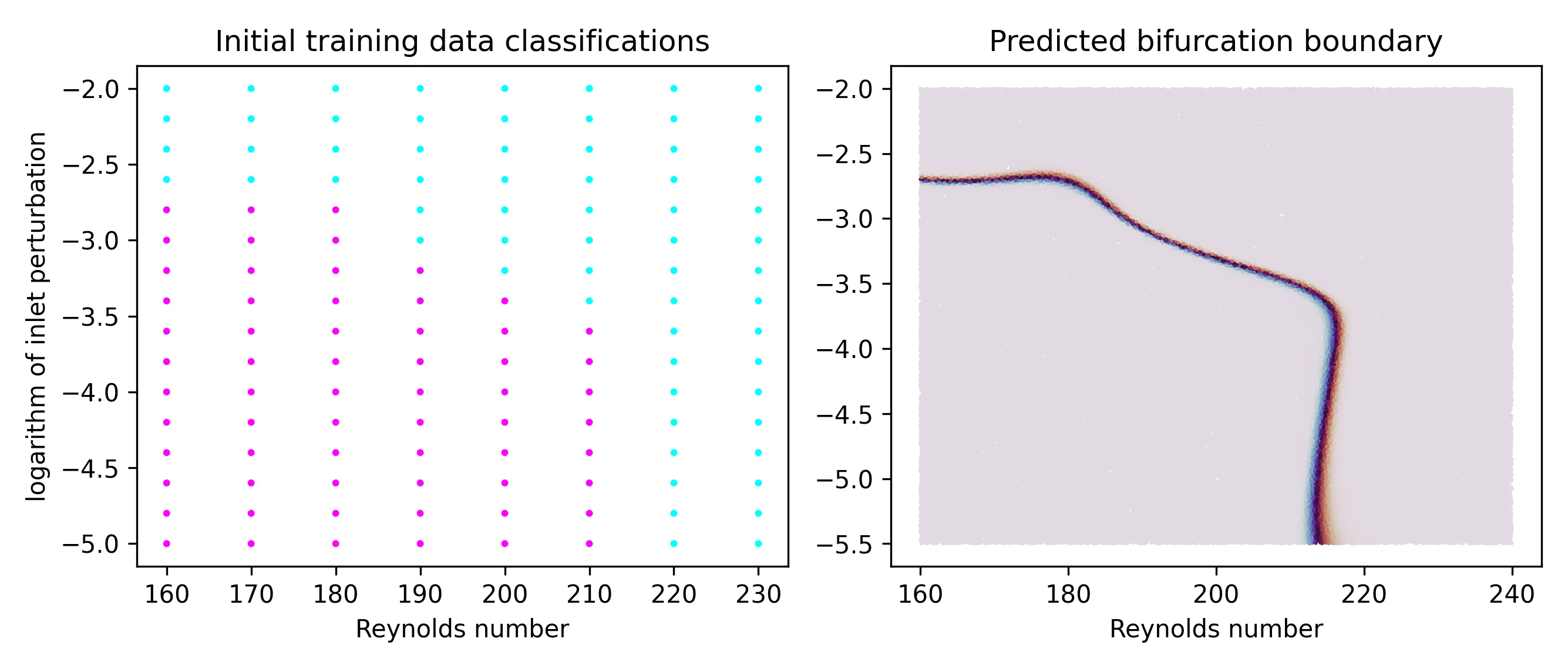
An adaptive sampling approach for efficient detection of bifurcation boundaries in parametrized fluid flow problems is presented herein. The study extends the machine-learning approach of Silvester (Machine Learning for Hydrodynamic Stability, arXiv:2407.09572), where a classifier network was trained on preselected simulation data to identify bifurcated and nonbifurcated flow regimes. In contrast, the proposed methodology introduces adaptivity through a flow-based deep generative model that automatically refines the sampling of the parameter space. The strategy has two components: a classifier network maps the flow parameters to a bifurcation probability, and a probability density estimation technique (KRnet) for the generation of new samples at each adaptive step. The classifier output provides a probabilistic measure of flow stability, and the Shannon entropy of these predictions is employed as an uncertainty indicator. KRnet is trained to approximate a probability density function that concentrates sampling in regions of high entropy, thereby directing computational effort towards the evolving bifurcation boundary. This coupling between classification and generative modeling establishes a feedback-driven adaptive learning process analogous to error-indicator based refinement in contemporary partial differential equation solution strategies. Starting from a uniform parameter distribution, the new approach achieves accurate bifurcation boundary identification with significantly fewer Navier--Stokes simulations, providing a scalable foundation for high-dimensional stability analysis.
Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) is an imaging technique in experimental fluid dynamics that quantifies flow fields around bluff bodies by analyzing the displacement of neutrally buoyant tracer particles immersed in the fluid. Traditional PIV approaches typically depend on tuning parameters specific to the imaging setup, making the performance sensitive to variations in illumination, flow conditions, and seeding density. On the other hand, even state-of-the-art machine learning methods for flow quantification are fragile outside their training set. In our experiments, we observed that flow quantification would improve if different tunings (or algorithms) were applied to different regions of the same image pair. In this work, we parallelize the instantaneous flow quantification with multiple algorithms and adopt a consensus framework based on the alternating direction method of multipliers, seamlessly incorporating priors such as smoothness and incompressibility. We perform several numerical experiments to demonstrate the benefits of this approach. For instance, we achieve a decrease in end-point-error of up to 20% of a dense-inverse-search estimator at an inference rate of 60Hz, and we show how this performance boost can be increased further with outlier rejection. Our method is implemented in JAX, effectively exploiting hardware acceleration, and integrated in Flow Gym, enabling (i) reproducible comparisons with the state-of-the-art, (ii) testing different base algorithms, (iii) straightforward deployment for active fluids control applications.
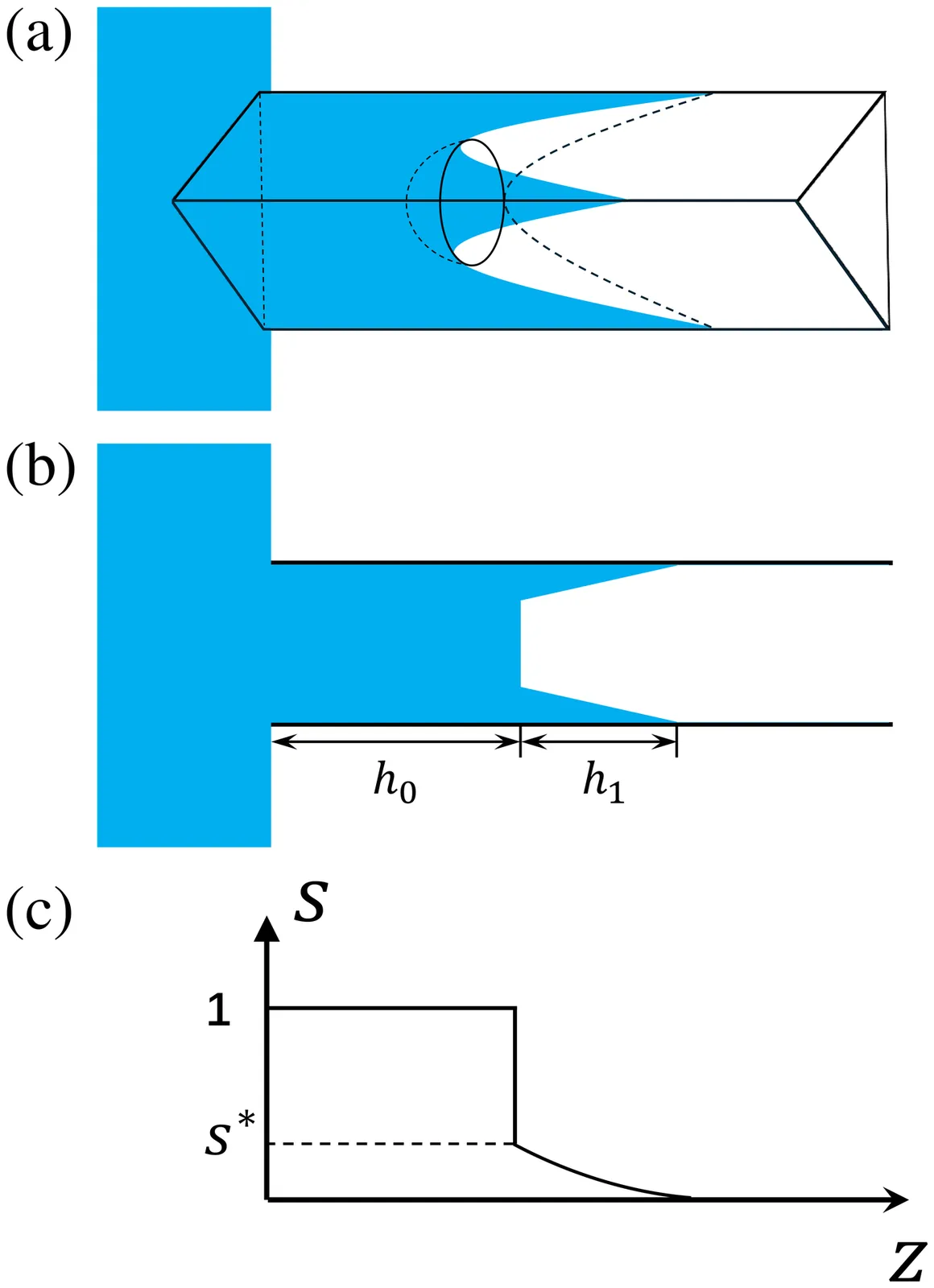
We study the dynamics of capillary filling in tubes of regular polygon cross-section. Using Onsager variational principle, we derive a coupled ordinary differential equation and partial differential equation, which respectively describe time evolution of the bulk flow and the saturation profile of the finger flow. We obtain both numerical solution and self-similar solution to the coupled equations, and the results indicate that the bulk flow and the finger flow both follow the $t^{1/2}$ time-scaling. We show that due to the coupling effect of the finger flow, the prefactor for the bulk flow is smaller than that of the Lucas-Washburn prediction. The reduction effect is more pronounced when the side number $n$ of the regular-polygon is small, while as $n$ increases, the prefactor approaches Lucas-Washburn prediction.
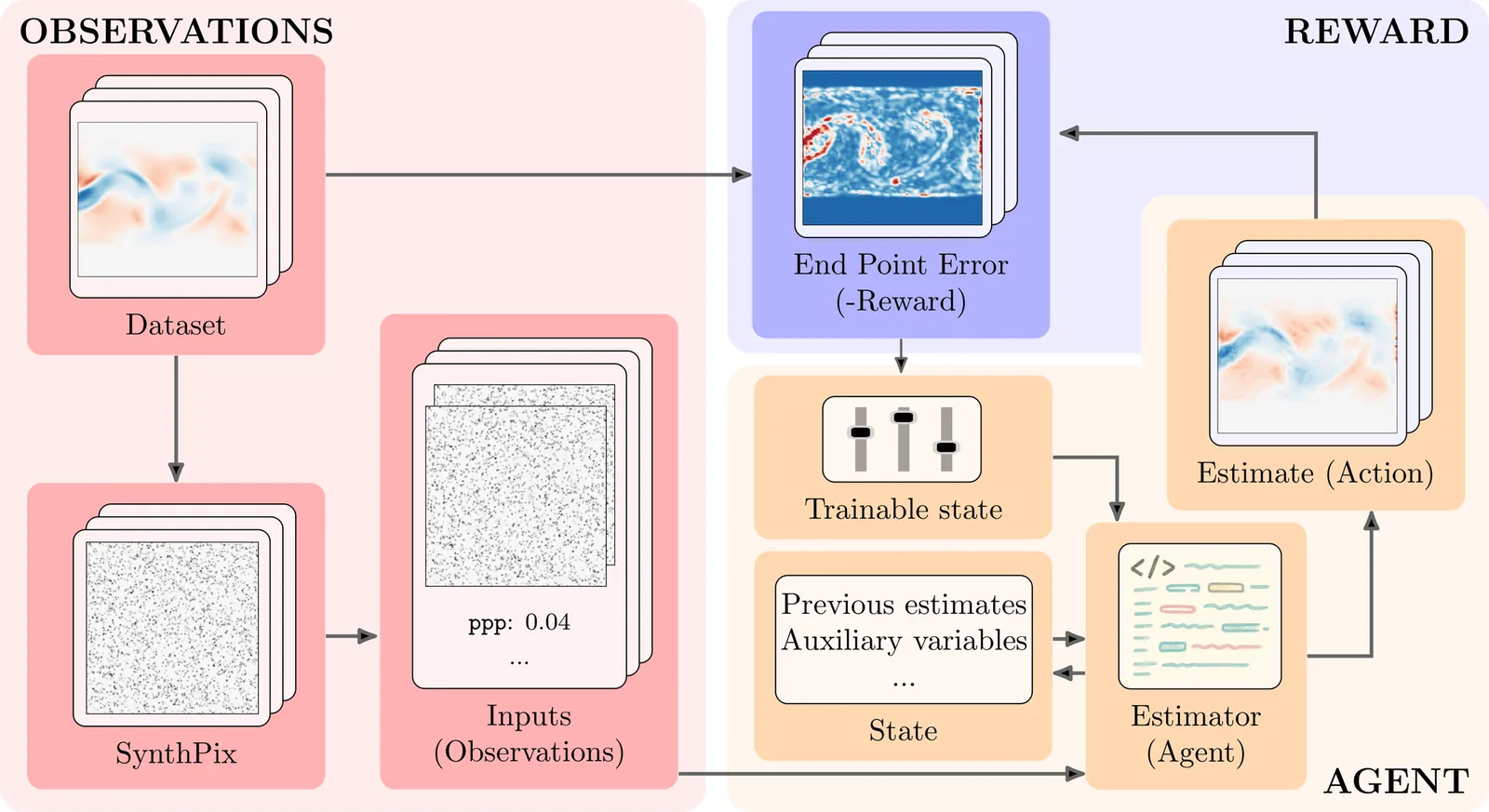
Flow Gym is a toolkit for research and deployment of flow-field quantification methods inspired by OpenAI Gym and Stable-Baselines3. It uses SynthPix as synthetic image generation engine and provides a unified interface for the testing, deployment and training of (learning-based) algorithms for flow-field quantification from a number of consecutive images of tracer particles. It also contains a growing number of integrations of existing algorithms and stable (re-)implementations in JAX.
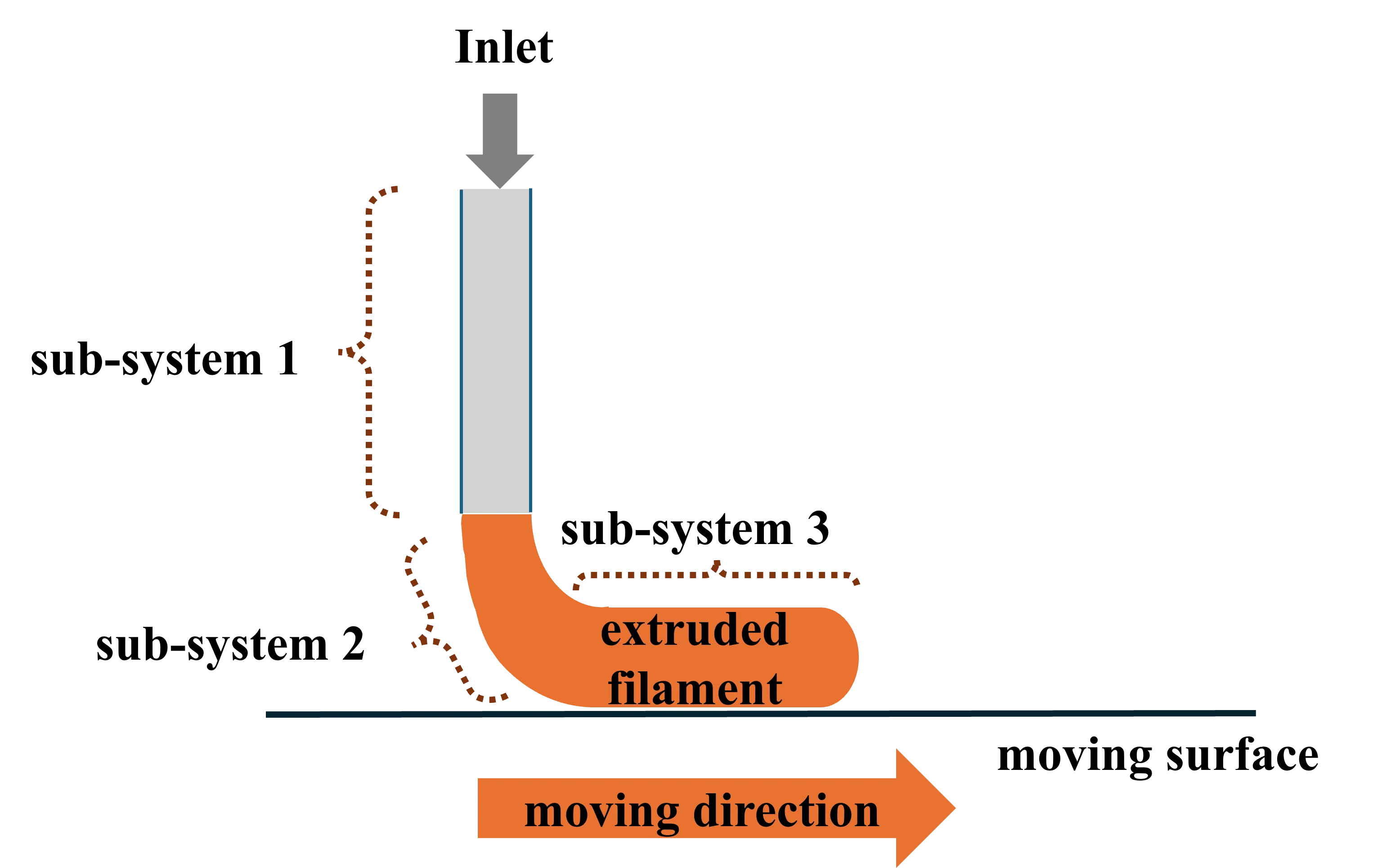
The trade off between model fidelity and computational cost remains a central challenge in the computational modeling of extrusion based 3D printing, particularly for real time optimization and control. Although high fidelity simulations have advanced considerably for offline analysis, dynamical modeling tailored for online, control oriented applications is still significantly underdeveloped. In this study, we propose a reduced order dynamical flow model that captures the transient behavior of extrusion based 3D printing. The model is grounded in physics based principles derived from the Navier Stokes equations and further simplified through spatial averaging and input dependent parameterization. To assess its performance, the model is identified via a nonlinear least squares approach using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation data spanning a range of printing conditions and subsequently validated across multiple combinations of training and testing scenarios. The results demonstrate strong agreement with the CFD data within the nozzle, the nozzle substrate gap, and the deposited layer regions. Overall, the proposed reduced order model successfully captures the dominant flow dynamics of the process while maintaining a level of simplicity compatible with real time control and optimization.