Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics
Atmospheric physics, climate science, ocean dynamics, weather modeling.
Atmospheric physics, climate science, ocean dynamics, weather modeling.
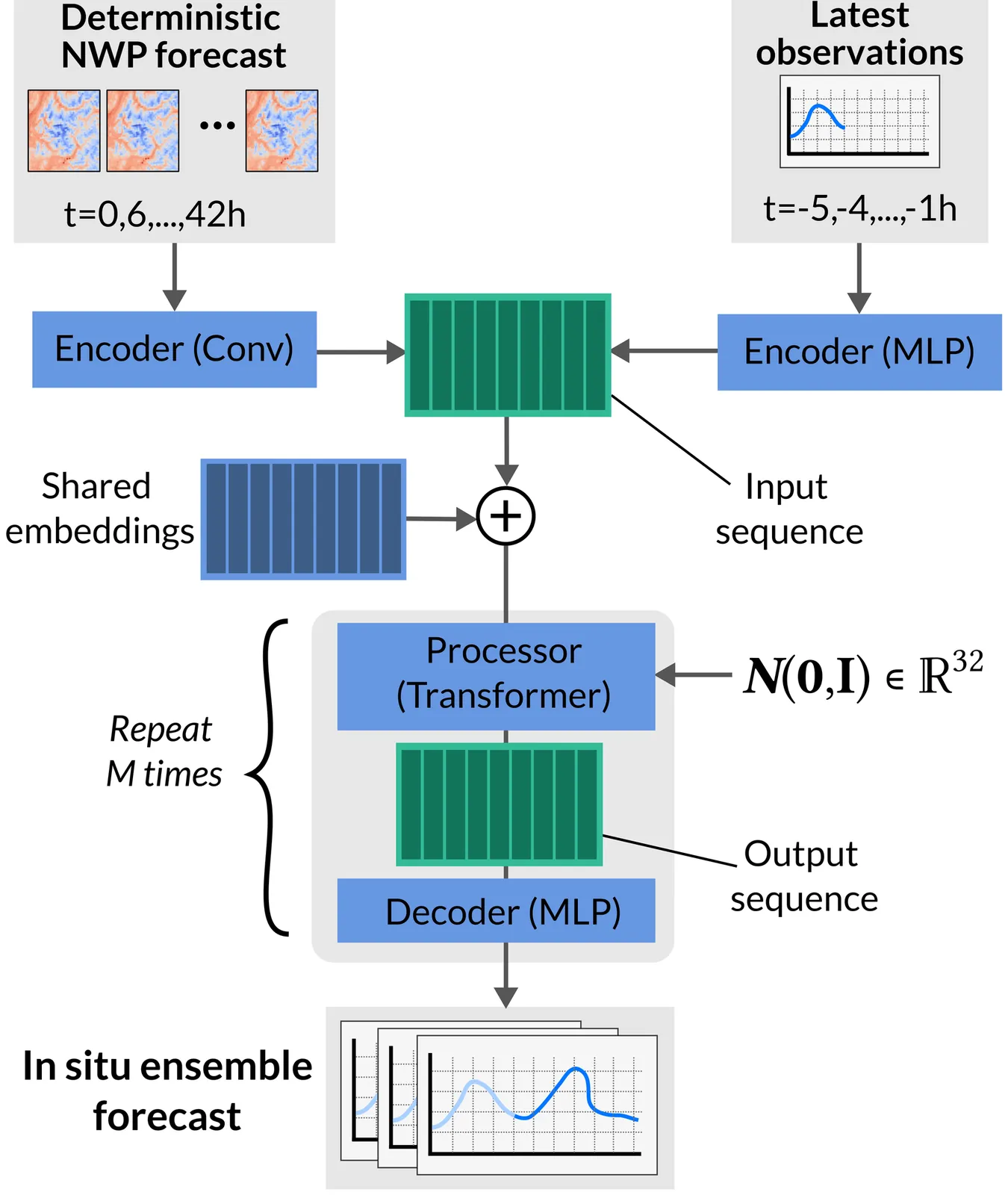
We propose Space-time in situ postprocessing (STIPP), a machine learning model that generates spatio-temporally consistent weather forecasts for a network of station locations. Gridded forecasts from classical numerical weather prediction or data-driven models often lack the necessary precision due to unresolved local effects. Typical statistical postprocessing methods correct these biases, but often degrade spatio-temporal correlation structures in doing so. Recent works based on generative modeling successfully improve spatial correlation structures but have to forecast every lead time independently. In contrast, STIPP makes joint spatio-temporal forecasts which have increased accuracy for surface temperature, wind, relative humidity and precipitation when compared to baseline methods. It makes hourly ensemble predictions given only a six-hourly deterministic forecast, blending the boundaries of postprocessing and temporal interpolation. By leveraging a multivariate proper scoring rule for training, STIPP contributes to ongoing work data-driven atmospheric models supervised only with distribution marginals.

Large data-driven physics models like DeepMind's weather model GraphCast have empirically succeeded in parameterizing time operators for complex dynamical systems with an accuracy reaching or in some cases exceeding that of traditional physics-based solvers. Unfortunately, how these data-driven models perform computations is largely unknown and whether their internal representations are interpretable or physically consistent is an open question. Here, we adapt tools from interpretability research in Large Language Models to analyze intermediate computational layers in GraphCast, leveraging sparse autoencoders to discover interpretable features in the neuron space of the model. We uncover distinct features on a wide range of length and time scales that correspond to tropical cyclones, atmospheric rivers, diurnal and seasonal behavior, large-scale precipitation patterns, specific geographical coding, and sea-ice extent, among others. We further demonstrate how the precise abstraction of these features can be probed via interventions on the prediction steps of the model. As a case study, we sparsely modify a feature corresponding to tropical cyclones in GraphCast and observe interpretable and physically consistent modifications to evolving hurricanes. Such methods offer a window into the black-box behavior of data-driven physics models and are a step towards realizing their potential as trustworthy predictors and scientifically valuable tools for discovery.
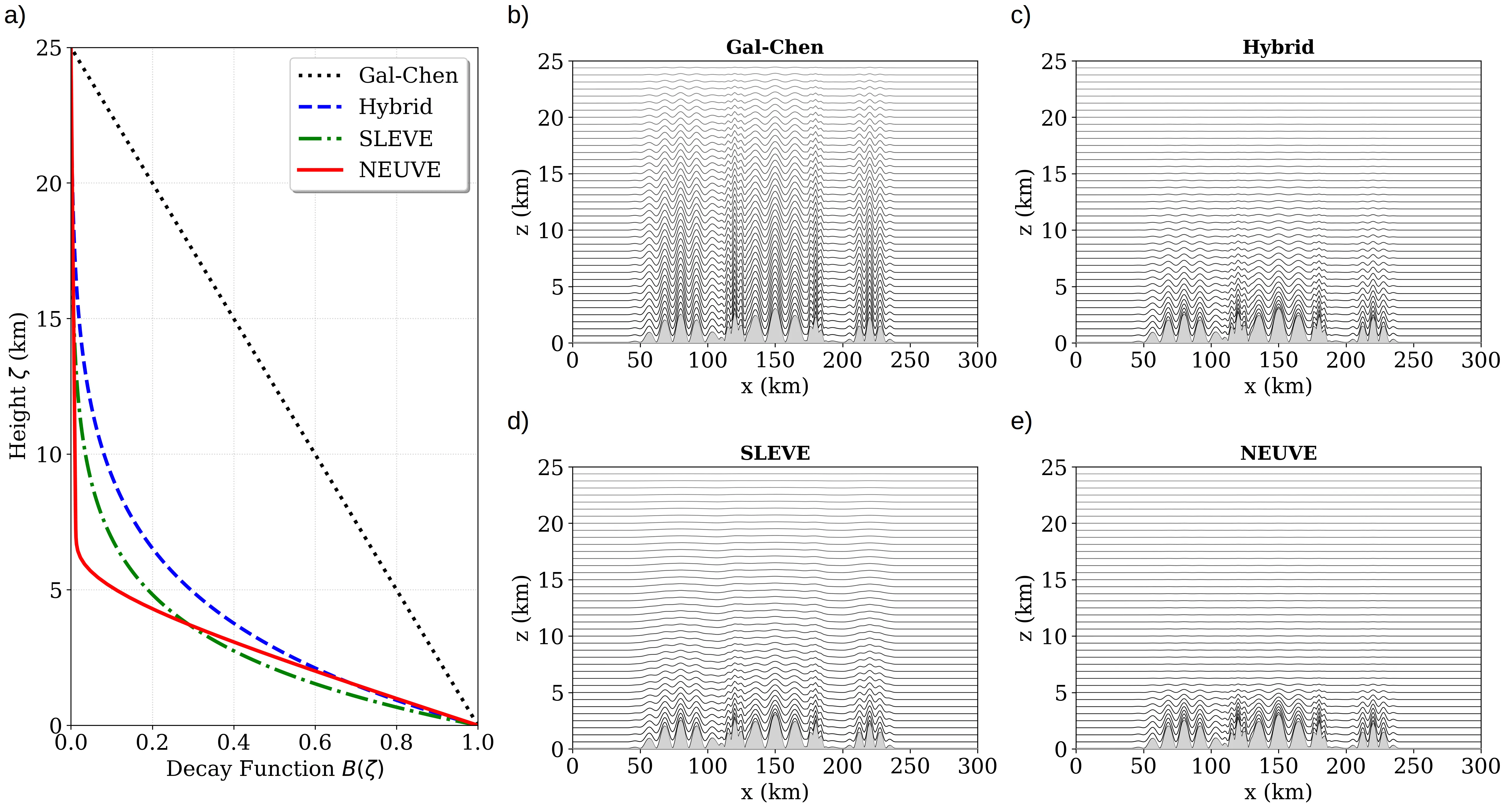
Terrain-following coordinates in atmospheric models often imprint their grid structure onto the solution, particularly over steep topography, where distorted coordinate layers can generate spurious horizontal and vertical motion. Standard formulations, such as hybrid or SLEVE coordinates, mitigate these errors by using analytic decay functions controlled by heuristic scale parameters that are typically tuned by hand and fixed a priori. In this work, we propose a framework to define a parametric vertical coordinate system as a learnable component within a differentiable dynamical core. We develop an end-to-end differentiable numerical solver for the two-dimensional non-hydrostatic Euler equations on an Arakawa C-grid, and introduce a NEUral Vertical Enhancement (NEUVE) terrain-following coordinate based on an integral transformed neural network that guarantees monotonicity. A key feature of our approach is the use of automatic differentiation to compute exact geometric metric terms, thereby eliminating truncation errors associated with finite-difference coordinate derivatives. By coupling simulation errors through the time integration to the parameterization, our formulation finds a grid structure optimized for both the underlying physics and numerics. Using several standard tests, we demonstrate that these learned coordinates reduce the mean squared error by a factor of 1.4 to 2 in non-linear statistical benchmarks, and eliminate spurious vertical velocity striations over steep topography.
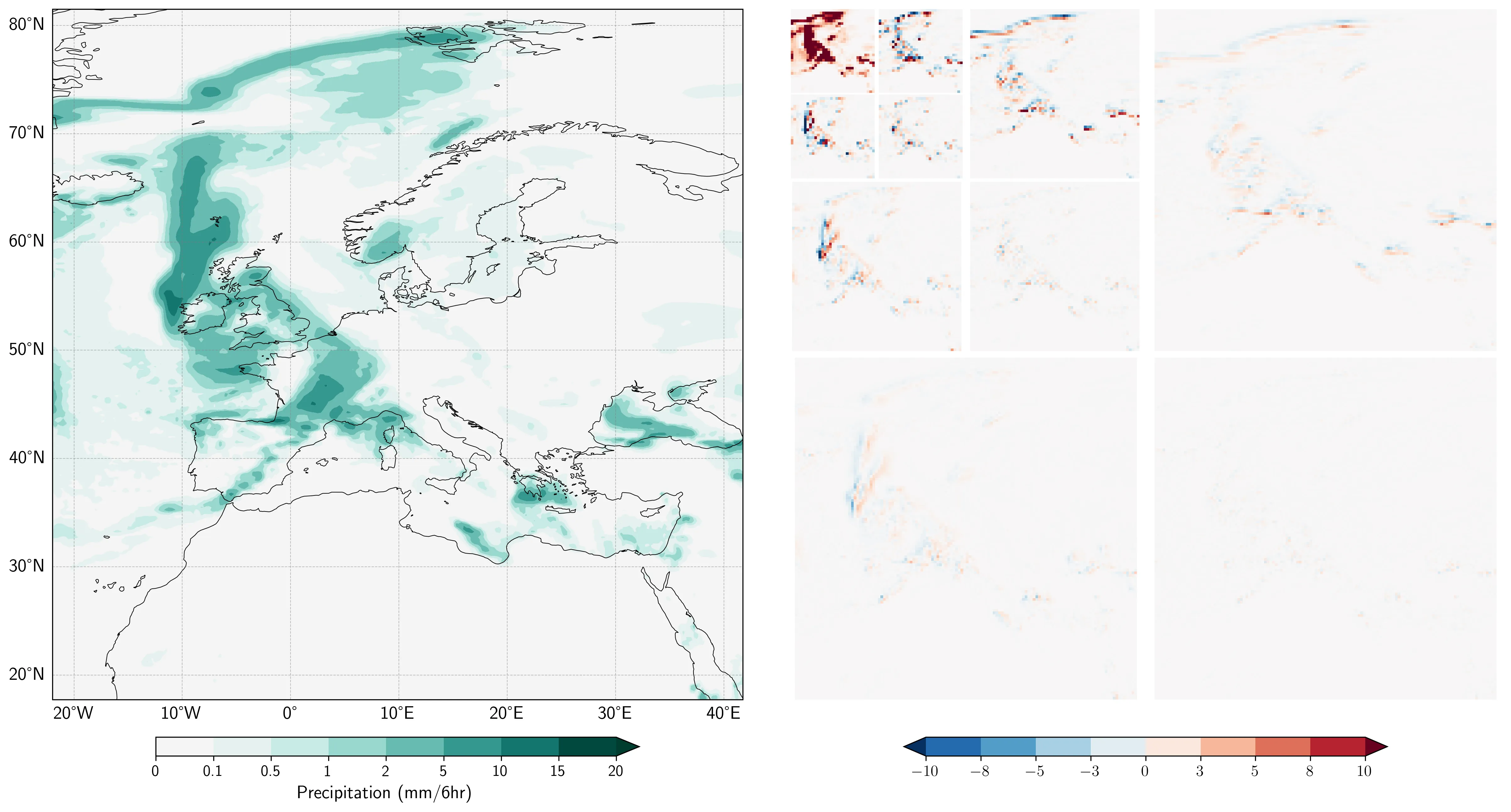
We introduce WaveSim, a multi-scale similarity metric for the evaluation of spatial fields in weather and climate applications. WaveSim exploits wavelet transforms to decompose input fields into scale-specific wavelet coefficients. The metric is built by multiplying three orthogonal components derived from these coefficients: Magnitude, which quantifies similarities in the energy distribution of the coefficients, i.e., the intensity of the field; Displacement, which captures spatial shift by comparing the centers of mass of normalized energy distributions; and Structure, which assesses pattern organization independent of location and amplitude. Each component yields a scale-specific similarity score ranging from 0 (no similarity) to 1 (perfect similarity), which are then combined across scales to produce an overall similarity measure. We first evaluate WaveSim using synthetic test cases, applying controlled spatial and temporal perturbations to systematically assess its sensitivity and expected behavior. We then demonstrate its applicability to physically relevant case studies of key modes of climate variability in Earth System Models. Traditional point-wise metrics lack a mechanism for attributing errors to physical scales or modes of dissimilarity. By operating in the wavelet domain and decomposing the signal along independent axes, WaveSim bypasses these limitations and provides an interpretable and diagnostically rich framework for assessing similarity in complex fields. Additionally, the WaveSim framework allows users to place emphasis on a specific scale or component, and lends itself to user-specific model intercomparison, model evaluation, and calibration and training of forecasting systems. We provide a PyTorch-ready implementation of WaveSim, along with all evaluation scripts, at: https://github.com/gabrieleaccarino/wavesim.
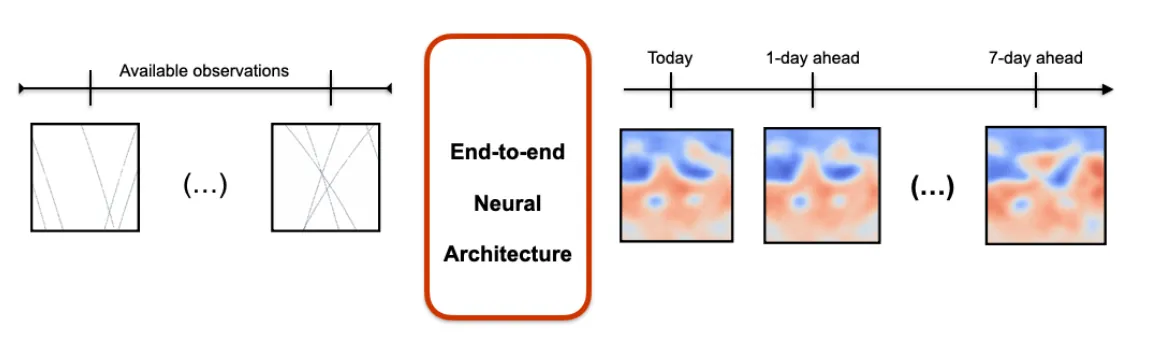
We present an end-to-end deep learning framework for short-term forecasting of global sea surface dynamics based on sparse satellite altimetry data. Building on two state-of-the-art architectures: U-Net and 4DVarNet, originally developed for image segmentation and spatiotemporal interpolation respectively, we adapt the models to forecast the sea level anomaly and sea surface currents over a 7-day horizon using sequences of sparse nadir altimeters observations. The model is trained on data from the GLORYS12 operational ocean reanalysis, with synthetic nadir sampling patterns applied to simulate realistic observational coverage. The forecasting task is formulated as a sequence-to-sequence mapping, with the input comprising partial sea level anomaly (SLA) snapshots and the target being the corresponding future full-field SLA maps. We evaluate model performance using (i) normalized root mean squared error (nRMSE), (ii) averaged effective resolution, (iii) percentage of correctly predicted velocities magnitudes and angles, and benchmark results against the operational Mercator Ocean forecast product. Results show that end-to-end neural forecasts outperform the baseline across all lead times, with particularly notable improvements in high variability regions. Our framework is developed within the OceanBench benchmarking initiative, promoting reproducibility and standardized evaluation in ocean machine learning. These results demonstrate the feasibility and potential of end-to-end neural forecasting models for operational oceanography, even in data-sparse conditions.
This paper documents a data set of UK rain radar image sequences for use in statistical modeling and machine learning methods for nowcasting. The main dataset contains 1,000 randomly sampled sequences of length 20 steps (15-minute increments) of 2D radar intensity fields of dimension 40x40 (at 5km spatial resolution). Spatially stratified sampling ensures spatial homogeneity despite removal of clear-sky cases by threshold-based truncation. For each radar sequence, additional atmospheric and geographic features are made available, including date, location, mean elevation, mean wind direction and speed and prevailing storm type. New R functions to extract data from the binary "Nimrod" radar data format are provided. A case study is presented to train and evaluate a simple convolutional neural network for radar nowcasting, including self-contained R code.
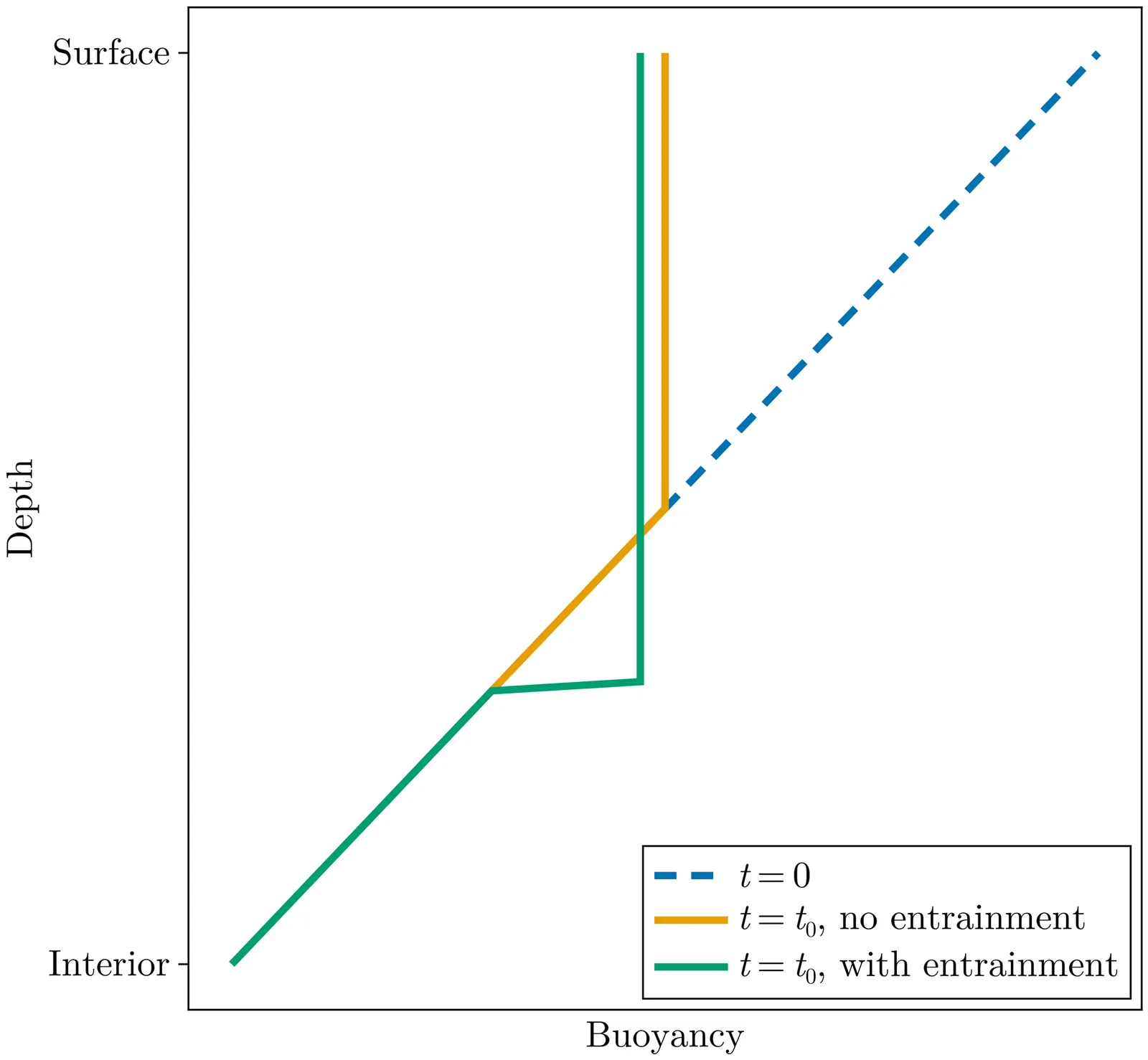
NORi is a machine-learned (ML) parameterization of ocean boundary layer turbulence that is physics-based and augmented with neural networks. NORi stands for neural ordinary differential equations (NODEs) Richardson number (Ri) closure. The physical parameterization is controlled by a Richardson number-dependent diffusivity and viscosity. The NODEs are trained to capture the entrainment through the base of the boundary layer, which cannot be represented with a local diffusive closure. The parameterization is trained using large-eddy simulations in an "a posteriori" fashion, where parameters are calibrated with a loss function that explicitly depends on the actual time-integrated variables of interest rather than the instantaneous subgrid fluxes, which are inherently noisy. NORi is designed for the realistic nonlinear equation of state of seawater and demonstrates excellent prediction and generalization capabilities in capturing entrainment dynamics under different convective strengths, oceanic background stratifications, rotation strengths, and surface wind forcings. NORi is numerically stable for at least 100 years of integration time in large-scale simulations, despite only being trained on 2-day horizons, and can be run with time steps as long as one hour. The highly expressive neural networks, combined with a physically-rigorous base closure, prove to be a robust paradigm for designing parameterizations for climate models where data requirements are drastically reduced, inference performance can be directly targeted and optimized, and numerical stability is implicitly encouraged during training.
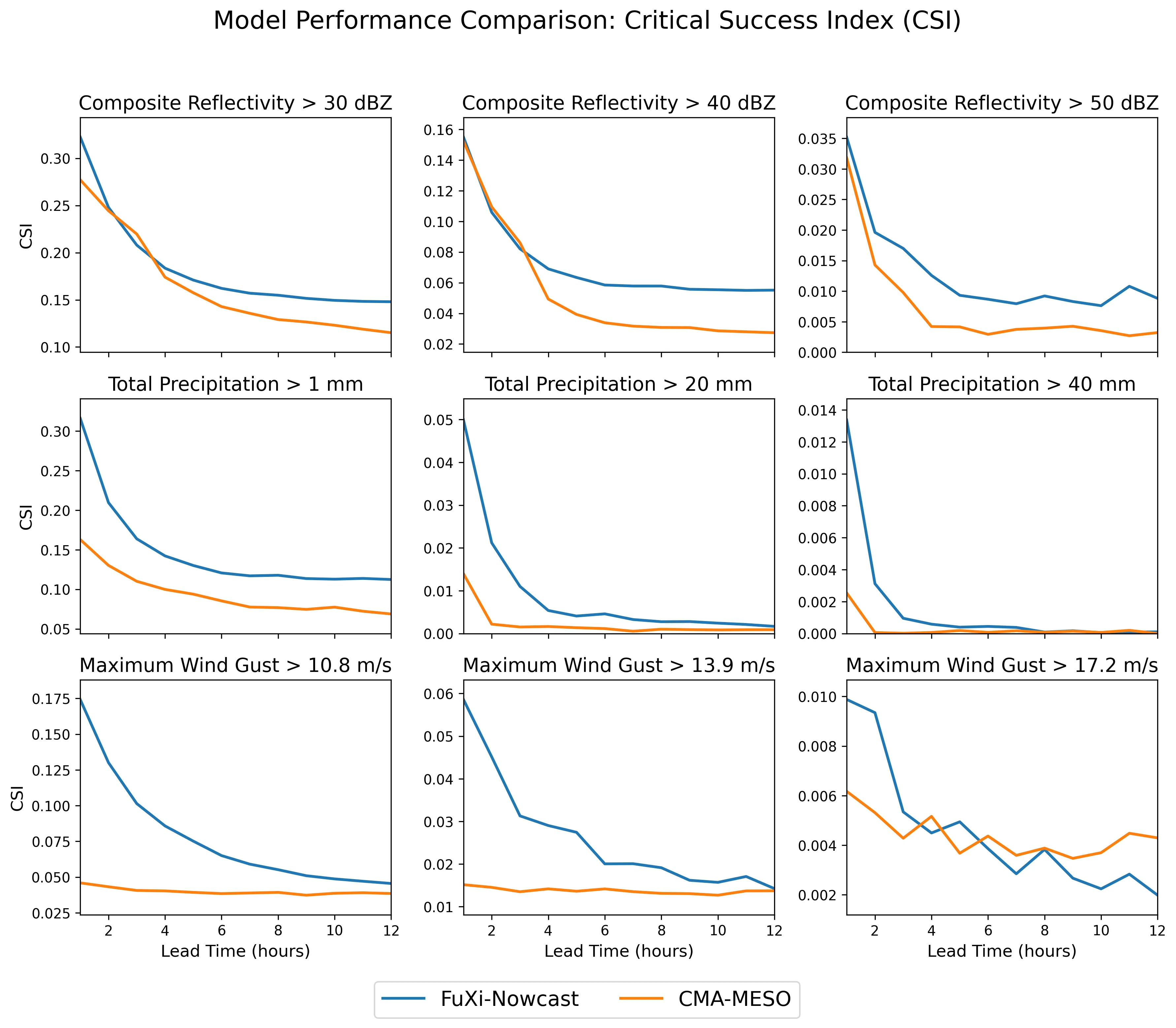
Accurate nowcasting of convective storms remains a major challenge for operational forecasting, particularly for convective initiation and the evolution of high-impact rainfall and strong winds. Here we present FuXi-Nowcast, a deep-learning system that jointly predicts composite radar reflectivity, surface precipitation, near-surface temperature, wind speed and wind gusts at 1-km resolution over eastern China. FuXi-Nowcast integrates multi-source observations, such as radar, surface stations and the High-Resolution Land Data Assimilation System (HRLDAS), with three-dimensional atmospheric fields from the machine-learning weather model FuXi-2.0 within a multi-task Swin-Transformer architecture. A convective signal enhancement module and distribution-aware hybrid loss functions are designed to preserve intense convective structures and mitigate the rapid intensity decay common in deep-learning nowcasts. FuXi-Nowcast surpasses the operational CMA-MESO 3-km numerical model in Critical Success Index for reflectivity, precipitation and wind gusts across thresholds and lead times up to 12 h, with the largest gains for heavy rainfall. Case studies further show that FuXi-Nowcast more accurately captures the timing, location and structure of convective initiation and subsequent evolution of convection. These results demonstrate that coupling three-dimensional machine-learning forecasts with high-resolution observations can provide multi-hazard, long-lead nowcasts that outperforms current operational systems.
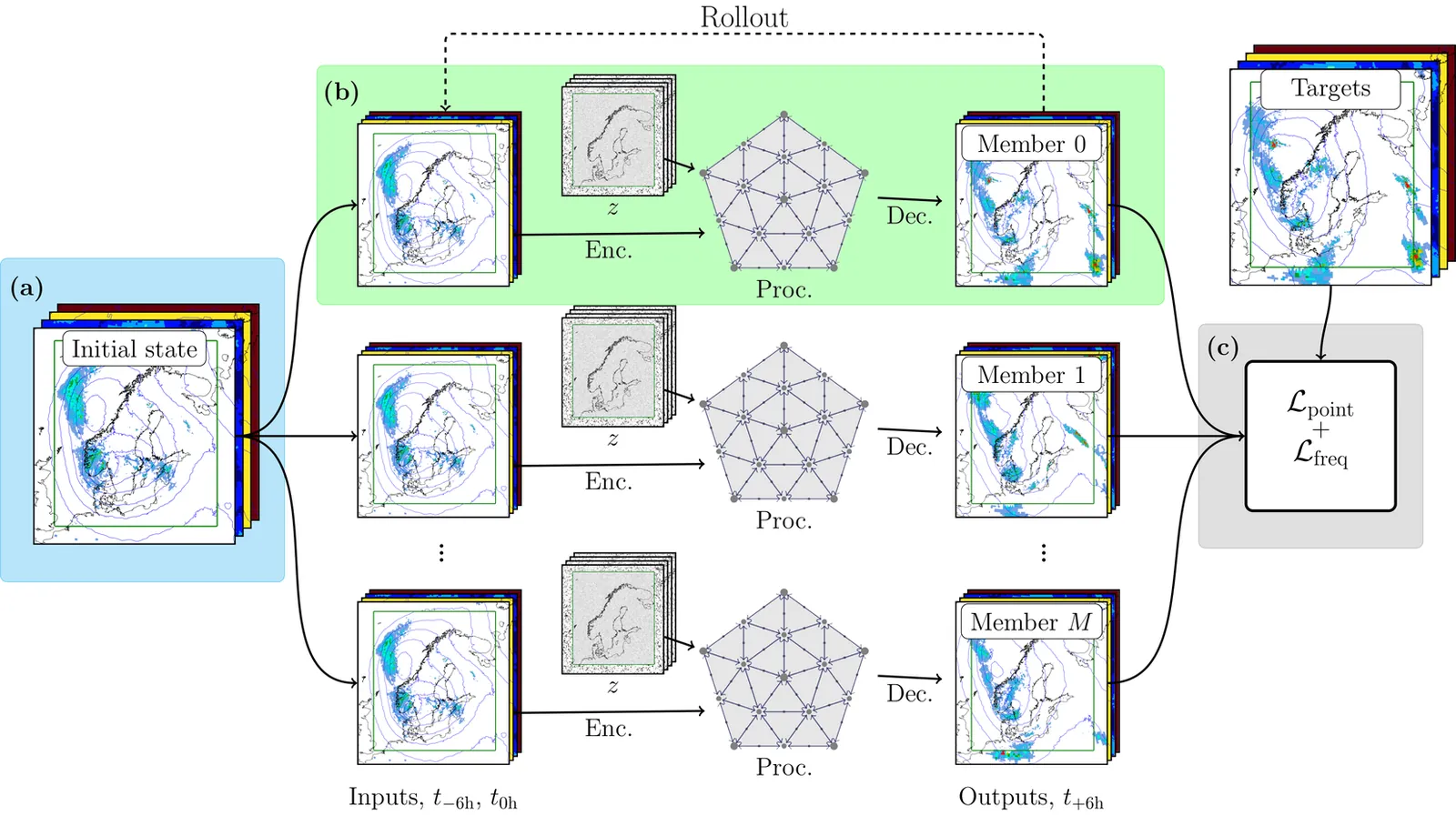
We present a probabilistic data-driven weather model capable of providing an ensemble of high spatial resolution realizations of 87 variables at arbitrary forecast length and ensemble size. The model uses a stretched grid, dedicating 2.5 km resolution to a region of interest, and 31 km resolution elsewhere. Based on a stochastic encoder-decoder architecture, the model is trained using a loss function based on the Continuous Ranked Probability Score (CRPS) evaluated point-wise in real and spectral space. The spectral loss components is shown to be necessary to create fields that are spatially coherent. The model is compared to high-resolution operational numerical weather prediction forecasts from the MetCoOp Ensemble Prediction System (MEPS), showing competitive forecasts when evaluated against observations from surface weather stations. The model produced fields that are more spatially coherent than mean squared error based models and CRPS based models without the spectral component in the loss.
Machine learning (ML) has shown significant promise in studying complex geophysical dynamical systems, including turbulence and climate processes. Such systems often display sensitive dependence on initial conditions, reflected in positive Lyapunov exponents, where even small perturbations in short-term forecasts can lead to large deviations in long-term outcomes. Thus, meaningful inference requires not only accurate short-term predictions, but also consistency with the system's long-term attractor that is captured by the marginal distribution of state variables. Existing approaches attempt to address this challenge by incorporating spatial and temporal dependence, but these strategies become impractical when data are extremely sparse. In this work, we show that prior knowledge of marginal distributions offers valuable complementary information to short-term observations, motivating a distribution-informed learning framework. We introduce a calibration algorithm based on normalization and the Kernelized Stein Discrepancy (KSD) to enhance ML predictions. The method here employs KSD within a reproducing kernel Hilbert space to calibrate model outputs, improving their fidelity to known physical distributions. This not only sharpens pointwise predictions but also enforces consistency with non-local statistical structures rooted in physical principles. Through synthetic experiments-spanning offline climatological CO2 fluxes and online quasi-geostrophic flow simulations-we demonstrate the robustness and broad utility of the proposed framework.

Predicting ocean wave behavior is challenging due to the difficulty in choosing suitable numerical models among many with varying capabilities. This review examines the development and performance of numerical wave models in coastal engineering and oceanography, focusing on the difference between phase-averaged spectral models and phase-resolving models. We evaluate the formulation, governing equations, and methods of widely used third-generation phase-averaged spectral models (SWAN, WAVEWATCH III, MIKE 21 SW, TOMAWAC, and WAM) alongside advanced phase-resolving models (FUNWAVE, SWASH, COULWAVE, and NHWAVE) that employ Boussinesq-type equations and non-hydrostatic formulations. The review begins with early parameterized models and progresses to contemporary third-generation models, which solve the wave action conservation equation with few spectral constraints. A comparison of the models' efficiency, accuracy in nearshore conditions, ability to resolve nonlinear wave-wave interaction, simulate wave breaking, diffraction, and wave-current interactions is provided. Applications in operational forecasting, extreme event simulation, coastal structure design, and assessing climate change impacts are discussed. The validation of these models and the statistical metrics and intercomparison studies used are addressed. A discussion of the limitations in computational scalability, physics parameterization, and model coupling is provided, along with emerging trends in high-resolution modeling and hybrid models. This review guides researchers in evaluating which models to use in coastal and oceanographic research.
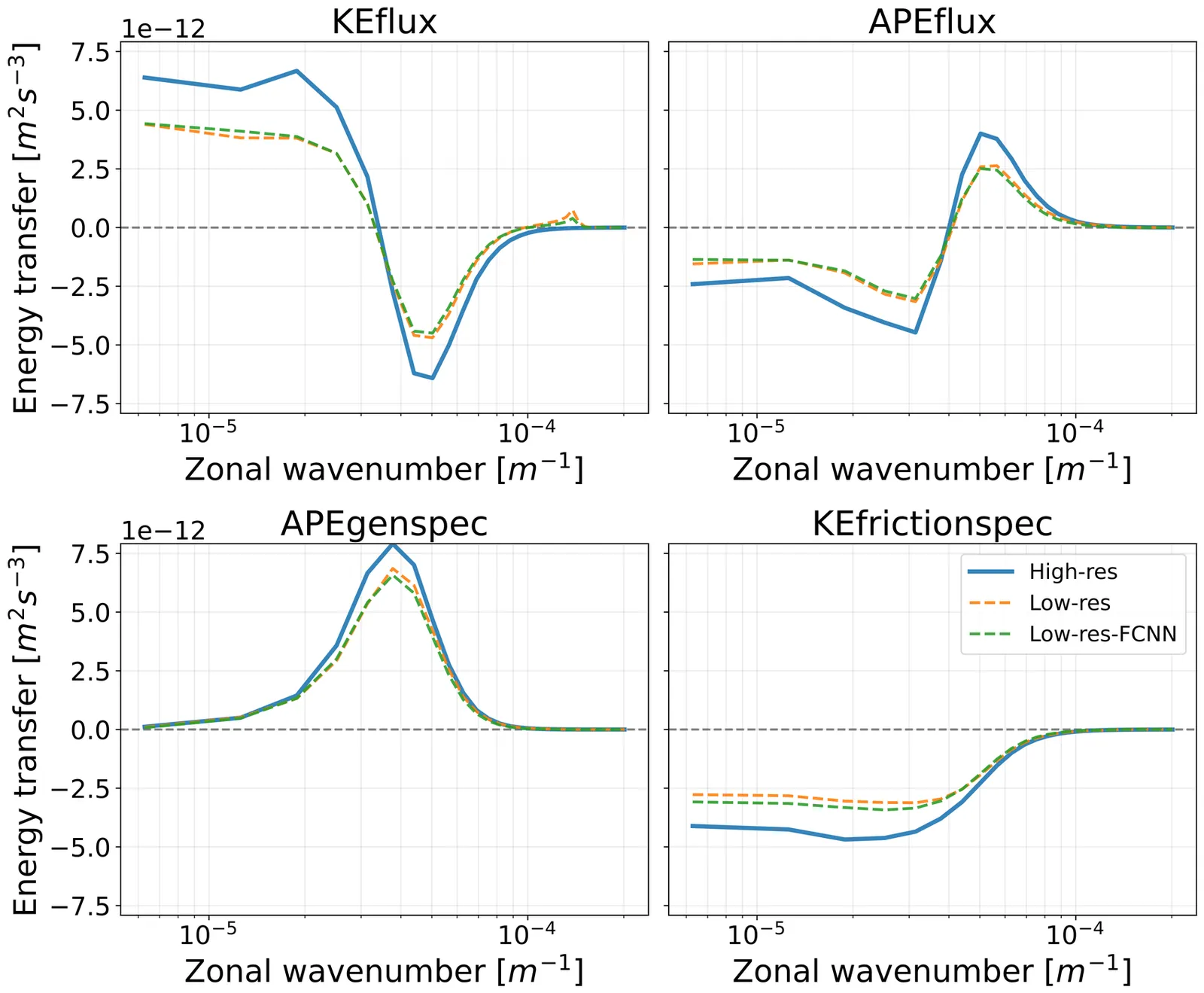
Subgrid machine-learning (ML) parameterizations have the potential to introduce a new generation of climate models that incorporate the effects of higher-resolution physics without incurring the prohibitive computational cost associated with more explicit physics-based simulations. However, important issues, ranging from online instability to inconsistent online performance, have limited their operational use for long-term climate projections. To more rapidly drive progress in solving these issues, domain scientists and machine learning researchers opened up the offline aspect of this problem to the broader machine learning and data science community with the release of ClimSim, a NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks publication, and an associated Kaggle competition. This paper reports on the downstream results of the Kaggle competition by coupling emulators inspired by the winning teams' architectures to an interactive climate model (including full cloud microphysics, a regime historically prone to online instability) and systematically evaluating their online performance. Our results demonstrate that online stability in the low-resolution, real-geography setting is reproducible across multiple diverse architectures, which we consider a key milestone. All tested architectures exhibit strikingly similar offline and online biases, though their responses to architecture-agnostic design choices (e.g., expanding the list of input variables) can differ significantly. Multiple Kaggle-inspired architectures achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on certain metrics such as zonal mean bias patterns and global RMSE, indicating that crowdsourcing the essence of the offline problem is one path to improving online performance in hybrid physics-AI climate simulation.
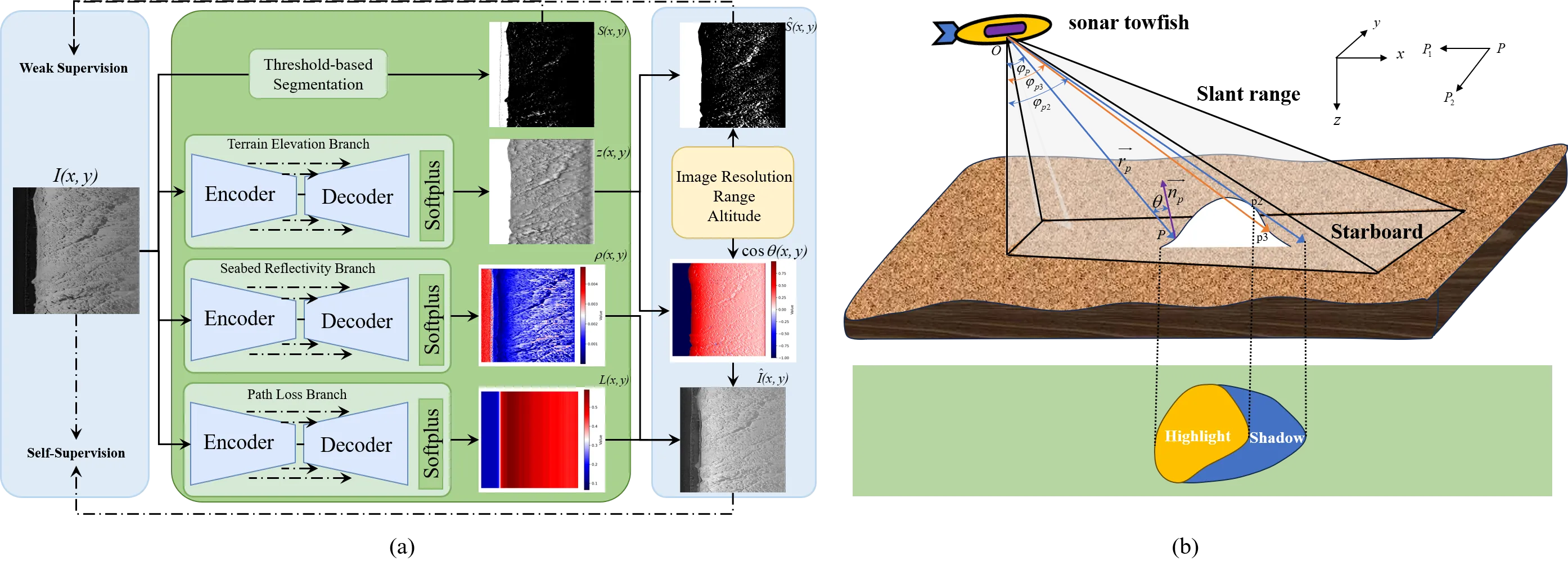
Side-scan sonar (SSS) imagery is widely used for seafloor mapping and underwater remote sensing, yet the measured intensity is strongly influenced by seabed reflectivity, terrain elevation, and acoustic path loss. This entanglement makes the imagery highly view-dependent and reduces the robustness of downstream analysis. In this letter, we present PhysDNet, a physics-guided multi-branch network that decouples SSS images into three interpretable fields: seabed reflectivity, terrain elevation, and propagation loss. By embedding the Lambertian reflection model, PhysDNet reconstructs sonar intensity from these components, enabling self-supervised training without ground-truth annotations. Experiments show that the decomposed representations preserve stable geological structures, capture physically consistent illumination and attenuation, and produce reliable shadow maps. These findings demonstrate that physics-guided decomposition provides a stable and interpretable domain for SSS analysis, improving both physical consistency and downstream tasks such as registration and shadow interpretation.
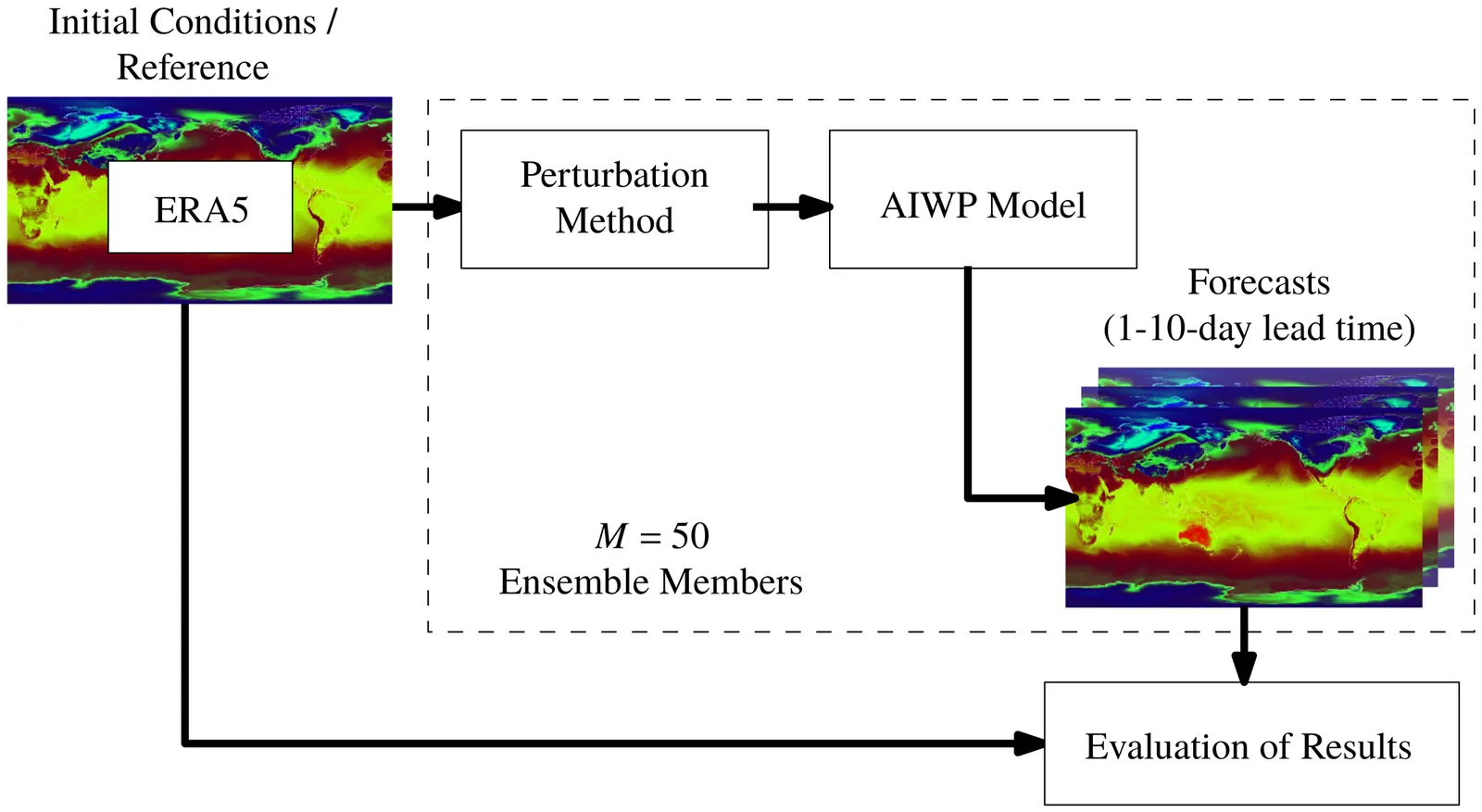
Accurate prediction of extreme weather events remains a major challenge for artificial intelligence based weather prediction systems. While deterministic models such as FuXi, GraphCast, and SFNO have achieved competitive forecast skill relative to numerical weather prediction, their ability to represent uncertainty and capture extremes is still limited. This study investigates how state of the art deterministic artificial intelligence based models respond to initial-condition perturbations and evaluates the resulting ensembles in forecasting extremes. Using three perturbation strategies (Gaussian noise, Hemispheric Centered Bred Vectors, and Huge Ensembles), we generate 50 member ensembles for two major events in August 2022: the Pakistan floods and the China heatwave. Ensemble skill is assessed against ERA5 and compared with IFS ENS and the probabilistic AIFSENS model using deterministic and probabilistic metrics. Results show that flow dependent perturbations produce the most realistic ensemble spread and highest probabilistic skill, narrowing but not closing the performance gap with numerical weather prediction ensembles. Across variables, artificial intelligence based weather models capture temperature extremes more effectively than precipitation. These findings demonstrate that input perturbations can extend deterministic models toward probabilistic forecasting, paving the way for approaches that combine flow dependent perturbations with generative or latent-space uncertainty modeling for reliable artificial intelligence-driven early warning systems.
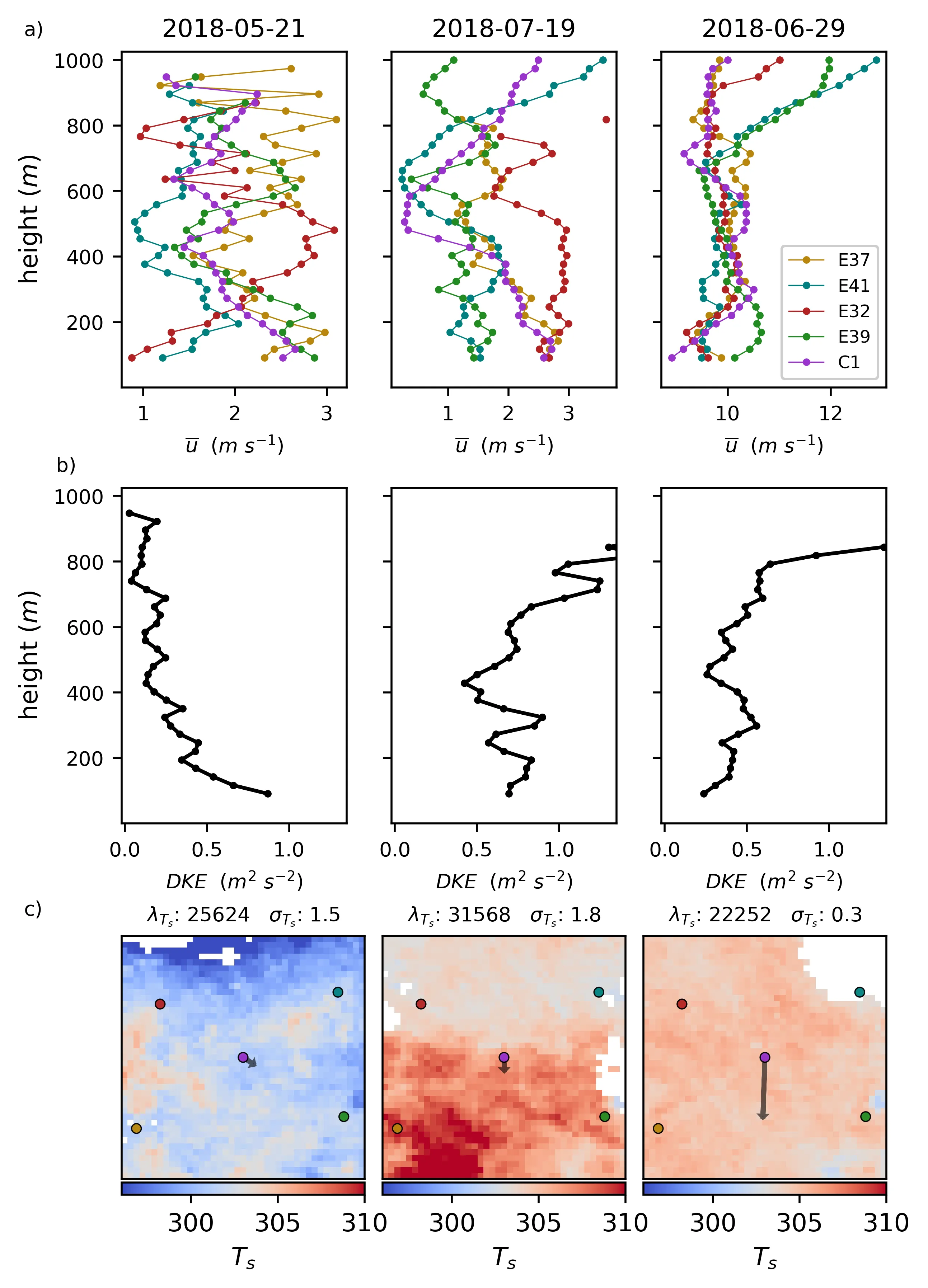
Surface heterogeneity, particularly complex patterns of surface heating, significantly influences mesoscale atmospheric flows, yet observational constraints and modeling limitations have hindered comprehensive understanding and model parameterization. This study introduces a framework combining satellite remote sensing and Doppler LiDAR to observationally evaluate heterogeneity-driven mesoscale flows in the atmospheric boundary layer. We quantify surface heterogeneity using metrics derived from GOES land surface temperature fields, and assess atmospheric impact through the Dispersive Kinetic Energy (DKE) calculated from a network of Doppler LiDAR profiles at the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) site. Results demonstrate that DKE and its ratio to the Mean Kinetic Energy (MKE) serve as effective indicators of heterogeneity driven flows, including breezes and circulations. The DKE and DKE ratio are correlated with metrics for surface heterogeneity, including the spatial correlation lengthscale, the spatial standard deviation, and the orientation of the surface heating gradient relative to the wind. The correlation becomes stronger when other flows that would affect DKE, including deep convection, low level jets, and storm fronts, are accounted for. Large Eddy Simulations contextualize the findings and validate the metric's behavior, showing general agreement with expectations from prior literature. Simulations also illustrate the sensitivity to configuration of LiDAR networks using virtual LiDAR sites, indicating that even smaller networks can be used effectively. This approach offers a scalable, observationally grounded method to explore heterogeneity-driven flows, advancing understanding of land-atmosphere interactions as well as efforts to parameterize these dynamics in climate and weather prediction models.
Traditional methods for enhancing tropical cyclone (TC) intensity from climate model outputs or projections have primarily relied on either dynamical or statistical downscaling. With recent advances in deep learning (DL) techniques, a natural question is whether DL can provide an alternative approach for improving TC intensity estimation from climate data. Using a common DL architecture based on convolutional neural networks (CNN) and selecting a set of key environmental features, we show that both TC intensity and structure can be effectively downscaled from climate reanalysis data as compared to common vortex detection methods, even when applied to coarse-resolution (0.5-degree) data. Our results thus highlight that TC intensity and structure are governed not only by its internal dynamics but also by local environments during TC development, for which DL models can learn and capture beyond the potential intensity framework. The performance of our DL model depends on several factors such as data sampling strategy, season, or the stage of TC development, with root-mean-square errors ranging from 3-9 ms$^{-1}$ for maximum 10 m wind and 10-20 hPa for minimum central pressure. Although these errors are better than direct vortex detection methods, their wide ranges also suggest that 0.5-degree resolution climate data may contain limited TC information for DL models to learn from, regardless of model optimizations or architectures. Possible improvements and challenges in addressing the lack of fine-scale TC information in coarse resolution climate reanalysis datasets will be discussed.
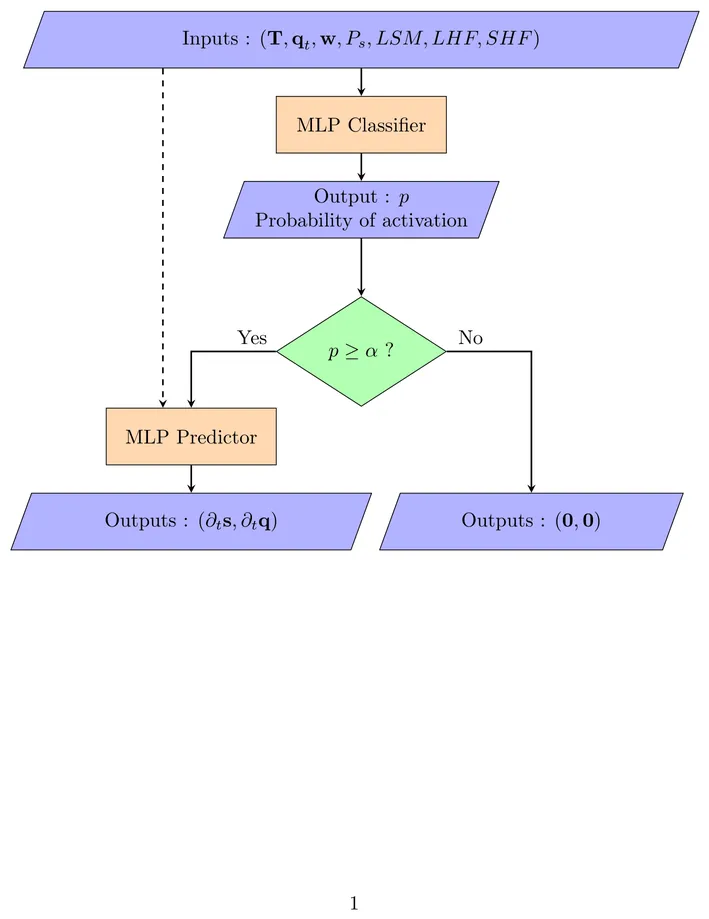
In this study, we improve a neural network (NN) parameterization of deep convection in the global atmosphere model ARP-GEM. To take into account the sporadic nature of convection, we develop a NN parameterization that includes a triggering mechanism that can detect whether deep convection is active or not within a grid-cell. This new data-driven parameterization outperforms the existing NN parameterization in present climate when replacing the original deep convection scheme of ARP-GEM. Online simulations with the NN parameterization run without stability issues. Then, this NN parameterization is evaluated online in a warmer climate. We confirm that using relative humidity instead of the specific total humidity as input for the NN (trained with present data) improves the performance and generalization in warmer climate. Finally, we perform the training of the NN parameterization with data from a warmer climate and this configuration get similar results when used in simulations in present or warmer climates.
Arctic sea ice is rapidly retreating due to global warming, and emerging evidence suggests that the rate of decline may have been underestimated. A key factor contributing to this underestimation is the coarse resolution of current climate models, which fail to accurately represent eddy floe interactions, climate extremes, and other critical small scale processes. Here, we elucidate the roles of these dynamics in accelerating sea ice melt and emphasize the need for higher resolution models to improve projections of Arctic sea ice.
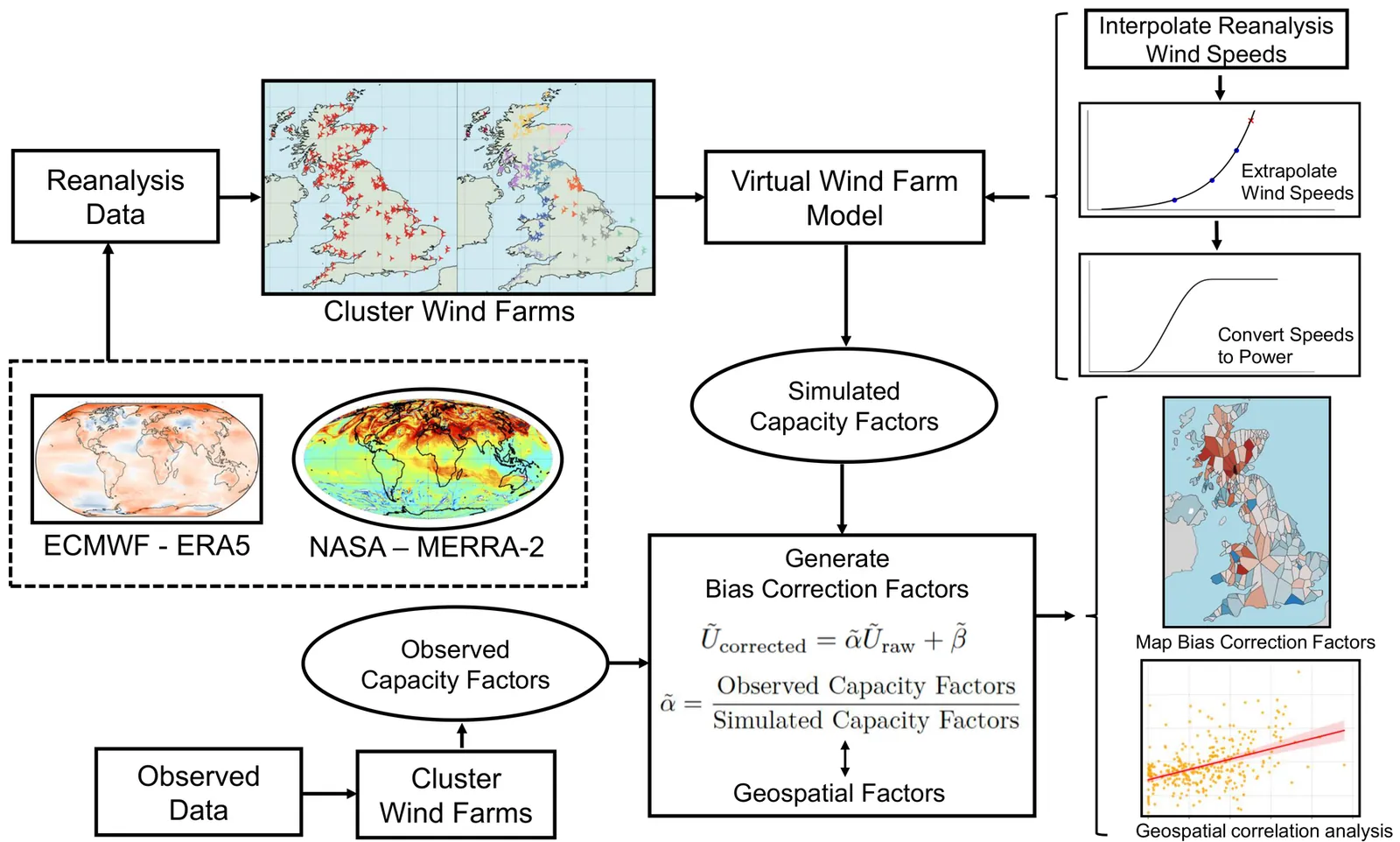
Reanalysis datasets have become indispensable tools for wind resource assessment and wind power simulation, offering long-term and spatially continuous wind fields across large regions. However, they inherently contain systematic wind speed biases arising from various factors, including simplified physical parameterizations, observational uncertainties, and limited spatial resolution. Among these, low spatial resolution poses a particular challenge for capturing local variability accurately. Whereas prevailing industry practice generally relies on either no bias correction or coarse, nationally uniform adjustments, we extend and thoroughly analyse a recently proposed spatially resolved, cluster-based bias correction framework. This approach is designed to better account for local heterogeneity and is applied to 319 wind farms across the United Kingdom to evaluate its effectiveness. Results show that this method reduced monthly wind power simulation errors by more than 32% compared to the uncorrected ERA5 reanalysis dataset. The method is further applied to the MERRA-2 dataset for comparative evaluation, demonstrating its effectiveness and robustness for different reanalysis products. In contrast to prior studies, which rarely quantify the influence of topography on reanalysis biases, this research presents a detailed spatial mapping of bias correction factors across the UK. The analysis reveals that for wind energy applications, ERA5 wind speed errors exhibit strong spatial variability, with the most significant underestimations in the Scottish Highlands and mountainous areas of Wales. These findings highlight the importance of explicitly accounting for geographic variability when correcting reanalysis wind speeds, and provide new insights into region-specific bias patterns relevant for high-resolution wind energy modelling.
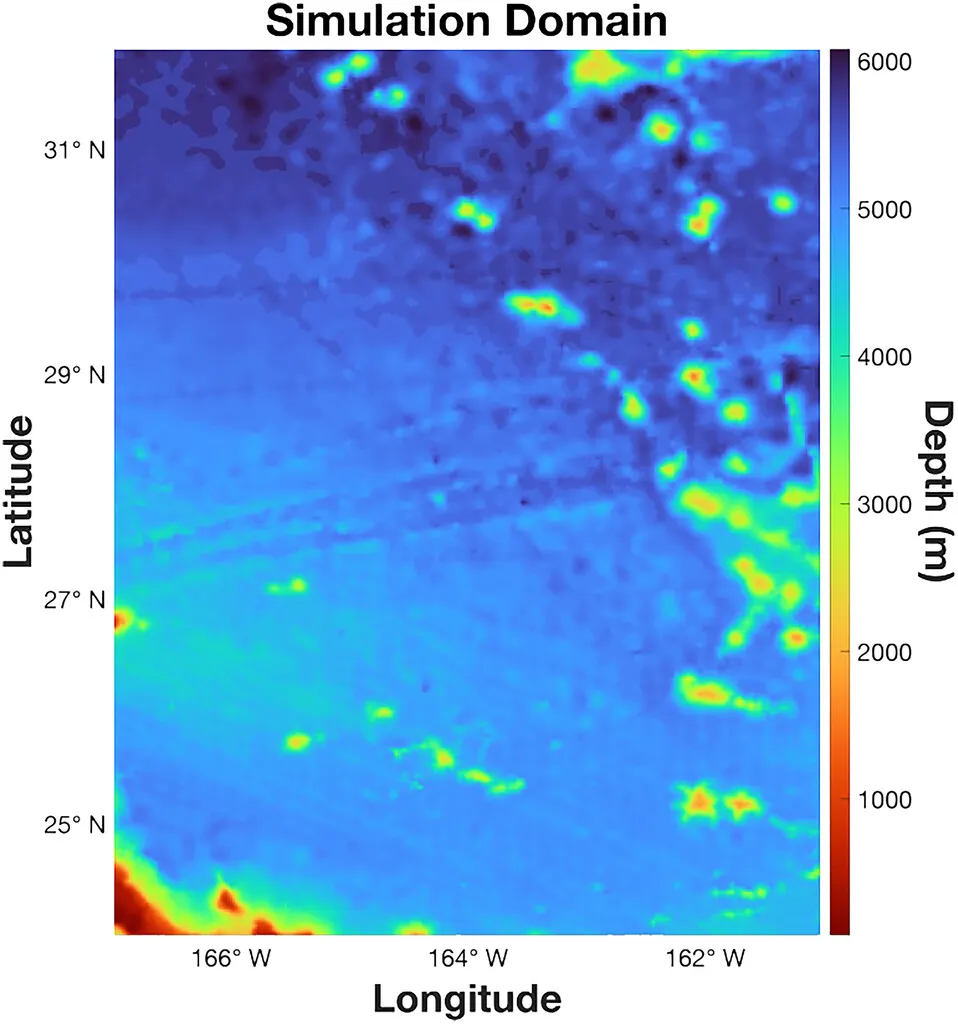
Consistency relations of internal gravity waves (IGWs) describe ratios of cross-spectral quantities as functions of frequency. It has been a common practice to evaluate the measured or simulated signals (e.g., time series of velocity, density, etc.) against the consistency relations, as a way to determine whether an oceanic field of interest is comprised of IGWs. One such study is carried out in Nelson et al. (JGR Oceans, 125(5), 2020, e2019JC015974), which certifies that the ocean interior field in a numerical simulation of a region southwest of Hawaii is dominated by IGWs, through evaluating the consistency relations derived from time series at a depth of 620 m. However, we find that when the same procedure is applied at greater depths (e.g., 2362 m, 3062 m, and 4987 m), a clear deviation of the simulated signal from the classical consistency relations is observed. In this paper, we identify the reason for the unexpected deviation and show that it is a general phenomenon due to interference of low vertical modes under the reflection by the ocean bottom. We further derive a new set of formulae to characterize the consistency relations of these low modes and validate these formulae using model output.