Astrophysics
Cosmology, galaxies, stellar physics, and astronomical instrumentation
Cosmology, galaxies, stellar physics, and astronomical instrumentation
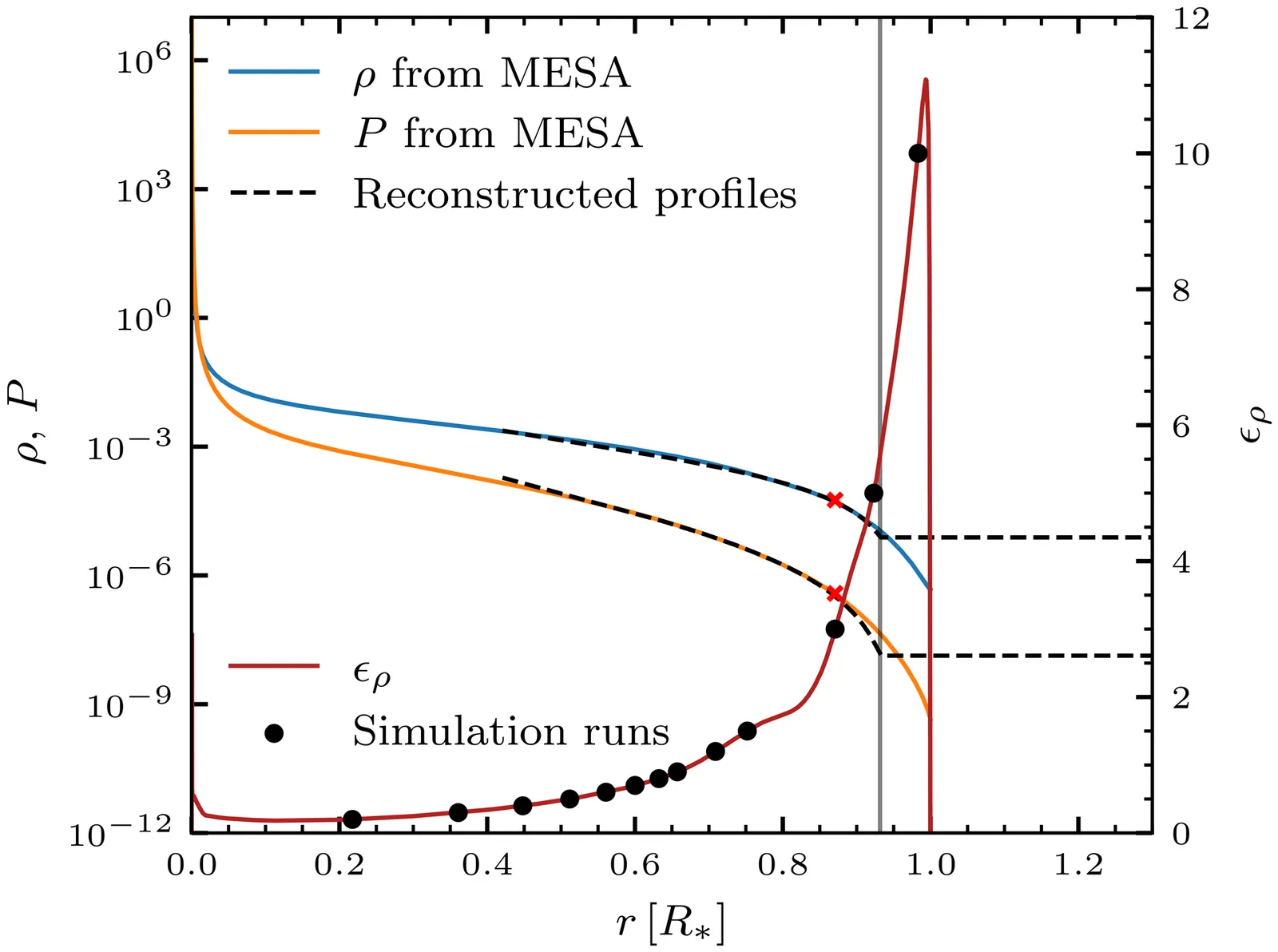
Common envelope evolution (CEE) is a crucial phase in binary stellar evolution. Current global three-dimensional simulations lack the resolution to capture the small-scale dynamics around the embedded companion, while local wind-tunnel simulations always approximate the companion's orbital motion as linear rather than as rotation around the center of mass. We investigate how rotation, accretion, and stratification influence small-scale gas dynamics, gravitational drag and lift forces, and the spin-up rate of the companion. We perform three-dimensional local hydrodynamic simulations of a $0.2\, M_\odot$ compact companion plunging into the envelope of a $2\, M_\odot$ red giant in a reference frame rotating at the companion's orbital angular velocity, using the Athena++ code. The presence of stratification generates an inward-directed force, partially opposed by a rotation-induced outward lift force. Both the resulting inward directed force and the drag force, strongly influenced by stratification, would affect the evolution of the binary separation. We propose revised semi-analytical prescriptions for both drag and lift forces. Without accretion and for sufficiently small gravitational softening radii, a quasi-hydrostatic bubble forms around the companion, while accretion prevents its formation and converts kinetic energy into heat that could contribute to the envelope ejection. Drag and lift forces are only marginally affected by accretion. The companion spin-up rate varies non-monotonically in time, first increasing and then decreasing as it plunges deeper into the envelope. These results motivate future magnetohydrodynamic simulations to investigate how accretion, rotation, and stratification affect magnetic amplification, and how magnetic fields, in turn, influence mass and angular momentum accretion rates, as well as the drag and lift force exerted on the companion.

The long GRB 180728A, at a redshift of $z = 0.1171$, stands out due to its high isotropic energy of $E_{γ,iso} \sim 2.5 \times 10^{51}$ erg, in contrast with most events at redshift $z<0.2$. We analyze the properties of GRB 180728A's prompt emission, afterglow, and associated supernova SN 2018fip, comparing them with other GRB-SN events. This study employs a dense photometric and spectroscopic follow-up of the afterglow and the SN up to 80 days after the burst, supported by image subtraction to remove the presence of a nearby bright star, and modelling of both the afterglow and the supernova. GRB 180728A lies on the $E_{p,i}-E_{γ,iso}$ plane occupied by classical collapsar events, and the prompt emission is one of the most energetic at $z < 0.2$ after GRB 030329 and GRB 221009A. The afterglow of GRB 180728A is less luminous than that of most long GRBs, showing a shallow early phase that steepens around 5 hours (0.2 days). The GRB exploded in an irregular, low-mass, blue, star-forming galaxy, typical of low-z collapsar events. Because of the relatively faint afterglow, the light curve bump of SN 2018fip dominates the optical emission already after $\sim$3 days and is one of the best sampled to date. The strong suppression below $\sim$ 4000 angstrom and a largely featureless continuum in the early 6--9 days spectra favor aspherical two-component ejecta with a high-velocity collimated component ($> 20,000 km s^{-1}$), dominant early-on, and a more massive, low-velocity component, which dominates at much later epochs. Our findings indicate that asymmetries need to be considered in order to better understand GRB-SNe. In any case, SN 2018fip shares many characteristics with typical GRB-SNe. Its kinetic energy is below the common range of $10^{52}-10^{53}$ erg and does not correlate with the high energy of the GRB, highlighting the diversity of the GRB-SN energy budget partition.
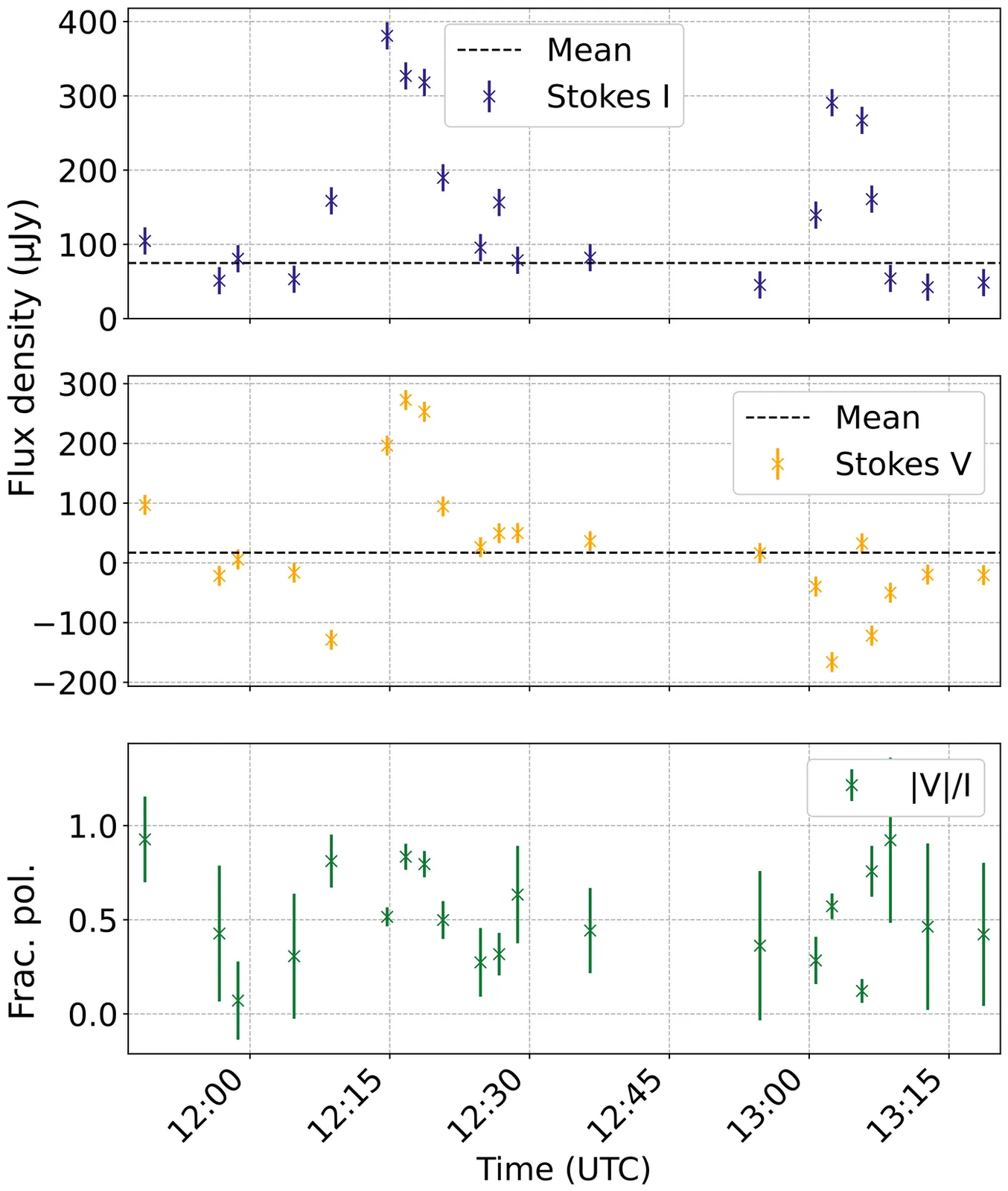
We present the detection of 2MASS J22282889-4310262 (2M2228), a T6/T6.5 brown dwarf, using the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) archival data observed at C band (4-8 GHz) over two observing epochs ($2\times96$ minutes). 2M2228 is detected at time and frequency averaged Stokes I and V peak flux densities of $67.3\pm4.9\ μ \rm{Jy beam}^{-1}$ and $14.4\pm3.0\ μ\text{Jy beam}^{-1}$ in the first epoch and $107.2\pm5.2\ μ\rm{Jy\ beam}^{-1}$ and $-20.7\pm1.2\ μ\text{Jy beam}^{-1}$ in the second epoch. This discovery constitutes the eighth and, notably, the most rapidly rotating T dwarf detected to date at radio wavelengths. Our observations reveal highly polarised bursts at fractional polarisation ratios $f_\text{c}>50$%. Using Stokes I light curves, we measure occurrence intervals of $\sim47$ and $\sim58$ minutes in the two observing epochs respectively with the first burst aligning within a half period timescale of the the previously measured mid infrared photometric period of $85.8\pm0.32$ minutes. We attribute the emission to the electron cyclotron maser emission (ECME) and constrain the magnetic field strength to $B\gtrsim1.4$ kG. We emphasise that the periods inferred are provisional considering the short observing durations. The combination of previously demonstrated atmospheric stability and newly detected radio emission in 2M2228 makes it a promising laboratory for testing magnetospheric currents-driven auroral models and for guiding future coordinated James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and radio observations to probe the link between auroral activity and atmospheric dynamics in T-type brown dwarfs.
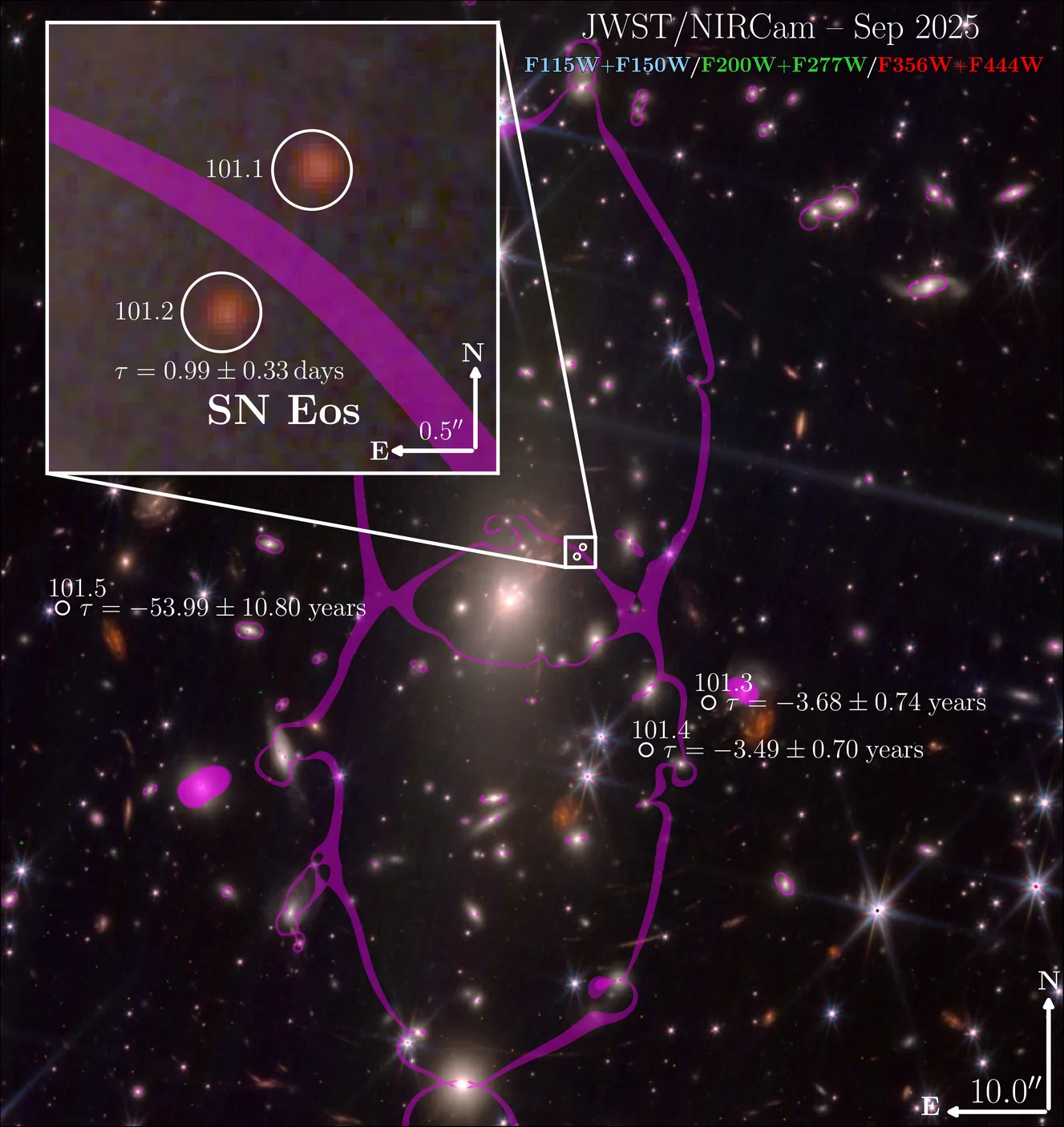
Observing supernovae (SNe) in the early Universe (z > 3) provides a window into how both galaxies and individual stars have evolved over cosmic time, yet a detailed study of high-redshift stars and SNe has remained difficult due to their extreme distances and cosmological redshifting. To overcome the former, searches for gravitationally lensed sources allow for the discovery of magnified SNe that appear as multiple images - further providing the opportunity for efficient follow-up. Here we present the discovery of "SN Eos": a strongly lensed, multiply-imaged, SN II at a spectroscopic redshift of z = 5.133 +/- 0.001. SN Eos exploded in a Lyman-α emitting galaxy when the Universe was only ~1 billion years old, shortly after it reionized and became transparent to ultraviolet radiation. A year prior to our discovery in JWST data, archival HST imaging of SN Eos reveals rest-frame far ultraviolet (~1,300Å) emission, indicative of shock breakout or interaction with circumstellar material in the first few (rest-frame) days after explosion. The JWST spectroscopy of SN Eos, now the farthest spectroscopically confirmed SN ever discovered, shows that SN Eos's progenitor star likely formed in a metal-poor environment (<= 0.1 Z_{\odot}), providing the first direct evidence of massive star formation in the metal-poor, early Universe. SN Eos would not have been detectable without the extreme lensing magnification of the system, highlighting the potential of such discoveries to eventually place constraints on the faint end of the cosmic star-formation rate density in the very early Universe.
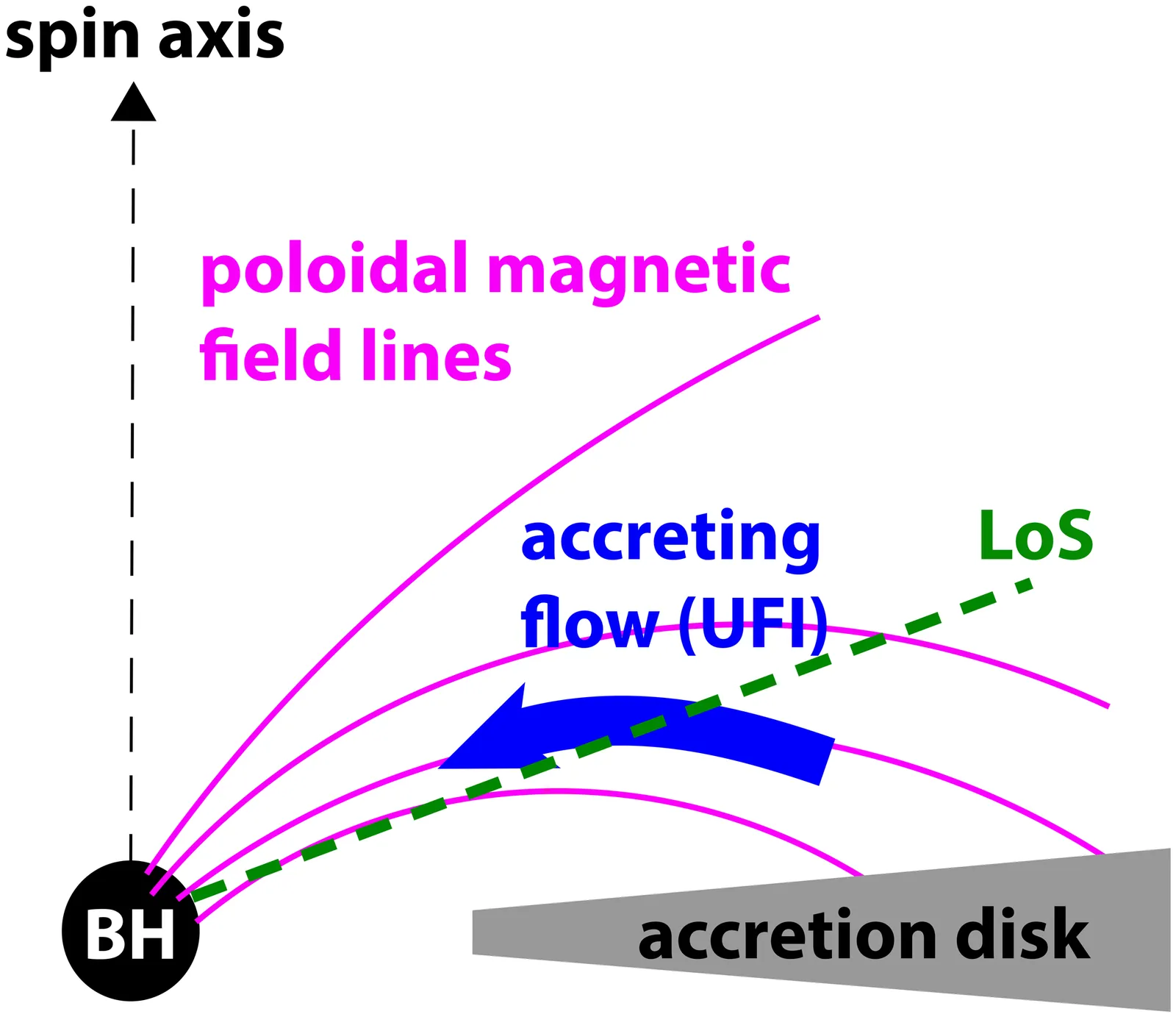
Motivated by a number of X-ray observations of active galactic nuclei (AGNs) that exhibit a potential signature of ultra-fast inflows (UFIs), we consider in this work a scenario that UFIs can be physically identified as weakly-magnetized hydrodynamic accretion flows that is guided and channeled by poloidal magnetic field into low-to-mid latitude above the equatorial disk. In the context of general relativistic hydrodynamics (GRHD) under a weak-field limit in Kerr spacetime, we present a set of preliminary results by numerically calculating the physical property of GRHD flows (e.g. kinematics and density distribution) in an effort to simulate redshifted absorption line spectra. Our model demonstrates that such GRHD accretion off the equatorial plane (i.e. $v \gsim 0.1c$ where $c$ is the speed of light in the vicinity of AGN closer than $\sim 100$ \sw radii) can manifest itself as UFIs in the form of redshifted absorption signature assuming the observed characteristics such as column density of $N_H \sim 10^{23}$ cm$^{-2}$ and ionization parameter of $\log (ξ\rm{[erg~cm~s^{-1}])} \sim 3$ as also seen in recent multi-epoch {\it NuSTAR} observations among other data.
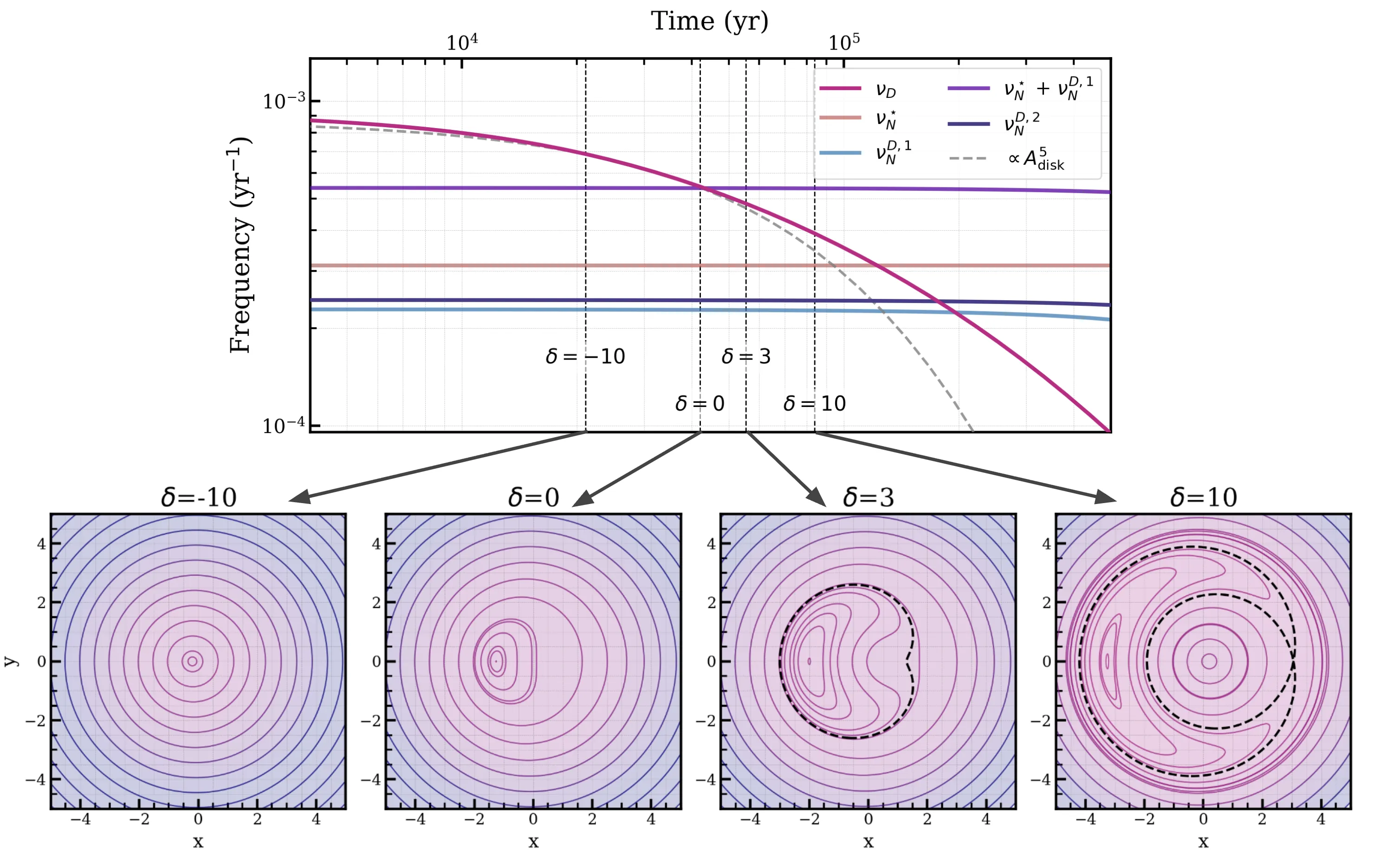
The stellar spin-orbit angles of Neptune-sized planets present a primordial yet puzzling view of the planetary formation epoch. The striking dichotomy of aligned and perpendicular orbital configurations are suggestive of obliquity excitation through secular resonance -- a process where the precession of a hot Neptune becomes locked onto a forcing frequency, and is slowly guided into a perpendicular state. Previous models of resonant capture have involved the presence of companion perturbers to the star-planet-disk system, but in most cases, such companions are not confirmed to be present. In this work, we present a mechanism for exciting Neptunes to polar orbits in systems without giant perturbers, where photo-evaporation is the self-contained mechanism. Photo-evaporation opens a gap in the protoplanetary disk at ~1 au, and the inner disk continues to viscously accrete onto the host star, precessing quickly due to the perturbation of the outer disk. As the inner disk shrinks, it precesses more slowly, and encounters a resonance with the J2 precession of the Neptune, quickly exciting it to a polar configuration. While likely not applicable to more massive planets which trigger back-reactions onto the disk, this mechanism reproduces the obliquities of small planets in multiple respects.
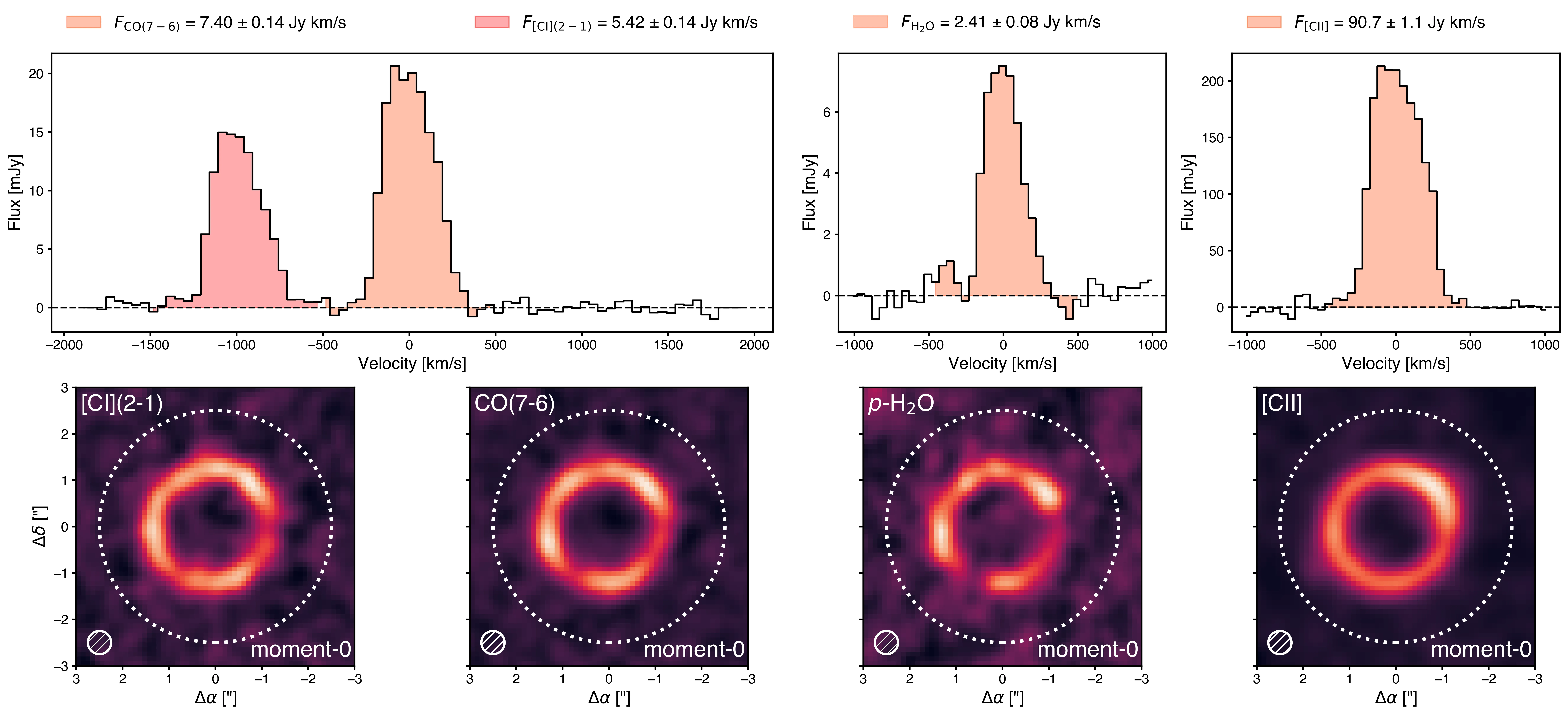
We present new and archival Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) observations of two strongly lensed dusty star-forming galaxies (DSFGs) selected from the South Pole Telescope survey, SPT0418-47 $(z = 4.225)$ and SPT2147-50 $(z = 3.760)$. We study the [C II], CO(7-6), [C I](2-1), and, in SPT0418-47, $p$-H$_2$O emission, which along with the underlying continuum (rest-frame 160 $μ$m and 380 $μ$m) are routinely used as tracers of gas mass and/or star-formation rate (SFR). We perform a pixel-by-pixel analysis of both sources in the image plane to study the resolved Kennicutt-Schmidt relation, finding generally good agreement between the slopes of the SFR versus gas mass surface density using the different tracers. Using lens modeling methods, we find that the dust emission is more compact than the line emission in both sources, with CO(7-6) and [C I](2-1) similar in extent and [C II] the most extended, reminiscent of recent findings of extended [C II] spatial distributions in galaxies at similar cosmic epochs. We develop the [C I](2-1) / CO(7-6) flux density ratio as an observable proxy for gas depletion timescale ($τ_{\rm dep}$), which can be applied to large samples of DSFGs, in lieu of more detailed inferences of this timescale which require analysis of observations at multiple wavelengths. Furthermore, the extended [C II] emission in both sources, compared to the total continuum and line emission, suggests that [C II], used in recent years as a molecular gas mass and SFR tracer in high-$z$ galaxies, may not always be a suitable tracer of these physical quantities.
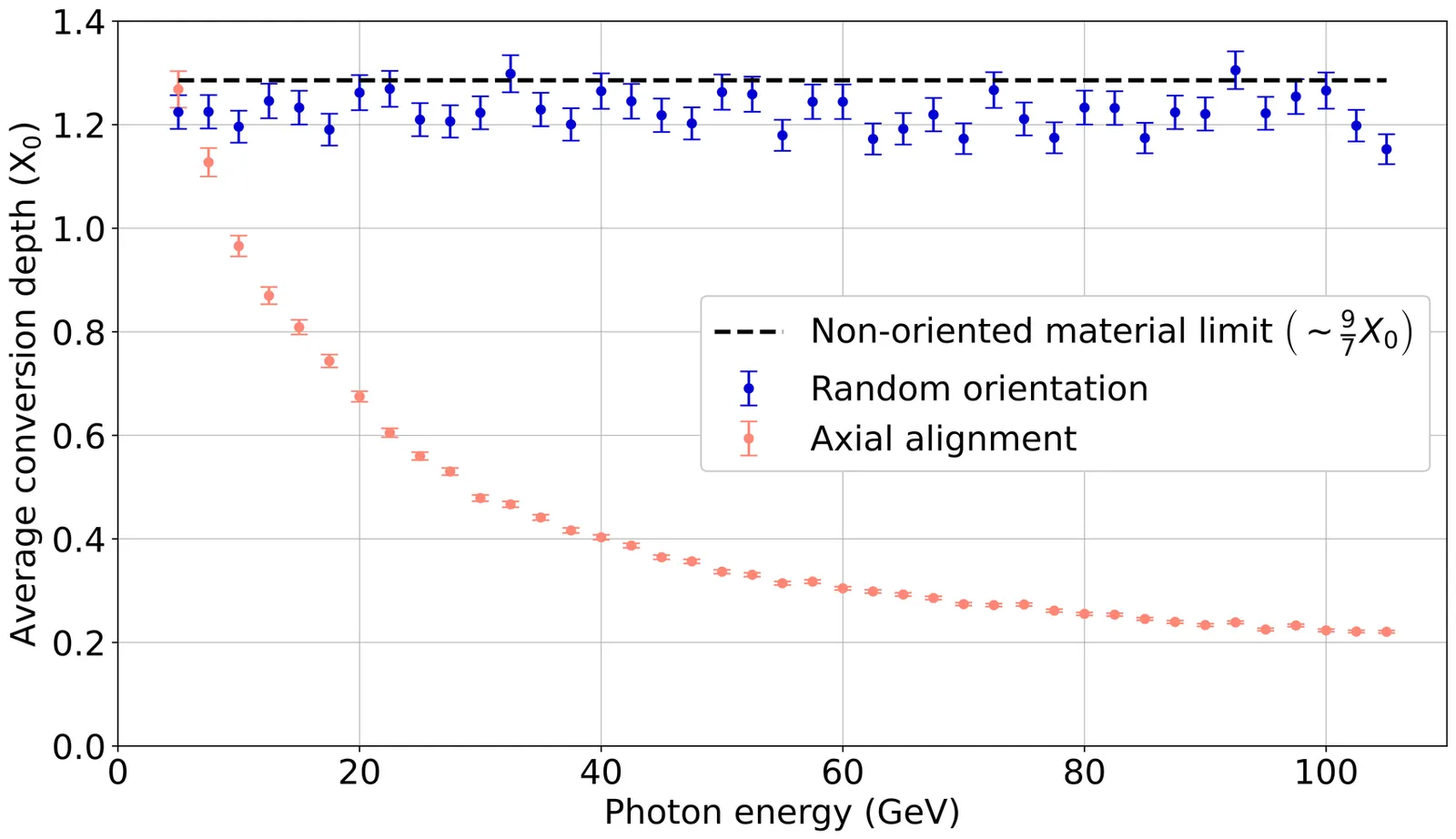
High-density and high-Z crystals are a key element of most space-borne $γ$-ray telescopes operating at GeV energies (such as Fermi-LAT). The lattice structure is usually neglected in the development of a crystalline detector, although its effects on the energy deposit development should be taken into account, since the interactions of a high energy ($\sim$~GeV) photon or e$^\pm$ impinging along the axis of an oriented crystal are different than the ones observed in a fully isotropic medium. Specifically, if the angle between a photon (e$^\pm$) trajectory and the crystal axis is smaller than $\sim$ 0.1$^\circ$, a large enhancement of the pair production (bremsstrahlung) cross-section is observed. Consequently, a photon-induced shower inside an oriented crystal develops within a much more compact region than in an amorphous medium. Moreover, for photon energies above a few GeV and incidence angles up to several degrees, the pair-production cross-section exhibits a pronounced dependence on the angle between the crystal axis and the photon polarization vector. \\ In this work we show that these effects could be exploited to develop a novel class of light-weight pointing space-borne $γ$-ray telescopes, capable of achieving an improved sensitivity and resolution, thanks to a better shower containment in a smaller volume with respect to non-oriented crystalline detectors. We also show that an oriented tracker-converter system could be used to measure the polarization of a $γ$-ray source above few GeV, in a regime that remains unexplorable through any other detection technique. This novel detector concept could open new pathways in the study of the physics of extreme astrophysical environments and potentially improve the detector sensitivity for indirect Dark Matter searches in space.
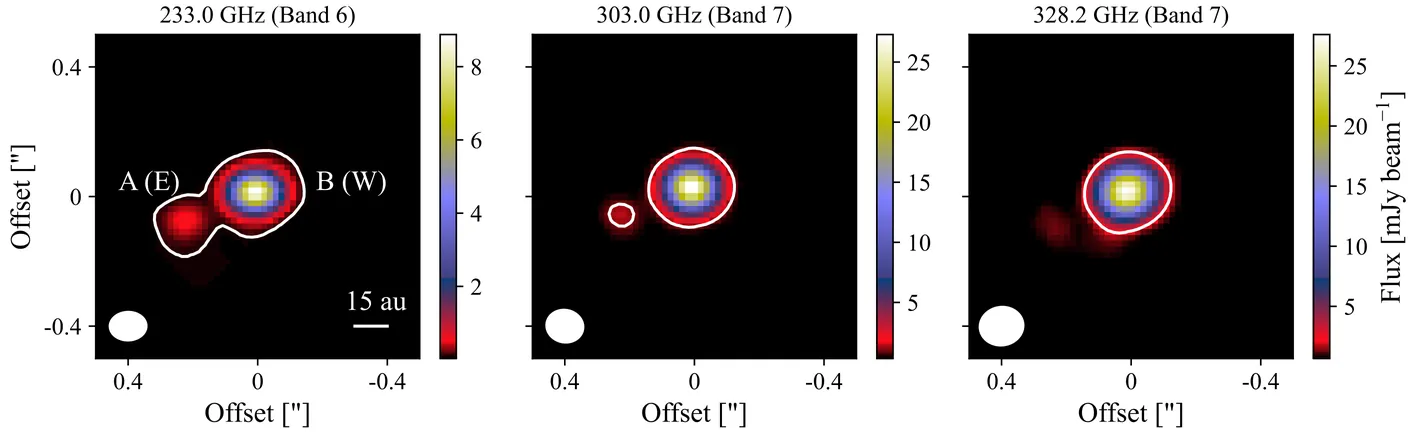
(Abridged) In the low-mass star formation process, theoretical models predict that material from the infalling envelope could be shocked as it encounters the outer regions of the disk. Nevertheless, only a few protostars show evidence of these shocks at the disk-envelope interface, and the main formation path of shocked-related species is still unclear. We present new ALMA observations of IRS 44, a Class I source that has previously been associated with accretion shocks, taken at high angular resolution (0.1"). We target multiple molecular transitions of CO, H2CO, and simple sulfur-bearing species. In continuum emission, the binary nature of IRS 44 is observed for the first time at sub-millimeter wavelengths. Infalling signatures are seen for the CO line and the emission peaks at the edges of the continuum emission around IRS 44 B, the same region where bright SO and SO2 emission is seen. Weak CS and H2CO emission is observed, while OCS, H2S, and H2CS transitions are not detected. IRS 44 B seems to be more embedded than IRS 44 A, indicating a non-coeval formation scenario or the rejuvenation of source B due to late infall. CO emission is tracing the outflow component at large scales, infalling envelope material at intermediate scales, and two infalling streamer candidates are identified at disk scales. Infalling streamers might produce accretion shocks when they encounter the outer regions of the infalling-rotating envelope. These shocks heat the dust and release S-bearing species as well as promoting a lukewarm chemistry in the gas phase. With the majority of carbon locked in CO, there is little free C available to form CS and H2CS in the gas, leaving an oxygen-rich environment. The high column densities of SO and SO2 might be a consequence of two processes: direct thermal desorption from dust grains and gas-phase formation due to the availability of O and S.
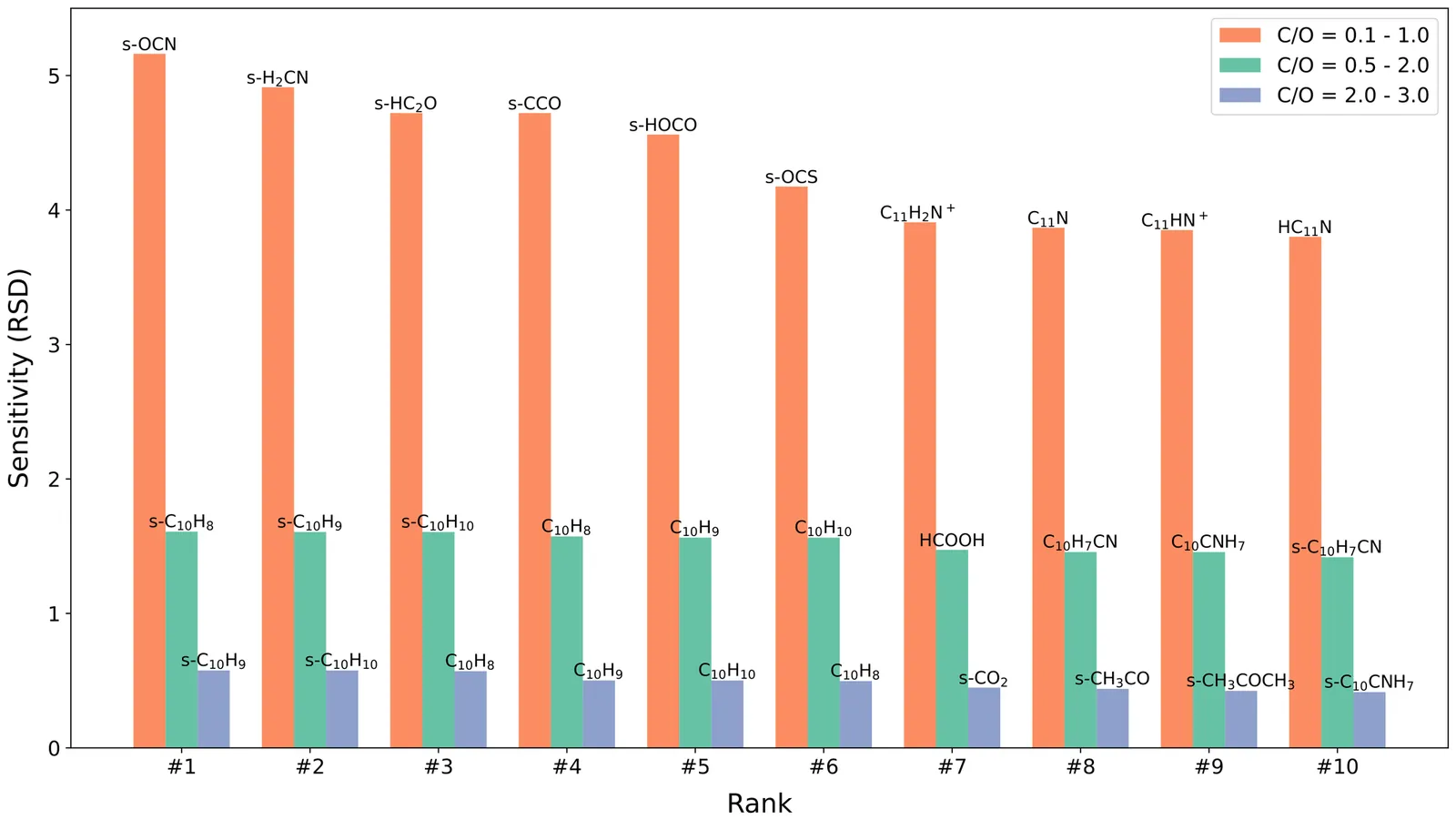
Elemental abundances, which are often depleted with respect to the solar values, are important input parameters for kinetic models of interstellar chemistry. In particular, the amount of carbon relative to oxygen is known to have a strong effect on modeled abundances of many species. While previous studies have focused on comparison of modeled and observed abundances to constrain the C/O ratio, the effects of this parameter on the underlying chemistry have not been well-studied. We investigated the role of the C/O ratio on dark cloud chemistry using the NAUTILUS code and machine learning techniques for molecular representation. We find that modeled abundances are quite sensitive to the C/O ratio, especially for carbon-rich species such as carbon chains and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). CO and simple ice-phase species are found to be major carbon reservoirs under both oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich conditions. The appearance of C3H4 isomers as significant carbon reservoirs, even under oxygen-rich conditions, indicates the efficiency of gas-phase C3 formation followed by adsorption and grain-surface hydrogenation. Our model is not able to reproduce the observed, gas-phase C/H ratio of TMC-1 CP at the time of best fit with any C/O ratio between 0.1 and 3, suggesting that the modeled freeze-out of carbon-bearing molecules may be too rapid. Future investigations are needed to understand the reactivity of major carbon reservoirs and their conversion to complex organic molecules.
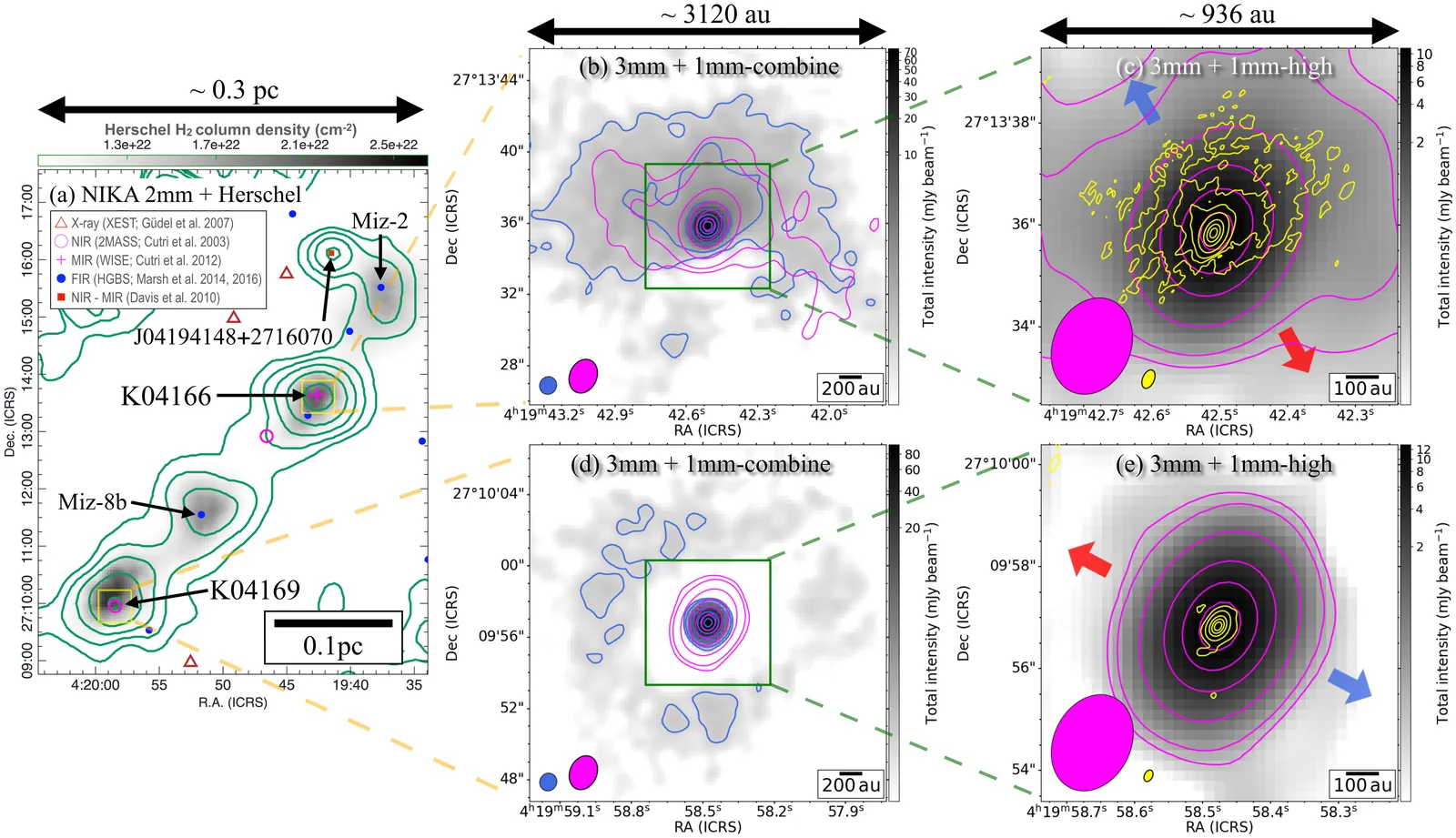
The earliest stages of disk formation and dust evolution during the protostellar phase remain poorly constrained. Millimeter dust emission and its polarization provide key insights into the physical processes and material distribution at the envelope-disk interface. We present ALMA polarimetric observations at 1.4 mm and 3 mm of two young stellar objects in Taurus, IRAS 04166+2706 (K04166) and IRAS 04169+2702 (K04169), probing scales from 25 au to 3000 au. We model the Stokes I emission to separate disk and envelope contributions and analyze the polarization properties to identify the dominant polarization mechanisms. K04166 shows extended Stokes I and polarized emission tracing a tentative hourglass magnetic field morphology in its envelope. In the inner envelope and disk (< 100 au), the properties of the polarized emission change, suggesting either a toroidal magnetic field or the presence of large grains. In contrast, K04169 exhibits compact Stokes I and polarized emission consistent with self-scattering from the disk. Both disks are extremely compact, but only K04166 retains a substantial envelope. Our multiscale ALMA polarimetric observations reveal a transition from magnetically aligned grains in envelopes to self-scattering in disks within the transition region of 20-50 au. These results provide important clues on dust grain growth and magnetic field morphology at the disk-envelope scales. Despite being embedded in the same filament, the two sources display striking differences, indicating that K04166 is a young embedded object with a substantial envelope threaded by relatively organized magnetic fields. Meanwhile, K04169 is more evolved, likely to be a young T-Tauri star. However, in both disks, the presence of large grains already suggests a scenario of early dust evolution in disks of the Class 0 stage.
We consider the oxygen abundance distributions for a sample of massive spiral galaxies from the MaNGA survey in which the radial abundance gradient flattens to a constant value outside of the outer break radius, Rb,outer. The outer break radius can be considered as a dividing radius between the galaxy and the circumgalactic medium (CGM). The values of the Rb,outer range from 0.8R_{25} to 1.45R_{25}, where R_{25} is the optical radius of the galaxy. The oxygen abundances in the CGM range from 12+log(O/H) ~ 8.0 to ~ 8.5. The O/H distribution in each of our galaxies also shows the inner break in the radial abundance profile at the radius Rb,inner. The metallicity gradient in the outer part of the galaxy is steeper than in the inner part. The behaviour of the radial abundance distributions in these galaxies can be explained by assuming an interaction with (capture of the gas from) a small companion and adopting the model for the chemical evolution of galaxies with a radial gas flow. The interaction with a companion results in the mixing of gas and a flat metallicity gradient in the CGM. The capture of the gas from a companion increases the radial gas inflow rate and changes the slope of the radial abundance gradient in the outer part of the galaxy.
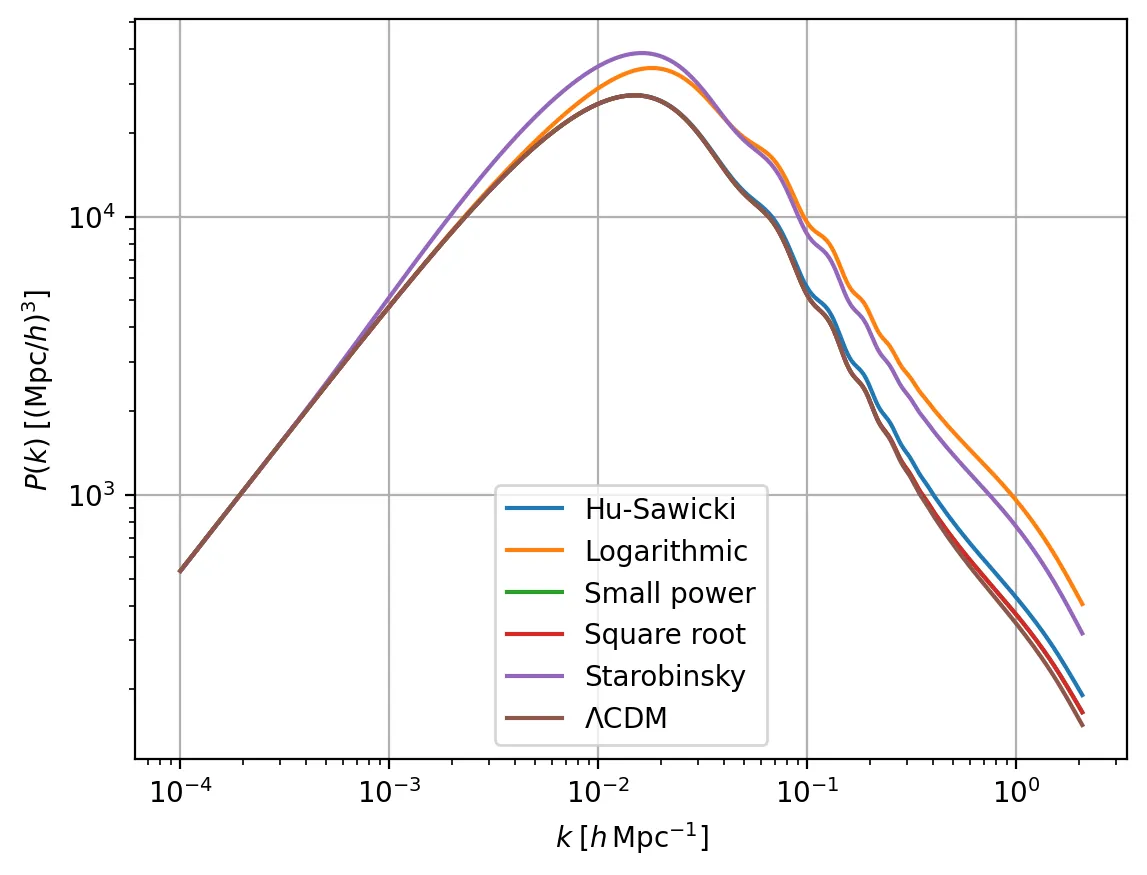
The accelerated expansion of the Universe remains one of the central open problems in modern cosmology. While the $Λ$CDM model successfully describes a wide range of observations, the physical nature of dark energy is still unknown, motivating the study of alternative theories of gravity. Among these, $f(R)$ models provide a well-established extension of General Relativity, capable of reproducing a $Λ$CDM-like background evolution without introducing an explicit dark energy component. However, they can induce deviations in the growth of cosmic structures, making them testable through observables sensitive to cosmological perturbations. In this work, we use weak gravitational lensing to constrain several viable $f(R)$ gravity models. We analyze their impact on the matter power spectrum, as well as on the convergence and cosmic shear power spectra. Our analysis is carried out within a Bayesian framework using the \textit{Cobaya} code and its modified gravity extension, \textit{MGCobaya}, which enables consistent theoretical predictions and their comparison with current weak lensing and CMB lensing data. We find that standard cosmological parameters remain consistent with the $Λ$CDM scenario for all models considered, as expected from their background degeneracy. Nevertheless, we obtain non-trivial and model-dependent constraints on the characteristic parameters of several $f(R)$ theories.
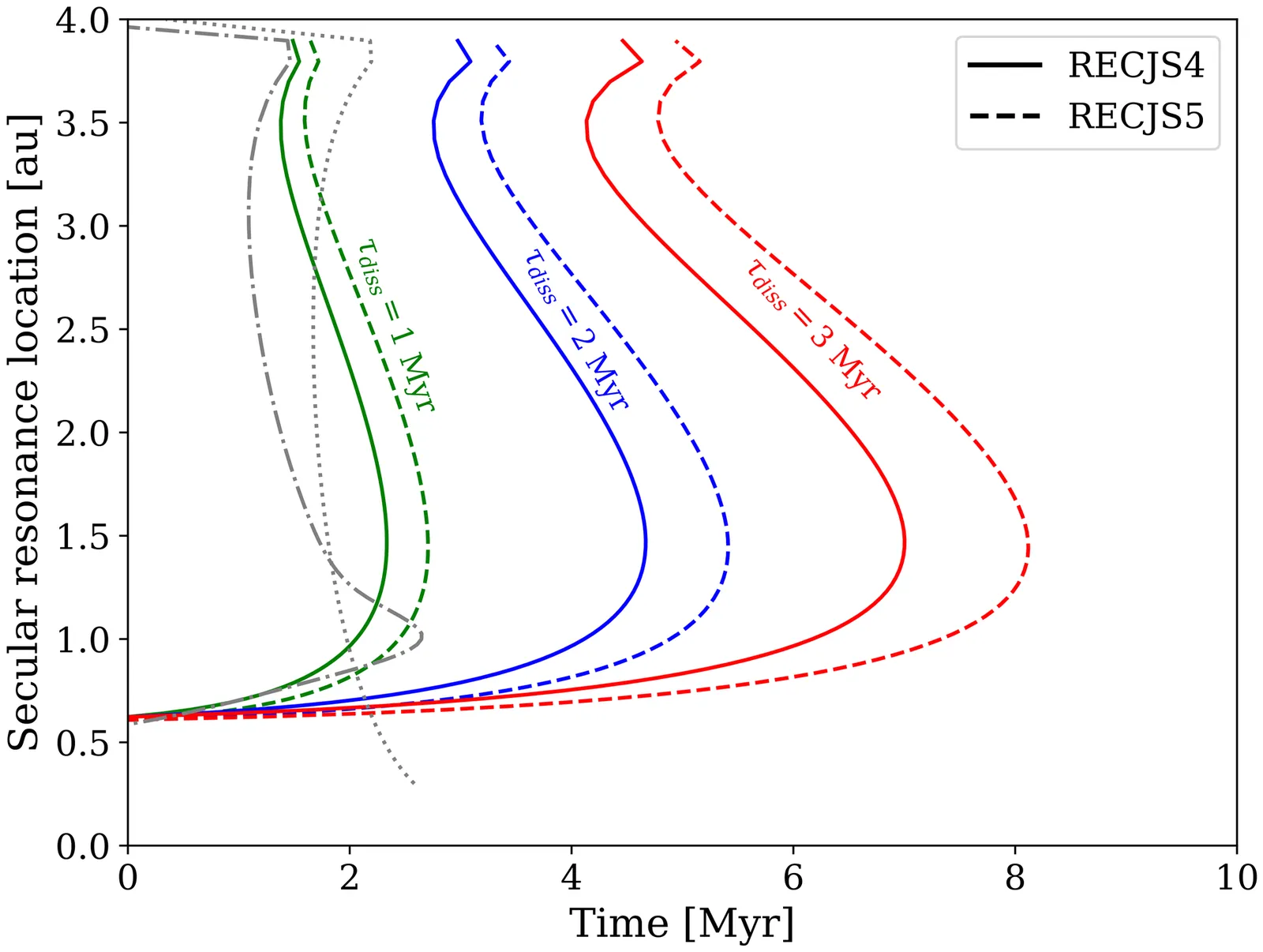
The models that most successfully reproduce the orbital architecture of the Solar System terrestrial planets start from a narrow annulus of material that grows into embryos and then planets. However, it is not clear how this ring model can be made consistent with the chemical structure of the inner Solar System, which shows a reduced-to-oxidized gradient from Mercury to Mars and a parallel gradient in the asteroid belt. We propose that there were two primary reservoirs in the early inner Solar System: a narrow, refractory enriched ring inside of 1 au, and a less massive, extended planetesimal disk outside of 1 au with oxidation states ranging from enstatite chondrites to ordinary chondrites. We show through a suite of N-body simulations that an inwardly sweeping secular resonance, caused by aerodynamic drag and perturbations from a mean-motion resonant Jupiter and Saturn, gathers the outer planetesimal disk into a narrow ring that migrates radially, forms Mars, and contributes oxidized material to proto-Earth. Remaining unaccreted planetesimals can be implanted into the asteroid belt as the parent bodies of aubrites and non-carbonaceous iron meteorites, while the most reduced material is not implanted and thus unsampled in the meteorite collection. This model explains the oxidation and isotopic gradients within the inner Solar System within the context of a low-viscosity, magnetic wind-driven disk.
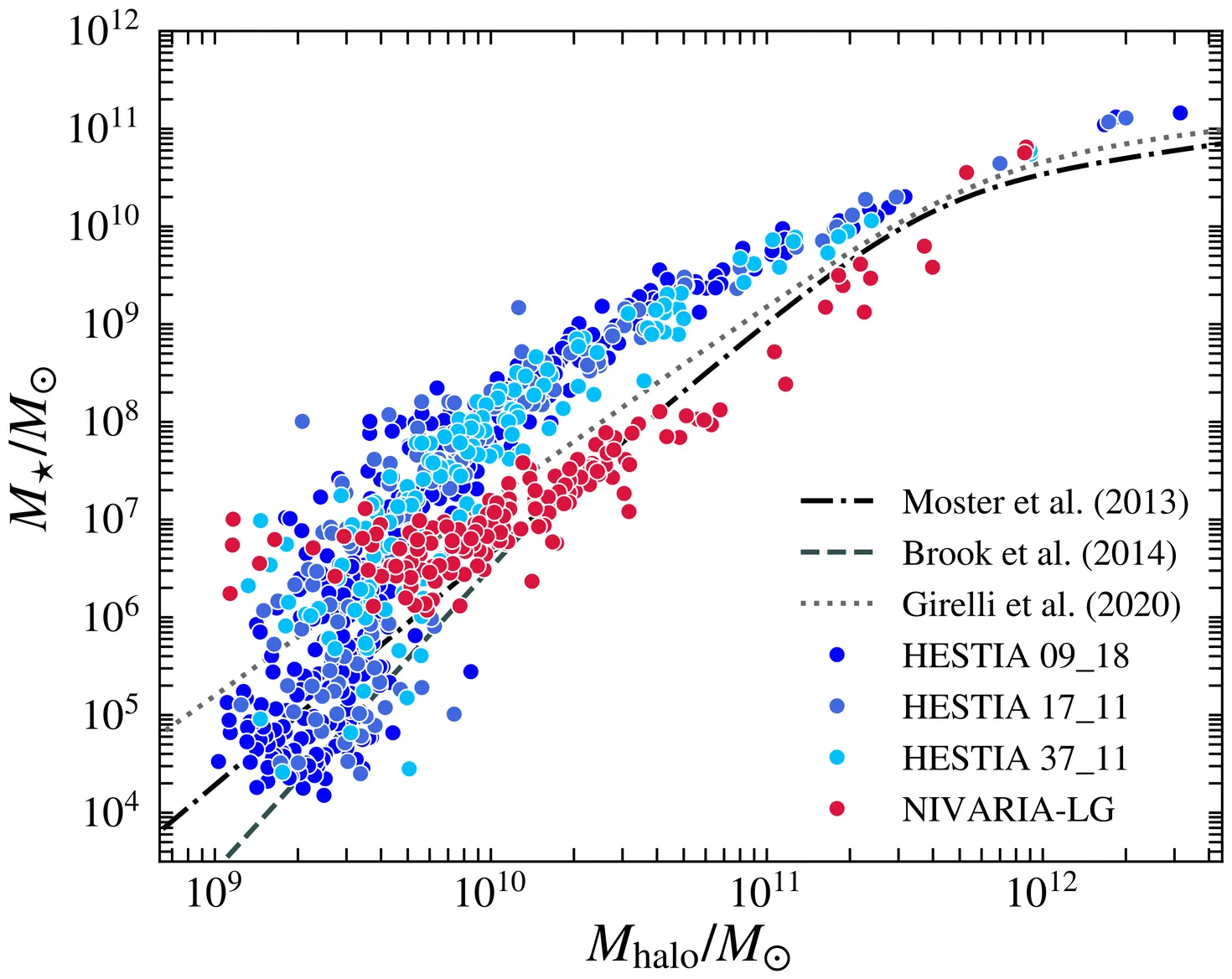
Dark galaxies are small, DM-dominated halos whose gas remains in hydrostatic and thermal equilibrium and has never formed stars. They are of particular interest because they represent a strong prediction of the LCDM model. As of today, only a handful of candidates have been observed, the most intriguing of which being Cloud-9. Using several state-of-the-art hydrodynamical simulations, we aim to predict the abundance of dark galaxies expected within our Local Group (LG), characterise their properties and provide guidance for their potential detection. We analyse LG simulations with constrained initial conditions, run with different codes, implementing different baryonic physics, feedback prescriptions, and employing two distinct values of SF density threshold, n_th=0.13 and 10 cm^-3, to select samples of dark and bright galaxies harboured in haloes of similar mass. We demonstrate that dark galaxies exist in such simulations, though their number is larger in simulations that use a higher, more realistic n_th. These galaxies, whose gas remains diffuse and never forms stars, predominantly inhabit less-concentrated, higher-spin DM halos than their luminous counterparts. Dark galaxies are typically found in low-density regions at the outskirts of the LG, and their evolution across z indicate that both the DM and gas densities in their surroundings were consistently lower than those found around bright galaxies, making them less susceptible to interactions, mergers, or gas inflows. We estimate that up to 8 dark galaxies should be detectable in HI emission within 2.5 Mpc of the LG, with the FAST telescope, accounting for its sky coverage and minimum M_HI and N_HI. Current hydrodynamical simulations of galaxies, combined with upcoming HI surveys, will offer a direct and powerful test of LCDM through their ability to predict and measure properties of dark galaxies within and beyond the LG.
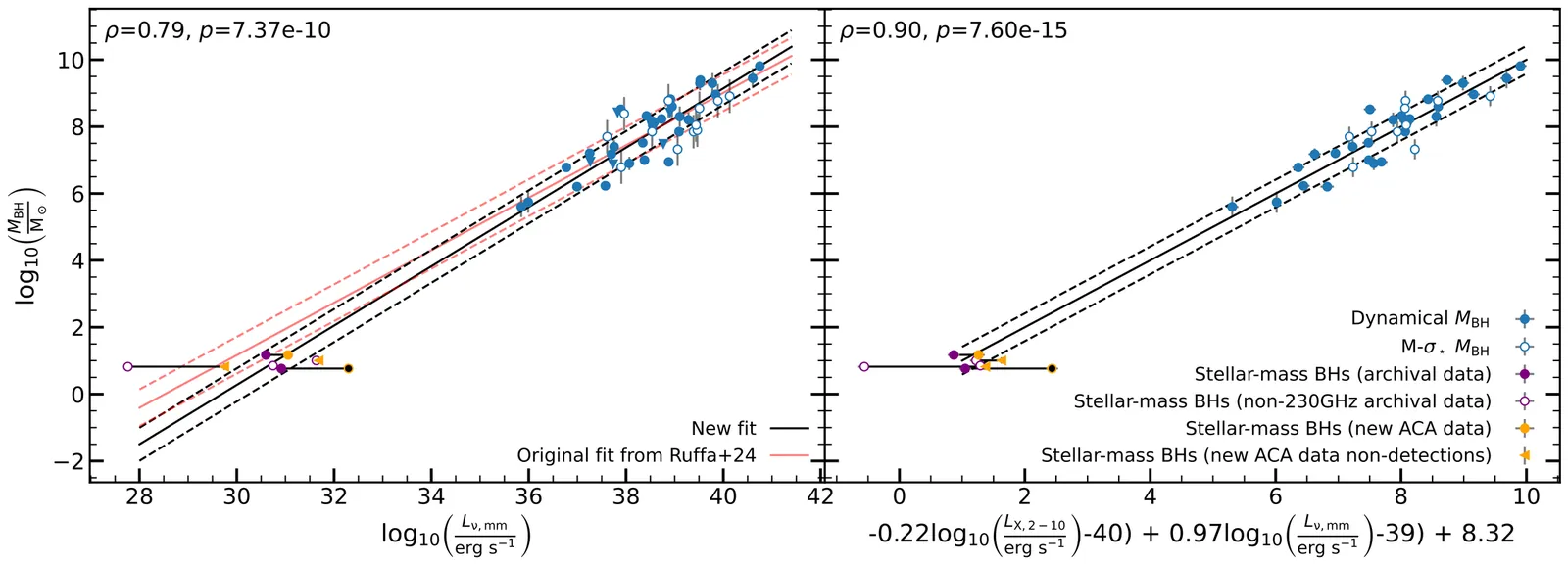
Recent work revealed the existence of a galaxy "millimetre fundamental plane of black hole accretion", a tight correlation between nuclear $1$mm luminosity, intrinsic $2$ - $10$keV X-ray luminosity and supermassive black hole mass, originally discovered for nearby low- and high-luminosity active galactic nuclei. Here we use mm and X-ray data of $5$ X-ray binaries (XRBs) to demonstrate that these stellar-mass black holes also lie on the mm fundamental plane, as they do at radio wavelengths. One source for which we have multi-epoch observations shows evidence of deviations from the plane after a state change, suggesting that the plane only applies to XRBs in the hard state, as is true again at radio wavelengths. We show that both advection-dominated accretion flows and compact jet models predict the existence of the plane across the entire range of black hole masses, although these models vary in their ability to accurately predict the XRB black hole masses.
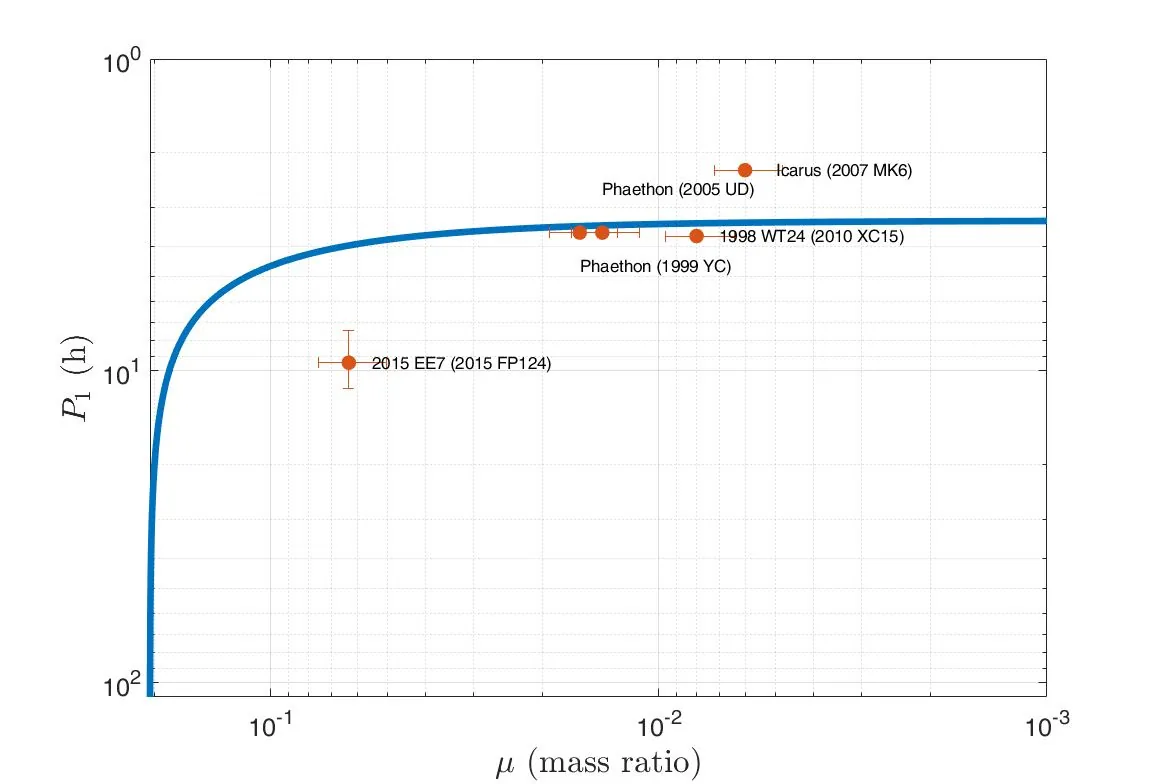
We analyse the association between the NEAs 2021 PH27 and 2025 GN1, which share similar heliocentric Keplerian elements and the same taxonomic classification. First, we confirm the spectral similarity by getting independent colours measurements of 2025 GN1 and confirming that they are both X-type. From numerical integration of the orbits up to 100 kyr in the past, taking into account relativistic corrections, we found that the two asteroids experienced five similar flybys with Venus, but none of them were closer than the Roche limit. The perihelion distance also reached values between 0.1 and 0.08 au about 17/21 kyr and 45/48 kyr ago, but still well outside the Roche limit with the Sun. So, the origin of the pair by tidal disruption of a progenitor rubble-pile asteroid appears unlikely. On the other hand, we found periods lasting several thousand years where the perihelion was below 0.1 au, and this can lead to thermal fracturing of the surface. We found that the rotation period of the primary and the mass ratio secondary/primary make the pair indistinguishable from the binary systems known among the NEAs, and the YORP effect can double the rotation period of 2021 PH27 in $150 \pm 50$ kyr. So it is plausible that the pair was formed by the rotational disintegration of a rubble-pile asteroid due to anisotropic gas emission or the YORP effect, which formed a binary system that later dissolved due to the internal dynamics of the pair. We are unable to give a value for the separation age; we can only say that it occurred more than 10.5 kyr ago and may have occurred between 17/21 kyr ago during the last and longer phase of lower perihelion distance. In this scenario, little meteoroids released in space due to the fragmentation event are still near the pair's orbit and can generate a meteor shower in Venus' atmosphere.
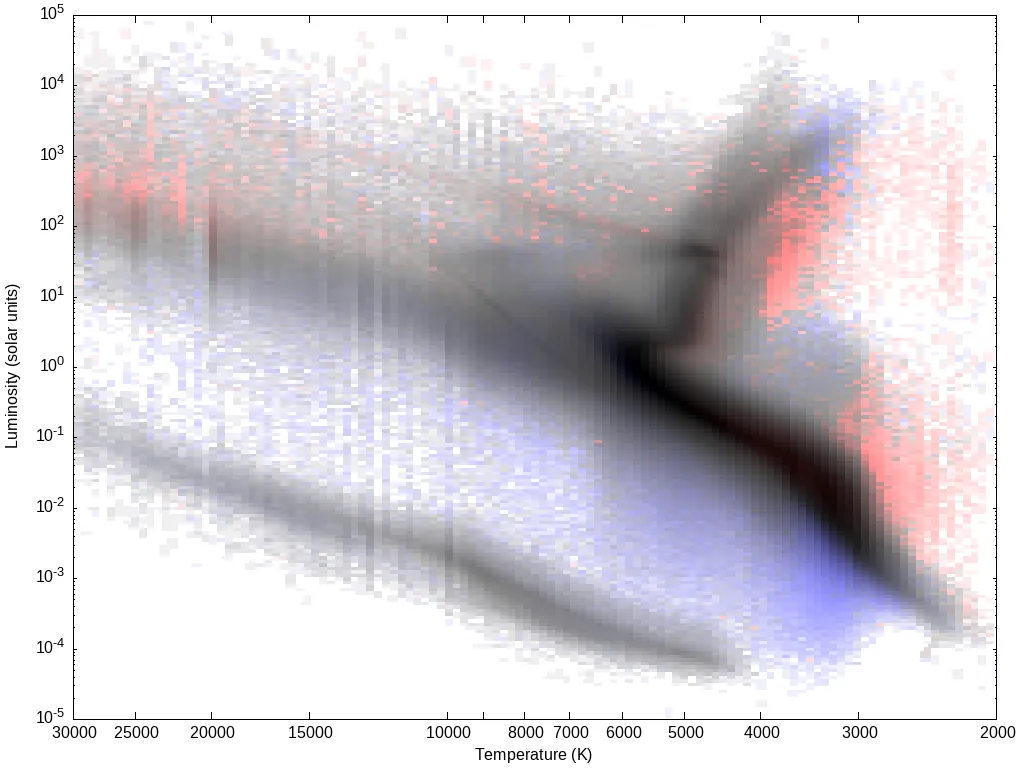
Temperature and luminosity are the two key diagnostics of a star, yet these cannot come directly from survey data, but must be imputed by comparing those data to models. SED fitting offers a high-precision method to obtain both parameters for stars where both their distance and extinction are well known. The recent publication of many all-sky or large-area surveys coincides the publication of parallaxes and 3D extinction cubes from the Gaia satellite, making it possible to perform SED fitting of truly large ($>10^8$) numbers of Galactic stars for the first time. The analysis of this data requires a high level of automation. Here, we describe the ongoing Gaia All-Sky Stellar Parameters Service (GASPS): the fitting of 240 million SEDs from Gaia DR3 and the extraction of temperatures and luminosities for the corresponding stars using the PySSED code. We demonstrate the quality of the initial results, and the promise that these data show, from wavelength-specific information such as the ultraviolet and infrared excess of each star, to stellar classification, to expansion of the project beyond our own Galaxy, and mineralogical mapping of the Milky Way's interstellar medium.
 2601.03966
2601.03966Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) is increasingly promoted as a key element of modern spectrum policy, driven by the rising demand from commercial wireless systems and advances in spectrum access technologies. Passive radio sciences, including radio astronomy, Earth remote sensing, and meteorology, operate under fundamentally different constraints. They rely on exceptionally low interference spectrum and are highly vulnerable to even brief radio frequency interference. We examine whether DSS can benefit passive services or whether it introduces new failure modes and enforcement challenges. We propose just-in-time quiet zones (JITQZ) as a mechanism for protecting high value observations and assess hybrid frameworks that preserve static protection for core passive bands while allowing constrained dynamic access in adjacent frequencies. We analyze the roles of propagation uncertainty, electromagnetic compatibility constraints, and limited spectrum awareness. Using a game theoretic framework, we show why non-cooperative sharing fails, identify conditions for sustained cooperation, and examine incentive mechanisms including pseudonymetry-enabled attribution that promote compliance. We conclude that DSS can support passive radio sciences only as a high-reliability, safety-critical system. Static allocations remain essential, and dynamic access is viable only with conservative safeguards and enforceable accountability.

In this paper, we investigate how external photo-evaporation influences the formation, dynamical evolution and the resultant planetary architecture of multi-planet systems born in stellar clusters. We use a model of N-body simulations of multiple planet formation via pebble accretion coupled with a 1-D viscous disc subject to external photo-evaporation. We found that external photo-evaporation reduces the planet growth by reducing the pebble mass reservoir in discs containing multiple planetary embryos across a wide range of disc masses, and is particularly effective in suppressing planet growth in less initially massive discs (< 0.1 M$_{\odot}$). However, in more initially massive ($\geq$ 0.1 M$_{\oplus}$) discs planets lost due to planet-planet interactions dominate the outcome for final resultant total planet mass, masking the effects of external photo-evaporation in curbing the planet mass growth. In terms of the final resulting planetary architectures, the signature of external photo-evaporation is visible in less massive (< 0.1 M$_{\odot}$) discs, with fewer numbers and lower masses of planets surviving in discs irradiated with stronger external FUV radiation. External photo-evaporation also leaves a signature for the wide orbit (> 10 au) terrestrial planets (0.1 - 1 M$_{\oplus}$), with fewer planets populating this region for stronger FUV field. Finally, the 1st-order resonant pairs fraction decreases with stronger FUV radiation, although the resonant pairs occur rarely regardless of the FUV radiation environment, due to the small number of planets that survive gravitational encounters.