Trending in Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics
Dissecting the Hubble tension: Insights from a diverse set of Sound Horizon-free H0 measurements
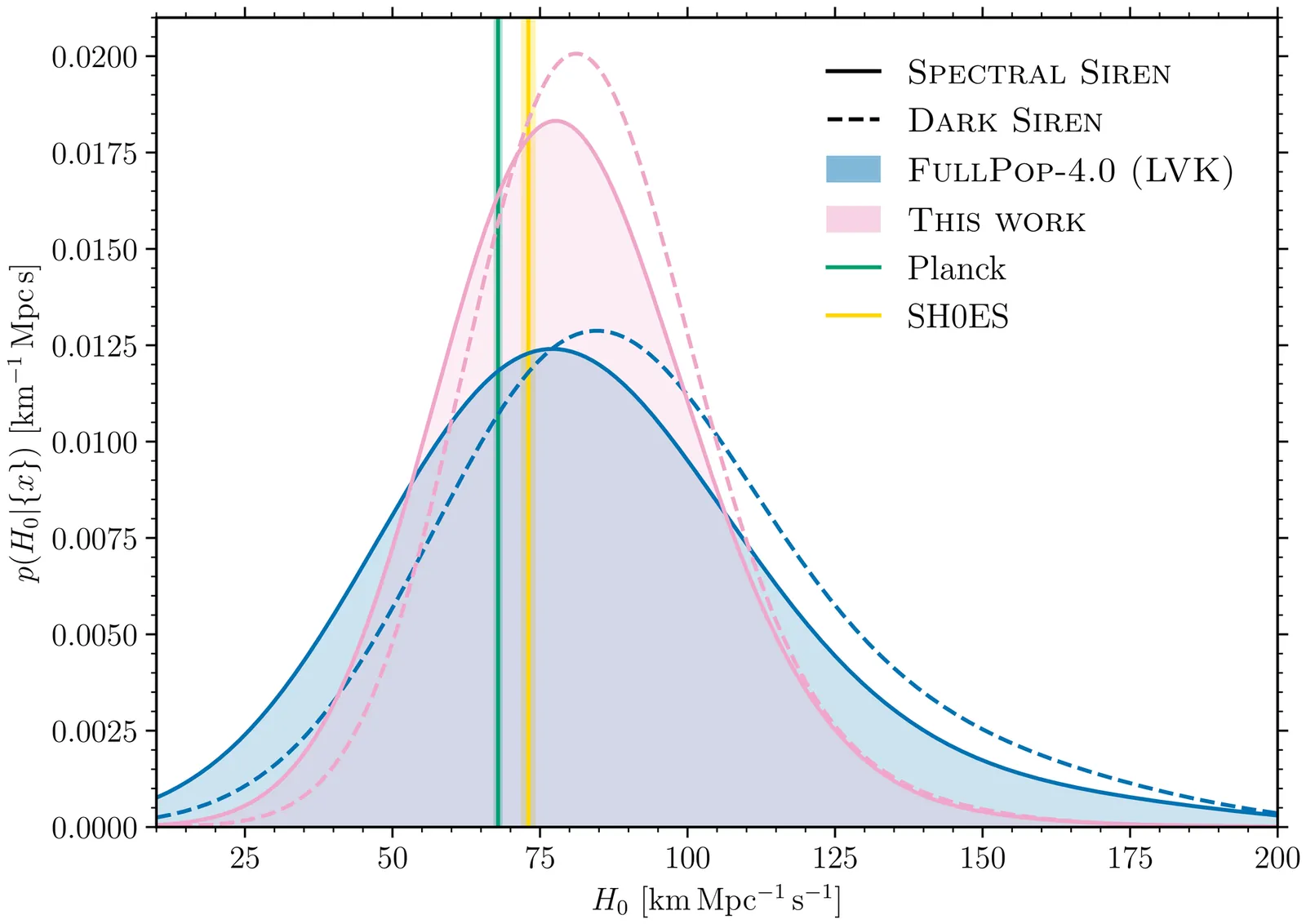
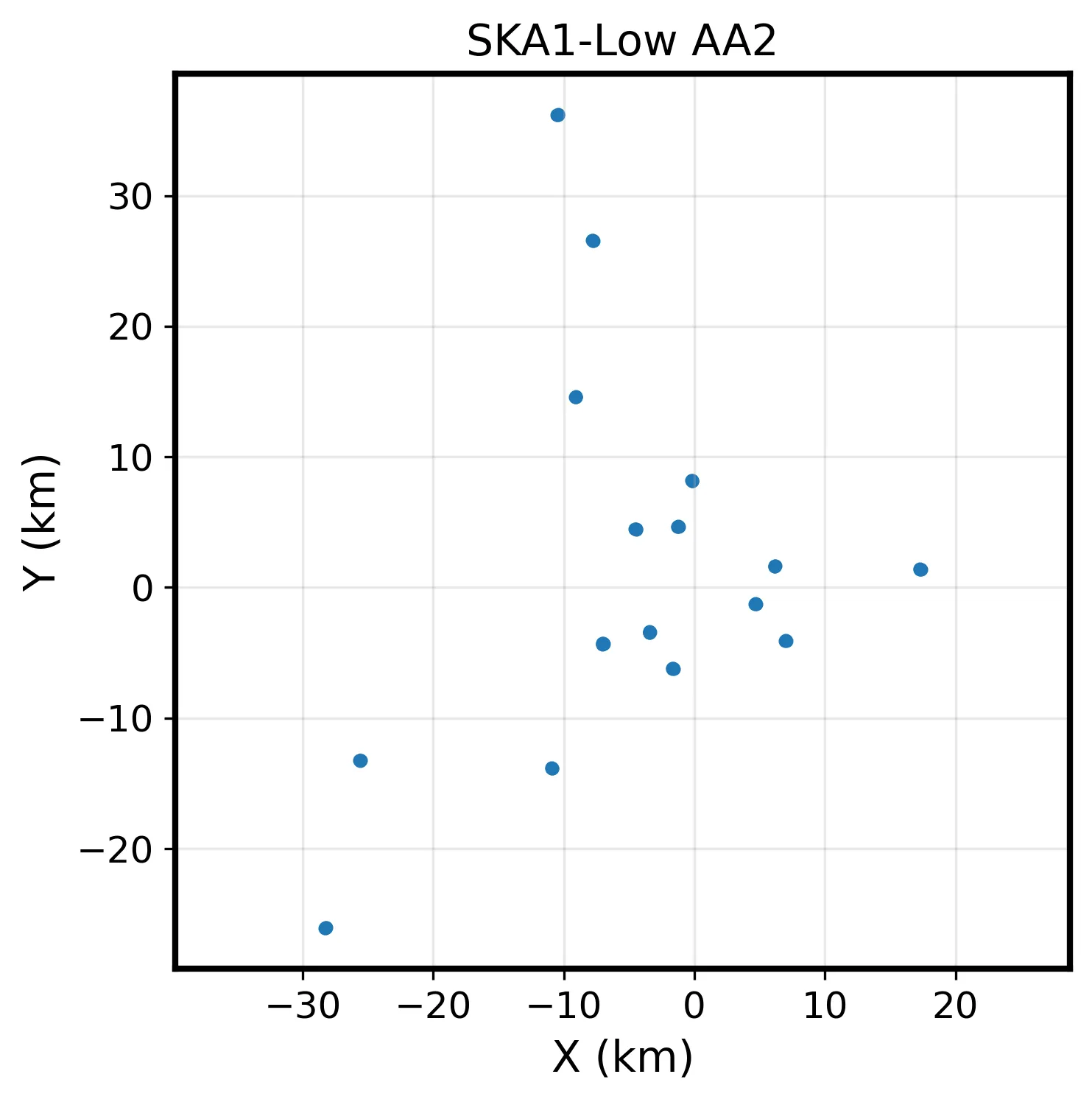
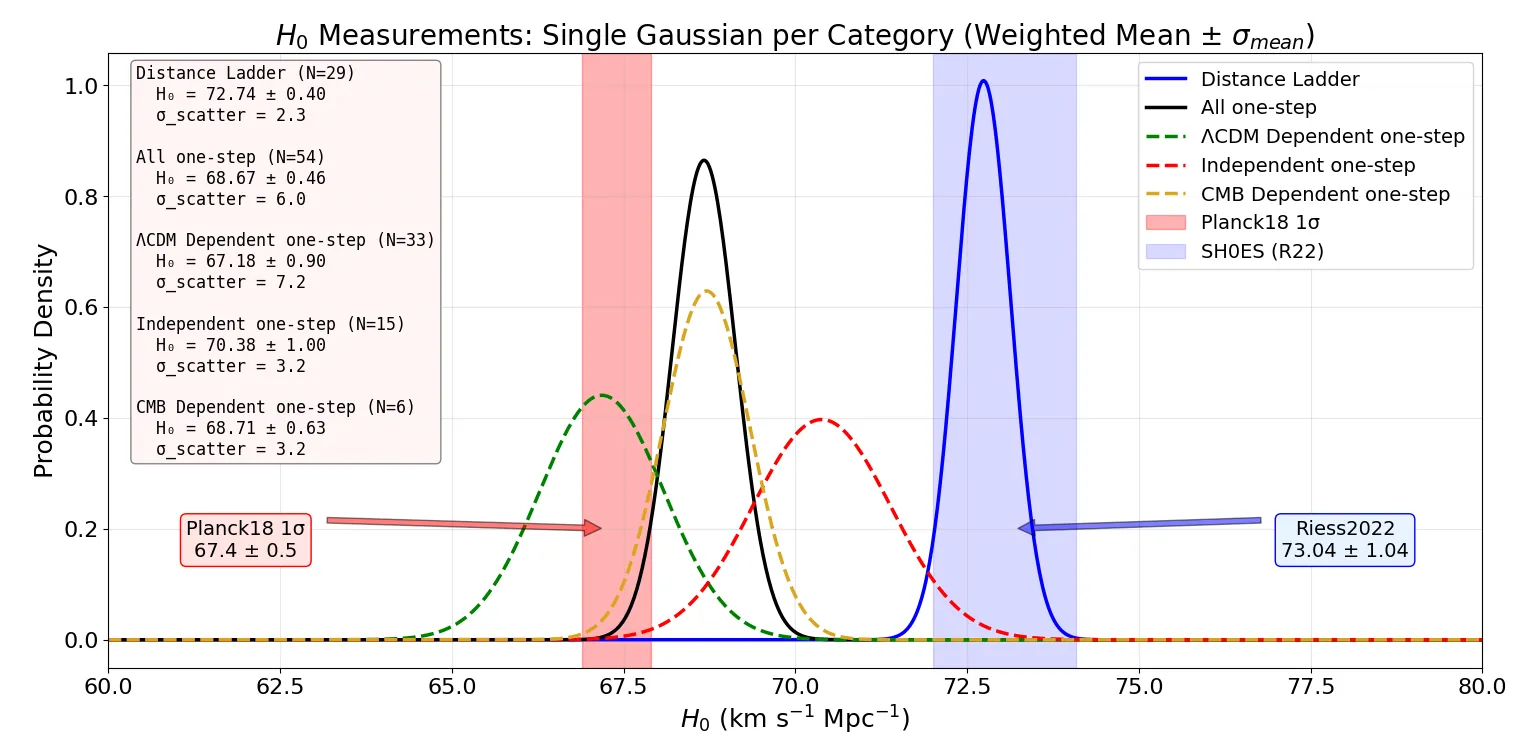
The Hubble tension is commonly framed as a discrepancy between local, late-time measurements favoring $H_0 \approx 73$ km s$^{-1}$ Mpc$^{-1}$ and early-time, Sound-Horizon-based measurements favoring $H_0 \approx 67$ km s$^{-1}$ Mpc$^{-1}$. We challenge this viewpoint by analyzing 83 Sound-Horizon-independent $H_0$ measurements, categorized into four classes: Distance Ladder measurements using local calibrators; Local One-Step $Λ$CDM measurements assuming the standard expansion history; Pure Local One-Step measurements independent of $H(z)$ shape; and CMB Sound Horizon free measurements using CMB data without the Sound Horizon scale. We find that the 29 Distance Ladder measurements yield $H_0 = 72.74 \pm 0.40$ km s$^{-1}$ Mpc$^{-1}$ ($χ^2_ν\equiv χ^2/d.o.f= 0.74$), while the 54 One-Step measurements collectively yield $H_0 = 68.67 \pm 0.46$ km s$^{-1}$ Mpc$^{-1}$ ($χ^2_ν= 0.85$), a $6.7σ$ tension exceeding the Planck--SH0ES discrepancy. This tension remains significant at $4.5σ$ after accounting for correlations. Among One-Step categories, Local One-Step $Λ$CDM measurements favor the lowest value ($H_0 = 67.18 \pm 0.90$ km s$^{-1}$ Mpc$^{-1}$), Pure Local One-Step yield an intermediate value ($H_0 = 70.38 \pm 1.00$ km s$^{-1}$ Mpc$^{-1}$), and CMB Sound Horizon Free measurements give $H_0 = 68.71 \pm 0.63$ km s$^{-1}$ Mpc$^{-1}$. Thus, that the Hubble tension is better characterized as a discrepancy between the Distance Ladder and all other methodologies, rather than an early-vs-late-time split. We also identify a $2.4σ$ internal tension among One-Step measurements: analyses assuming $Λ$CDM systematically recover lower $H_0$ values by about 3.2 km s$^{-1}$ Mpc$^{-1}$ compared to model-independent methods. This suggests either unrecognized systematics/physics in the Distance Ladder or deviations from $Λ$CDM in the late-time Universe.
2601.00650
Jan 2026Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics
Dynamical Dark Energy Imprints in the Lyman-Alpha Forest
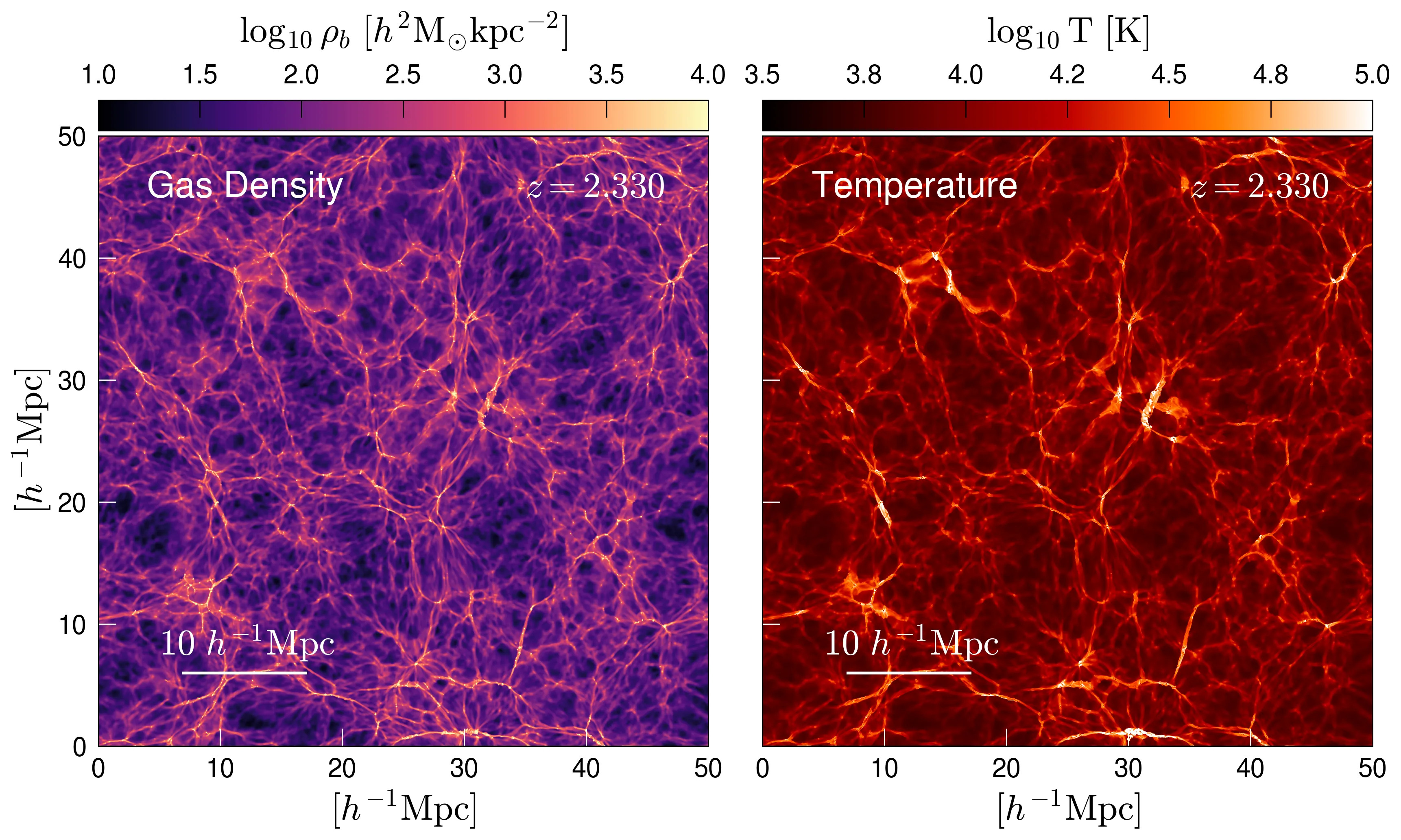
The nature of dark energy (DE) remains elusive, even though it constitutes the dominant energy-density component of the Universe and drives the late-time acceleration of cosmic expansion. By combining measurements of the expansion history from baryon acoustic oscillations, supernova surveys, and cosmic microwave background data, the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) Collaboration has inferred that the DE equation of state may evolve over time. The profound implications of a time-variable, ``dynamical" DE (DDE) that departs from a cosmological constant motivate the need for independent observational tests. In this work, we use cosmological hydrodynamical simulations of structure formation to investigate how DDE affects the properties of the Lyman-Alpha ``forest'' of absorption features produced by neutral hydrogen in the cosmic web. We find that DDE models consistent with the DESI constraints induce a spectral tilt in the forest transmitted flux power spectrum, imprinting a scale- and redshift-dependent signature relative to standard Lambda-CDM cosmologies. These models also yield higher intergalactic medium temperatures and reduced Lyman-Alpha opacity compared to Lambda-CDM. We discuss the observational implications of these trends as potential avenues for independent confirmation of DDE.
2601.00767
Jan 2026Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics
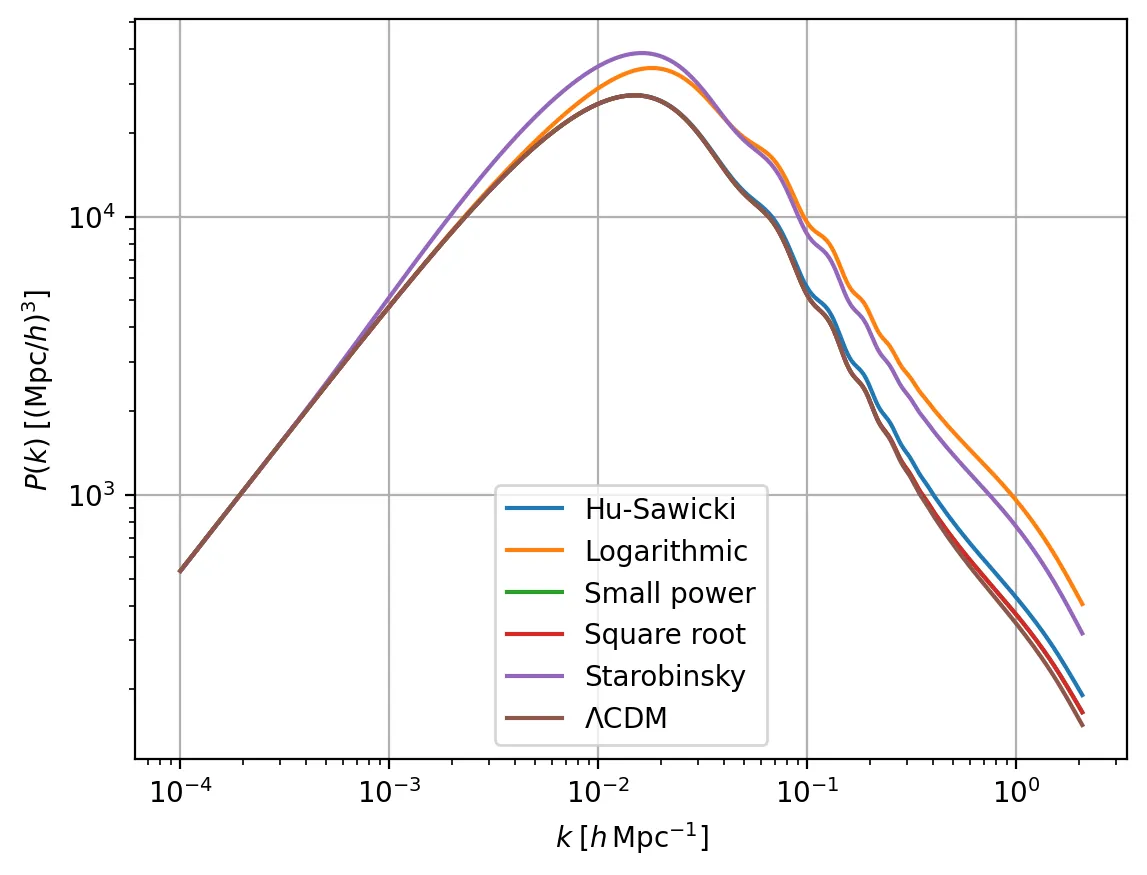
One-loop power spectrum corrections in interacting dark energy cosmologies
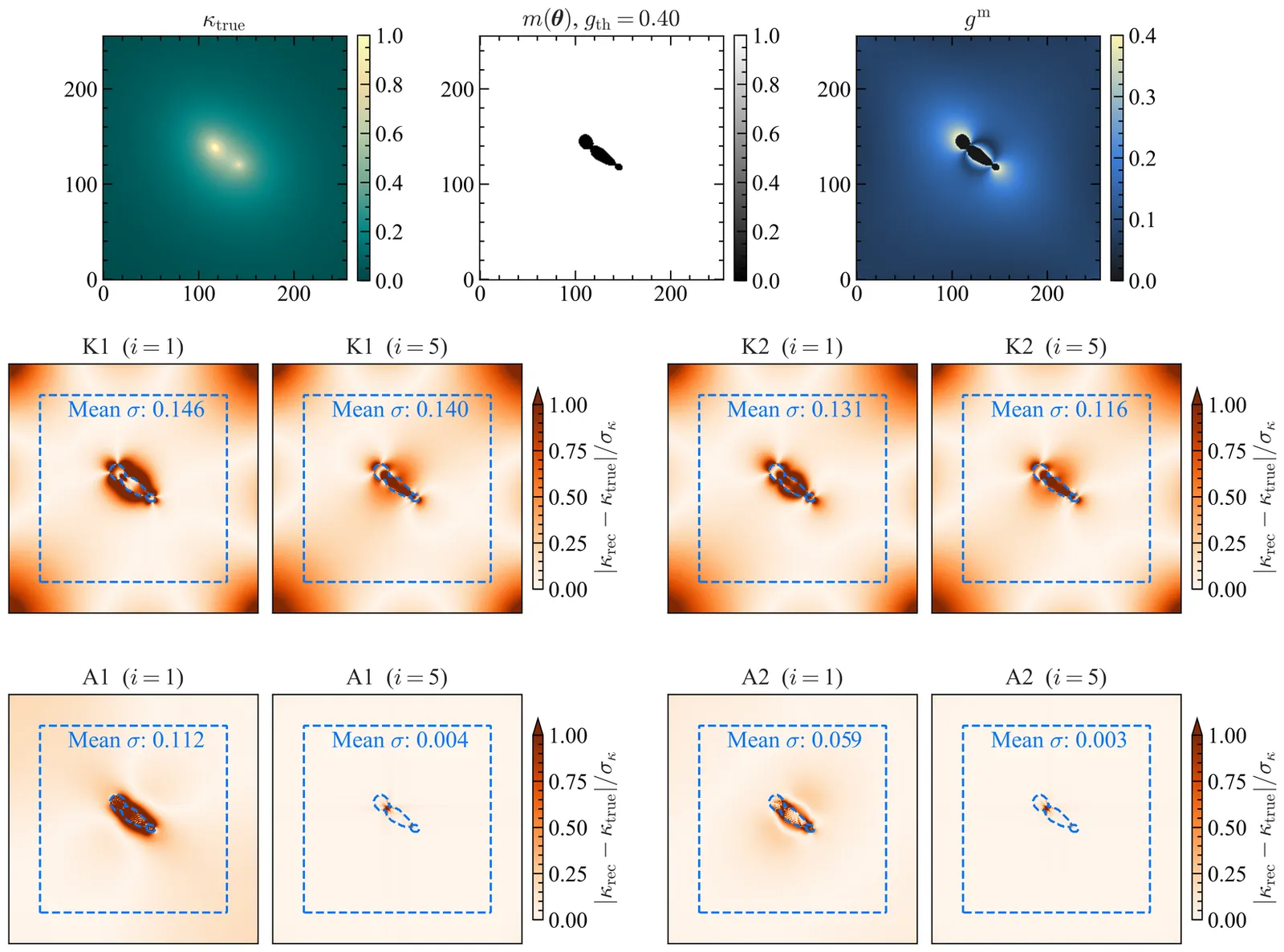
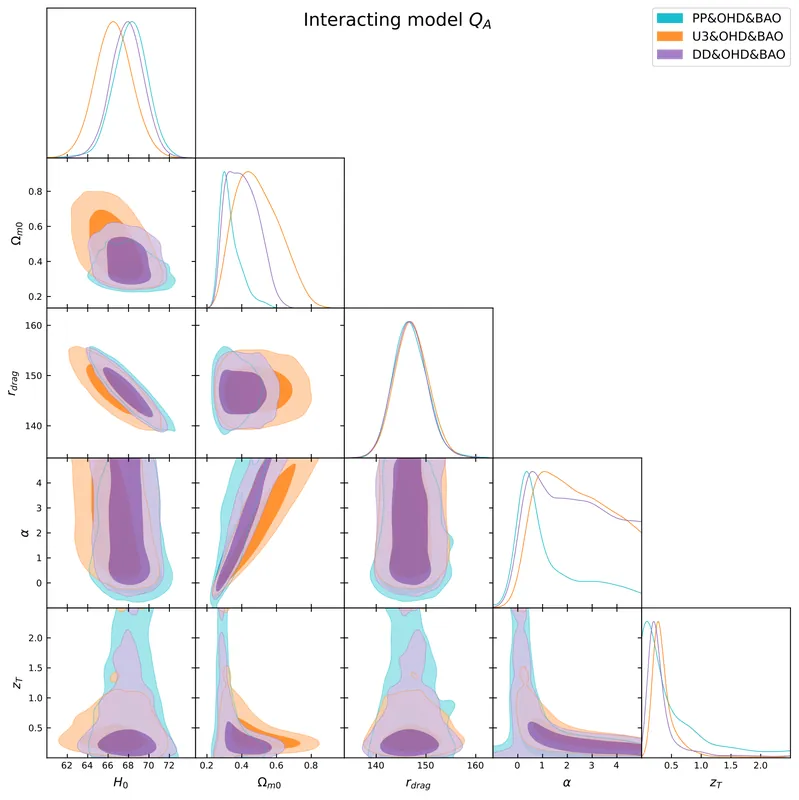
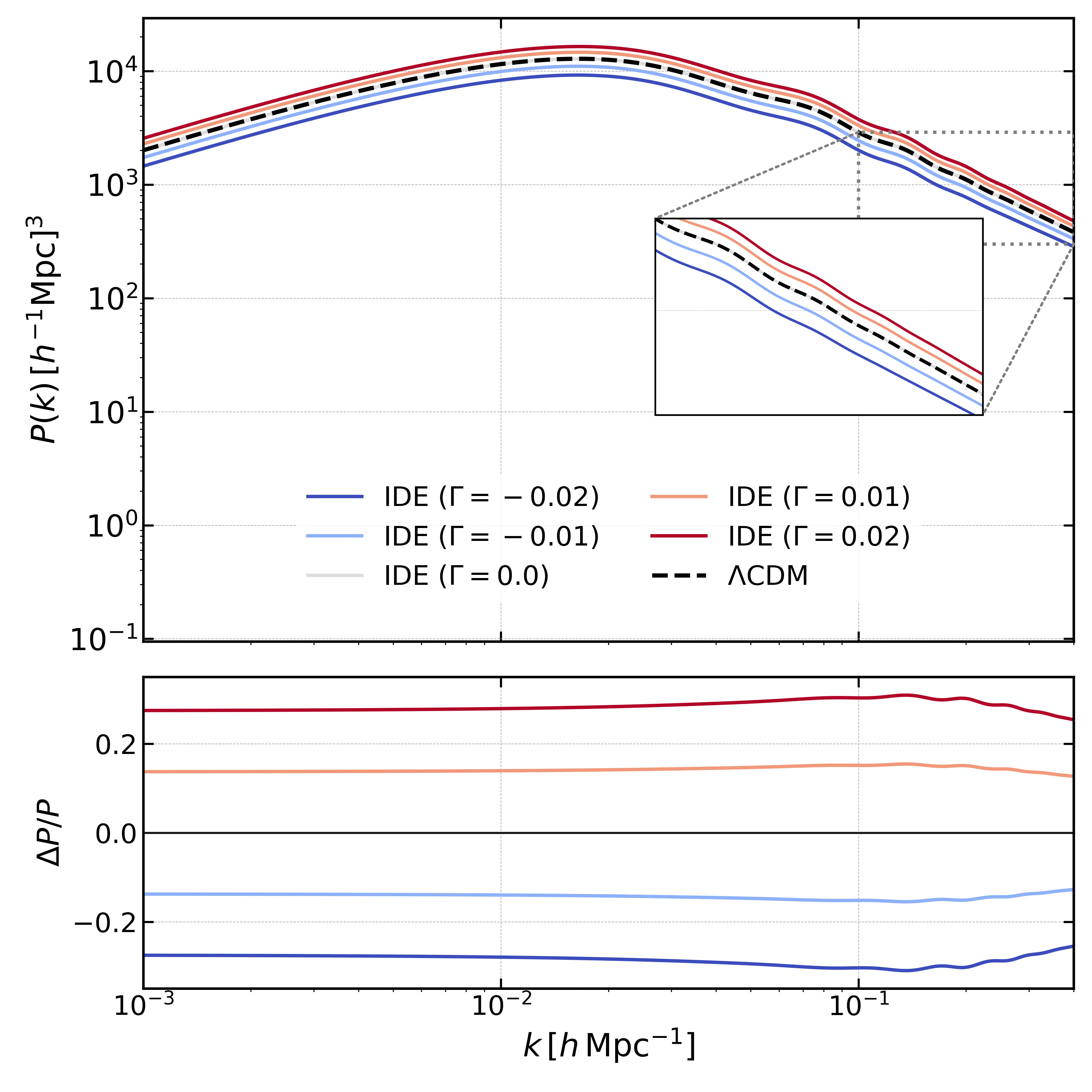
Interacting Dark Energy (IDE) models offer a promising avenue to explore possible exchanges of energy and momentum between dark matter and dark energy, providing a dynamical extension of the standard $Λ$CDM paradigm. Such interactions modify the growth of cosmic structures, imprinting distinctive signatures on the matter power spectrum that can be tested through large-scale structure (LSS) observations. In this work, we compute the one-loop corrections to the matter power spectrum in IDE models. We then reinterpret these results within the standard framework of the Effective Field Theory of Large-Scale Structure (EFTofLSS), which provides a consistent description of mildly non-linear scales and allows for reliable comparisons with observational data. We investigate two commonly studied forms of the coupling function, $Q$, namely $Q = ξ\mathcal{H} ρ_{\rm m}$ and $Q = ξ\mathcal{H} ρ_{\rm DE}$, and introduce a novel interaction term, $Q = Γ\, ρ_{\rm m} \, ρ_{\rm DE} \, θ_{\rm m}$, characterized by the non-linear coupling constant $Γ$, which links the interaction strength to the velocity divergence of dark matter. This coupling function is proposed to isolate the effects solely of the IDE model on mildly non-linear scales. Using Full-Shape (FS) measurements of the galaxy power spectrum from BOSS DR12, we constrain the interaction rate $Γ$, the cosmological parameters, and the bias parameters. We find $Γ= 0.0039 \pm 0.0082$, which is highly consistent with the $Λ$CDM model. This work opens the possibility of testing IDE models at mildly non-linear scales, potentially providing new insights for this class of models beyond the standard $Λ$CDM framework.
2512.11678
Dec 2025Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics