Atomic & Molecular Physics
Atomic structure, cold atoms, and molecular spectroscopy
Atomic structure, cold atoms, and molecular spectroscopy
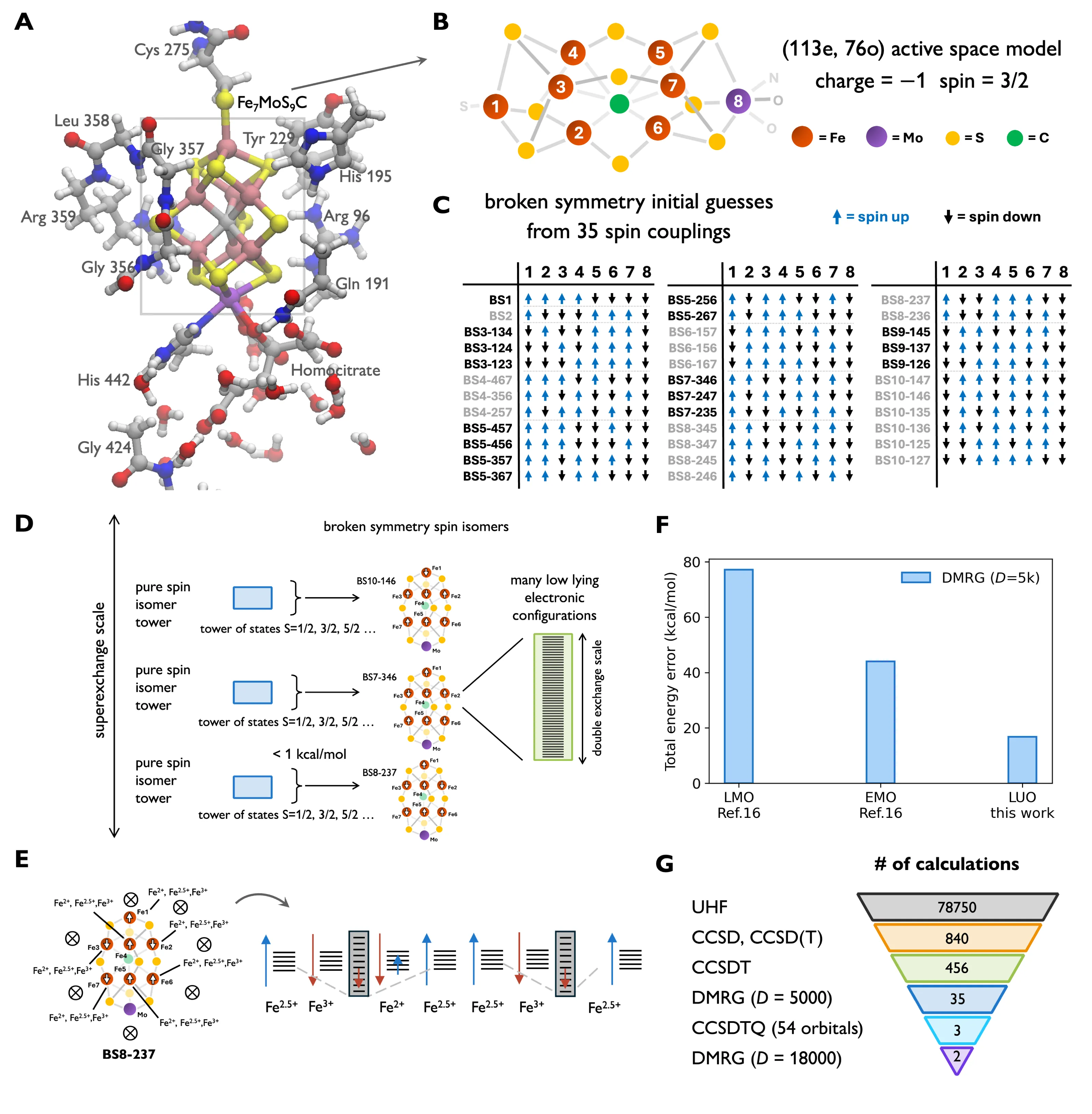
The main source of reduced nitrogen for living things comes from nitrogenase, which converts N2 to NH3 at the FeMo-cofactor (FeMo-co). Because of its role in supporting life, the uncertainty surrounding the catalytic cycle, and its compositional richness with eight transition metal ions, FeMo-co has fascinated scientists for decades. After much effort, the complete atomic structure was resolved. However, its electronic structure, central to reactivity, remains under intense debate. FeMo-co's complexity, arising from many unpaired electrons, has led to suggestions that it lies beyond the reach of classical computing. Consequently, there has been much interest in the potential of quantum algorithms to compute its electronic structure. Estimating the cost to compute the ground-state to chemical accuracy (~1 kcal/mol) within one or more FeMo-co models is a common benchmark of quantum algorithms in quantum chemistry, with numerous resource estimates in the literature. Here we address how to perform the same task using classical computation. We use a 76 orbital/152 qubit resting state model, the subject of most quantum resource estimates. Based on insight into the multiple configuration nature of the states, we devise classical protocols that yield rigorous or empirical upper bounds to the ground-state energy. Extrapolating these we predict the ground-state energy with an estimated uncertainty on the order of chemical accuracy. Having performed this long-discussed computational task, we next consider implications beyond the model. We distill a simpler computational procedure which we apply to reveal the electronic landscape in realistic representations of the cofactor. We thus illustrate a path to a precise computational understanding of FeMo-co electronic structure.
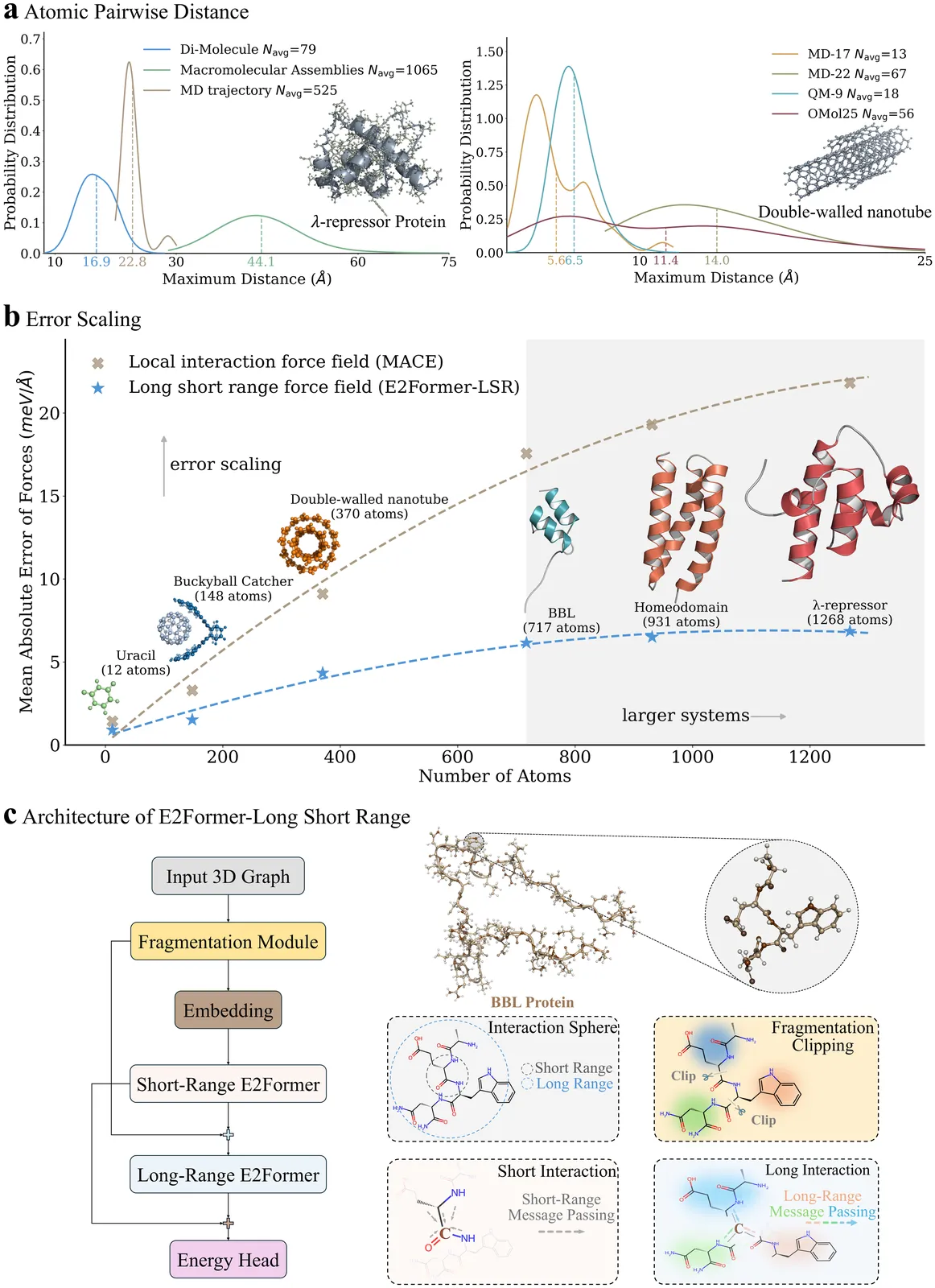
Machine learning force fields (MLFFs) have revolutionized molecular simulations by providing quantum mechanical accuracy at the speed of molecular mechanical computations. However, a fundamental reliance of these models on fixed-cutoff architectures limits their applicability to macromolecular systems where long-range interactions dominate. We demonstrate that this locality constraint causes force prediction errors to scale monotonically with system size, revealing a critical architectural bottleneck. To overcome this, we establish the systematically designed MolLR25 ({Mol}ecules with {L}ong-{R}ange effect) benchmark up to 1200 atoms, generated using high-fidelity DFT, and introduce E2Former-LSR, an equivariant transformer that explicitly integrates long-range attention blocks. E2Former-LSR exhibits stable error scaling, achieves superior fidelity in capturing non-covalent decay, and maintains precision on complex protein conformations. Crucially, its efficient design provides up to 30% speedup compared to purely local models. This work validates the necessity of non-local architectures for generalizable MLFFs, enabling high-fidelity molecular dynamics for large-scale chemical and biological systems.

We have extended the origin-invariant length gauge (LG(OI)) approach -- originally developed by Caricato and co-workers for optical rotation (OR) and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) -- to vibrational circular dichroism (VCD). This approach avoids the need for gauge-including atomic orbitals (GIAOs), which are typically required to circumvent the unphysical dependence of the CD rotatory strengths on the arbitrary choice of coordinate origin for length gauge (LG) computations. Benchmark VCD spectra are presented for (P)-hydrogen peroxide, (S)-methyloxirane, (1R, 5R)-α-pinene, and (1R, 4R)-camphor using Hartree-Fock (HF) theory and density functional theory (DFT) methods across a range of basis sets and compared to those obtained from LG, velocity-gauge (VG), and GIAO computations. These analyses show that for VCD the LG(OI) approach does not converge to the basis-set limit as rapidly as the GIAO approach, but does yield similar quality spectra as GIAO for all major VCD peaks for quadruple-zeta-quality basis sets. The LG(OI) and VG VCD spectra are less reliable compared to GIAOs for smaller basis sets.
 2601.02113
2601.02113We have developed an analytical framework for magnetically induced transparency-absorption (MITA) and normal-anomalous dispersion (MINAD) in a weakly driven ${}^{87}\text{Rb}$ vapor, or any J-type three-level system, under a vector magnetic field. By solving the Bloch equations in the stationary, quasi-stationary, and short-pulse regimes, we obtained closed-form expressions for the atomic populations and coherences and identified a bifurcation in the oscillatory dynamics at zero longitudinal Zeeman splitting. The Fourier-domain analysis reveals alternating transparency/absorption and normal/anomalous dispersion with frequency-dependent sign reversals, enabling spectrally selective filtering and group-delay effects. Slow oscillatory behavior in the radio-frequency range makes the system suitable for weak magnetic-field sensing, while fast oscillations at optical frequencies suggest applications in spectral filtering and frequency-comb-like signal shaping. The results provide a theoretical basis for experimental observation of MITA/MINAD and for optimizing atomic-vapor platforms for precision magnetometry and related photonic functionalities.
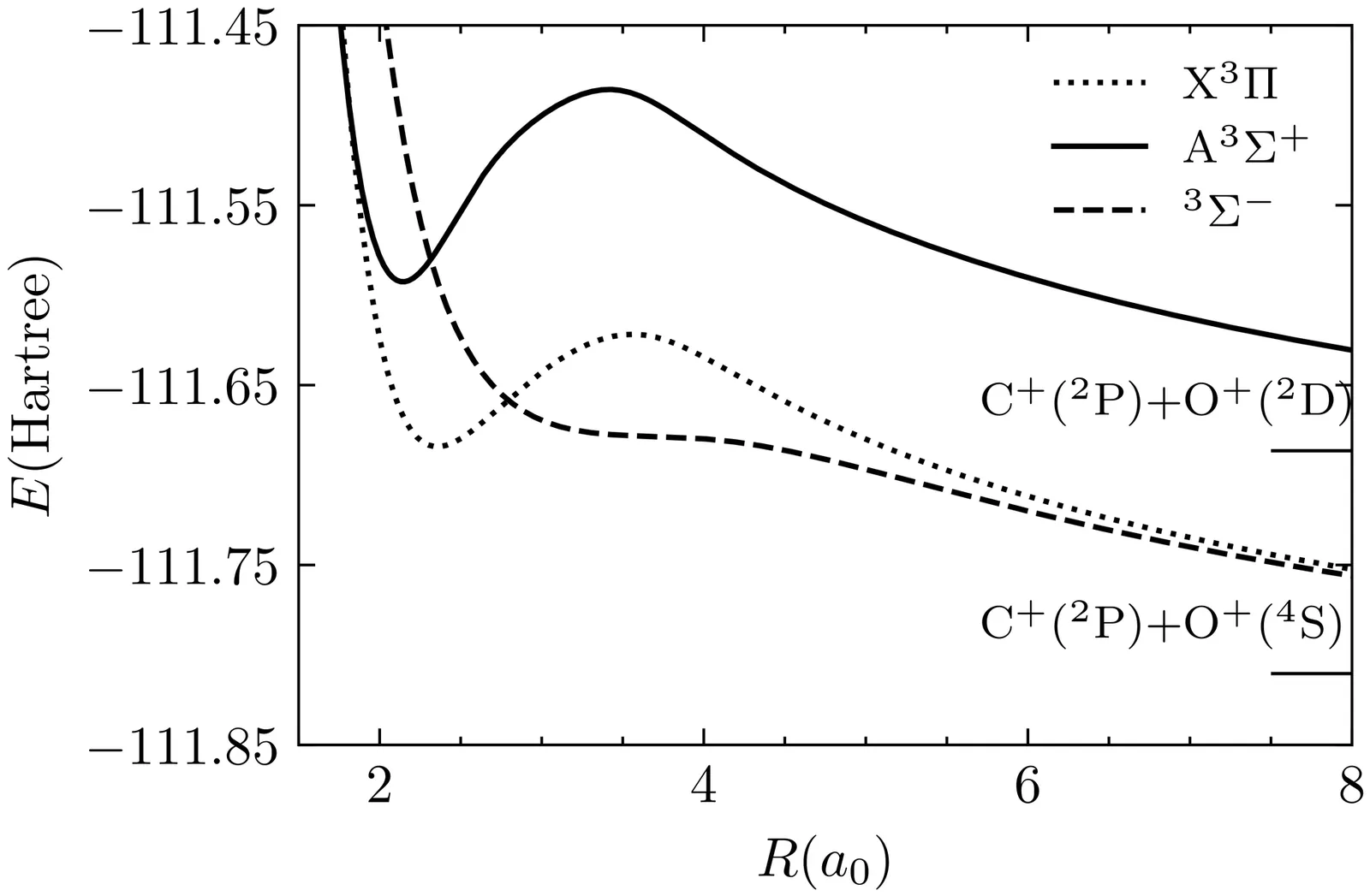
We report rovibronic spectra of the A $^3Σ^+$($v'=0-2$) - X $^3Π_Ω(v=0)$ rovibronic transitions ($|Ω|=0, 1$ and 2) of the CO$^{2+}$ doubly-charged molecular ion. Spectra were recorded at high resolution ($\sim 5$~cm$^{-1}$) in a fast beam of CO$^{2+}$ molecules by detecting the Coulomb explosion of the molecules upon excitation to the A state. Measurements were guided by \textit{ab initio} calculations which then assisted the assignment of the observed spectral features. Our results resolve the spin-orbit splittings of the ground vibronic state X $^3Π_Ω(v=0)$, but not the rotational structure of the bands due to spectral congestion, and provide spectroscopic information on CO$^{2+}$ with unprecedented resolution. In doing so they expand our knowledge of this benchmark doubly charged molecular ion and expand the short list of doubly charged molecules studied at high resolution.
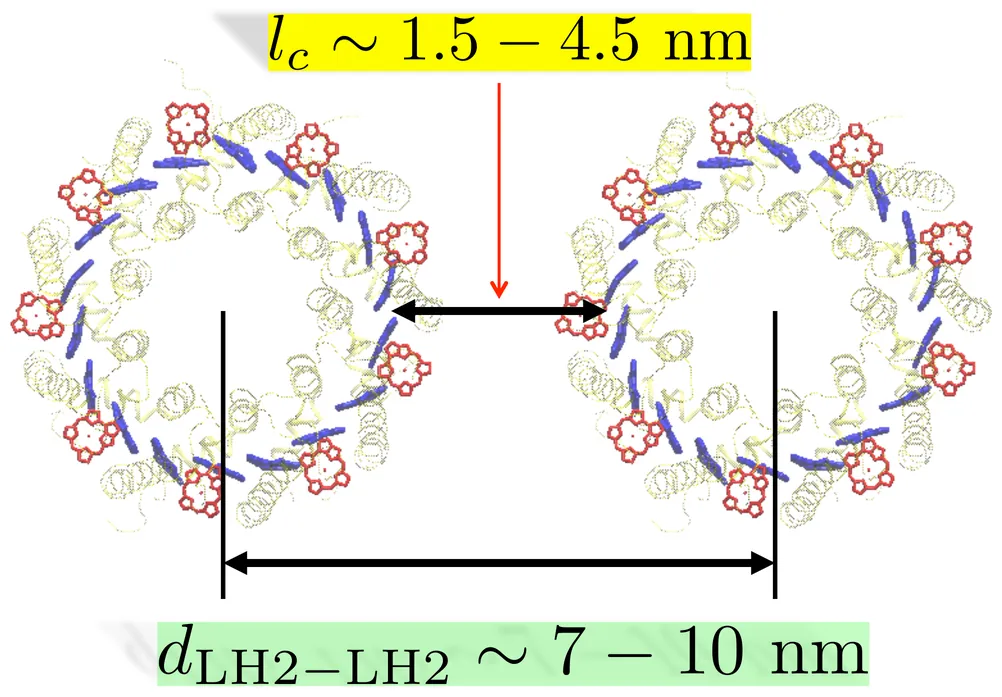
Aggregates of light harvesting 2 (LH2) complexes form the major exciton-relaying domain in the photosynthetic unit of purple bacteria. Application of a generalized master equation to pairs of the B850 units of LH2 complexes, where excitons predominantly reside, provide quantitative information on how the inter-LH2 exciton transfer depends on the distance, relative rotational angle, and the relative energies of the two LH2s. The distance dependence demonstrates significant enhancement of the rate due to quantum delocalization of excitons, the qualitative nature of which remains robust against the disorder. The angle dependence reflects isotropic nature of exciton transfer, which remains similar for the ensemble of disorder. The variation of the rate on relative excitation energies of LH2 exhibits resonance peaks, which however is fragile as the disorder becomes significant. Overall, the average transfer times between two LH2s are estimated to be in the range of 4 - 25 ps for physically plausible inter-LH2 distances.
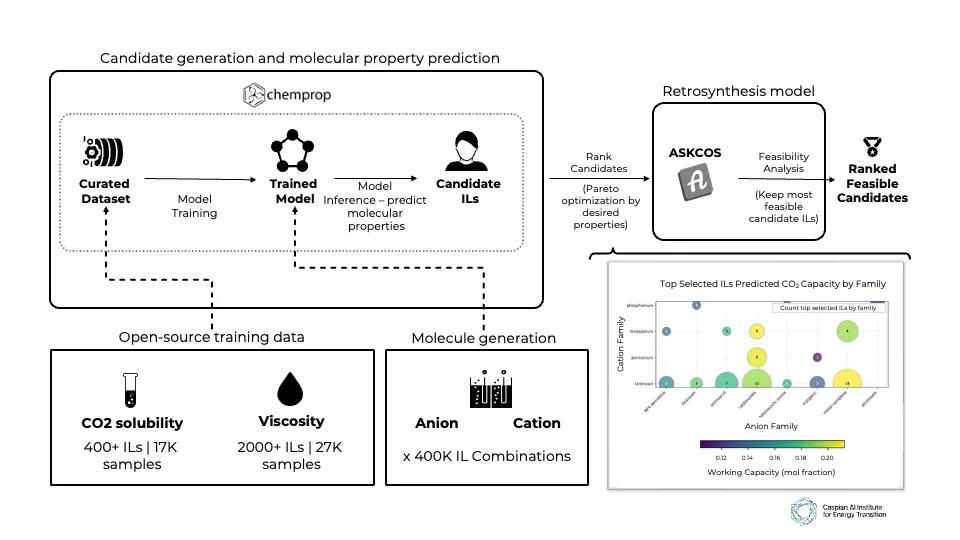
We present an AI-driven approach to discover compounds with optimal properties for CO2 capture from flue gas-refinery emissions' primary source. Focusing on ionic liquids (ILs) as alternatives to traditional amine-based solvents, we successfully identify new IL candidates with high working capacity, manageable viscosity, favorable regeneration energy, and viable synthetic routes. Our approach follows a five-stage pipeline. First, we generate IL candidates by pairing available cation and anion molecules, then predict temperature- and pressure-dependent CO2 solubility and viscosity using a GNN-based molecular property prediction model. Next, we convert solubility to working capacity and regeneration energy via Van't Hoff modeling, and then find the best set of candidates using Pareto optimization, before finally filtering those based on feasible synthesis routes. We identify 36 feasible candidates that could enable 5-10% OPEX savings and up to 10% CAPEX reductions through lower regeneration energy requirements and reduced corrosivity-offering a novel carbon-capture strategy for refineries moving forward.
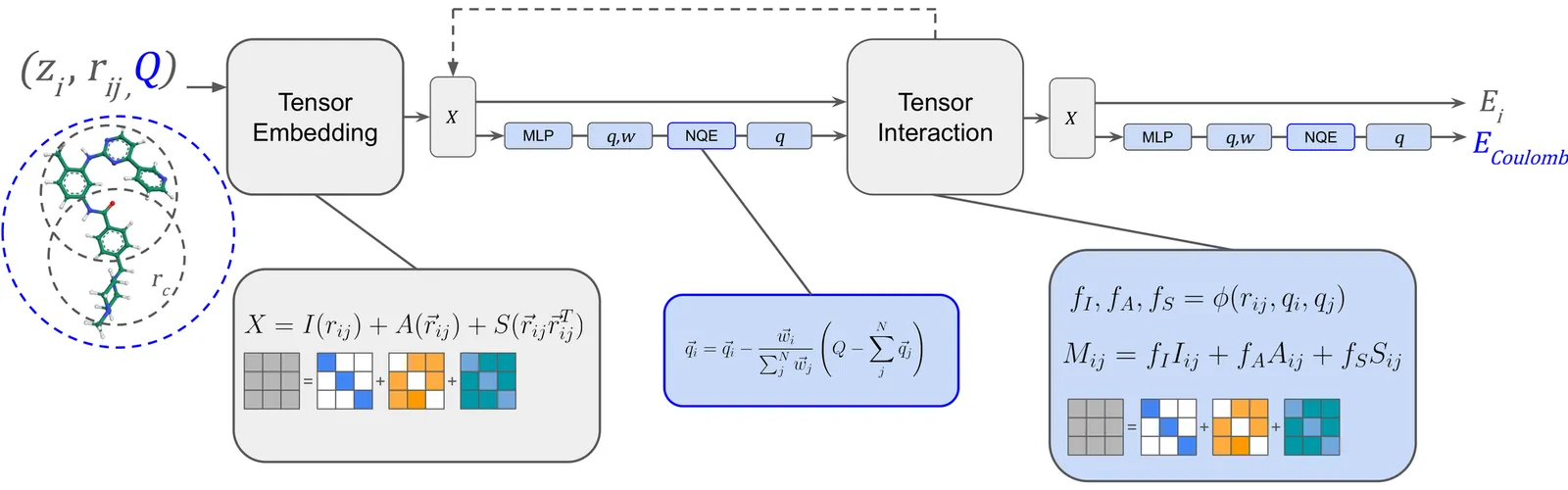
We introduce AceFF, a pre-trained machine learning interatomic potential (MLIP) optimized for small molecule drug discovery. While MLIPs have emerged as efficient alternatives to Density Functional Theory (DFT), generalizability across diverse chemical spaces remains difficult. AceFF addresses this via a refined TensorNet2 architecture trained on a comprehensive dataset of drug-like compounds. This approach yields a force field that balances high-throughput inference speed with DFT-level accuracy. AceFF fully supports the essential medicinal chemistry elements (H, B, C, N, O, F, Si, P, S, Cl, Br, I) and is explicitly trained to handle charged states. Validation against rigorous benchmarks, including complex torsional energy scans, molecular dynamics trajectories, batched minimizations, and forces and anergy accuracy demonstrates that AceFF establishes a new state-of-the-art for organic molecules. The AceFF-2 model weights and inference code are available at https://huggingface.co/Acellera/AceFF-2.0.
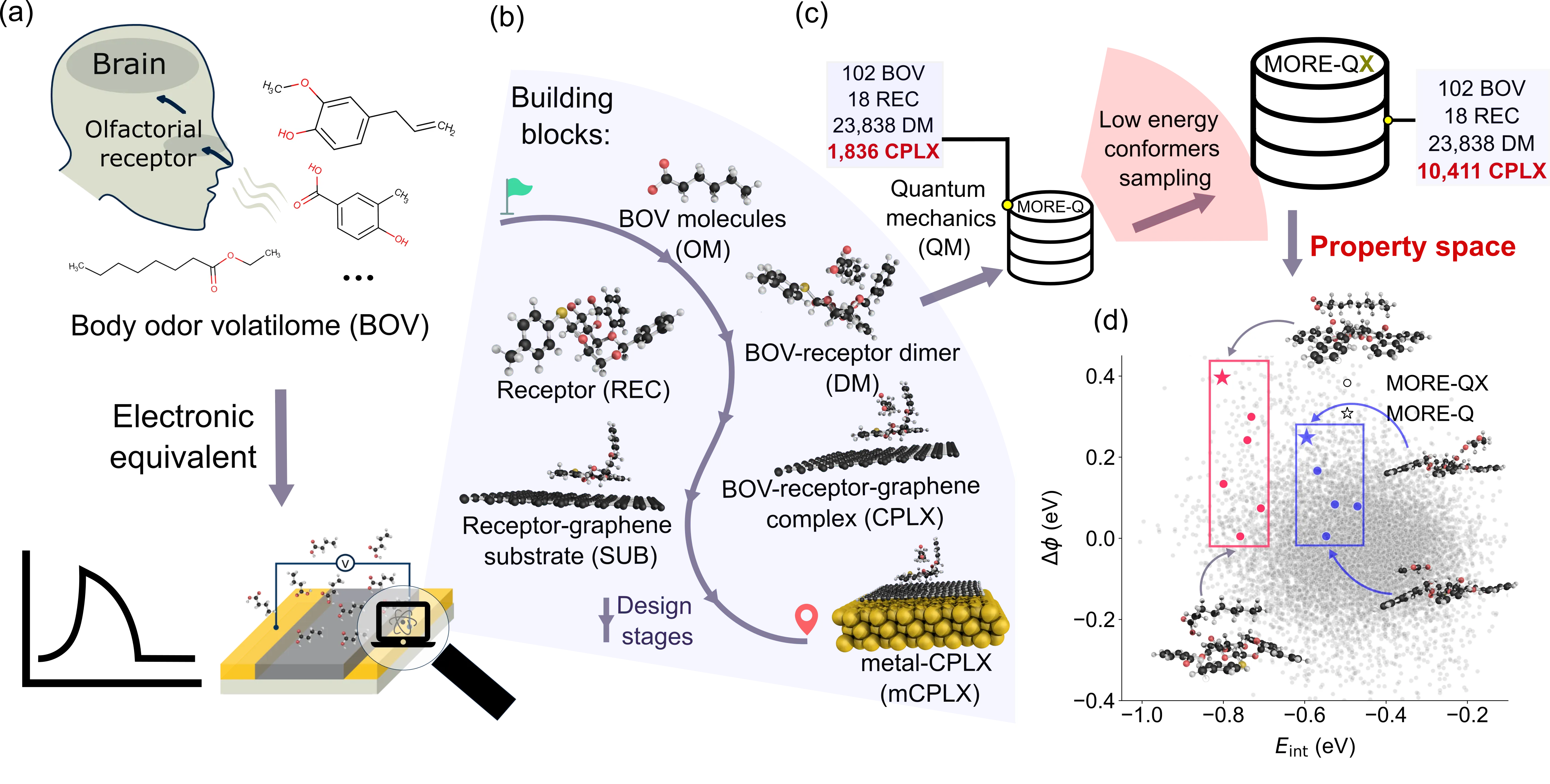
Digital sensing faces challenges in developing sustainable methods to extend the applicability of customized e-noses to complex body odor volatilome (BOV). To address this challenge, we developed MORE-ML, a computational framework that integrates quantum-mechanical (QM) property data of e-nose molecular building blocks with machine learning (ML) methods to predict sensing-relevant properties. Within this framework, we expanded our previous dataset, MORE-Q, to MORE-QX by sampling a larger conformational space of interactions between BOV molecules and mucin-derived receptors. This dataset provides extensive electronic binding features (BFs) computed upon BOV adsorption. Analysis of MORE-QX property space revealed weak correlations between QM properties of building blocks and resulting BFs. Leveraging this observation, we defined electronic descriptors of building blocks as inputs for tree-based ML models to predict BFs. Benchmarking showed CatBoost models outperform alternatives, especially in transferability to unseen compounds. Explainable AI methods further highlighted which QM properties most influence BF predictions. Collectively, MORE-ML combines QM insights with ML to provide mechanistic understanding and rational design principles for molecular receptors in BOV sensing. This approach establishes a foundation for advancing artificial sensing materials capable of analyzing complex odor mixtures, bridging the gap between molecular-level computations and practical e-nose applications.
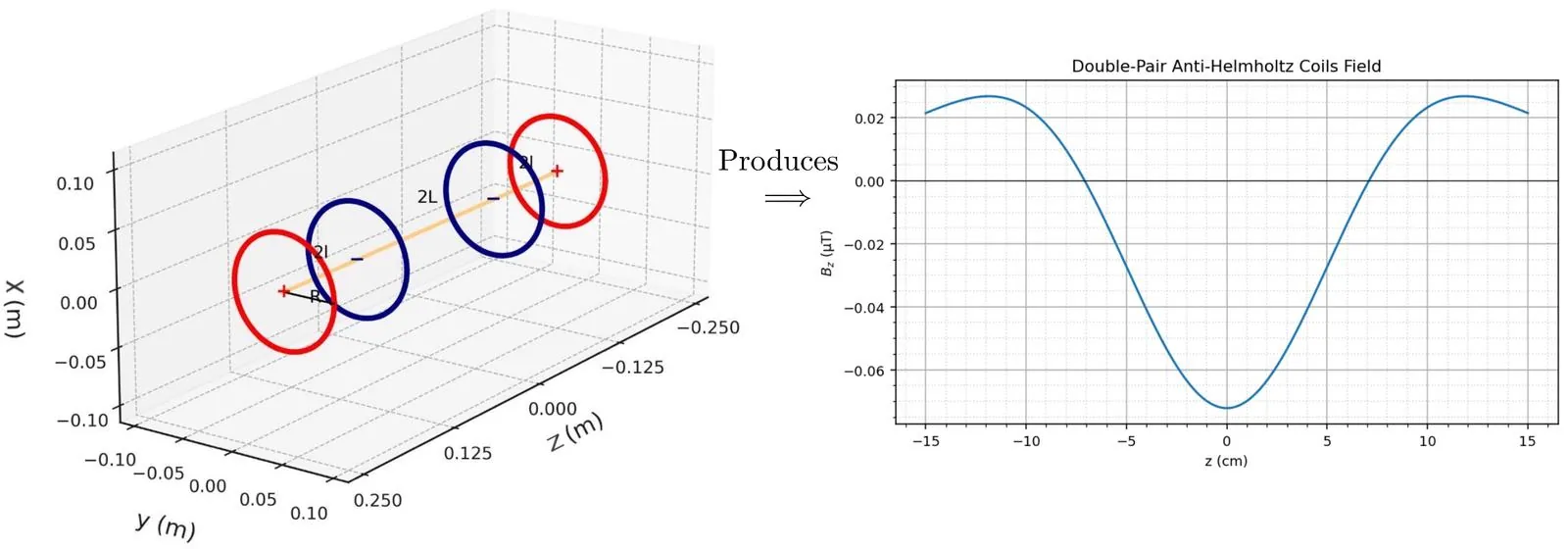
This work has investigated the Magneto-Optical Trap (MOT) system used to produce Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC). A primary challenge addressed in this study concerns the geometric limitations of traditional single-pair anti-Helmholtz coil configurations, where the magnetic field peaks occur outside the accessible inter-coil region. To overcome this limitation, we have explored the use of double-pair anti-Helmholtz coil configurations that create well-shaped magnetic field potentials centered at the experimentally accessible $z=0$ location. This investigation encompasses the three sequential processes of atom cooling: cooling in a linear external magnetic field through Doppler cooling, cooling in a well-shaped magnetic field through trapping, and evaporative cooling of atoms to achieve sub-microkelvin temperatures. Through theoretical analysis and numerical simulation, we have determined optimal geometric parameters for the coil configuration and operational parameters including laser detuning, saturation intensity, and initial atom populations for ${}^{87}\text{Rb}$ BEC production. The results indicate that with the optimized configuration, the system can achieve final temperatures of approximately $T_f \sim 60\,\mathrm{nK}$ and produce condensate populations of $\sim 10^5$ atoms with a mean density of $n_0 = 4.9 \times 10^{15}\,\mathrm{m}^{-3}$, providing systematic design guidance for experimental BEC systems
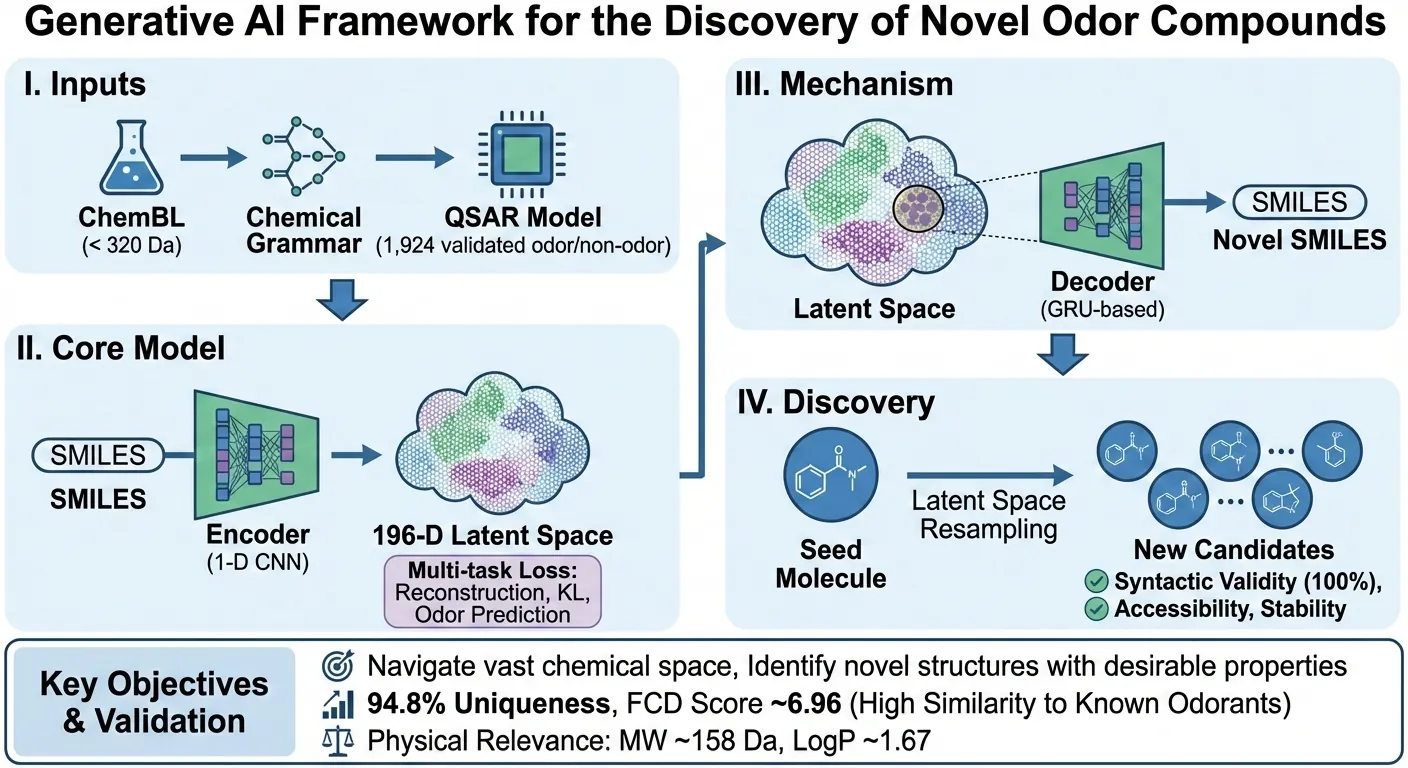
The discovery of novel odorant molecules is key for the fragrance and flavor industries, yet efficiently navigating the vast chemical space to identify structures with desirable olfactory properties remains a significant challenge. Generative artificial intelligence offers a promising approach for \textit{de novo} molecular design but typically requires large sets of molecules to learn from. To address this problem, we present a framework combining a variational autoencoder (VAE) with a quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) model to generate novel odorants from limited training sets of odor molecules. The self-supervised learning capabilities of the VAE allow it to learn SMILES grammar from ChemBL database, while its training objective is augmented with a loss term derived from an external QSAR model to structure the latent representation according to odor probability. While the VAE demonstrated high internal consistency in learning the QSAR supervision signal, validation against an external, unseen ground truth dataset (Unique Good Scents) confirms the model generates syntactically valid structures (100\% validity achieved via rejection sampling) and 94.8\% unique structures. The latent space is effectively structured by odor likelihood, evidenced by a Fréchet ChemNet Distance (FCD) of $\approx$ 6.96 between generated molecules and known odorants, compared to $\approx$ 21.6 for the ChemBL baseline. Structural analysis via Bemis-Murcko scaffolds reveals that 74.4\% of candidates possess novel core frameworks distinct from the training data, indicating the model performs extensive chemical space exploration beyond simple derivatization of known odorants. Generated candidates display physicochemical properties ....
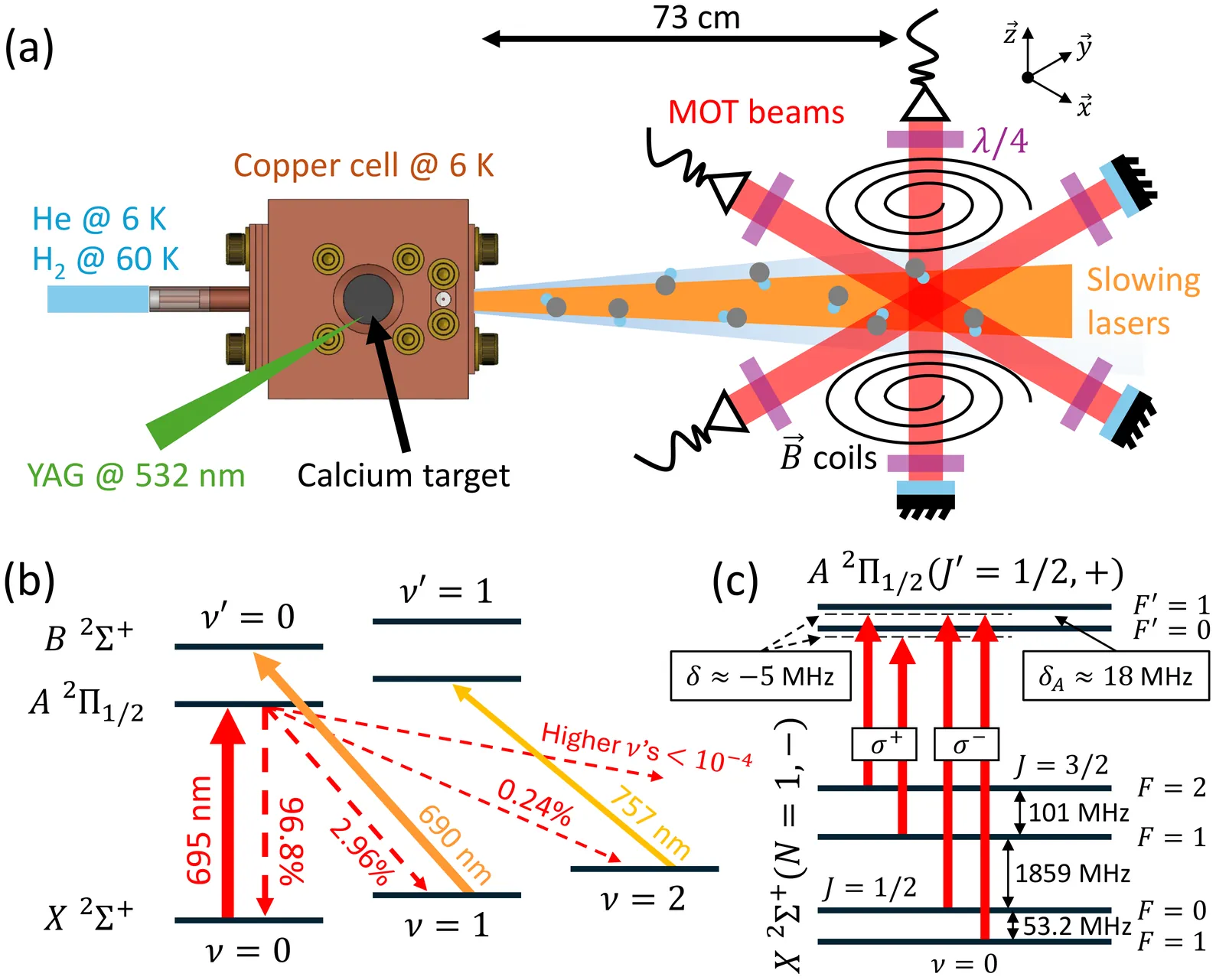
We demonstrate a three-dimensional magneto-optical trap (MOT) of a metal hydride molecule, CaH. We are able to scatter $\sim$$10^{4}$ photons with vibrational loss covered up to vibrational quantum number $ν=2$. This allows us to laser slow the molecular beam near zero velocity with a "white-light" technique and subsequently load it into a radio-frequency MOT. The MOT contains 230(40) molecules, limited by beam source characteristics and predissociative loss of CaH. The temperature of the MOT is below one millikelvin. The predissociative loss mechanism could, in turn, facilitate controlled dissociation of the molecule, offering a possible route to optical trapping of hydrogen atoms for precision spectroscopy.
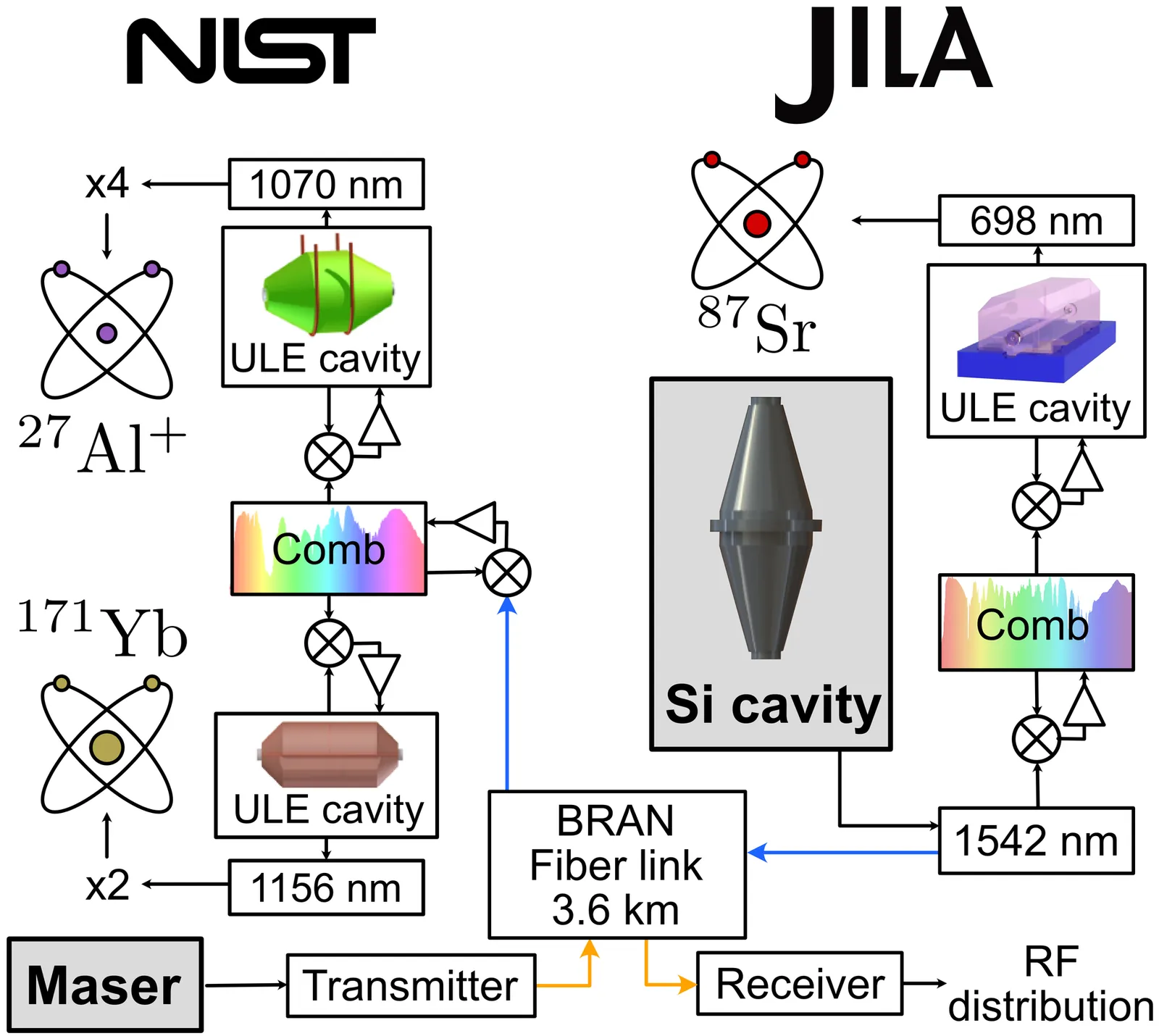
We report high-precision frequency ratio measurements between optical atomic clocks based on $^{27}$Al$^+$, $^{171}$Yb, and $^{87}$Sr. With total fractional uncertainties at or below $3.2 \times 10^{-18}$, these measurements meet an important milestone criterion for redefinition of the second in the International System of Units. Discrepancies in $^{87}$Sr ratios at approximately $1\times10^{-16}$ and the Al$^+$/Yb ratio at $1.6\times10^{-17}$ in fractional units compared to our previous measurements underscore the importance of repeated, high-precision comparisons by different laboratories. A key innovation in this work is the use of a common ultrastable reference delivered to all clocks via a 3.6 km phase-stabilized fiber link between two institutions. Derived from a cryogenic single-crystal silicon cavity, this reference improves comparison stability by a factor of 2 to 3 over previous systems, with an optical lattice clock ratio achieving a fractional instability of $1.3 \times 10^{-16}$ at 1 second. By enabling faster comparisons, this stability will improve sensitivity to non-white noise processes and other underlying limits of state-of-the-art optical frequency standards.
Solving molecular energy levels via the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) algorithm represents one of the most promising applications for demonstrating practically meaningful quantum advantage in the noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) era. To strike a balance between ansatz complexity and computational stability in VQE calculations, we propose the HiUCCSD, a novel symmetry-respecting ansatz engineered from the intrinsic information of the Hamiltonian. We theoretically prove the effectiveness of HiUCCSD within the scope of Abelian point groups. Furthermore, we compare the performance of HiUCCSD and the established SymUCCSD via VQE and Adaptive Derivative-Assembled Pseudo-Trotter (ADAPT)-VQE numerical experiments on ten molecules with distinct point groups. The results show that HiUCCSD achieves equivalent performance to SymUCCSD for Abelian point group molecules, while avoiding the potential performance failure of SymUCCSD in the case of non-Abelian point group molecules. Across the studied molecular systems, HiUCCSD cuts the parameter count by 18%-83% for VQE and reduces the excitation operator pool size by 27%-84% for ADAPT-VQE, as compared with the UCCSD ansatz. With enhanced robustness and broader applicability, HiUCCSD offers a new ansatz option for advancing large-scale molecular VQE implementation.
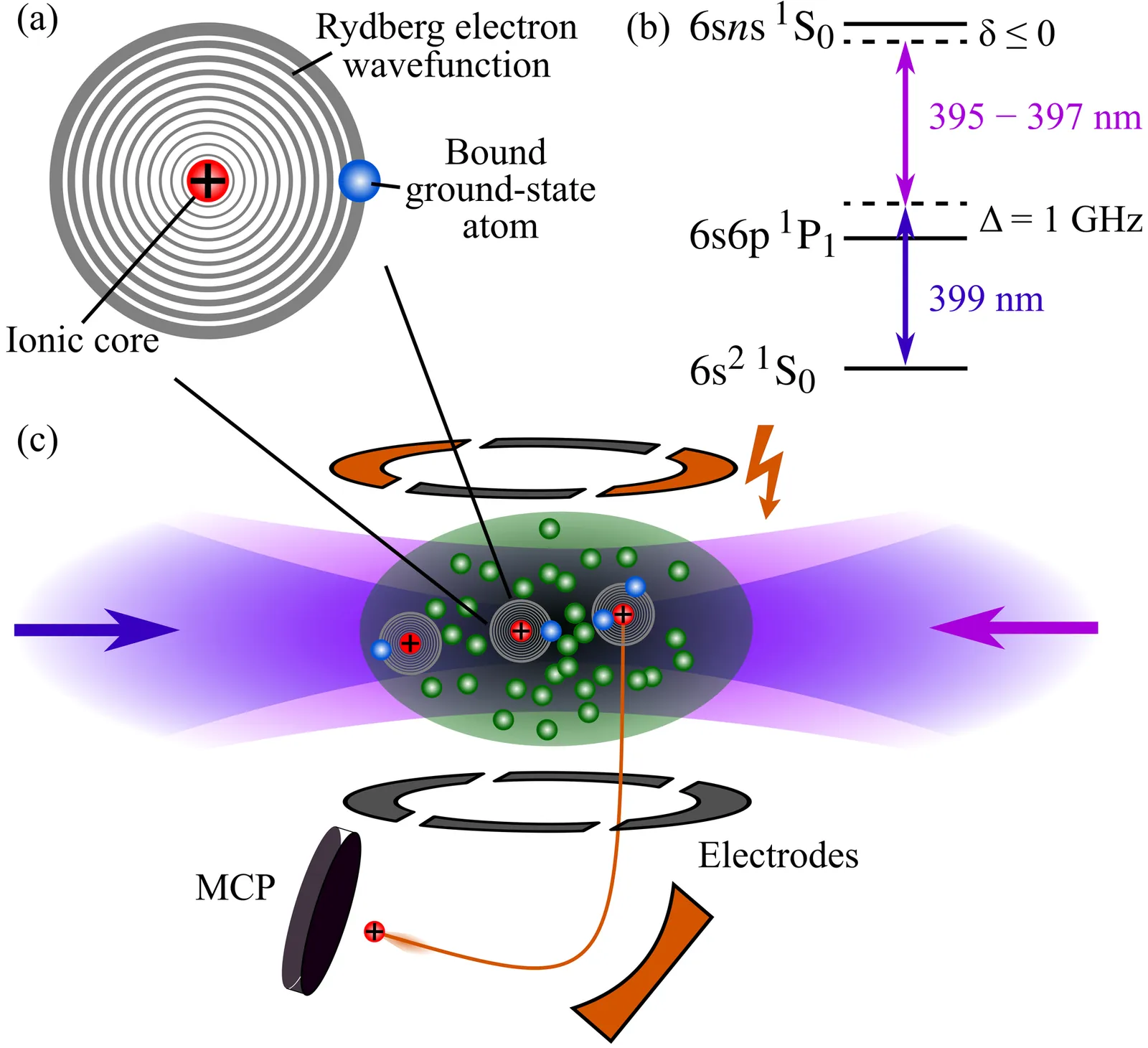
Divalent atoms have emerged as powerful alternatives to alkalis in ultracold atom platforms, offering unique advantages arising from their two-electron structure. Among these species, ytterbium (Yb) is especially promising, yet its anionic properties and its Rydberg spectrum remain comparatively unexplored. In this work, we perform a first and comprehensive experimental and theoretical investigation of ultralong-range Rydberg molecules (ULRMs) of $^{174}$Yb in $6sns\,^1S_0$ Rydberg states across nearly two decades in principal quantum number $n$ and three orders of magnitude in molecular binding energy. Using the Coulomb Green's function formalism, we compute Born-Oppenheimer molecular potentials describing the Rydberg atom in the presence of a ground-state perturber and achieve quantitative agreement with high-resolution molecular spectra. This enables the extraction of low-energy electron-Yb scattering phase shifts, including the zero-energy $s$-wave scattering length and the positions of two spin-orbit split $p$-wave shape resonances. Our results provide strong evidence that the Yb$^{-}$ anion exists only as a metastable resonance. We additionally show the sensitivity of ULRM spectra to the atomic quantum defects, using this to refine the value for the $6s23f\, ^1F_3$ quantum defect. Together, these findings establish Yb ULRMs as a powerful probe of electron-Yb interactions and lay essential groundwork for future Rydberg experiments with divalent atoms.

The rigorous description of Conical Intersections (CIs) remains the central challenge of non-adiabatic quantum chemistry. While the ``Yarkony Seam'' -- the $(3N-8)$-dimensional manifold of degeneracy -- is well-understood geometrically, its accurate characterization by high-level electronic structure methods is plagued by numerical instabilities. Specifically, standard Coupled Cluster (CC) theory suffers from root bifurcations near Ground State CIs, rendering the ``Gold Standard'' of chemistry inapplicable where it is needed most. Here, we present \textbf{QuMorpheus}, an open-source computational package that resolves these singularities by implementing a topological framework based on Dissipative Mixed Hodge Modules (DMHM) [P. Saurabh, arXiv:2512.19487 (2025)]. By algorithmically mapping the CC polynomial equations to a spectral sheaf, we compute the exact Monodromy ($μ$) invariants of the intersection. We demonstrate that this automated algebraic geometry approach correctly identifies the physical ground state topology in the Köhn-Tajti model and resolves the intersection seams of realistic chemical systems, including Ethylene and the Chloronium ion ($\mathrm{H_2Cl^+}$). Furthermore, we apply QuMorpheus to the photoisomerization of Previtamin D, proving that the experimentally observed Woodward-Hoffmann selection rules are a direct consequence of a topological ``Monodromy Wall'' ($μ=1, γ=π$) rather than purely energetic barriers. This establishes a general software solution to the ``Yarkony Problem,'' enabling the robust, automated mapping of global intersection seams in complex molecular systems. The topological stability of these intersections allows for the control protocols discussed in Ref.[P. Saurabh, Submitted to Phys. Rev. X (2025)].
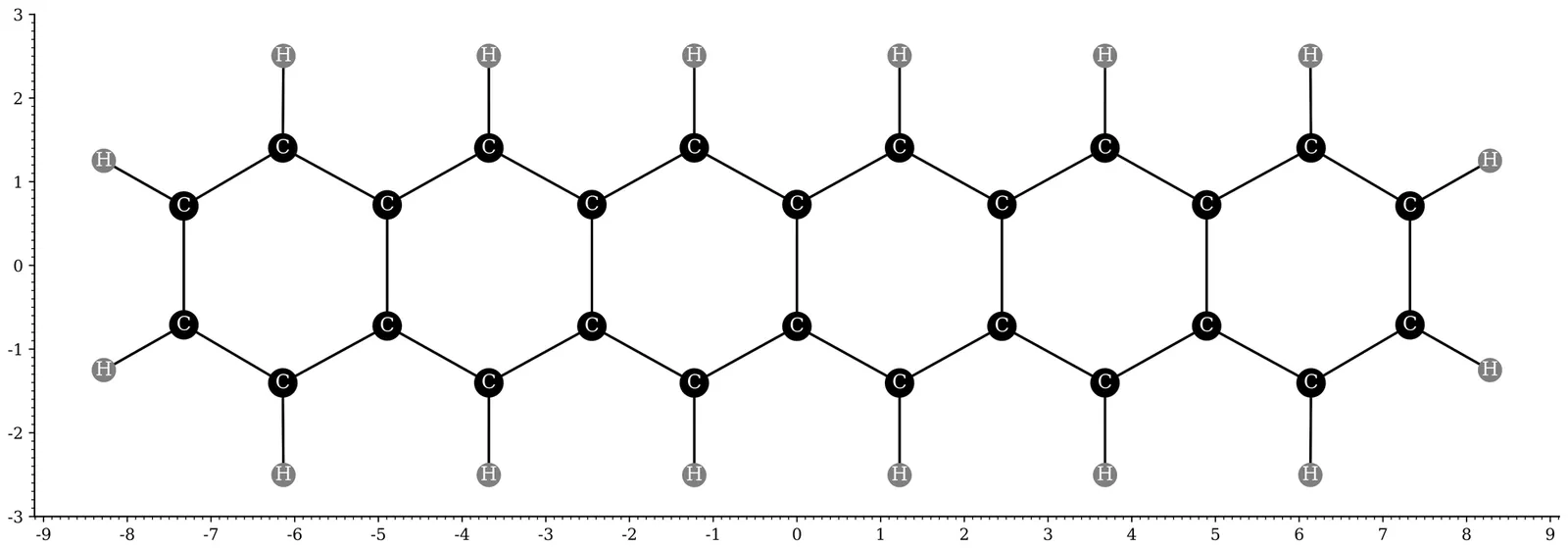
Recently, thermally-assisted-occupation density functional theory (TAO-DFT) [J.-D. Chai, J. Chem. Phys. 136, 154104 (2012)] has been demonstrated to be an efficient and accurate electronic structure method for studying the ground-state properties of large multi-reference (MR) systems at absolute zero. To explore the thermal equilibrium properties of large MR systems at finite electronic temperatures, in the present work, we propose the finite-temperature (FT) extension of TAO-DFT, denoted as FT-TAO-DFT. Besides, to unlock the dynamical information of large MR systems at finite temperatures, FT-TAO-DFT is combined with ab initio molecular dynamics, leading to FT-TAO-AIMD. In addition, we also develop FT-TAO-DFT-based quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM), denoted as FT-TAO-QM/MM, to provide a cost-effective description of the thermal equilibrium properties of a QM subsystem with MR character embedded in an MM environment at finite temperatures. Moreover, the FT-TAO-DFT, FT-TAO-AIMD, and FT-TAO-QM/MM methods are employed to explore the radical nature and infrared (IR) spectra of n-acenes (n = 2--6), consisting of n linearly fused benzene rings, in vacuum and in an argon (Ar) matrix at finite temperatures. According to our calculations, for n-acenes at 1000 K or below, the electronic temperature effects on the radical nature and IR spectra are very minor, while the nuclear temperature effects on these properties are noticeable. For n-acene in an Ar matrx at absolute zero, the Ar matrix has minimal impact on the radical nature of n-acene, while the co-deposition procedure of n-acene and Ar atoms may affect the IR spectrum of n-acene.
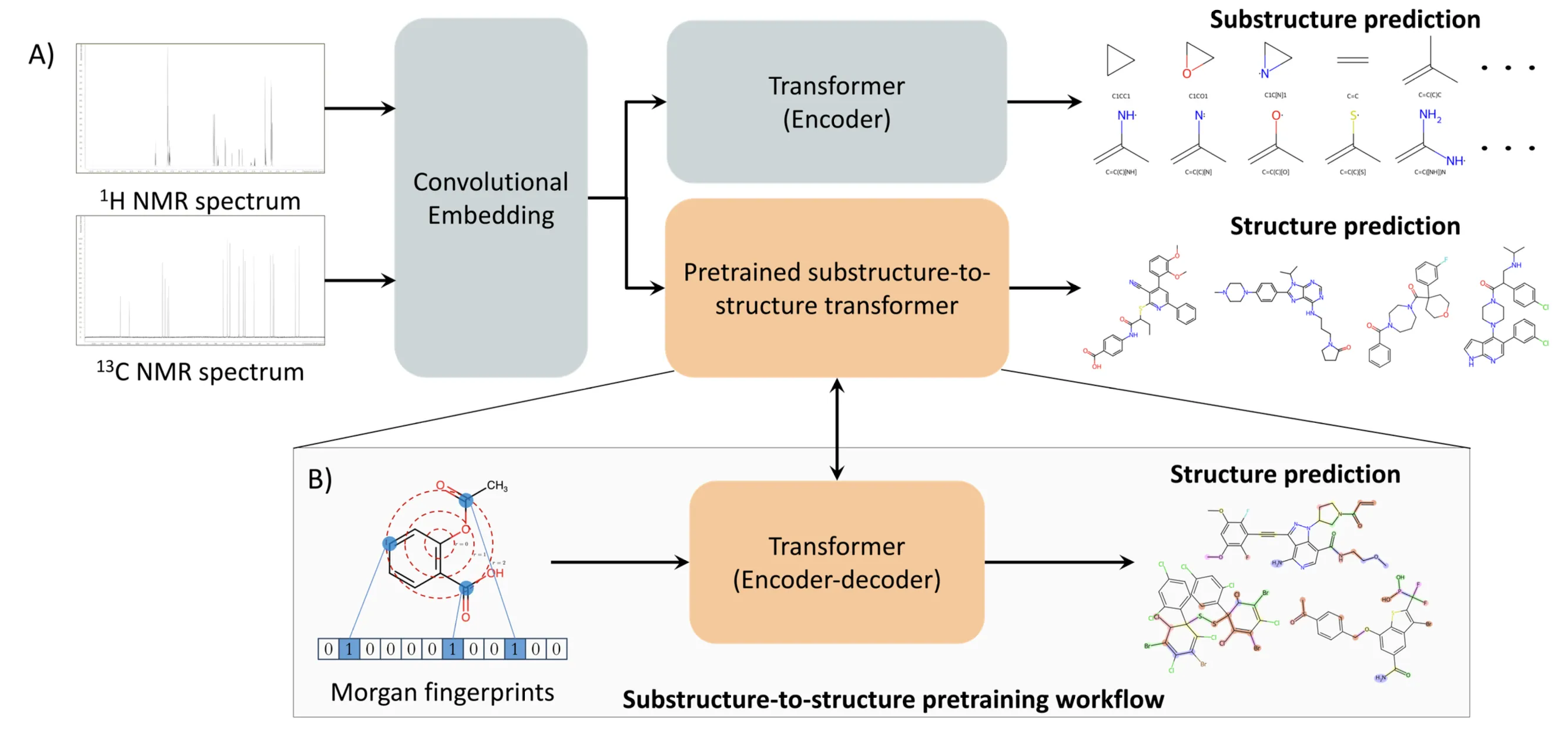
One-dimensional NMR spectroscopy is one of the most widely used techniques for the characterization of organic compounds and natural products. For molecules with up to 36 non-hydrogen atoms, the number of possible structures has been estimated to range from $10^{20} - 10^{60}$. The task of determining the structure (formula and connectivity) of a molecule of this size using only its one-dimensional $^1$H and/or $^{13}$C NMR spectrum, i.e. de novo structure generation, thus appears completely intractable. Here we show how it is possible to achieve this task for systems with up to 40 non-hydrogen atoms across the full elemental coverage typically encountered in organic chemistry (C, N, O, H, P, S, Si, B, and the halogens) using a deep learning framework, thus covering a vast portion of the drug-like chemical space. Leveraging insights from natural language processing, we show that our transformer-based architecture predicts the correct molecule with 55.2% accuracy within the first 15 predictions using only the $^1$H and $^{13}$C NMR spectra, thus overcoming the combinatorial growth of the chemical space while also being extensible to experimental data via fine-tuning.

Strong light-matter coupling enables hybrid states in which photonic and electronic degrees of freedom become correlated even in the ground state. While many-body effects in long-range dispersion interactions are known to reshape electronic properties under such conditions, their impact on quantum-optical observables remains largely unexplored. Here, we address this problem using quantum electrodynamical density-functional theory (QEDFT) combined with the recently developed photon-many-body dispersion (pMBD) functional, which can capture higher-order electron-photon correlations and multi-photon processes. We compute ground-state photonic observables including photon number fluctuations, second-order correlations, and quadrature variances, and find squeezing and super-Poissonian photon statistics emerging from light-matter interactions in the strong coupling regime. Our results demonstrate that capturing the full hierarchy of many-body, electron-photon and multi-photon correlations is essential for a consistent description of quantum-optical properties in strongly coupled molecular systems, establishing QEDFT as a first-principles framework for predicting nonclassical photonic features in the ground state of complex systems.
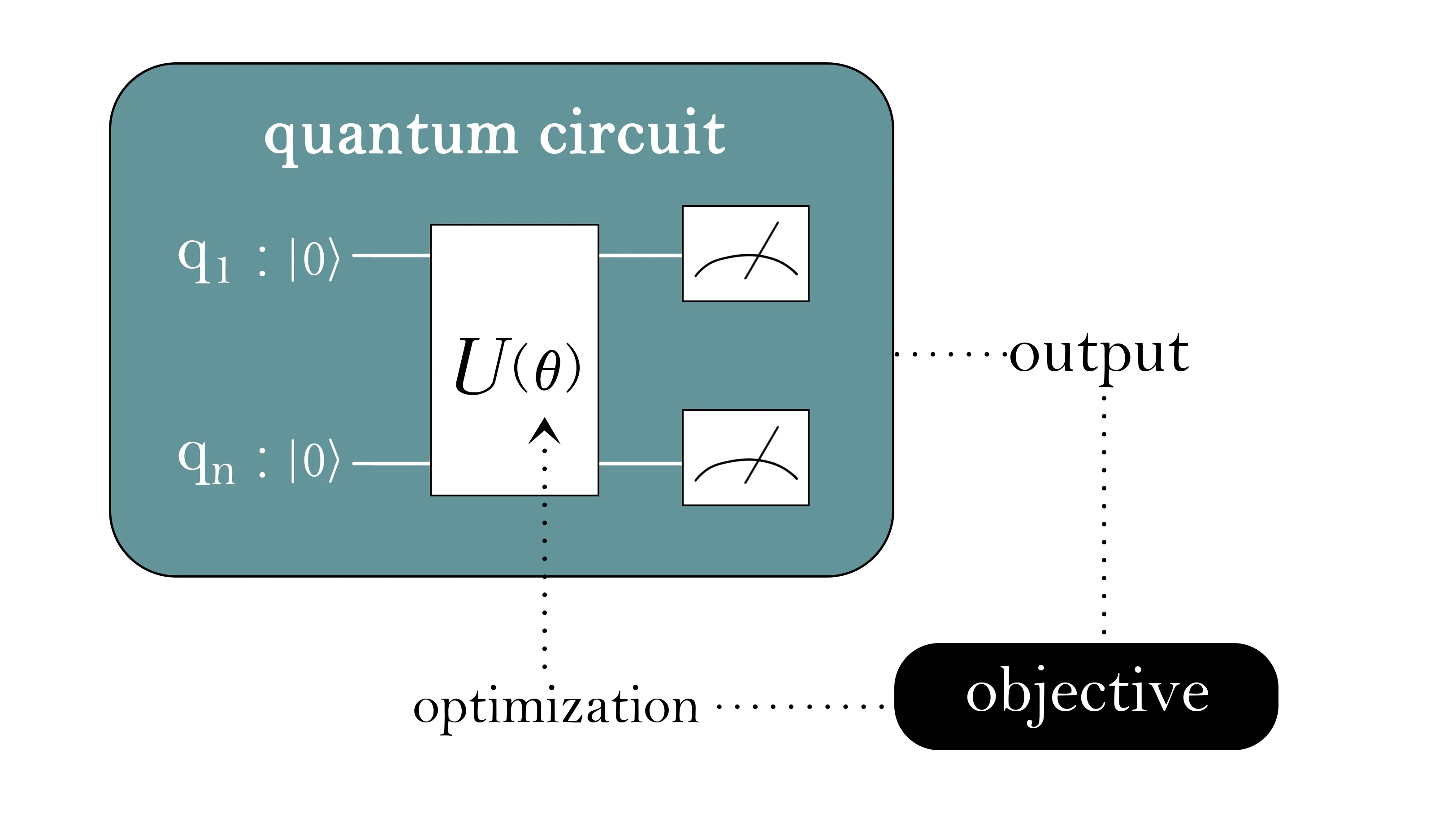
Quantum computers promise scalable treatments of electronic structure, yet applying variational quantum eigensolvers (VQE) on realistic drug-like molecules remains constrained by the performance limitations of near-term quantum hardwares. A key strategy for addressing this challenge which effectively leverages current Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) hardwares yet remains under-benchmarked is active space selection. We introduce a benchmark that heuristically proposes criteria based on chemically grounded metrics to classify the suitability of a molecule for using quantum computing and then quantifies the impact of active space choices across the VQE pipeline for quantum drug discovery. The suite covers several representative drug-like molecules (e.g., lovastatin, oseltamivir, morphine) and uses chemically motivated active spaces. Our VQE evaluations employ both simulation and quantum processing unit (QPU) execution using unitary coupled-cluster with singles and doubles (UCCSD) and hardware-efficient ansatz (HEA). We adopt a more comprehensive evaluation, including chemistry metrics and architecture-centric metrics. For accuracy, we compare them with classical quantum chemistry methods. This work establishes the first systematic benchmark for active space driven VQE and lays the groundwork for future hardware-algorithm co-design studies in quantum drug discovery.