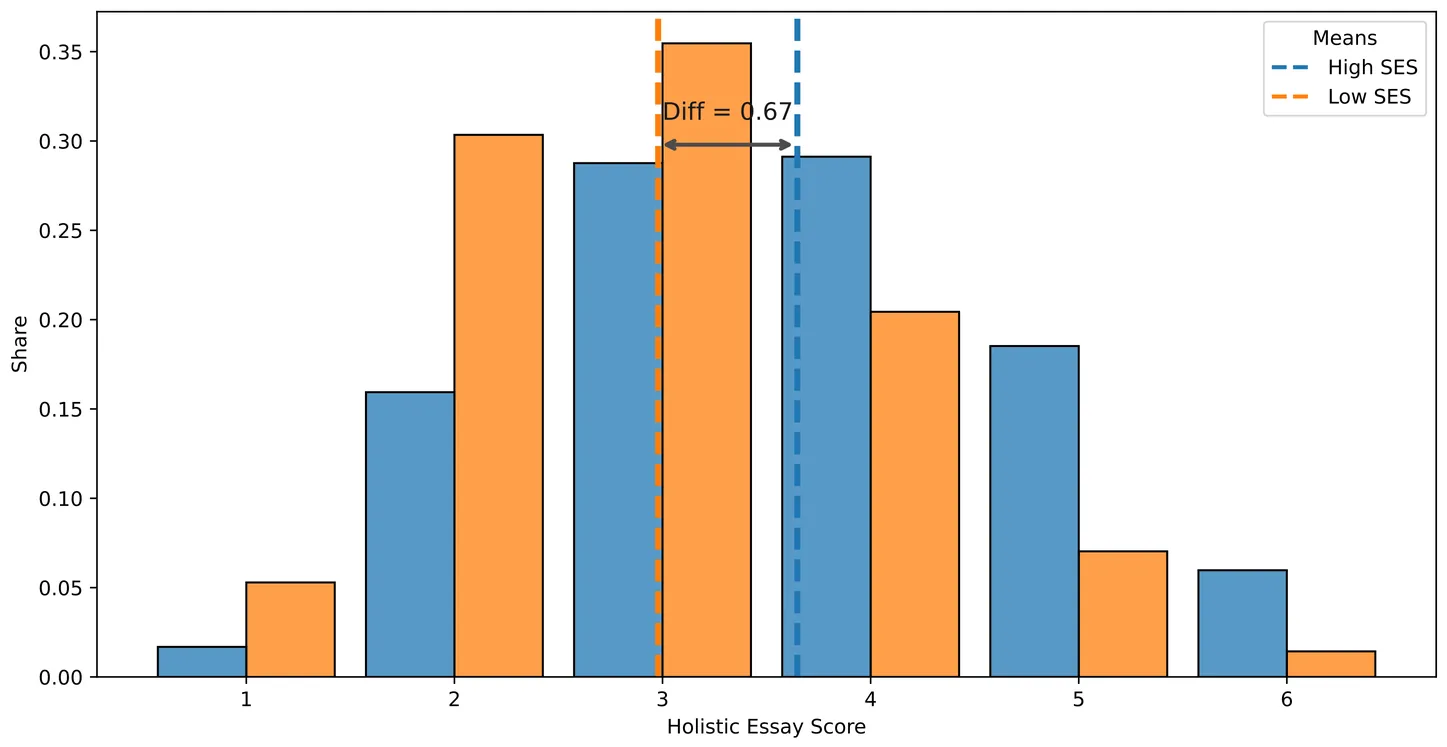
Content vs. Form: What Drives the Writing Score Gap Across Socioeconomic Backgrounds? A Generated Panel Approach
Students from different socioeconomic backgrounds exhibit persistent gaps in test scores, gaps that can translate into unequal educational and labor-market outcomes later in life. In many assessments, performance reflects not only what students know, but also how effectively they can communicate that knowledge. This distinction is especially salient in writing assessments, where scores jointly reward the substance of students' ideas and the way those ideas are expressed. As a result, observed score gaps may conflate differences in underlying content with differences in expressive skill. A central question, therefore, is how much of the socioeconomic-status (SES) gap in scores is driven by differences in what students say versus how they say it. We study this question using a large corpus of persuasive essays written by U.S. middle- and high-school students. We introduce a new measurement strategy that separates content from style by leveraging large language models to generate multiple stylistic variants of each essay. These rewrites preserve the underlying arguments while systematically altering surface expression, creating a "generated panel" that introduces controlled within-essay variation in style. This approach allows us to decompose SES gaps in writing scores into contributions from content and style. We find an SES gap of 0.67 points on a 1-6 scale. Approximately 69% of the gap is attributable to differences in essay content quality, Style differences account for 26% of the gap, and differences in evaluation standards across SES groups account for the remaining 5%. These patterns seems stable across demographic subgroups and writing tasks. More broadly, our approach shows how large language models can be used to generate controlled variation in observational data, enabling researchers to isolate and quantify the contributions of otherwise entangled factors.
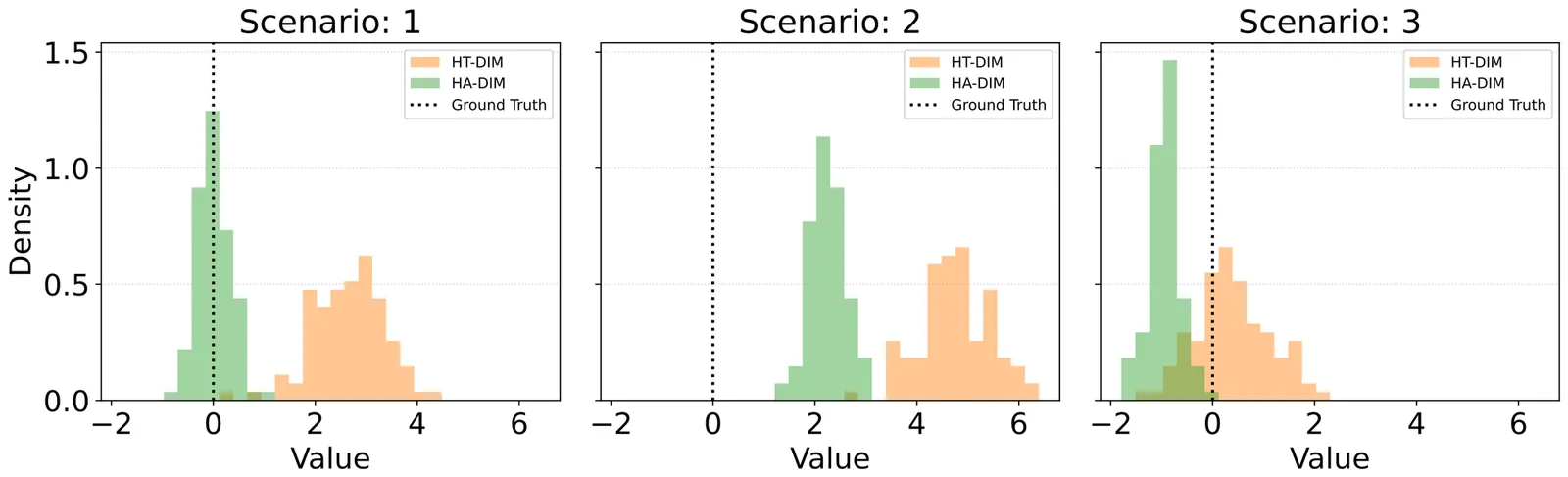
Detecting and Mitigating Treatment Leakage in Text-Based Causal Inference: Distillation and Sensitivity Analysis
Text-based causal inference increasingly employs textual data as proxies for unobserved confounders, yet this approach introduces a previously undertheorized source of bias: treatment leakage. Treatment leakage occurs when text intended to capture confounding information also contains signals predictive of treatment status, thereby inducing post-treatment bias in causal estimates. Critically, this problem can arise even when documents precede treatment assignment, as authors may employ future-referencing language that anticipates subsequent interventions. Despite growing recognition of this issue, no systematic methods exist for identifying and mitigating treatment leakage in text-as-confounder applications. This paper addresses this gap through three contributions. First, we provide formal statistical and set-theoretic definitions of treatment leakage that clarify when and why bias occurs. Second, we propose four text distillation methods -- similarity-based passage removal, distant supervision classification, salient feature removal, and iterative nullspace projection -- designed to eliminate treatment-predictive content while preserving confounder information. Third, we validate these methods through simulations using synthetic text and an empirical application examining International Monetary Fund structural adjustment programs and child mortality. Our findings indicate that moderate distillation optimally balances bias reduction against confounder retention, whereas overly stringent approaches degrade estimate precision.
 2512.22846
2512.22846Causal-Policy Forest for End-to-End Policy Learning
This study proposes an end-to-end algorithm for policy learning in causal inference. We observe data consisting of covariates, treatment assignments, and outcomes, where only the outcome corresponding to the assigned treatment is observed. The goal of policy learning is to train a policy from the observed data, where a policy is a function that recommends an optimal treatment for each individual, to maximize the policy value. In this study, we first show that maximizing the policy value is equivalent to minimizing the mean squared error for the conditional average treatment effect (CATE) under $\{-1, 1\}$ restricted regression models. Based on this finding, we modify the causal forest, an end-to-end CATE estimation algorithm, for policy learning. We refer to our algorithm as the causal-policy forest. Our algorithm has three advantages. First, it is a simple modification of an existing, widely used CATE estimation method, therefore, it helps bridge the gap between policy learning and CATE estimation in practice. Second, while existing studies typically estimate nuisance parameters for policy learning as a separate task, our algorithm trains the policy in a more end-to-end manner. Third, as in standard decision trees and random forests, we train the models efficiently, avoiding computational intractability.
 2512.20523
2512.20523ScoreMatchingRiesz: Auto-DML with Infinitesimal Classification
This study proposes Riesz representer estimation methods based on score matching. The Riesz representer is a key component in debiased machine learning for constructing $\sqrt{n}$-consistent and efficient estimators in causal inference and structural parameter estimation. To estimate the Riesz representer, direct approaches have garnered attention, such as Riesz regression and the covariate balancing propensity score. These approaches can also be interpreted as variants of direct density ratio estimation (DRE) in several applications such as average treatment effect estimation. In DRE, it is well known that flexible models can easily overfit the observed data due to the estimand and the form of the loss function. To address this issue, recent work has proposed modeling the density ratio as a product of multiple intermediate density ratios and estimating it using score-matching techniques, which are often used in the diffusion model literature. We extend score-matching-based DRE methods to Riesz representer estimation. Our proposed method not only mitigates overfitting but also provides insights for causal inference by bridging marginal effects and average policy effects through time score functions.
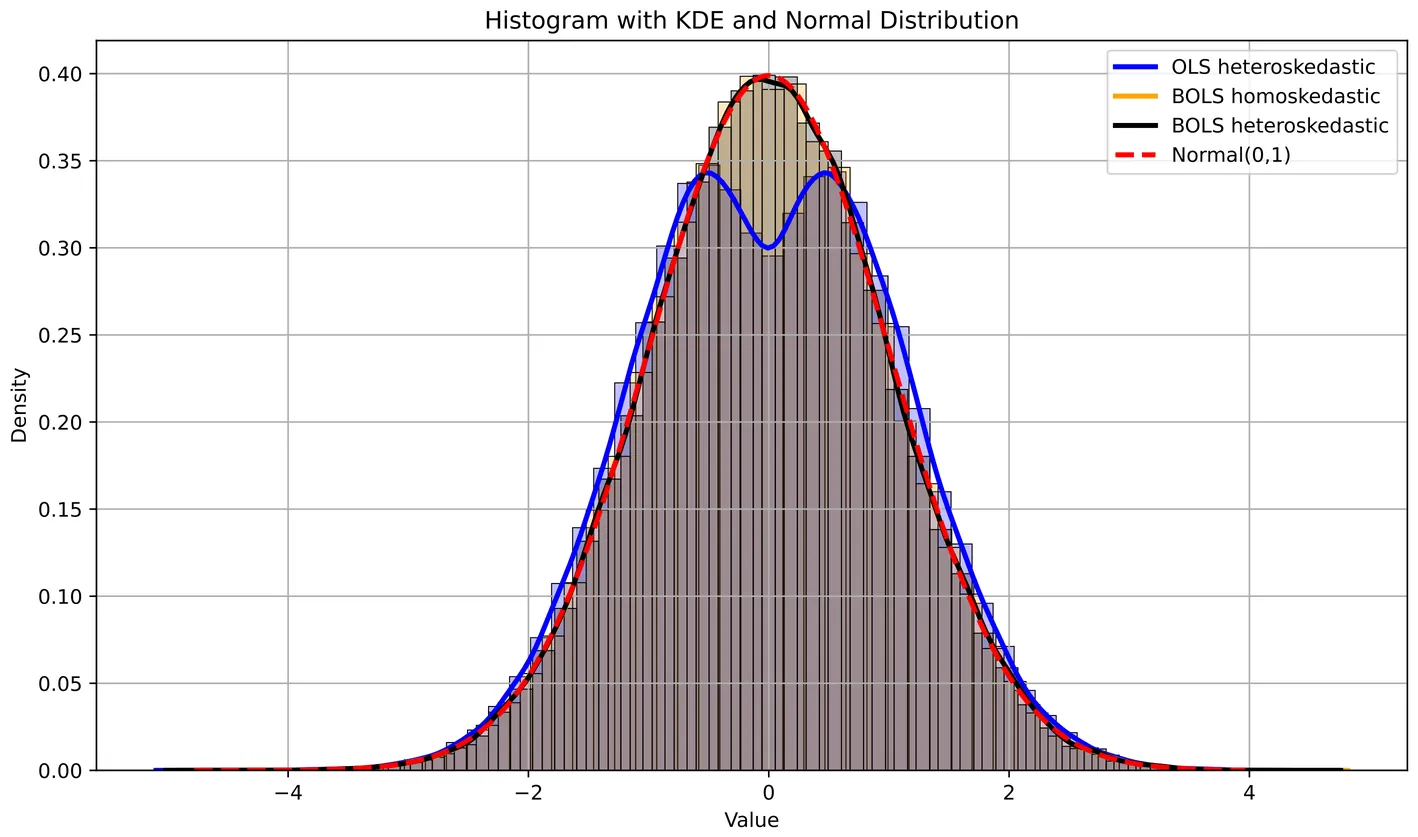
Inference for Batched Adaptive Experiments
The advantages of adaptive experiments have led to their rapid adoption in economics, other fields, as well as among practitioners. However, adaptive experiments pose challenges for causal inference. This note suggests a BOLS (batched ordinary least squares) test statistic for inference of treatment effects in adaptive experiments. The statistic provides a precision-equalizing aggregation of per-period treatment-control differences under heteroskedasticity. The combined test statistic is a normalized average of heteroskedastic per-period z-statistics and can be used to construct asymptotically valid confidence intervals. We provide simulation results comparing rejection rates in the typical case with few treatment periods and few (or many) observations per batch.
 2512.08513
2512.08513Minimax and Bayes Optimal Adaptive Experimental Design for Treatment Choice
We consider an adaptive experiment for treatment choice and design a minimax and Bayes optimal adaptive experiment with respect to regret. Given binary treatments, the experimenter's goal is to choose the treatment with the highest expected outcome through an adaptive experiment, in order to maximize welfare. We consider adaptive experiments that consist of two phases, the treatment allocation phase and the treatment choice phase. The experiment starts with the treatment allocation phase, where the experimenter allocates treatments to experimental subjects to gather observations. During this phase, the experimenter can adaptively update the allocation probabilities using the observations obtained in the experiment. After the allocation phase, the experimenter proceeds to the treatment choice phase, where one of the treatments is selected as the best. For this adaptive experimental procedure, we propose an adaptive experiment that splits the treatment allocation phase into two stages, where we first estimate the standard deviations and then allocate each treatment proportionally to its standard deviation. We show that this experiment, often referred to as Neyman allocation, is minimax and Bayes optimal in the sense that its regret upper bounds exactly match the lower bounds that we derive. To show this optimality, we derive minimax and Bayes lower bounds for the regret using change-of-measure arguments. Then, we evaluate the corresponding upper bounds using the central limit theorem and large deviation bounds.
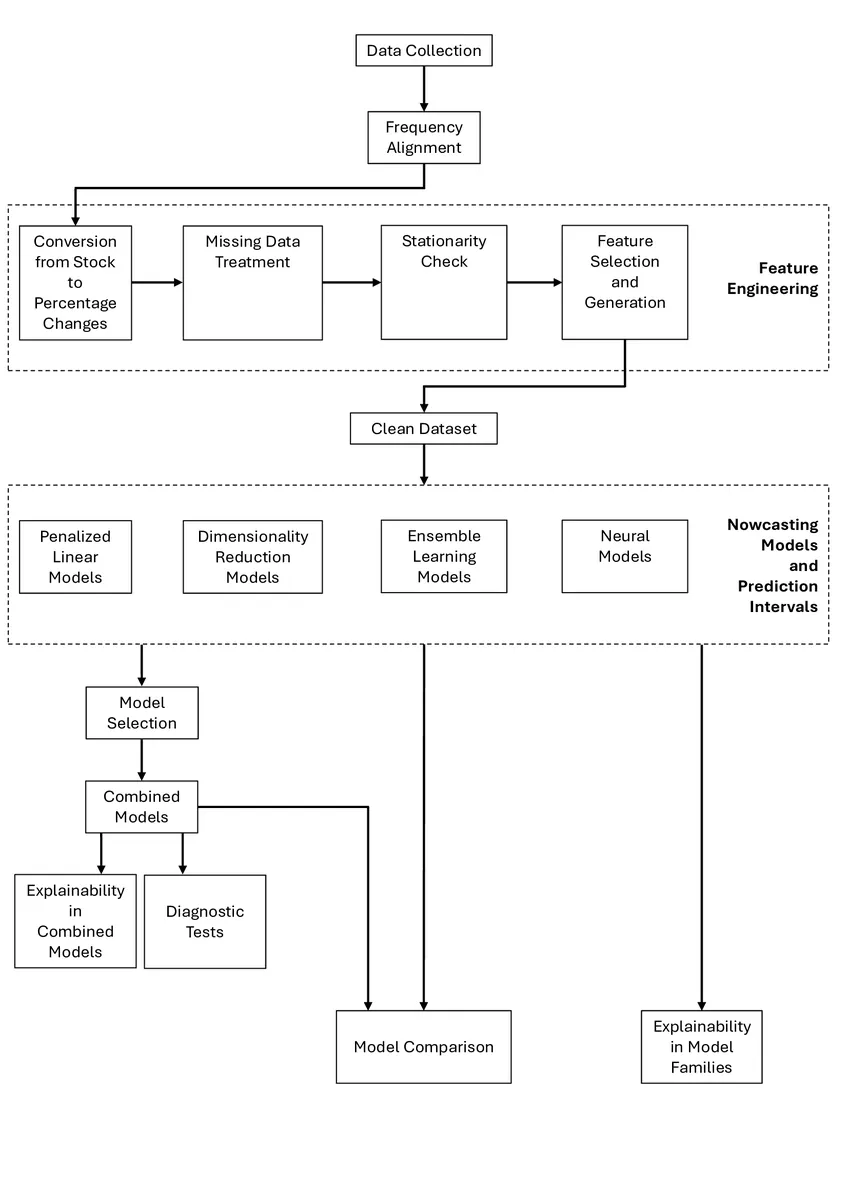
Opening the Black Box: Nowcasting Singapore's GDP Growth and its Explainability
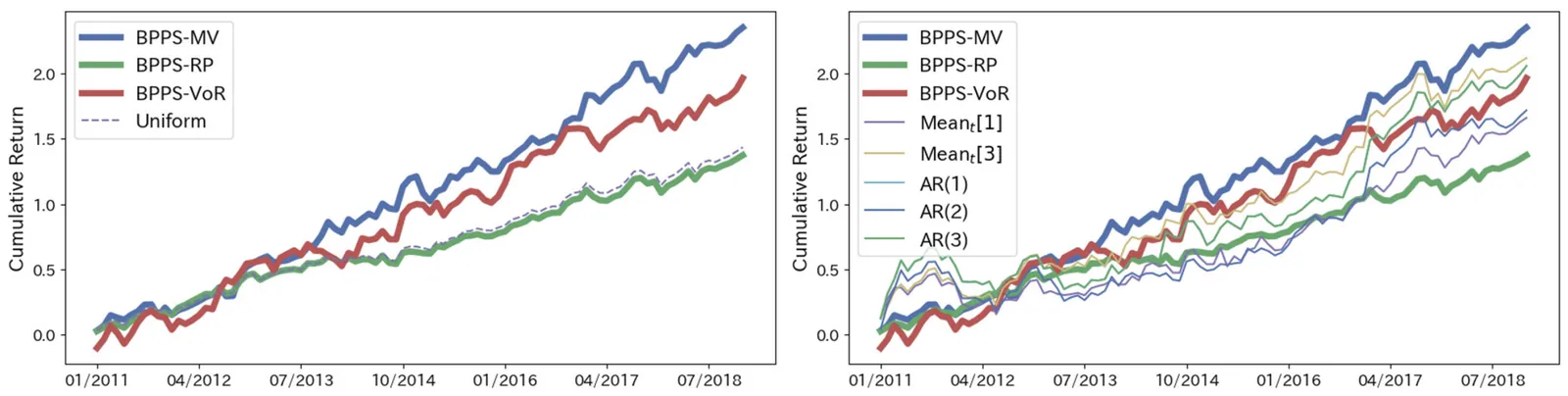
Timely assessment of current conditions is essential especially for small, open economies such as Singapore, where external shocks transmit rapidly to domestic activity. We develop a real-time nowcasting framework for quarterly GDP growth using a high-dimensional panel of approximately 70 indicators, encompassing economic and financial indicators over 1990Q1-2023Q2. The analysis covers penalized regressions, dimensionality-reduction methods, ensemble learning algorithms, and neural architectures, benchmarked against a Random Walk, an AR(3), and a Dynamic Factor Model. The pipeline preserves temporal ordering through an expanding-window walk-forward design with Bayesian hyperparameter optimization, and uses moving block-bootstrap procedures both to construct prediction intervals and to obtain confidence bands for feature-importance measures. It adopts model-specific and XAI-based explainability tools. A Model Confidence Set procedure identifies statistically superior learners, which are then combined through simple, weighted, and exponentially weighted schemes; the resulting time-varying weights provide an interpretable representation of model contributions. Predictive ability is assessed via Giacomini-White tests. Empirical results show that penalized regressions, dimensionality-reduction models, and GRU networks consistently outperform all benchmarks, with RMSFE reductions of roughly 40-60%; aggregation delivers further gains. Feature-attribution methods highlight industrial production, external trade, and labor-market indicators as dominant drivers of Singapore's short-run growth dynamics.
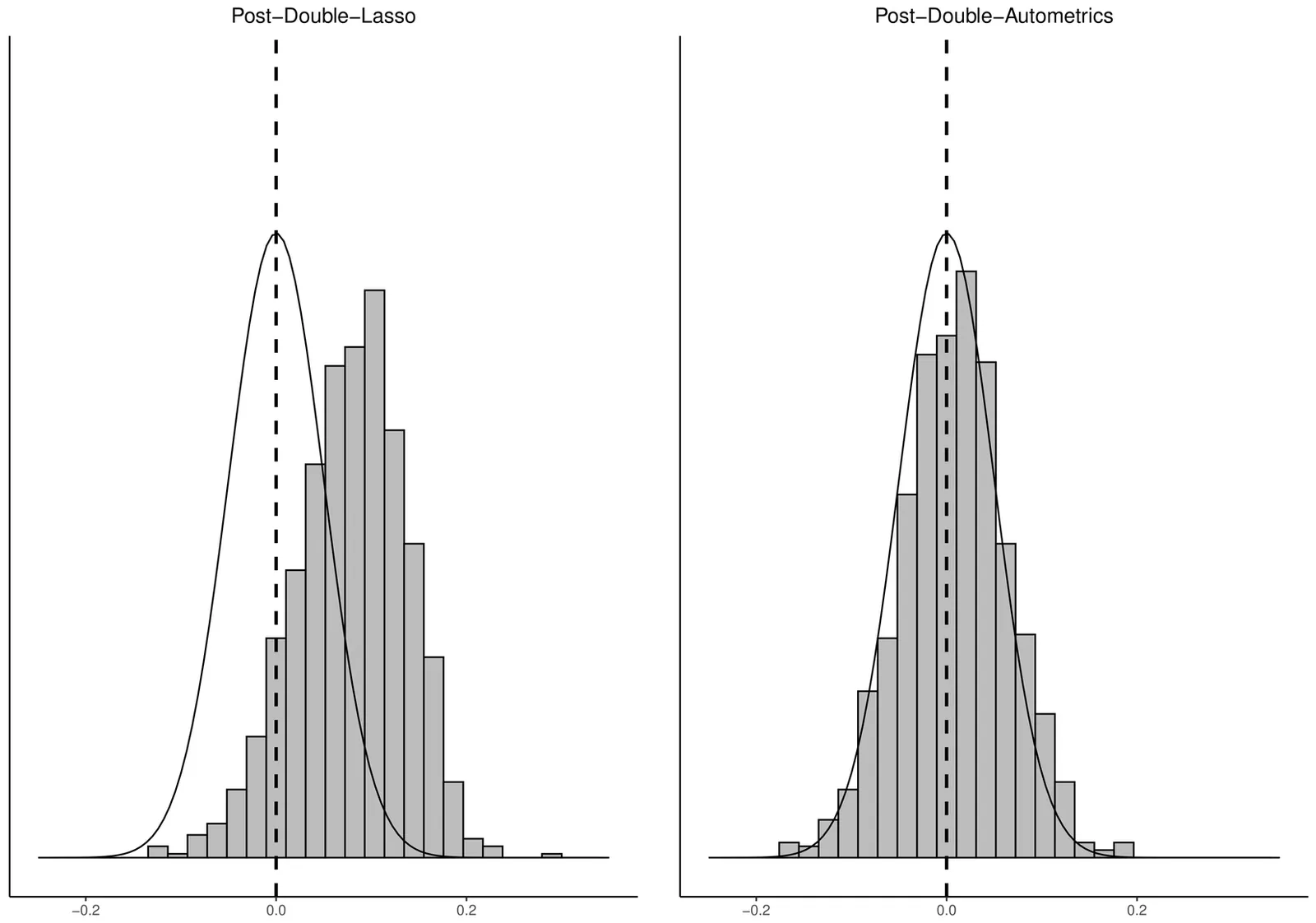
Estimation in high-dimensional linear regression: Post-Double-Autometrics as an alternative to Post-Double-Lasso
Post-Double-Lasso is becoming the most popular method for estimating linear regression models with many covariates when the purpose is to obtain an accurate estimate of a parameter of interest, such as an average treatment effect. However, this method can suffer from substantial omitted variable bias in finite sample. We propose a new method called Post-Double-Autometrics, which is based on Autometrics, and show that this method outperforms Post-Double-Lasso. Its use in a standard application of economic growth sheds new light on the hypothesis of convergence from poor to rich economies.
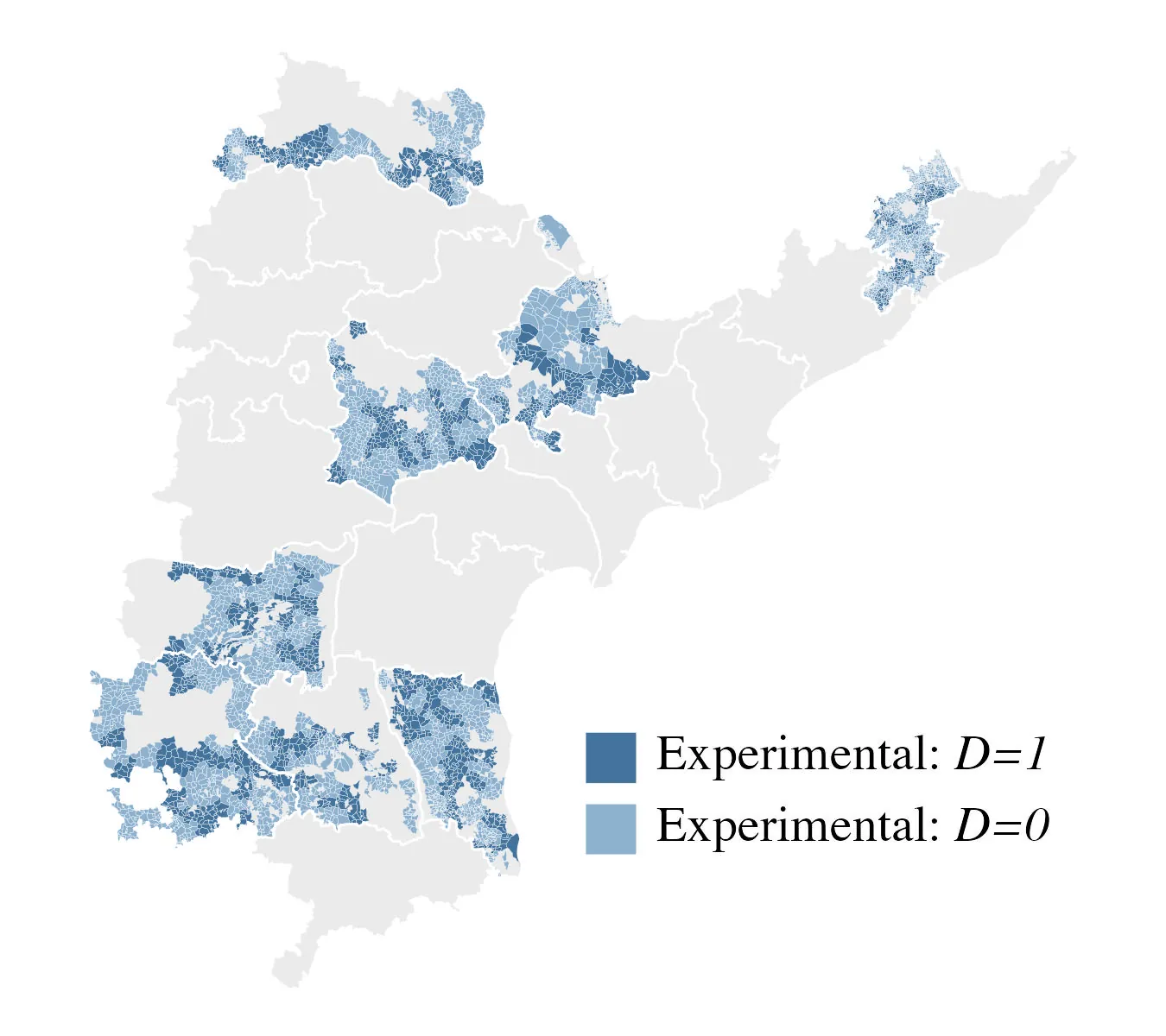
Individual and group fairness in geographical partitioning
Socioeconomic segregation often arises in school districting and other contexts, causing some groups to be over- or under-represented within a particular district. This phenomenon is closely linked with disparities in opportunities and outcomes. We formulate a new class of geographical partitioning problems in which the population is heterogeneous, and it is necessary to ensure fair representation for each group at each facility. We prove that the optimal solution is a novel generalization of the additively weighted Voronoi diagram, and we propose a simple and efficient algorithm to compute it, thus resolving an open question dating back to Dvoretzky et al. (1951). The efficacy and potential for practical insight of the approach are demonstrated in a realistic case study involving seven demographic groups and $78$ district offices.
 2511.17928
2511.17928Limit Theorems for Network Data without Metric Structure
This paper develops limit theorems for random variables with network dependence, without requiring that individuals in the network to be located in a Euclidean or metric space. This distinguishes our approach from most existing limit theorems in network econometrics, which are based on weak dependence concepts such as strong mixing, near-epoch dependence, and $ψ$-dependence. By relaxing the assumption of an underlying metric space, our theorems can be applied to a broader range of network data, including financial and social networks. To derive the limit theorems, we generalize the concept of functional dependence (also known as physical dependence) from time series to random variables with network dependence. Using this framework, we establish several inequalities, a law of large numbers, and central limit theorems. Furthermore, we verify the conditions for these limit theorems based on primitive assumptions for spatial autoregressive models, which are widely used in network data analysis.
Approximate Least-Favorable Distributions and Nearly Optimal Tests via Stochastic Mirror Descent
We consider a class of hypothesis testing problems where the null hypothesis postulates $M$ distributions for the observed data, and there is only one possible distribution under the alternative. We show that one can use a stochastic mirror descent routine for convex optimization to provably obtain - after finitely many iterations - both an approximate least-favorable distribution and a nearly optimal test, in a sense we make precise. Our theoretical results yield concrete recommendations about the algorithm's implementation, including its initial condition, its step size, and the number of iterations. Importantly, our suggested algorithm can be viewed as a slight variation of the algorithm suggested by Elliott, Müller, and Watson (2015), whose theoretical performance guarantees are unknown.
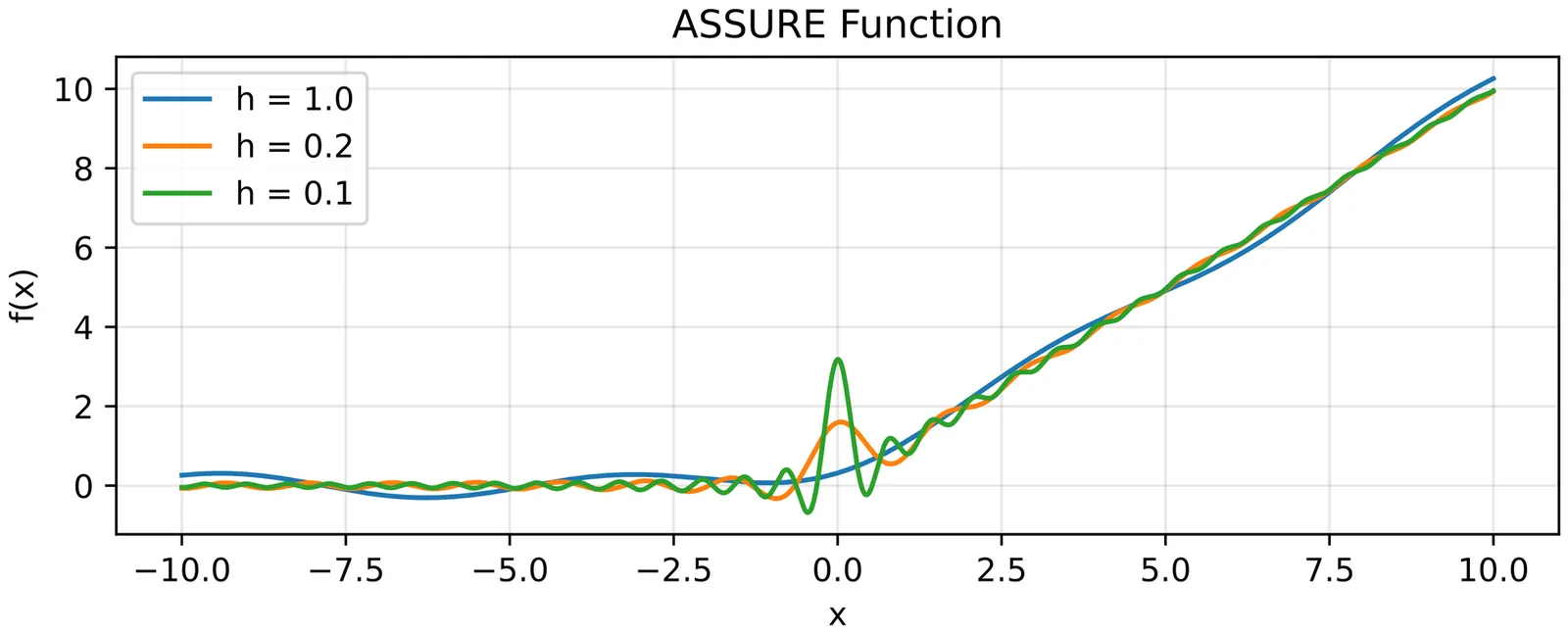
Compound Selection Decisions: An Almost SURE Approach
This paper proposes methods for producing compound selection decisions in a Gaussian sequence model. Given unknown, fixed parameters $μ_ {1:n}$ and known $σ_{1:n}$ with observations $Y_i \sim \textsf{N}(μ_i, σ_i^2)$, the decision maker would like to select a subset of indices $S$ so as to maximize utility $\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i\in S} (μ_i - K_i)$, for known costs $K_i$. Inspired by Stein's unbiased risk estimate (SURE), we introduce an almost unbiased estimator, called ASSURE, for the expected utility of a proposed decision rule. ASSURE allows a user to choose a welfare-maximizing rule from a pre-specified class by optimizing the estimated welfare, thereby producing selection decisions that borrow strength across noisy estimates. We show that ASSURE produces decision rules that are asymptotically no worse than the optimal but infeasible decision rule in the pre-specified class. We apply ASSURE to the selection of Census tracts for economic opportunity, the identification of discriminating firms, and the analysis of $p$-value decision procedures in A/B testing.
Robust Cauchy-Based Methods for Predictive Regressions
This paper develops robust inference methods for predictive regressions that address key challenges posed by endogenously persistent or heavy-tailed regressors, as well as persistent volatility in errors. Building on the Cauchy estimation framework, we propose two novel tests: one based on $t$-statistic group inference and the other employing a hybrid approach that combines Cauchy and OLS estimation. These methods effectively mitigate size distortions that commonly arise in standard inference procedures under endogeneity, near nonstationarity, heavy tails, and persistent volatility. The proposed tests are simple to implement and applicable to both continuous- and discrete-time models. Extensive simulation experiments demonstrate favorable finite-sample performance across a range of realistic settings. An empirical application examines the predictability of excess stock returns using the dividend-price and earnings-price ratios as predictors. The results suggest that the dividend-price ratio possesses predictive power, whereas the earnings-price ratio does not significantly forecast returns.
Unlocking the Regression Space
This paper introduces and analyzes a framework that accommodates general heterogeneity in regression modeling. It demonstrates that regression models with fixed or time-varying parameters can be estimated using the OLS and time-varying OLS methods, respectively, across a broad class of regressors and noise processes not covered by existing theory. The proposed setting facilitates the development of asymptotic theory and the estimation of robust standard errors. The robust confidence interval estimators accommodate substantial heterogeneity in both regressors and noise. The resulting robust standard error estimates coincide with White's (1980) heteroskedasticity-consistent estimator but are applicable to a broader range of conditions, including models with missing data. They are computationally simple and perform well in Monte Carlo simulations. Their robustness, generality, and ease of implementation make them highly suitable for empirical applications. Finally, the paper provides a brief empirical illustration.
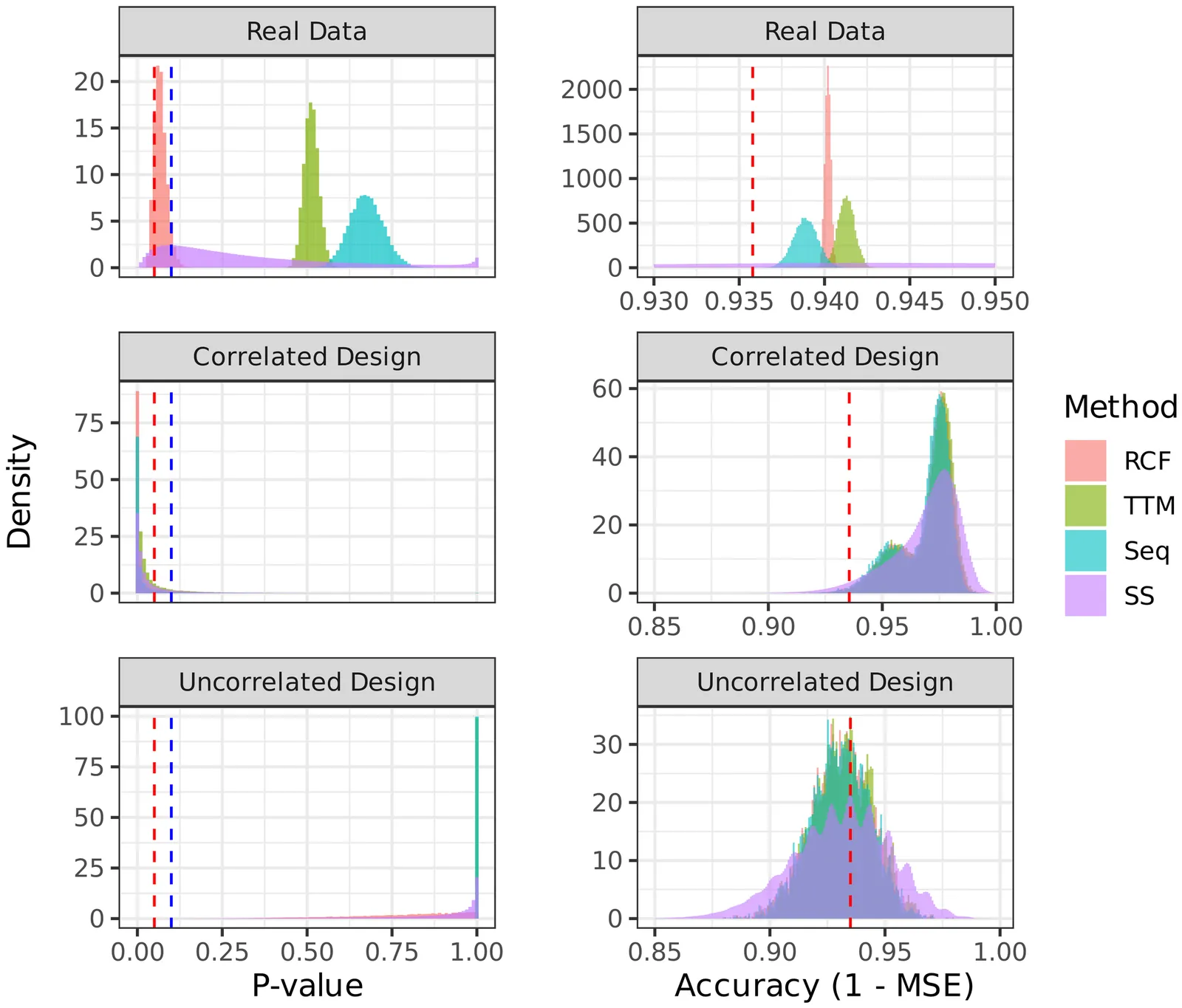
Training and Testing with Multiple Splits: A Central Limit Theorem for Split-Sample Estimators
As predictive algorithms grow in popularity, using the same dataset to both train and test a new model has become routine across research, policy, and industry. Sample-splitting attains valid inference on model properties by using separate subsamples to estimate the model and to evaluate it. However, this approach has two drawbacks, since each task uses only part of the data, and different splits can lead to widely different estimates. Averaging across multiple splits, I develop an inference approach that uses more data for training, uses the entire sample for testing, and improves reproducibility. I address the statistical dependence from reusing observations across splits by proving a new central limit theorem for a large class of split-sample estimators under arguably mild and general conditions. Importantly, I make no restrictions on model complexity or convergence rates. I show that confidence intervals based on the normal approximation are valid for many applications, but may undercover in important cases of interest, such as comparing the performance between two models. I develop a new inference approach for such cases, explicitly accounting for the dependence across splits. Moreover, I provide a measure of reproducibility for p-values obtained from split-sample estimators. Finally, I apply my results to two important problems in development and public economics: predicting poverty and learning heterogeneous treatment effects in randomized experiments. I show that my inference approach with repeated cross-fitting achieves better power than existing alternatives, often enough to reveal statistical significance that would otherwise be missed.
 2511.01680
2511.01680Making Interpretable Discoveries from Unstructured Data: A High-Dimensional Multiple Hypothesis Testing Approach
Social scientists are increasingly turning to unstructured datasets to unlock new empirical insights, e.g., estimating causal effects on text outcomes, measuring beliefs from open-ended survey responses. In such settings, unsupervised analysis is often of interest, in that the researcher does not want to pre-specify the objects of measurement or otherwise artificially delimit the space of measurable concepts; they are interested in discovery. This paper proposes a general and flexible framework for pursuing discovery from unstructured data in a statistically principled way. The framework leverages recent methods from the literature on machine learning interpretability to map unstructured data points to high-dimensional, sparse, and interpretable dictionaries of concepts; computes (test) statistics of these dictionary entries; and then performs selective inference on them using newly developed statistical procedures for high-dimensional exceedance control of the $k$-FWER under arbitrary dependence. The proposed framework has few researcher degrees of freedom, is fully replicable, and is cheap to implement -- both in terms of financial cost and researcher time. Applications to recent descriptive and causal analyses of unstructured data in empirical economics are explored. An open source Jupyter notebook is provided for researchers to implement the framework in their own projects.
 2511.00324
2511.00324Residual Balancing for Non-Linear Outcome Models in High Dimensions
We extend the approximate residual balancing (ARB) framework to nonlinear models, answering an open problem posed by Athey et al. (2018). Our approach addresses the challenge of estimating average treatment effects in high-dimensional settings where the outcome follows a generalized linear model. We derive a new bias decomposition for nonlinear models that reveals the need for a second-order correction to account for the curvature of the link function. Based on this insight, we construct balancing weights through an optimization problem that controls for both first and second-order sources of bias. We provide theoretical guarantees for our estimator, establishing its $\sqrt{n}$-consistency and asymptotic normality under standard high-dimensional assumptions.
 2510.24433
2510.24433Nearest Neighbor Matching as Least Squares Density Ratio Estimation and Riesz Regression
This study proves that Nearest Neighbor (NN) matching can be interpreted as an instance of Riesz regression for automatic debiased machine learning. Lin et al. (2023) shows that NN matching is an instance of density-ratio estimation with their new density-ratio estimator. Chernozhukov et al. (2024) develops Riesz regression for automatic debiased machine learning, which directly estimates the Riesz representer (or equivalently, the bias-correction term) by minimizing the mean squared error. In this study, we first prove that the density-ratio estimation method proposed in Lin et al. (2023) is essentially equivalent to Least-Squares Importance Fitting (LSIF) proposed in Kanamori et al. (2009) for direct density-ratio estimation. Furthermore, we derive Riesz regression using the LSIF framework. Based on these results, we derive NN matching from Riesz regression. This study is based on our work Kato (2025a) and Kato (2025b).
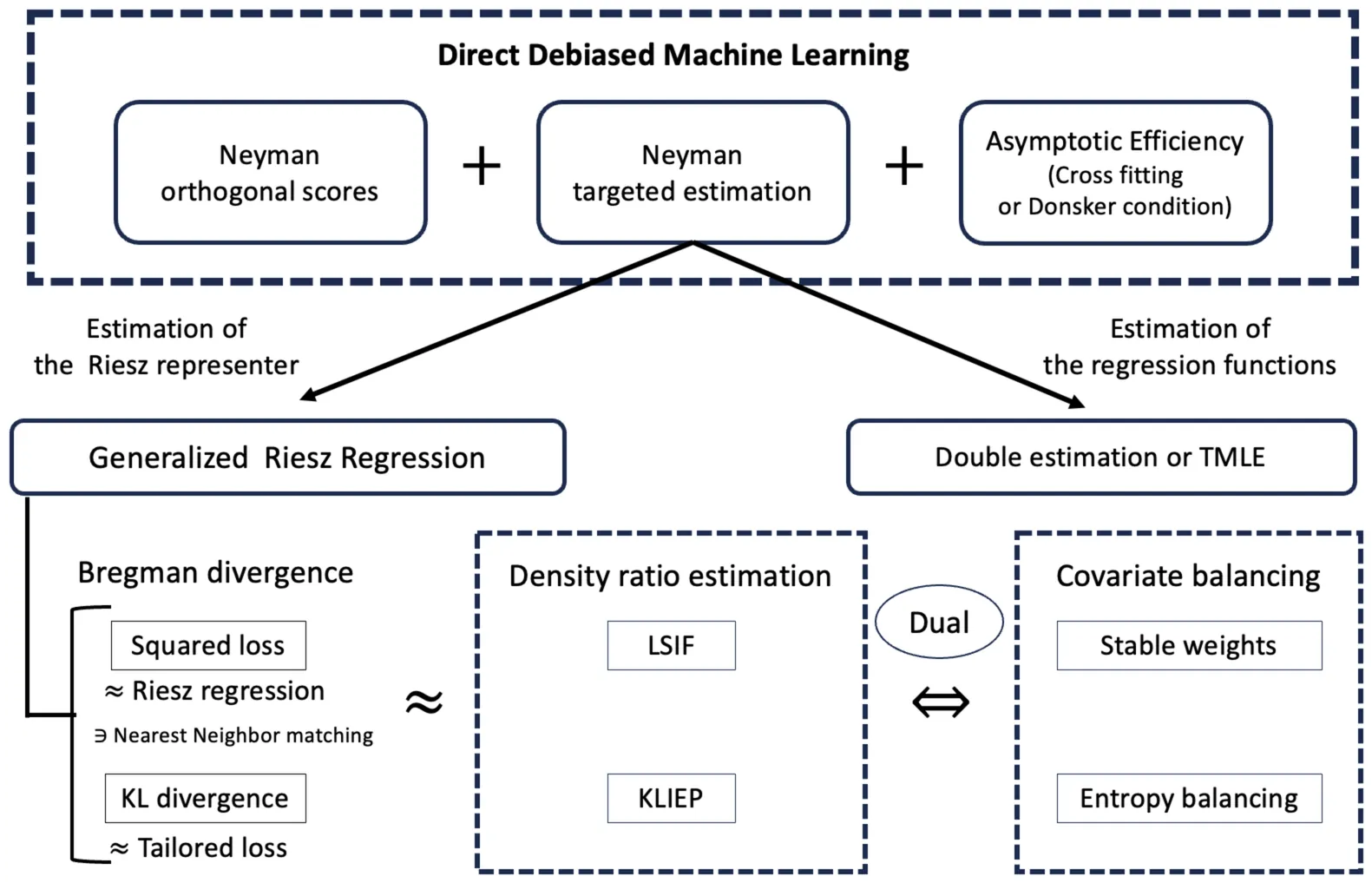
Direct Debiased Machine Learning via Bregman Divergence Minimization
We develop a direct debiased machine learning framework comprising Neyman targeted estimation and generalized Riesz regression. Our framework unifies Riesz regression for automatic debiased machine learning, covariate balancing, targeted maximum likelihood estimation (TMLE), and density-ratio estimation. In many problems involving causal effects or structural models, the parameters of interest depend on regression functions. Plugging regression functions estimated by machine learning methods into the identifying equations can yield poor performance because of first-stage bias. To reduce such bias, debiased machine learning employs Neyman orthogonal estimating equations. Debiased machine learning typically requires estimation of the Riesz representer and the regression function. For this problem, we develop a direct debiased machine learning framework with an end-to-end algorithm. We formulate estimation of the nuisance parameters, the regression function and the Riesz representer, as minimizing the discrepancy between Neyman orthogonal scores computed with known and unknown nuisance parameters, which we refer to as Neyman targeted estimation. Neyman targeted estimation includes Riesz representer estimation, and we measure discrepancies using the Bregman divergence. The Bregman divergence encompasses various loss functions as special cases, where the squared loss yields Riesz regression and the Kullback-Leibler divergence yields entropy balancing. We refer to this Riesz representer estimation as generalized Riesz regression. Neyman targeted estimation also yields TMLE as a special case for regression function estimation. Furthermore, for specific pairs of models and Riesz representer estimation methods, we can automatically obtain the covariate balancing property without explicitly solving the covariate balancing objective.
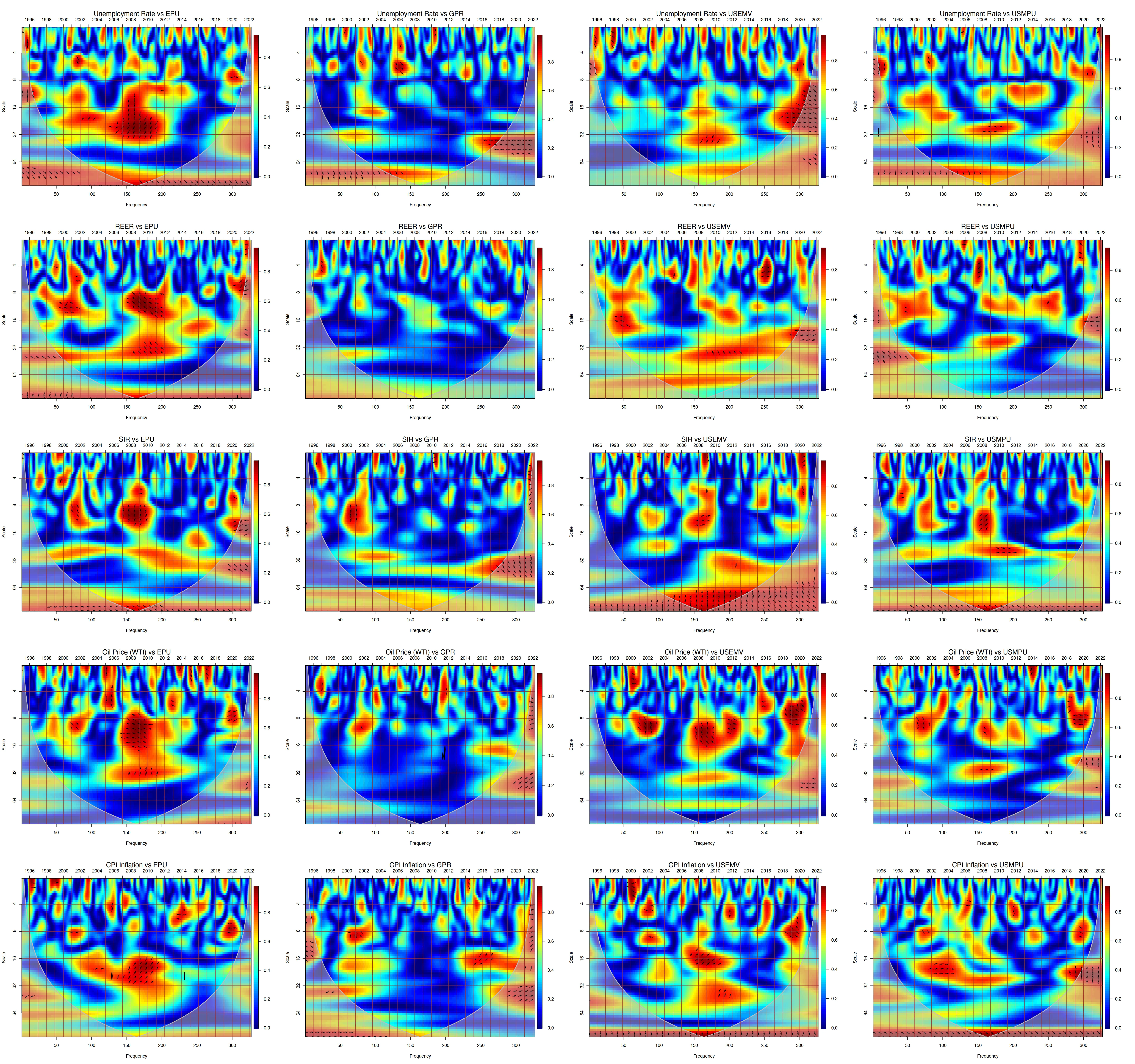
Macroeconomic Forecasting for the G7 countries under Uncertainty Shocks
Accurate macroeconomic forecasting has become harder amid geopolitical disruptions, policy reversals, and volatile financial markets. Conventional vector autoregressions (VARs) overfit in high dimensional settings, while threshold VARs struggle with time varying interdependencies and complex parameter structures. We address these limitations by extending the Sims Zha Bayesian VAR with exogenous variables (SZBVARx) to incorporate domain-informed shrinkage and four newspaper based uncertainty shocks such as economic policy uncertainty, geopolitical risk, US equity market volatility, and US monetary policy uncertainty. The framework improves structural interpretability, mitigates dimensionality, and imposes empirically guided regularization. Using G7 data, we study spillovers from uncertainty shocks to five core variables (unemployment, real broad effective exchange rates, short term rates, oil prices, and CPI inflation), combining wavelet coherence (time frequency dynamics) with nonlinear local projections (state dependent impulse responses). Out-of-sample results at 12 and 24 month horizons show that SZBVARx outperforms 14 benchmarks, including classical VARs and leading machine learning models, as confirmed by Murphy difference diagrams, multivariate Diebold Mariano tests, and Giacomini White predictability tests. Credible Bayesian prediction intervals deliver robust uncertainty quantification for scenario analysis and risk management. The proposed SZBVARx offers G7 policymakers a transparent, well calibrated tool for modern macroeconomic forecasting under pervasive uncertainty.