Statistical Learning
Statistical learning theory, inference, and methodology
Statistical learning theory, inference, and methodology
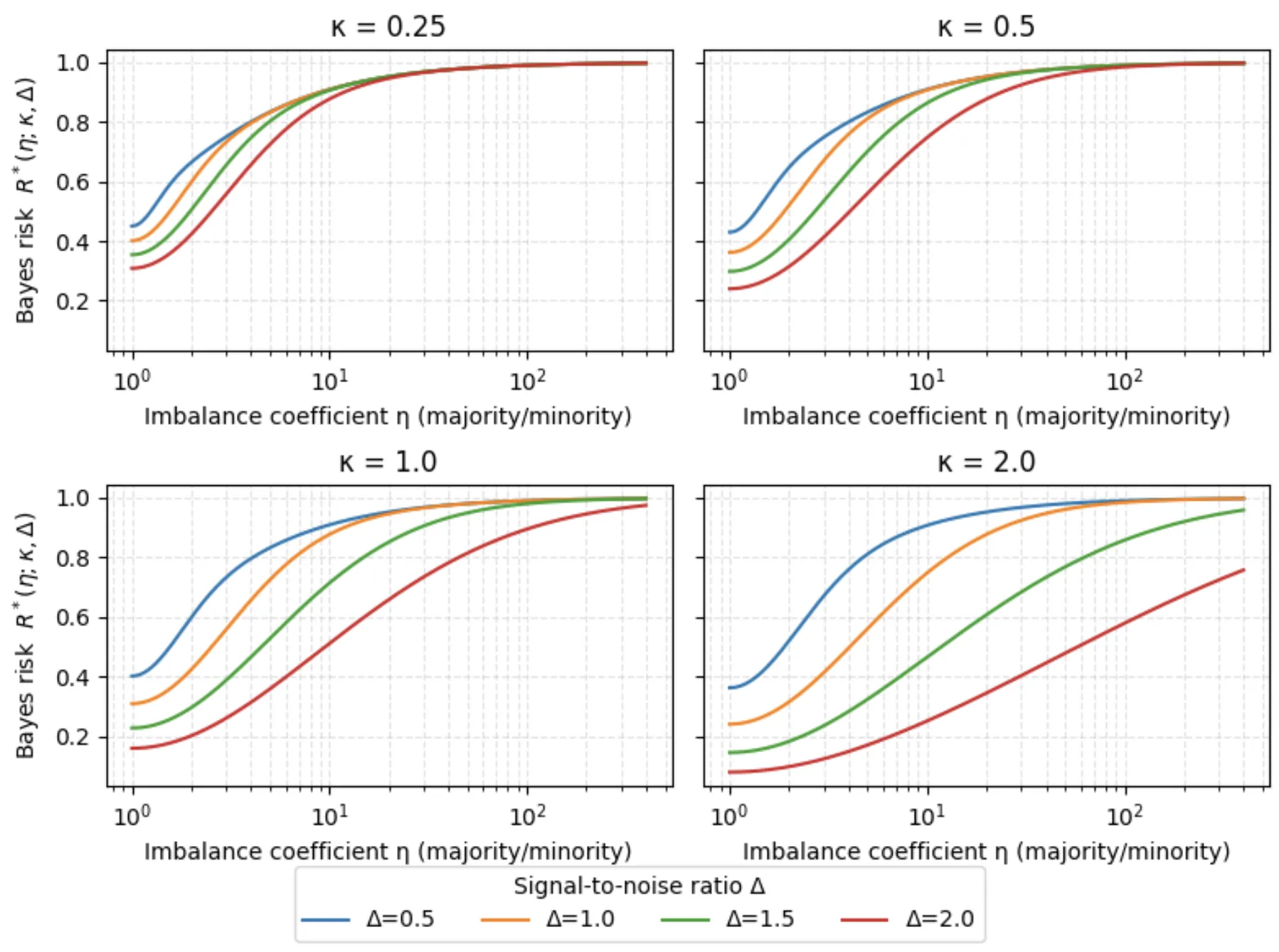
Class imbalance significantly degrades classification performance, yet its effects are rarely analyzed from a unified theoretical perspective. We propose a principled framework based on three fundamental scales: the imbalance coefficient $η$, the sample--dimension ratio $κ$, and the intrinsic separability $Δ$. Starting from the Gaussian Bayes classifier, we derive closed-form Bayes errors and show how imbalance shifts the discriminant boundary, yielding a deterioration slope that predicts four regimes: Normal, Mild, Extreme, and Catastrophic. Using a balanced high-dimensional genomic dataset, we vary only $η$ while keeping $κ$ and $Δ$ fixed. Across parametric and non-parametric models, empirical degradation closely follows theoretical predictions: minority Recall collapses once $\log(η)$ exceeds $Δ\sqrtκ$, Precision increases asymmetrically, and F1-score and PR-AUC decline in line with the predicted regimes. These results show that the triplet $(η,κ,Δ)$ provides a model-agnostic, geometrically grounded explanation of imbalance-induced deterioration.
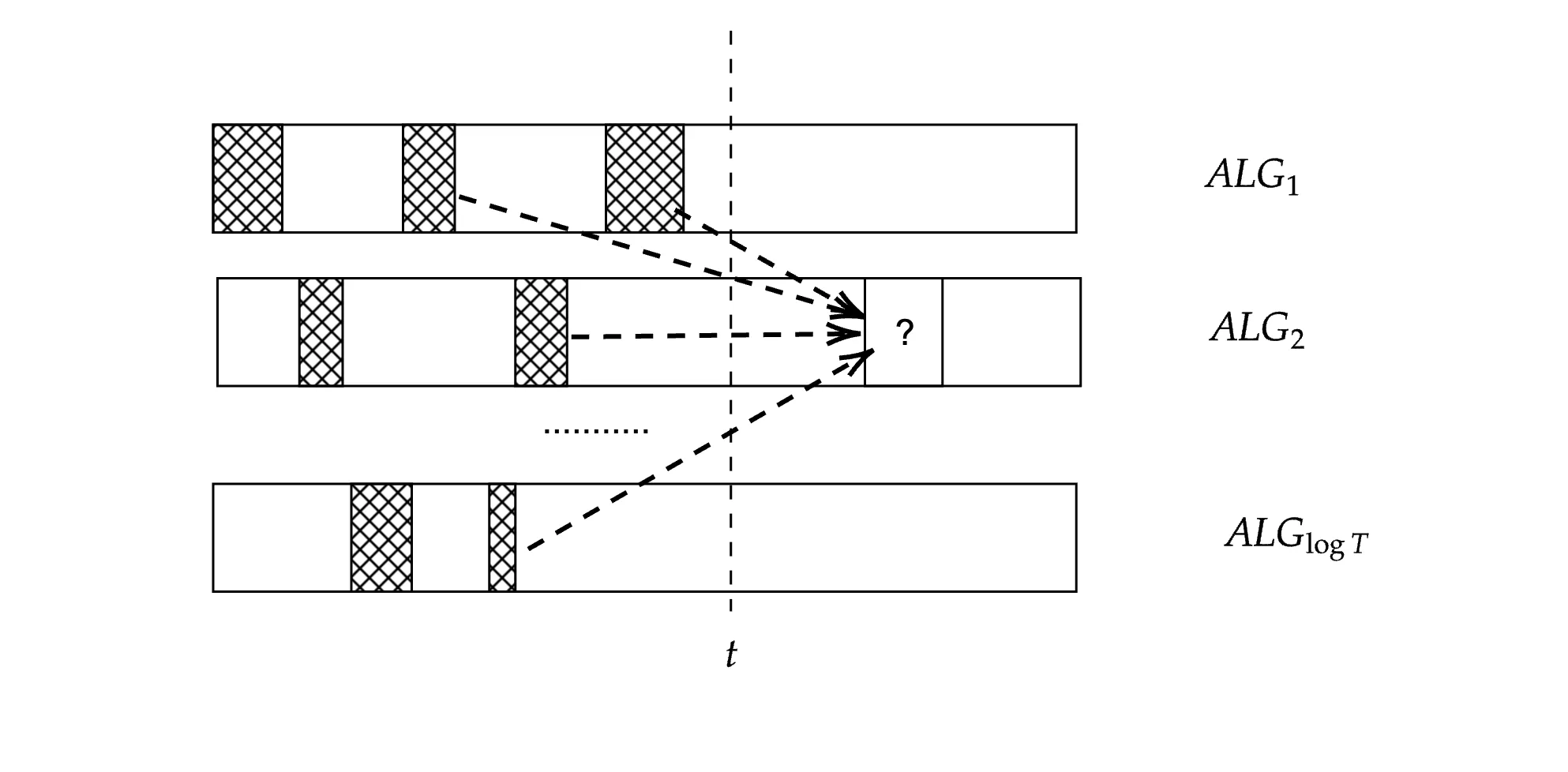
Motivated by recent work on the experts problem in the streaming model, we consider the experts problem in the sliding window model. The sliding window model is a well-studied model that captures applications such as traffic monitoring, epidemic tracking, and automated trading, where recent information is more valuable than older data. Formally, we have $n$ experts, $T$ days, the ability to query the predictions of $q$ experts on each day, a limited amount of memory, and should achieve the (near-)optimal regret $\sqrt{nW}\text{polylog}(nT)$ regret over any window of the last $W$ days. While it is impossible to achieve such regret with $1$ query, we show that with $2$ queries we can achieve such regret and with only $\text{polylog}(nT)$ bits of memory. Not only are our algorithms optimal for sliding windows, but we also show for every interval $\mathcal{I}$ of days that we achieve $\sqrt{n|\mathcal{I}|}\text{polylog}(nT)$ regret with $2$ queries and only $\text{polylog}(nT)$ bits of memory, providing an exponential improvement on the memory of previous interval regret algorithms. Building upon these techniques, we address the bandit problem in data streams, where $q=1$, achieving $n T^{2/3}\text{polylog}(T)$ regret with $\text{polylog}(nT)$ memory, which is the first sublinear regret in the streaming model in the bandit setting with polylogarithmic memory; this can be further improved to the optimal $\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{nT})$ regret if the best expert's losses are in a random order.

Modern AI systems increasingly operate inside markets and institutions where data, behavior, and incentives are endogenous. This paper develops an economic foundation for multi-agent learning by studying a principal-agent interaction in a Markov decision process with strategic externalities, where both the principal and the agent learn over time. We propose a two-phase incentive mechanism that first estimates implementable transfers and then uses them to steer long-run dynamics; under mild regret-based rationality and exploration conditions, the mechanism achieves sublinear social-welfare regret and thus asymptotically optimal welfare. Simulations illustrate how even coarse incentives can correct inefficient learning under stateful externalities, highlighting the necessity of incentive-aware design for safe and welfare-aligned AI in markets and insurance.
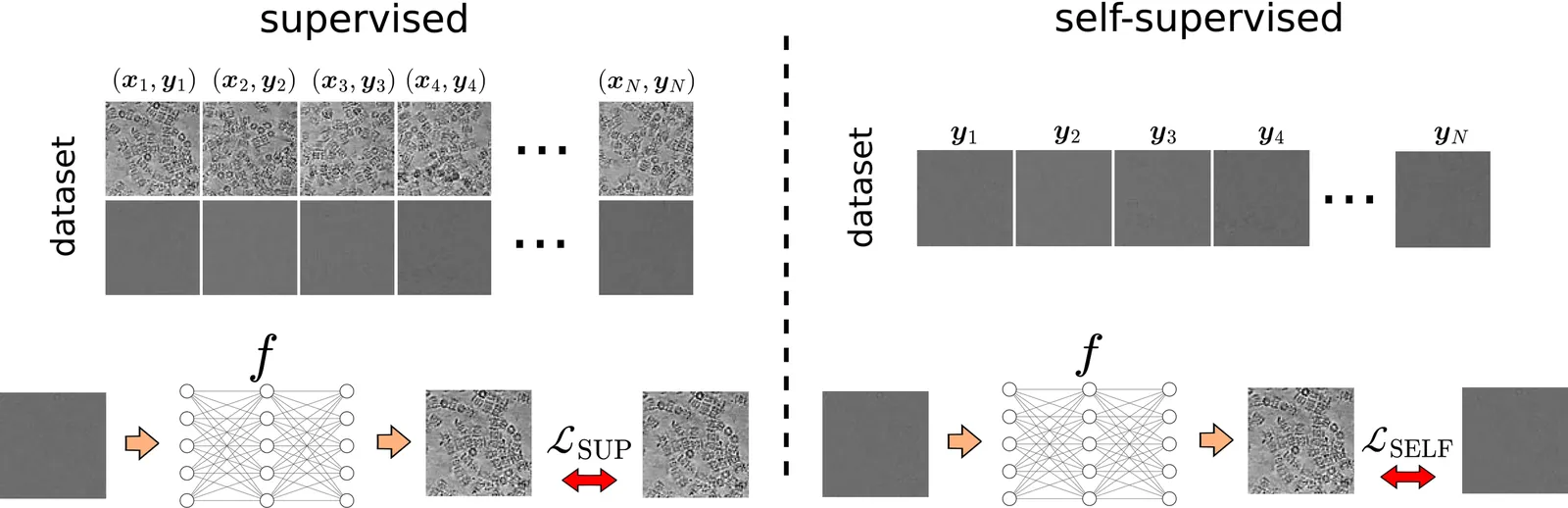
Many important problems in science and engineering involve inferring a signal from noisy and/or incomplete observations, where the observation process is known. Historically, this problem has been tackled using hand-crafted regularization (e.g., sparsity, total-variation) to obtain meaningful estimates. Recent data-driven methods often offer better solutions by directly learning a solver from examples of ground-truth signals and associated observations. However, in many real-world applications, obtaining ground-truth references for training is expensive or impossible. Self-supervised learning methods offer a promising alternative by learning a solver from measurement data alone, bypassing the need for ground-truth references. This manuscript provides a comprehensive summary of different self-supervised methods for inverse problems, with a special emphasis on their theoretical underpinnings, and presents practical applications in imaging inverse problems.
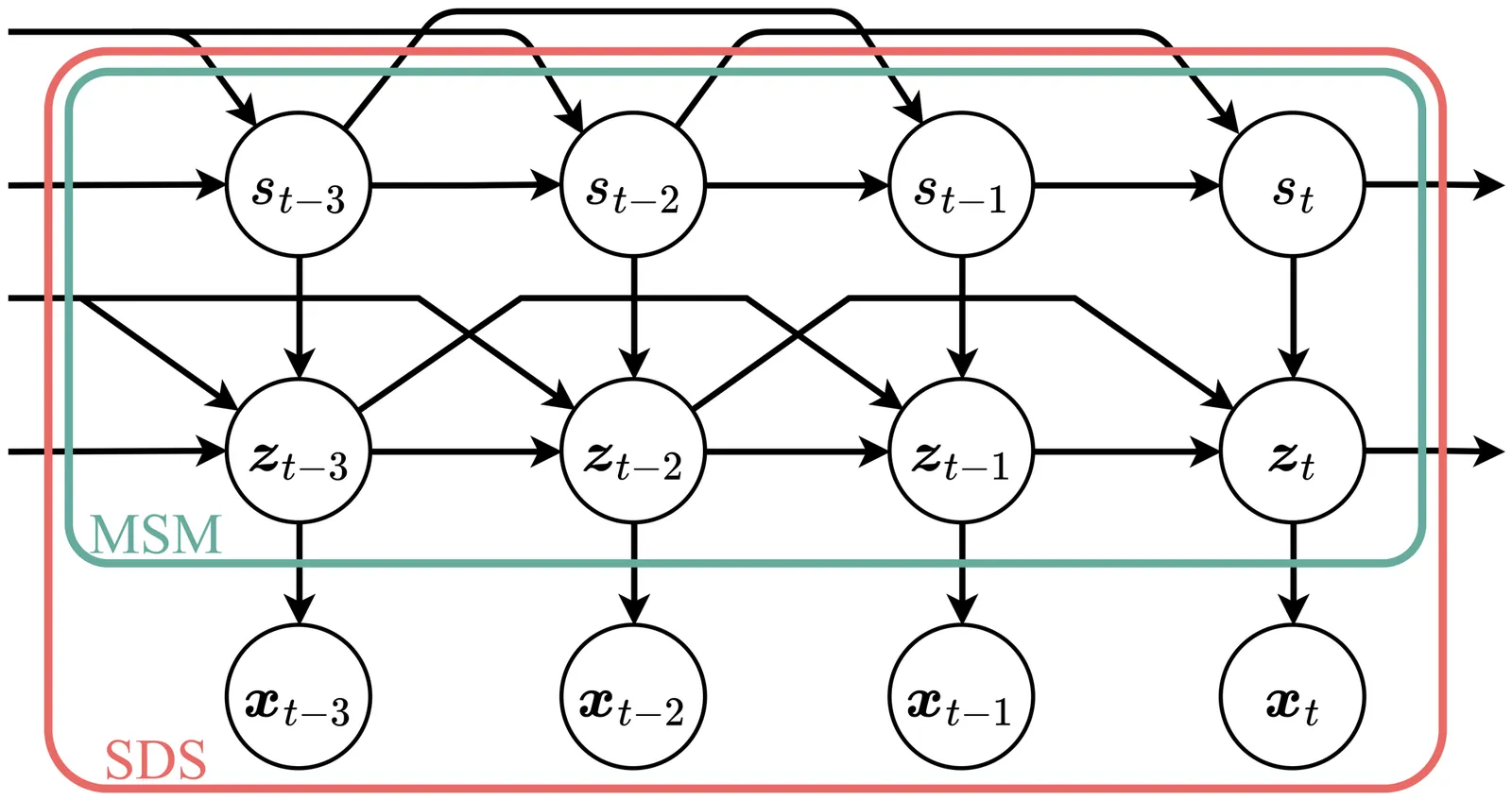
Identifiability is central to the interpretability of deep latent variable models, ensuring parameterisations are uniquely determined by the data-generating distribution. However, it remains underexplored for deep regime-switching time series. We develop a general theoretical framework for multi-lag Regime-Switching Models (RSMs), encompassing Markov Switching Models (MSMs) and Switching Dynamical Systems (SDSs). For MSMs, we formulate the model as a temporally structured finite mixture and prove identifiability of both the number of regimes and the multi-lag transitions in a nonlinear-Gaussian setting. For SDSs, we establish identifiability of the latent variables up to permutation and scaling via temporal structure, which in turn yields conditions for identifiability of regime-dependent latent causal graphs (up to regime/node permutations). Our results hold in a fully unsupervised setting through architectural and noise assumptions that are directly enforceable via neural network design. We complement the theory with a flexible variational estimator that satisfies the assumptions and validate the results on synthetic benchmarks. Across real-world datasets from neuroscience, finance, and climate, identifiability leads to more trustworthy interpretability analysis, which is crucial for scientific discovery.

We introduce Conformal Interquantile Regression (CIR), a conformal regression method that efficiently constructs near-minimal prediction intervals with guaranteed coverage. CIR leverages black-box machine learning models to estimate outcome distributions through interquantile ranges, transforming these estimates into compact prediction intervals while achieving approximate conditional coverage. We further propose CIR+ (Conditional Interquantile Regression with More Comparison), which enhances CIR by incorporating a width-based selection rule for interquantile intervals. This refinement yields narrower prediction intervals while maintaining comparable coverage, though at the cost of slightly increased computational time. Both methods address key limitations of existing distributional conformal prediction approaches: they handle skewed distributions more effectively than Conformalized Quantile Regression, and they achieve substantially higher computational efficiency than Conformal Histogram Regression by eliminating the need for histogram construction. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our methods optimally balance predictive accuracy and computational efficiency compared to existing approaches.

Graphs arise across diverse domains, from biology and chemistry to social and information networks, as well as in transportation and logistics. Inference on graph-structured data requires methods that are permutation-invariant, scalable across varying sizes and sparsities, and capable of capturing complex long-range dependencies, making posterior estimation on graph parameters particularly challenging. Amortized Bayesian Inference (ABI) is a simulation-based framework that employs generative neural networks to enable fast, likelihood-free posterior inference. We adapt ABI to graph data to address these challenges to perform inference on node-, edge-, and graph-level parameters. Our approach couples permutation-invariant graph encoders with flexible neural posterior estimators in a two-module pipeline: a summary network maps attributed graphs to fixed-length representations, and an inference network approximates the posterior over parameters. In this setting, several neural architectures can serve as the summary network. In this work we evaluate multiple architectures and assess their performance on controlled synthetic settings and two real-world domains - biology and logistics - in terms of recovery and calibration.
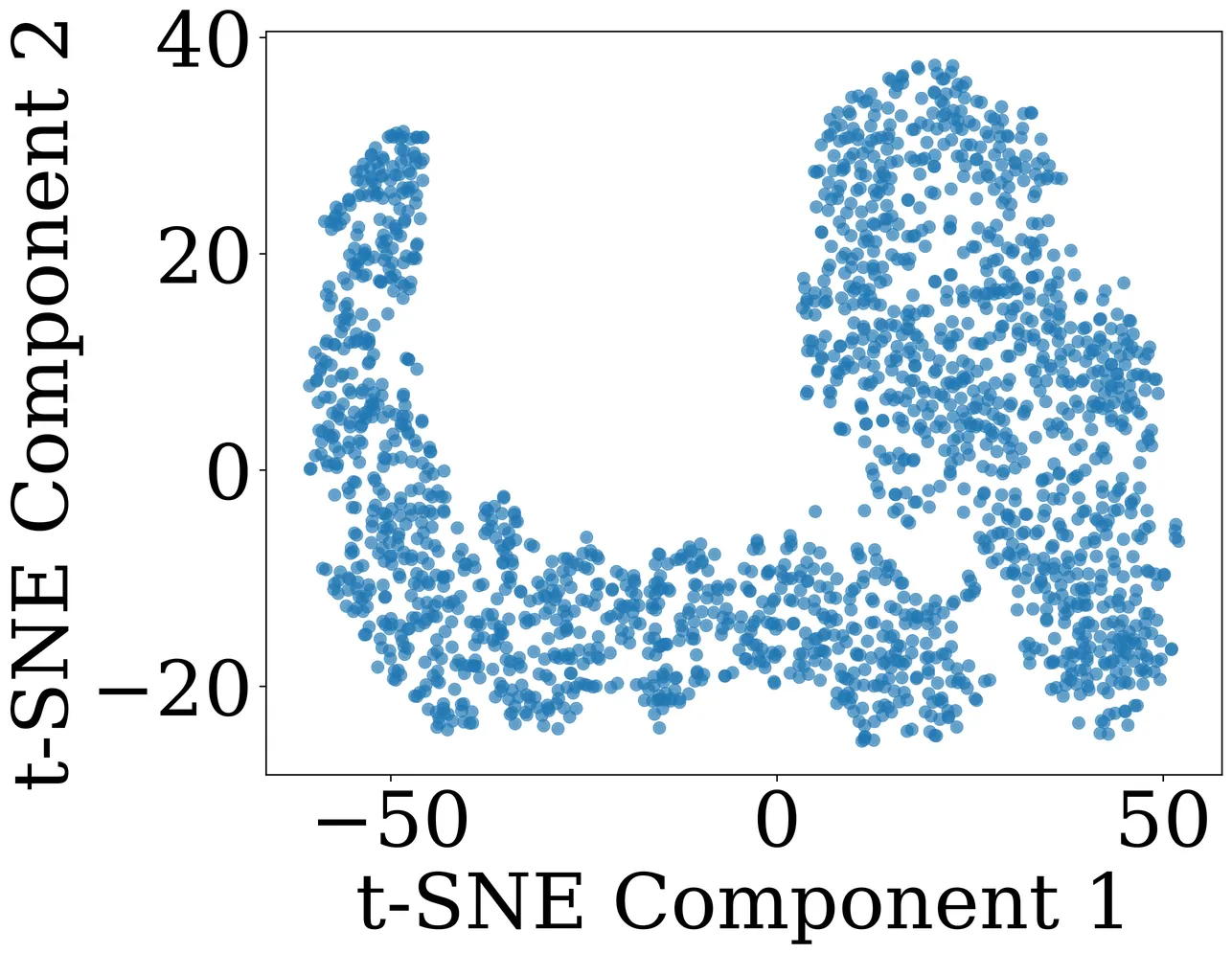
Anomaly detection is crucial in industrial applications for identifying rare and unseen patterns to ensure system reliability. Traditional models, trained on a single class of normal data, struggle with real-world distributions where normal data exhibit diverse patterns, leading to class imbalance and long-tailed anomaly score distributions (LTD). This imbalance skews model training and degrades detection performance, especially for minority instances. To address this issue, we propose a novel importance-weighted loss designed specifically for anomaly detection. Compared to the previous method for LTD in classification, our method does not require prior knowledge of normal data classes. Instead, we introduce a weighted loss function that incorporates importance sampling to align the distribution of anomaly scores with a target Gaussian, ensuring a balanced representation of normal data. Extensive experiments on three benchmark image datasets and three real-world hyperspectral imaging datasets demonstrate the robustness of our approach in mitigating LTD-induced bias. Our method improves anomaly detection performance by 0.043, highlighting its effectiveness in real-world applications.

Biclustering is an essential unsupervised machine learning technique for simultaneously clustering rows and columns of a data matrix, with widespread applications in genomics, transcriptomics, and other high-dimensional omics data. Despite its importance, existing biclustering methods struggle to meet the demands of modern large-scale datasets. The challenges stem from the accumulation of noise in high-dimensional features, the limitations of non-convex optimization formulations, and the computational complexity of identifying meaningful biclusters. These issues often result in reduced accuracy and stability as the size of the dataset increases. To overcome these challenges, we propose Sparse Convex Biclustering (SpaCoBi), a novel method that penalizes noise during the biclustering process to improve both accuracy and robustness. By adopting a convex optimization framework and introducing a stability-based tuning criterion, SpaCoBi achieves an optimal balance between cluster fidelity and sparsity. Comprehensive numerical studies, including simulations and an application to mouse olfactory bulb data, demonstrate that SpaCoBi significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in accuracy. These results highlight SpaCoBi as a robust and efficient solution for biclustering in high-dimensional and large-scale datasets.
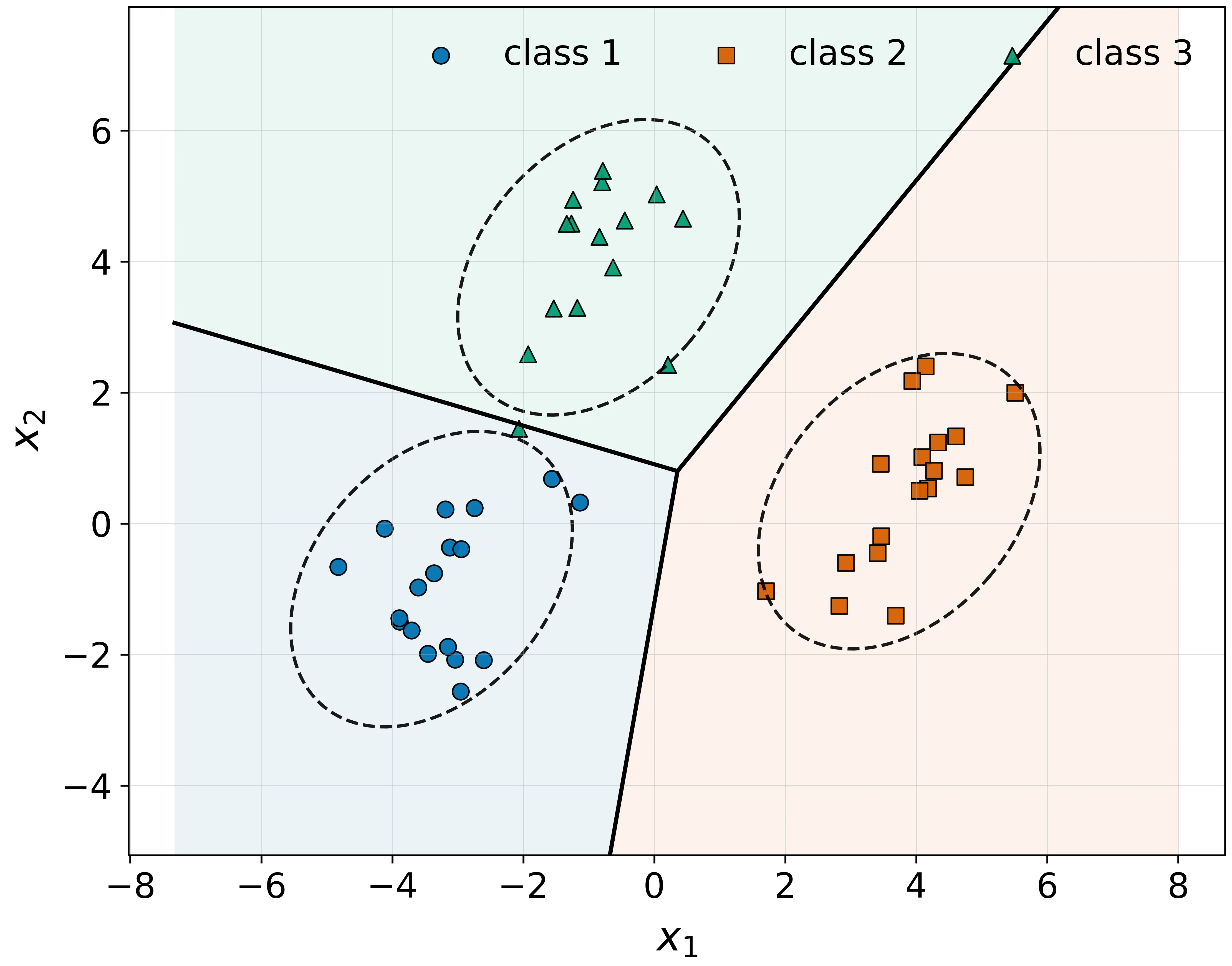
We revisit Deep Linear Discriminant Analysis (Deep LDA) from a likelihood-based perspective. While classical LDA is a simple Gaussian model with linear decision boundaries, attaching an LDA head to a neural encoder raises the question of how to train the resulting deep classifier by maximum likelihood estimation (MLE). We first show that end-to-end MLE training of an unconstrained Deep LDA model ignores discrimination: when both the LDA parameters and the encoder parameters are learned jointly, the likelihood admits a degenerate solution in which some of the class clusters may heavily overlap or even collapse, and classification performance deteriorates. Batchwise moment re-estimation of the LDA parameters does not remove this failure mode. We then propose a constrained Deep LDA formulation that fixes the class means to the vertices of a regular simplex in the latent space and restricts the shared covariance to be spherical, leaving only the priors and a single variance parameter to be learned along with the encoder. Under these geometric constraints, MLE becomes stable and yields well-separated class clusters in the latent space. On images (Fashion-MNIST, CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100), the resulting Deep LDA models achieve accuracy competitive with softmax baselines while offering a simple, interpretable latent geometry that is clearly visible in two-dimensional projections.

We show that for unconstrained Deep Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) classifiers, maximum-likelihood training admits pathological solutions in which class means drift together, covariances collapse, and the learned representation becomes almost non-discriminative. Conversely, cross-entropy training yields excellent accuracy but decouples the head from the underlying generative model, leading to highly inconsistent parameter estimates. To reconcile generative structure with discriminative performance, we introduce the \emph{Discriminative Negative Log-Likelihood} (DNLL) loss, which augments the LDA log-likelihood with a simple penalty on the mixture density. DNLL can be interpreted as standard LDA NLL plus a term that explicitly discourages regions where several classes are simultaneously likely. Deep LDA trained with DNLL produces clean, well-separated latent spaces, matches the test accuracy of softmax classifiers on synthetic data and standard image benchmarks, and yields substantially better calibrated predictive probabilities, restoring a coherent probabilistic interpretation to deep discriminant models.
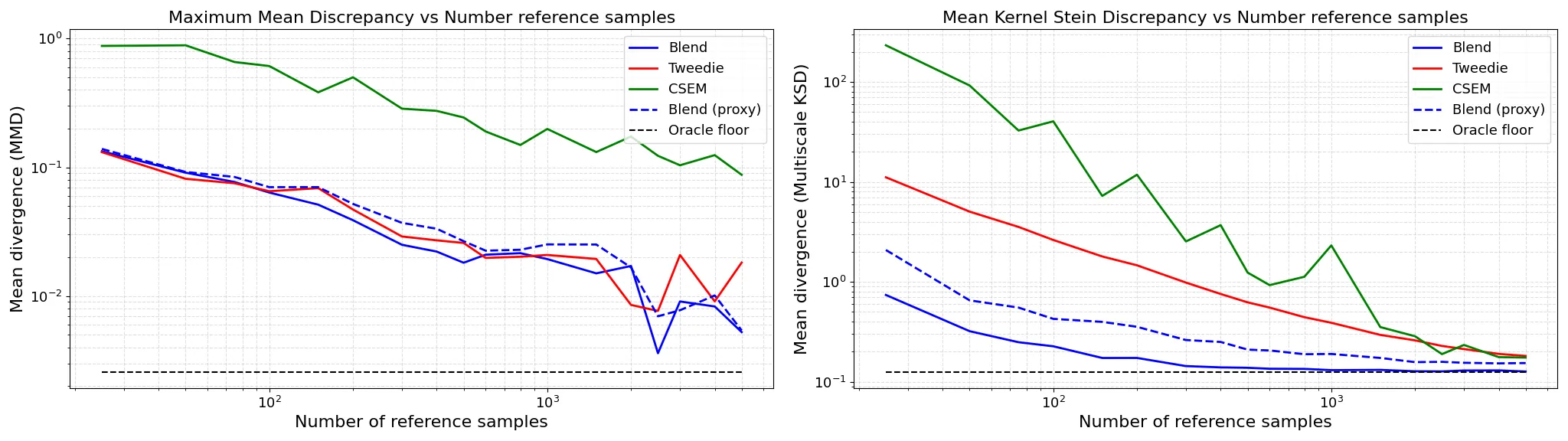
We introduce and prove a \textbf{Conditional Score Expectation (CSE)} identity: an exact relation for the marginal score of affine diffusion processes that links scores across time via a conditional expectation under the forward dynamics. Motivated by this identity, we propose a CSE-based statistical estimator for the score using a Self-Normalized Importance Sampling (SNIS) procedure with prior samples and forward noise. We analyze its relationship to the standard Tweedie estimator, proving anti-correlation for Gaussian targets and establishing the same behavior for general targets in the small time-step regime. Exploiting this structure, we derive a variance-minimizing blended score estimator given by a state--time dependent convex combination of the CSE and Tweedie estimators. Numerical experiments show that this optimal-blending estimator reduces variance and improves sample quality for a fixed computational budget compared to either baseline. We further extend the framework to Bayesian inverse problems via likelihood-informed SNIS weights, and demonstrate improved reconstruction quality and sample diversity on high-dimensional image reconstruction tasks and PDE-governed inverse problems.
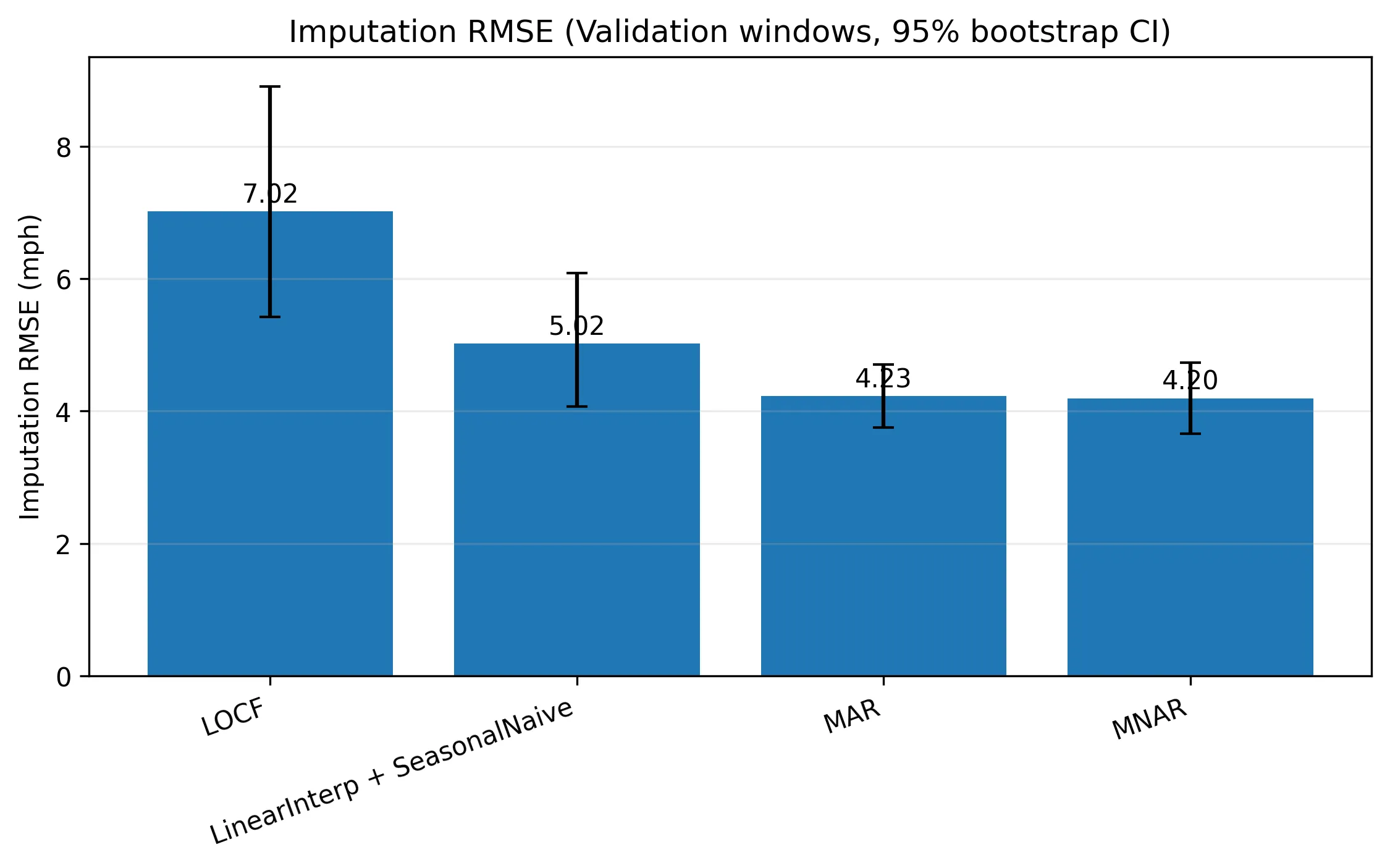
Large-scale traffic forecasting relies on fixed sensor networks that often exhibit blackouts: contiguous intervals of missing measurements caused by detector or communication failures. These outages are typically handled under a Missing At Random (MAR) assumption, even though blackout events may correlate with unobserved traffic conditions (e.g., congestion or anomalous flow), motivating a Missing Not At Random (MNAR) treatment. We propose a latent state-space framework that jointly models (i) traffic dynamics via a linear dynamical system and (ii) sensor dropout via a Bernoulli observation channel whose probability depends on the latent traffic state. Inference uses an Extended Kalman Filter with Rauch-Tung-Striebel smoothing, and parameters are learned via an approximate EM procedure with a dedicated update for detector-specific missingness parameters. On the Seattle inductive loop detector data, introducing latent dynamics yields large gains over naive baselines, reducing blackout imputation RMSE from 7.02 (LOCF) and 5.02 (linear interpolation + seasonal naive) to 4.23 (MAR LDS), corresponding to about a 64% reduction in MSE relative to LOCF. Explicit MNAR modeling provides a consistent but smaller additional improvement on real data (imputation RMSE 4.20; 0.8% RMSE reduction relative to MAR), with similar modest gains for short-horizon post-blackout forecasts (evaluated at 1, 3, and 6 steps). In controlled synthetic experiments, the MNAR advantage increases as the true missingness dependence on latent state strengthens. Overall, temporal dynamics dominate performance, while MNAR modeling offers a principled refinement that becomes most valuable when missingness is genuinely informative.
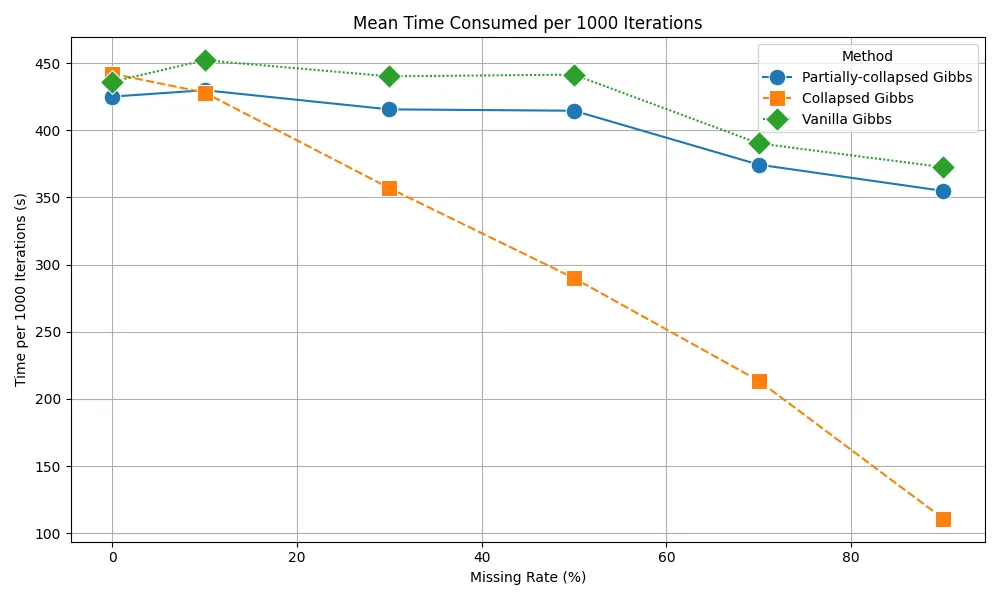
The Hidden Markov Model (HMM) is a widely-used statistical model for handling sequential data. However, the presence of missing observations in real-world datasets often complicates the application of the model. The EM algorithm and Gibbs samplers can be used to estimate the model, yet suffering from various problems including non-convexity, high computational complexity and slow mixing. In this paper, we propose a collapsed Gibbs sampler that efficiently samples from HMMs' posterior by integrating out both the missing observations and the corresponding latent states. The proposed sampler is fast due to its three advantages. First, it achieves an estimation accuracy that is comparable to existing methods. Second, it can produce a larger Effective Sample Size (ESS) per iteration, which can be justified theoretically and numerically. Third, when the number of missing entries is large, the sampler has a significant smaller computational complexity per iteration compared to other methods, thus is faster computationally. In summary, the proposed sampling algorithm is fast both computationally and theoretically and is particularly advantageous when there are a lot of missing entries. Finally, empirical evaluations based on numerical simulations and real data analysis demonstrate that the proposed algorithm consistently outperforms existing algorithms in terms of time complexity and sampling efficiency (measured in ESS).
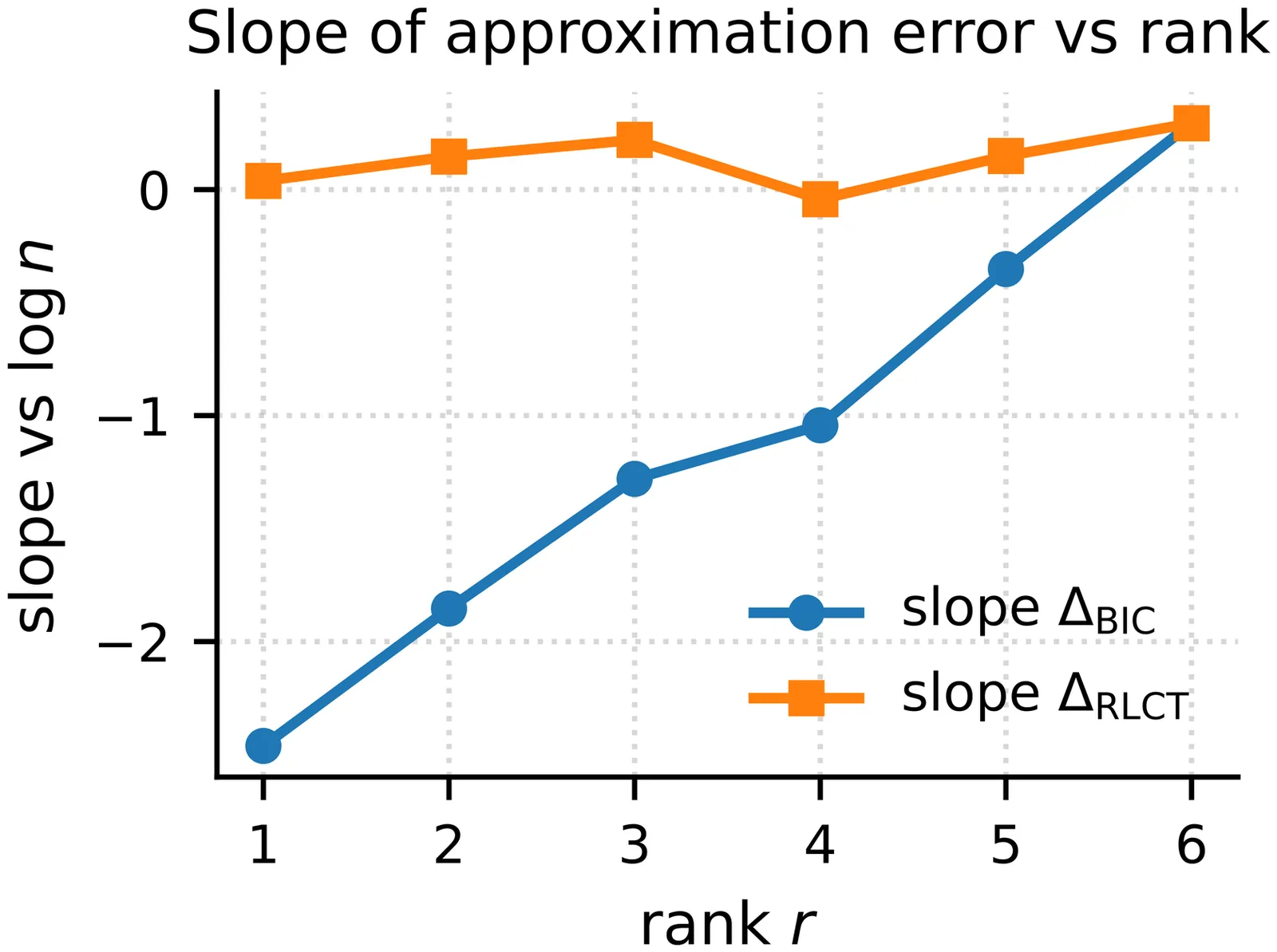
Bayesian model selection commonly relies on Laplace approximation or the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), which assume that the effective model dimension equals the number of parameters. Singular learning theory replaces this assumption with the real log canonical threshold (RLCT), an effective dimension that can be strictly smaller in overparameterized or rank-deficient models. We study linear-Gaussian rank models and linear subspace (dictionary) models in which the exact marginal likelihood is available in closed form and the RLCT is analytically tractable. In this setting, we show theoretically and empirically that the error of Laplace/BIC grows linearly with (d/2 minus lambda) times log n, where d is the ambient parameter dimension and lambda is the RLCT. An RLCT-aware correction recovers the correct evidence slope and is invariant to overcomplete reparameterizations that represent the same data subspace. Our results provide a concrete finite-sample characterization of Laplace failure in singular models and demonstrate that evidence slopes can be used as a practical estimator of effective dimension in simple linear settings.
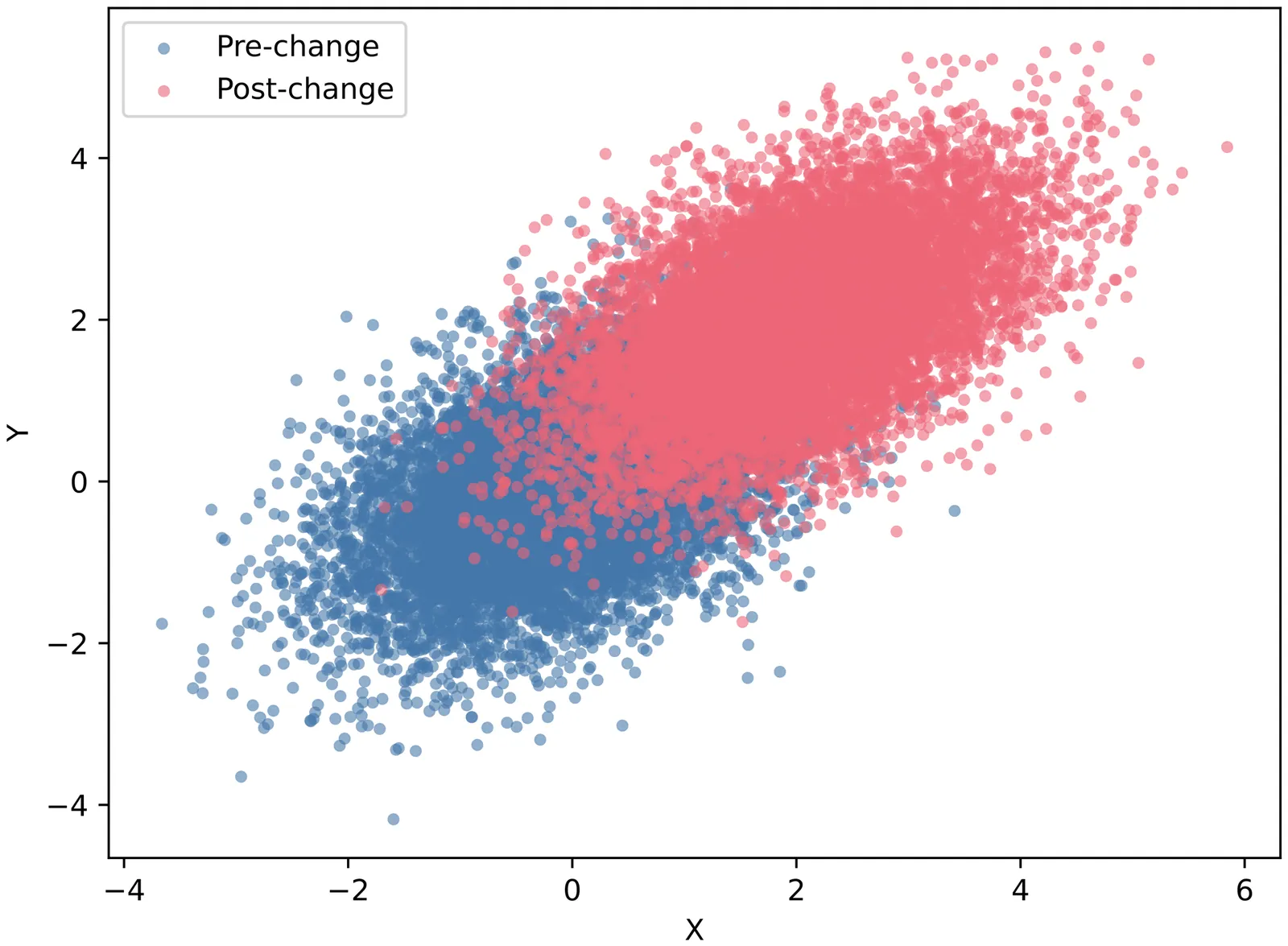
Conformal Test Martingales (CTMs) are a standard method within the Conformal Prediction framework for testing the crucial assumption of data exchangeability by monitoring deviations from uniformity in the p-value sequence. Although exchangeability implies uniform p-values, the converse does not hold. This raises the question of whether a significant break in exchangeability can occur, such that the p-values remain uniform, rendering CTMs blind. We answer this affirmatively, demonstrating the phenomenon of \emph{conformal blindness}. Through explicit construction, for the theoretically ideal ``oracle'' conformity measure (given by the true conditional density), we demonstrate the possibility of an \emph{$A$-cryptic change-point} (where $A$ refers to the conformity measure). Using bivariate Gaussian distributions, we identify a line along which a change in the marginal means does not alter the distribution of the conformity scores, thereby producing perfectly uniform p-values. Simulations confirm that even a massive distribution shift can be perfectly cryptic to the CTM, highlighting a fundamental limitation and emphasising the critical role of the alignment of the conformity measure with potential shifts.
 2601.01097
2601.01097Recent works have demonstrated promising performances of neural networks on hyperbolic spaces and symmetric positive definite (SPD) manifolds. These spaces belong to a family of Riemannian manifolds referred to as symmetric spaces of noncompact type. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for developing neural networks on such spaces. Our approach relies on a unified formulation of the distance from a point to a hyperplane on the considered spaces. We show that some existing formulations of the point-to-hyperplane distance can be recovered by our approach under specific settings. Furthermore, we derive a closed-form expression for the point-to-hyperplane distance in higher-rank symmetric spaces of noncompact type equipped with G-invariant Riemannian metrics. The derived distance then serves as a tool to design fully-connected (FC) layers and an attention mechanism for neural networks on the considered spaces. Our approach is validated on challenging benchmarks for image classification, electroencephalogram (EEG) signal classification, image generation, and natural language inference.
 2601.01055
2601.01055This paper develops the algorithmic and dynamical foundations of recursive ensemble learning driven by Fibonacci-type update flows. In contrast with classical boosting Freund and Schapire (1997); Friedman (2001), where the ensemble evolves through first-order additive updates, we study second-order recursive architectures in which each predictor depends on its two immediate predecessors. These Fibonacci flows induce a learning dynamic with memory, allowing ensembles to integrate past structure while adapting to new residual information. We introduce a general family of recursive weight-update algorithms encompassing Fibonacci, tribonacci, and higher-order recursions, together with continuous-time limits that yield systems of differential equations governing ensemble evolution. We establish global convergence conditions, spectral stability criteria, and non-asymptotic generalization bounds under Rademacher Bartlett and Mendelson (2002) and algorithmic stability analyses. The resulting theory unifies recursive ensembles, structured weighting, and dynamical systems viewpoints in statistical learning. Experiments with kernel ridge regression Rasmussen and Williams (2006), spline smoothers Wahba (1990), and random Fourier feature models Rahimi and Recht (2007) demonstrate that recursive flows consistently improve approximation and generalization beyond static weighting. These results complete the trilogy begun in Papers I and II: from Fibonacci weighting, through geometric weighting theory, to fully dynamical recursive ensemble learning systems.
This paper develops a practical framework for using observational data to audit the consumer surplus effects of AI-driven decisions, specifically in targeted pricing and algorithmic lending. Traditional approaches first estimate demand functions and then integrate to compute consumer surplus, but these methods can be challenging to implement in practice due to model misspecification in parametric demand forms and the large data requirements and slow convergence of flexible nonparametric or machine learning approaches. Instead, we exploit the randomness inherent in modern algorithmic pricing, arising from the need to balance exploration and exploitation, and introduce an estimator that avoids explicit estimation and numerical integration of the demand function. Each observed purchase outcome at a randomized price is an unbiased estimate of demand and by carefully reweighting purchase outcomes using novel cumulative propensity weights (CPW), we are able to reconstruct the integral. Building on this idea, we introduce a doubly robust variant named the augmented cumulative propensity weighting (ACPW) estimator that only requires one of either the demand model or the historical pricing policy distribution to be correctly specified. Furthermore, this approach facilitates the use of flexible machine learning methods for estimating consumer surplus, since it achieves fast convergence rates by incorporating an estimate of demand, even when the machine learning estimate has slower convergence rates. Neither of these estimators is a standard application of off-policy evaluation techniques as the target estimand, consumer surplus, is unobserved. To address fairness, we extend this framework to an inequality-aware surplus measure, allowing regulators and firms to quantify the profit-equity trade-off. Finally, we validate our methods through comprehensive numerical studies.

In this study, we introduce a sophisticated generative conditional strategy designed to impute missing values within datasets, an area of considerable importance in statistical analysis. Specifically, we initially elucidate the theoretical underpinnings of the Generative Conditional Missing Imputation Networks (GCMI), demonstrating its robust properties in the context of the Missing Completely at Random (MCAR) and the Missing at Random (MAR) mechanisms. Subsequently, we enhance the robustness and accuracy of GCMI by integrating a multiple imputation framework using a chained equations approach. This innovation serves to bolster model stability and improve imputation performance significantly. Finally, through a series of meticulous simulations and empirical assessments utilizing benchmark datasets, we establish the superior efficacy of our proposed methods when juxtaposed with other leading imputation techniques currently available. This comprehensive evaluation not only underscores the practicality of GCMI but also affirms its potential as a leading-edge tool in the field of statistical data analysis.