Optics & Photonics
Laser physics, optical systems, and photonic devices
Laser physics, optical systems, and photonic devices
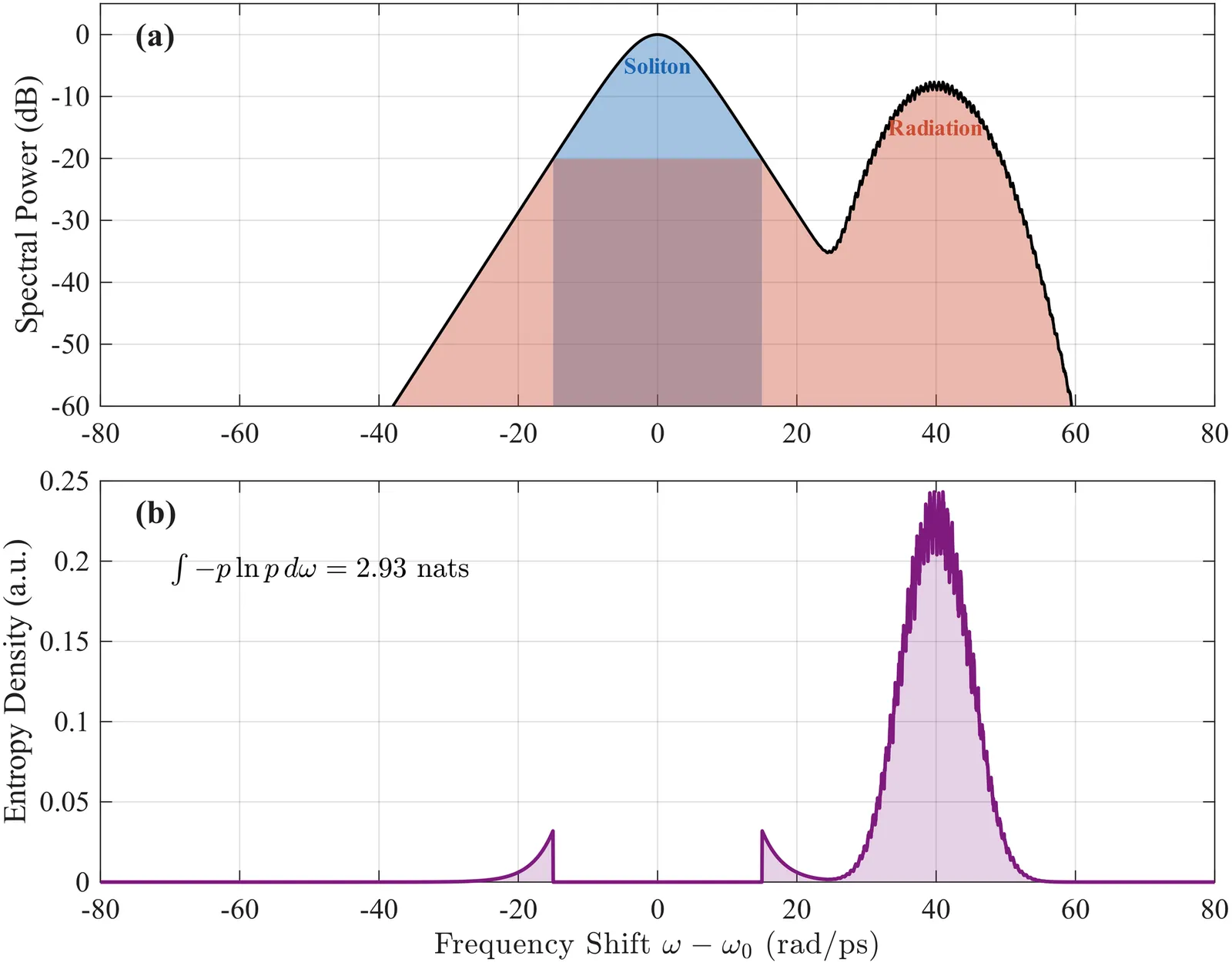
The realization of Hawking radiation in optical analogs has historically focused on kinematic observables, such as the effective temperature determined by the horizon's surface gravity. A complete thermodynamic description, however, necessitates a rigorous definition of entropy and irreversibility, which has remained elusive in Hamiltonian optical systems. In this work, we bridge this gap by introducing an operational entropy for solitonic event horizons, derived from the spectral partitioning of the optical field into coherent solitonic and incoherent radiative subsystems. We demonstrate that the emission of resonant radiation, mediated by the breaking of soliton integrability due to higher-order dispersion, serves as a fundamental mechanism for entropy production. Numerical simulations of the generalized nonlinear Schrodinger equation confirm that this process satisfies a generalized second law, where the change in total entropy is non-negative. These results establish optical event horizons as consistent nonequilibrium thermodynamic systems, offering a new pathway to explore the information-theoretic aspects of analog gravity in laboratory settings.
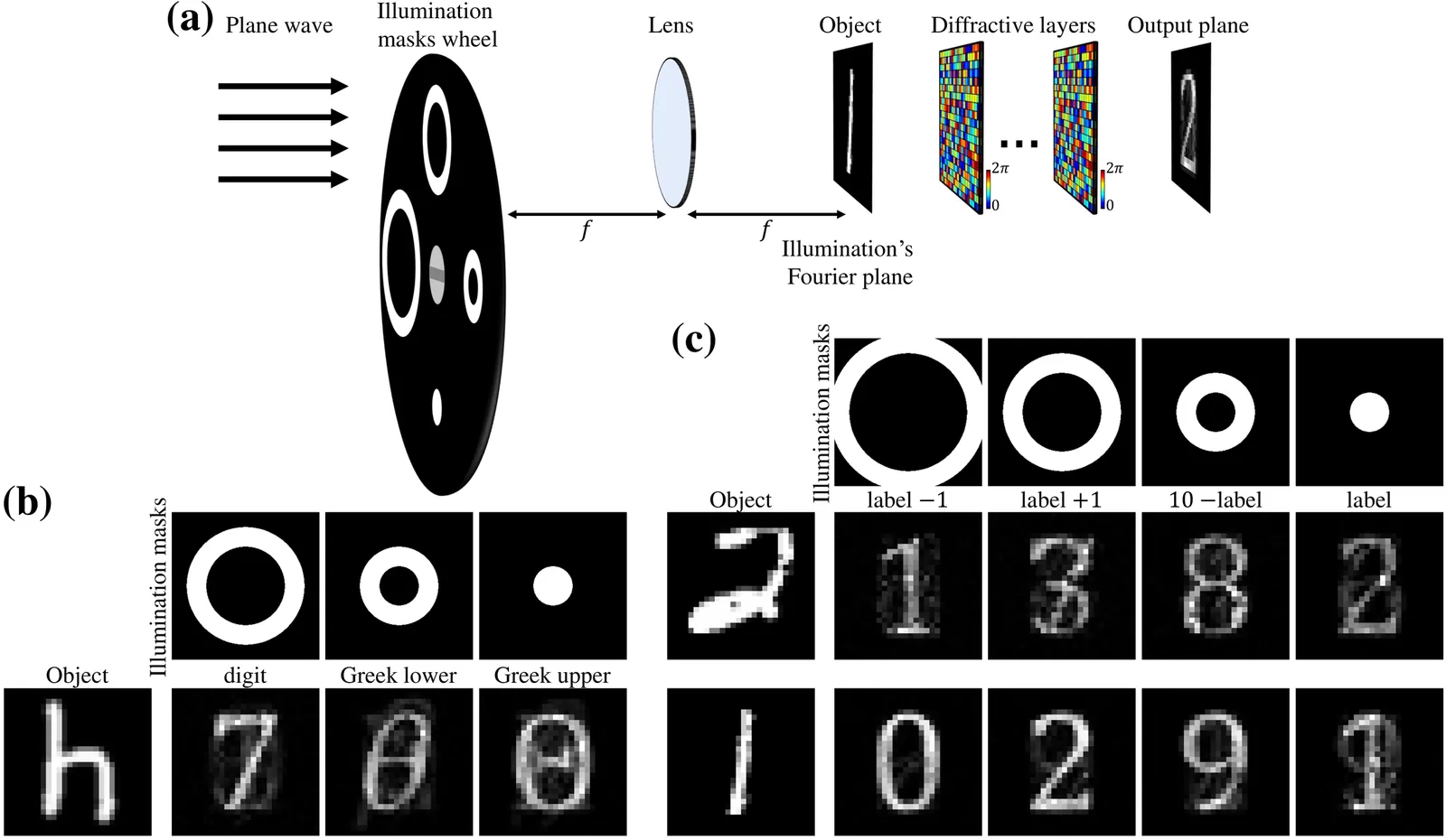
Diffractive neural networks have recently emerged as a promising framework for all-optical computing. However, these networks are typically trained for a single task, limiting their potential adoption in systems requiring multiple functionalities. Existing approaches to achieving multi-task functionality either modify the mechanical configuration of the network per task or use a different illumination wavelength or polarization state for each task. In this work, we propose a new control mechanism, which is based on the illumination's angular spectrum. Specifically, we shape the illumination using an amplitude mask that selectively controls its angular spectrum. We employ different illumination masks for achieving different network functionalities, so that the mask serves as a unique task encoder. Interestingly, we show that effective control can be achieved over a very narrow angular range, within the paraxial regime. We numerically illustrate the proposed approach by training a single diffractive network to perform multiple image-to-image translation tasks. In particular, we demonstrate translating handwritten digits into typeset digits of different values, and translating handwritten English letters into typeset numbers and typeset Greek letters, where the type of the output is determined by the illumination's angular components. As we show, the proposed framework can work under different coherence conditions, and can be combined with existing control strategies, such as different wavelengths. Our results establish the illumination angular spectrum as a powerful degree of freedom for controlling diffractive networks, enabling a scalable and versatile framework for multi-task all-optical computing.
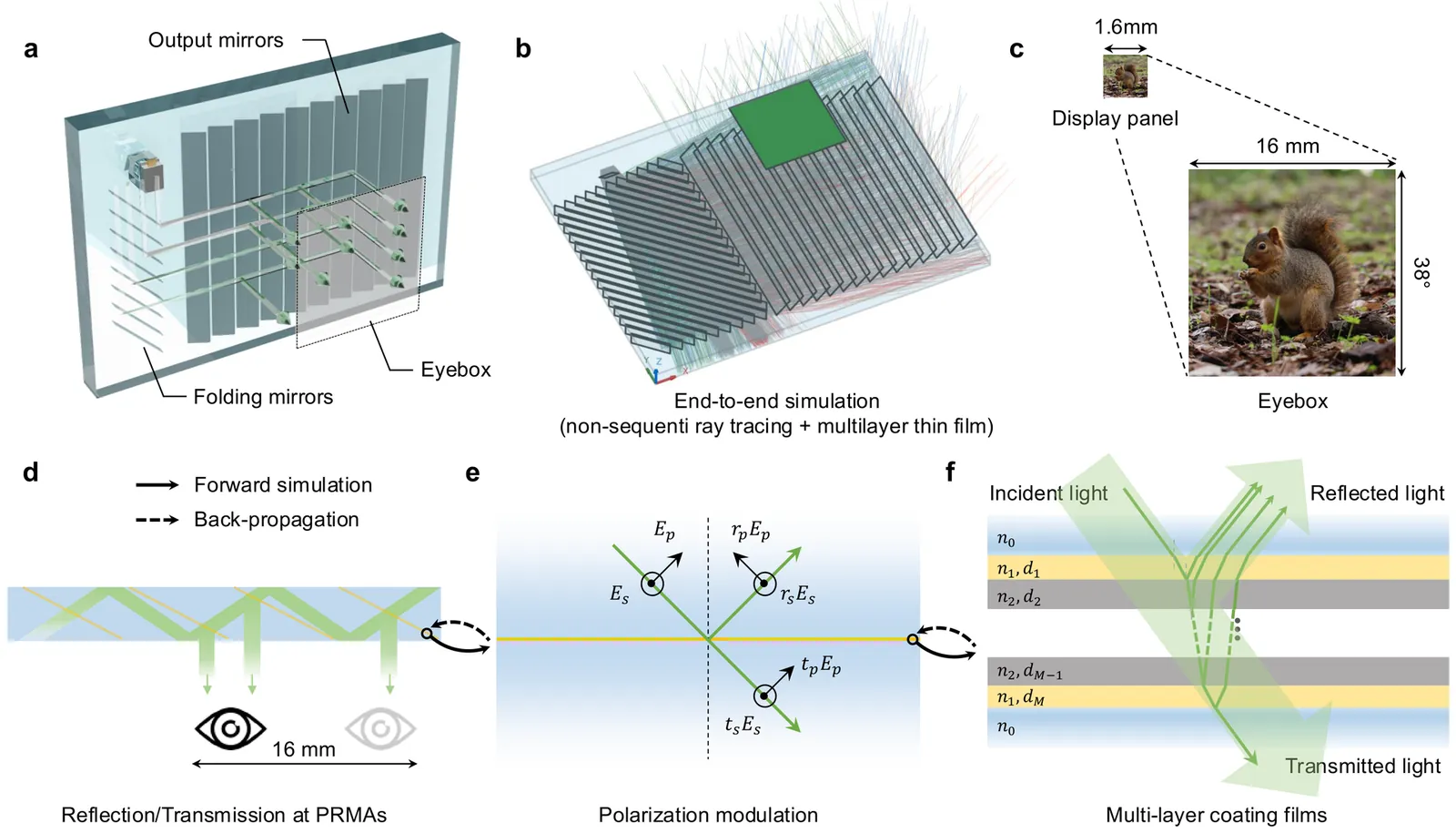
Geometric waveguides are a promising architecture for optical see-through augmented reality displays, but their performance is severely bottlenecked by the difficulty of jointly optimizing non-sequential light transport and polarization-dependent multilayer thin-film coatings. Here we present the first end-to-end differentiable optimization framework for geometric waveguide that couples non-sequential Monte Carlo polarization ray tracing with a differentiable transfer-matrix thin-film solver. A differentiable Monte Carlo ray tracer avoids the exponential growth of deterministic ray splitting while enabling gradients backpropagation from eyebox metrics to design parameters. With memory-saving strategies, we optimize more than one thousand layer-thickness parameters and billions of non-sequential ray-surface intersections on a single multi-GPU workstation. Automated layer pruning is achieved by starting from over-parameterized stacks and driving redundant layers to zero thickness under discrete manufacturability constraints, effectively performing topology optimization to discover optimal coating structures. On a representative design, starting from random initialization within thickness bounds, our method increases light efficiency from 4.1\% to 33.5\% and improves eyebox and FoV uniformity by $\sim$17$\times$ and $\sim$11$\times$, respectively. Furthermore, we jointly optimize the waveguide and an image preprocessing network to improve perceived image quality. Our framework not only enables system-level, high-dimensional coating optimization inside the waveguide, but also expands the scope of differentiable optics for next-generation optical design.
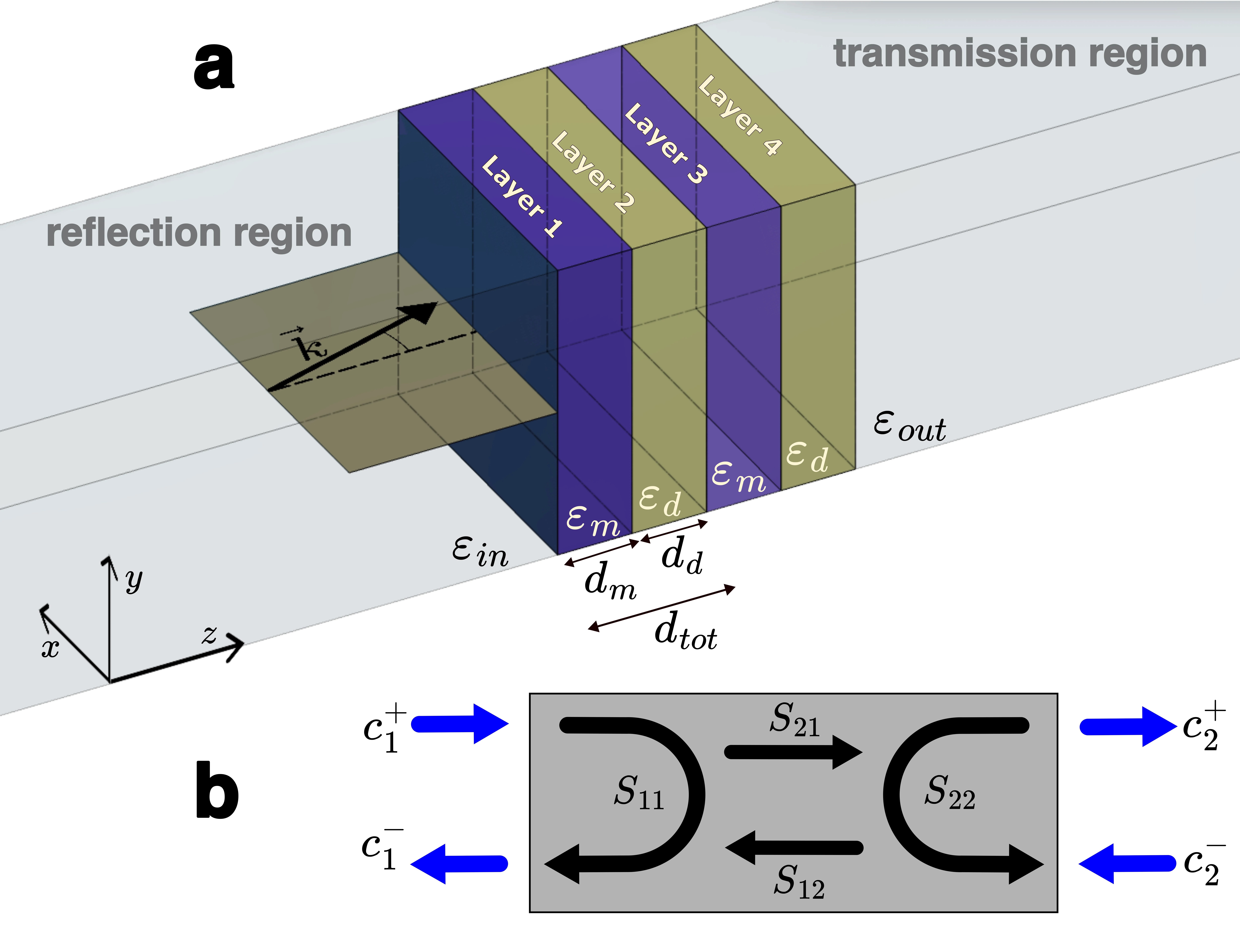
The development of plasmonics and related applications in the terahertz range faces limitations due to the intrinsic high electron density of standard metals. All-dielectric systems are profitable alternatives, which allows for customized modulation of the optical response upon doping. Here we focus on plasmon-based hyperbolic metamaterials realized stacking doped III-V semiconductors that have been shown to be optically active in the terahertz spectral region. By using a multi-physics multi-scale theoretical approach, we unravel the role of doping and geometrical characteristics (e.g., thickness, composition, grating) in the modulation of high-k plasmon-polariton modes across the metamaterial.
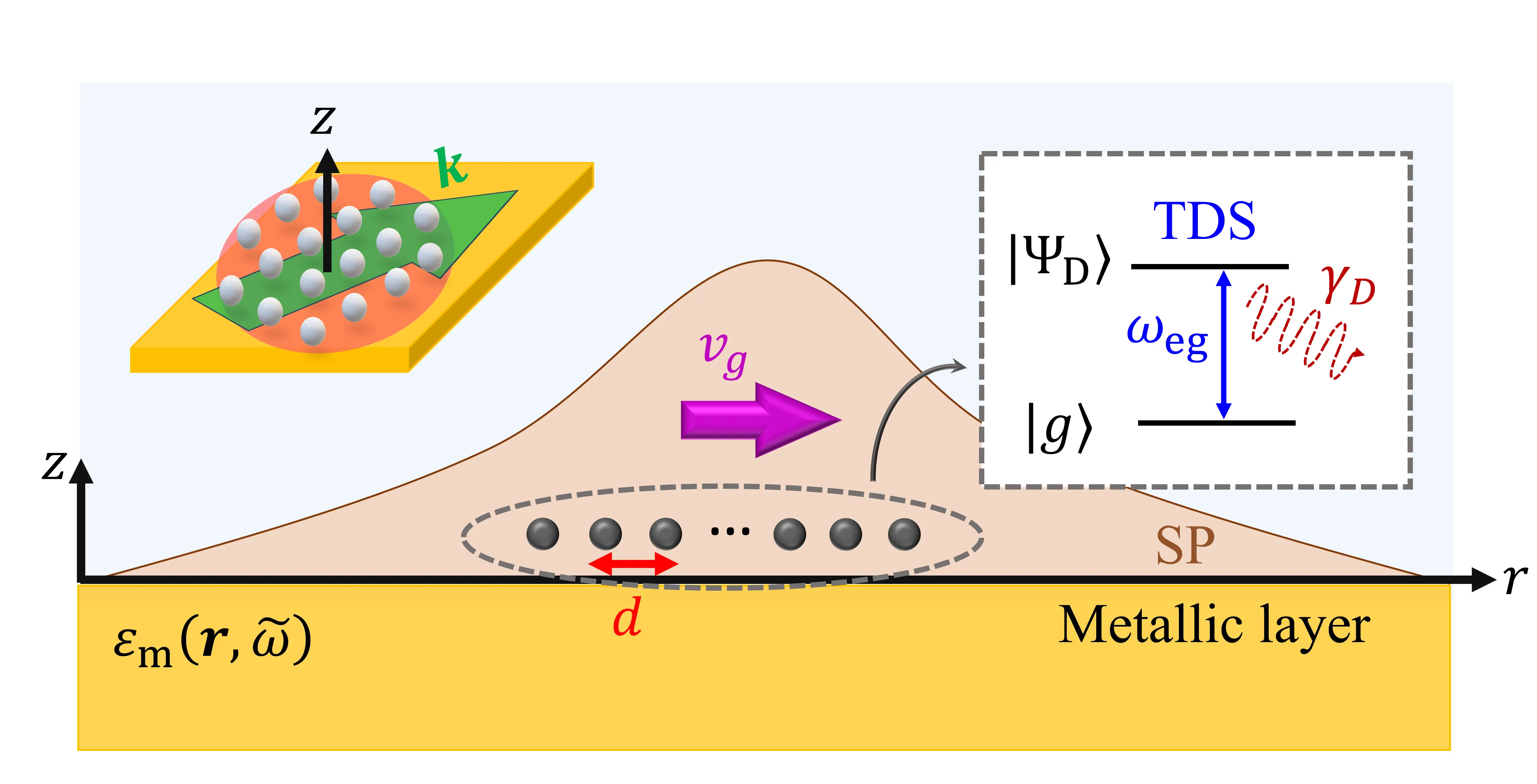
Rabi oscillations characterize light-matter hybridization in the waveguide quantum electrodynamics~(WQED) framework, with their associated decay rates reflecting excitation damping, yet their behavior remains unresolved when collective emitters are coupled to a collective waveguide mode. This scenario reveals a conceptually novel collective-light-collective-matter interaction, realizable when a timed-Dicke state~(TDS) of subwavelength emitters couples to a slow, delocalized surface-plasmon mode, forming a hybridized plasmon-polariton~(HPP). The HPP acquires its directionality from the TDS via momentum matching. It also exhibits plasmonic characteristics, with excitation frequencies following the surface-plasmon dispersion relation. We obtain a Rabi oscillation and a long-time decay that describe the HPP and use them to reveal weak- and strong-coupling regimes through the emergence of normal-mode splitting. By performing a finite-time Lyapunov-exponent analysis, we show that the HPP also exhibits instantaneous decay and identify three distinct decay regimes: early-time rapid, transient-time oscillatory, and long-time classical. Finally, by analyzing the emission spectrum, we observe an anticrossing of the peak doublets~(a feature also seen in cavity QED setups) which originates from quantum vacuum effects and the resulting non-Markovian HPP evolution in our WQED.
Single-photon emitters (SPEs) are central to quantum communication, computing, and metrology, yet their development remains constrained by trade-offs in purity, indistinguishability, and tunability. This review presents a mechanism-based classification of SPEs, offering a physics-oriented framework to clarify the performance limitations of conventional sources, including quantum emitters and nonlinear optical processes. Particular attention is given to hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite quantum dots (HOIP QDs), which provide size- and composition-tunable emission with narrow linewidths and room-temperature operation. Through comparative analysis of physical mechanisms and performance metrics, we show how HOIP QDs may address key limitations of established SPE platforms. Recognizing the constraints of current deterministic sources, we introduce a performance framework to guide the development of scalable SPEs, and examine the theoretical potential of bright squeezed vacuum (BSV) states, discussing how BSV mechanisms could serve as a promising avenue for multiplexable, high-purity photon generation beyond conventional heralded schemes. The review concludes by outlining future directions for integrating HOIP- and BSV-based concepts into scalable quantum photonic architectures.
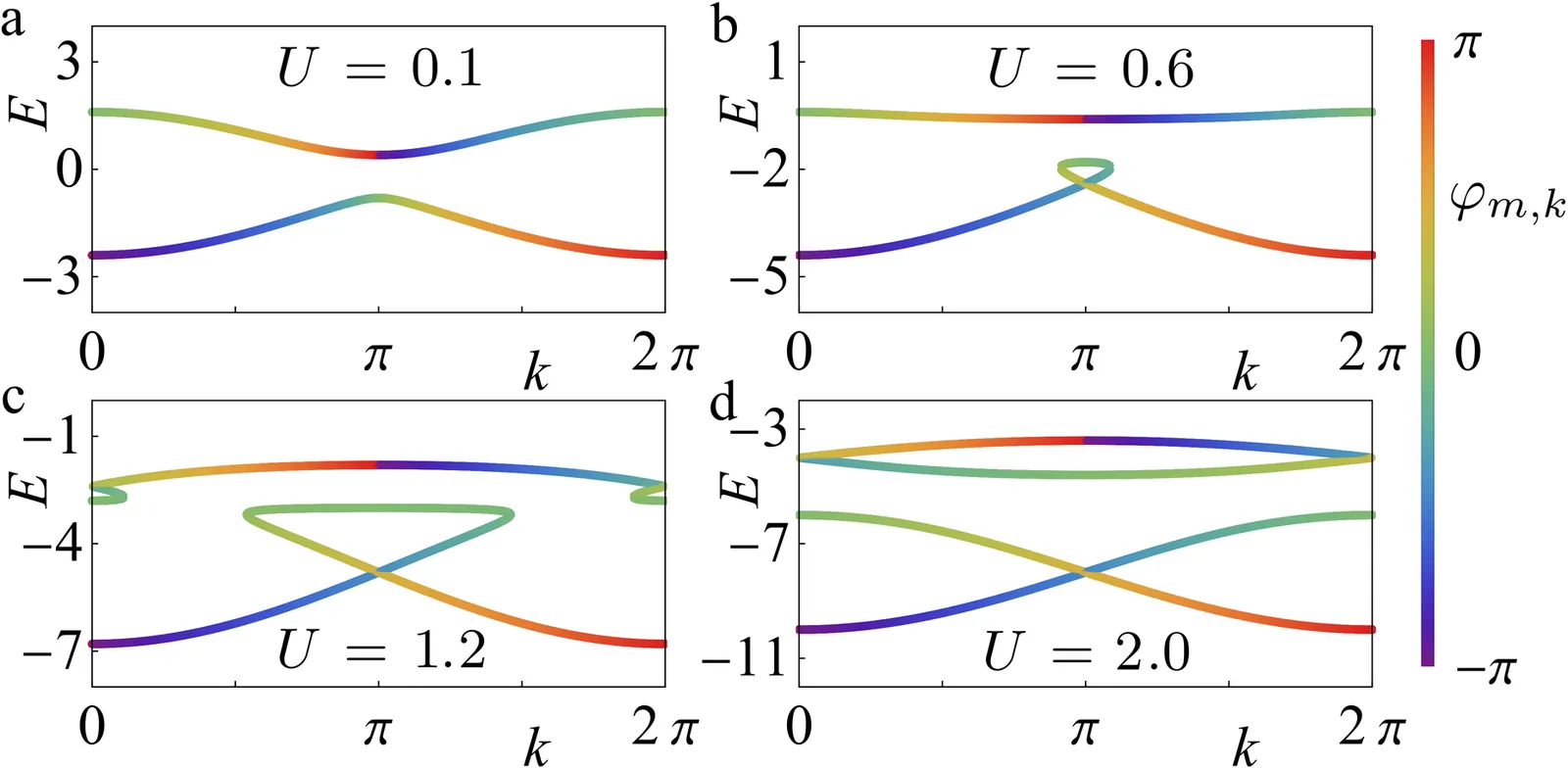
The interplay between topology and nonlinearity represents a central challenge in modern physics. Here, we investigate this interplay by considering a synthetic Su-Schrieffer-Heeger lattice with all-to-all nonlocal interactions. We find that the distinctive nonlinearity maintains an effective chiral symmetry and leads to a quantized nonlinear winding and Berry phase, as corroborated by the developed Bogoliubov nonlinear adiabatic theory. Increasing nonlinearity drives a sequence of topological transitions signaled by the appearance of characteristic swallowtail band structures at intermediate interaction strengths and band swapping in the strong nonlinear regime. The band swapping results in quantized fractional windings and double-period Bloch oscillations that are closely related to discrete time crystals. Remarkably, even starting from a topologically trivial linear system, nonlocal nonlinearity can induce an emergent topological phase with fractional windings. Experimentally, our model can be realized using photons in a degenerate optical cavity with Rydberg-mediated interactions. Our results establish a rigorous framework and pave the way for exploring nonlinear topological phenomena and their applications in synthetic quantum platforms.
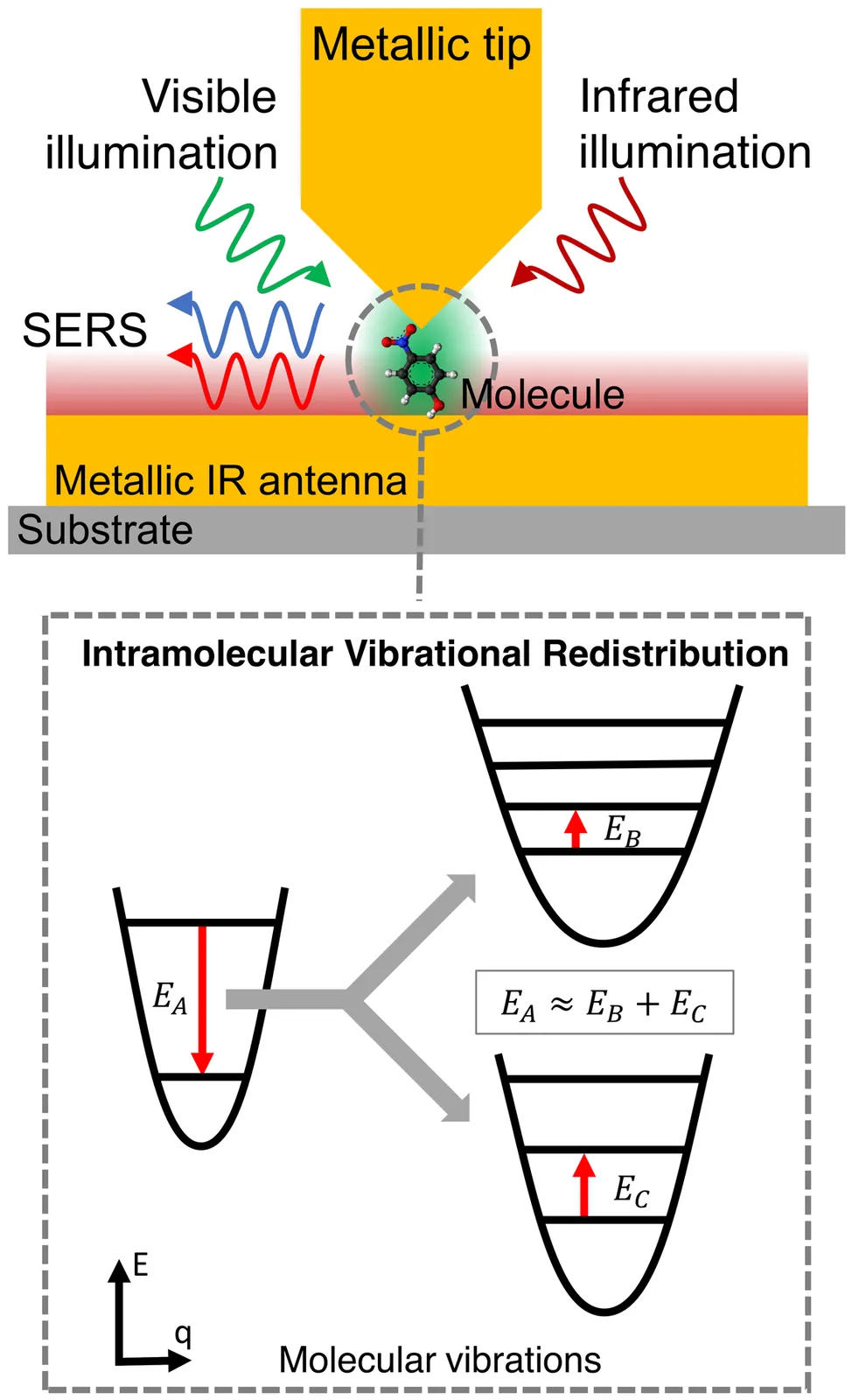
The development of accurate tools to characterize Intramolecular Vibrational Redistribution (IVR) is of major interest in chemistry. In this context, surface-enhanced vibrational spectroscopies stand up as well-established techniques to study molecular vibrational lines and populations with a sensitivity that can reach the singe-molecule level. However, to date, this possibility has not been fully developed to address IVR. Here, we establish a quantum mechanical framework based on molecular optomechanics that accounts for IVR, and adopt it to analyze strategies to optimize IVR characterization by vibrational spectroscopy. In particular, we model two different pump-and-probe configurations where the vibrational pumping is provided either by infrared laser illumination or by Stokes SERS. We show for the two pumping configurations the existence of clear signatures on the anti-Stokes SERS spectra of population transfer between coupled vibrational modes in a molecule. Our calculations adopt realistic molecular and SERS parameters, suggesting that these signatures of IVR are accessible at the single-molecule level with current experimental platforms.
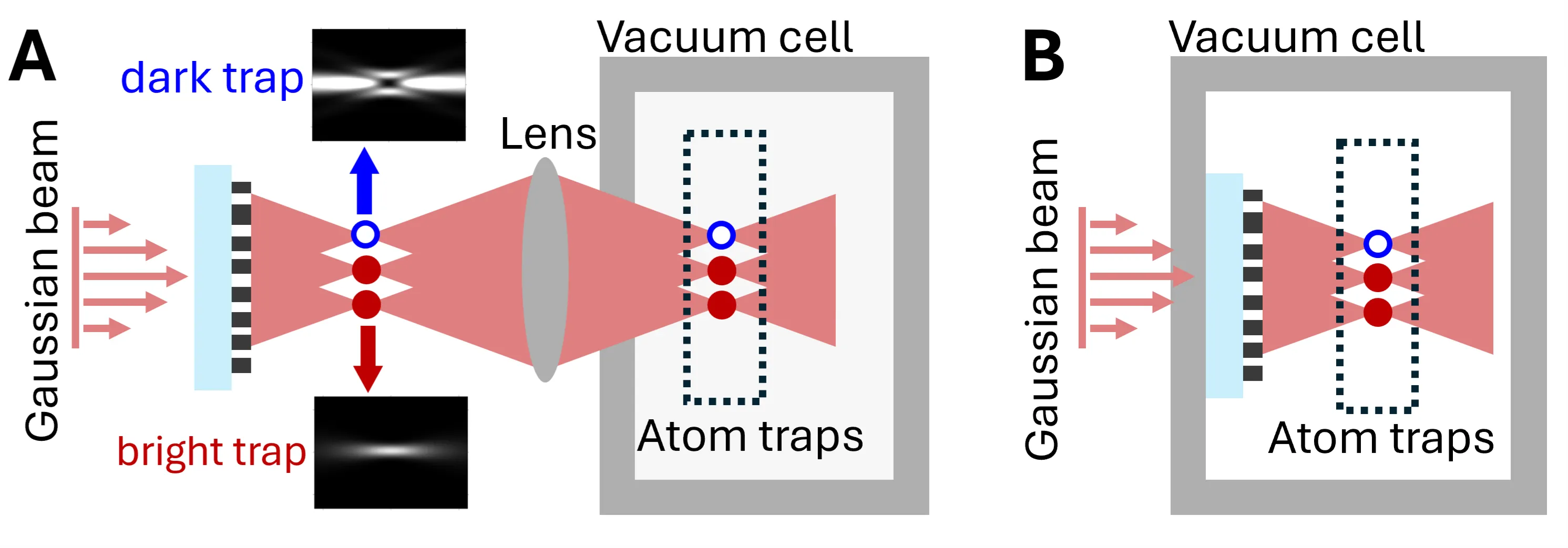
We demonstrated crystalline silicon-on-sapphire (c-SOS) metasurfaces that convert a Gaussian beam into arrays of complex optical traps, including arrays of optical bottle beams that trap atoms in dark regions interleaved with bright tweezer arrays. The high refractive index and indirect band gap of crystalline silicon makes it possible to design high-resolution near-infrared ($λ>700$ nm) metasurfaces that can be manufactured at scale using CMOS-compatible processes. Compared with active components like spatial light modulators (SLMs) that have become widely used to generate trap arrays, metasurfaces provide an indefinitely scalable number of pixels, enabling large arrays of complex traps in a very small form factor, as well as reduced dynamic noise. To design metasurfaces that can generate three-dimensional bottle beams to serve as dark traps, we modified the Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm to enforce complex-amplitude profiles at the focal plane of the metasurface and to optimize the uniformity of the traps across the array. We fabricated and measured c-SOS metasurfaces that convert a Gaussian laser beam into arrays of bright traps, dark traps, and interleaved bright/dark traps.
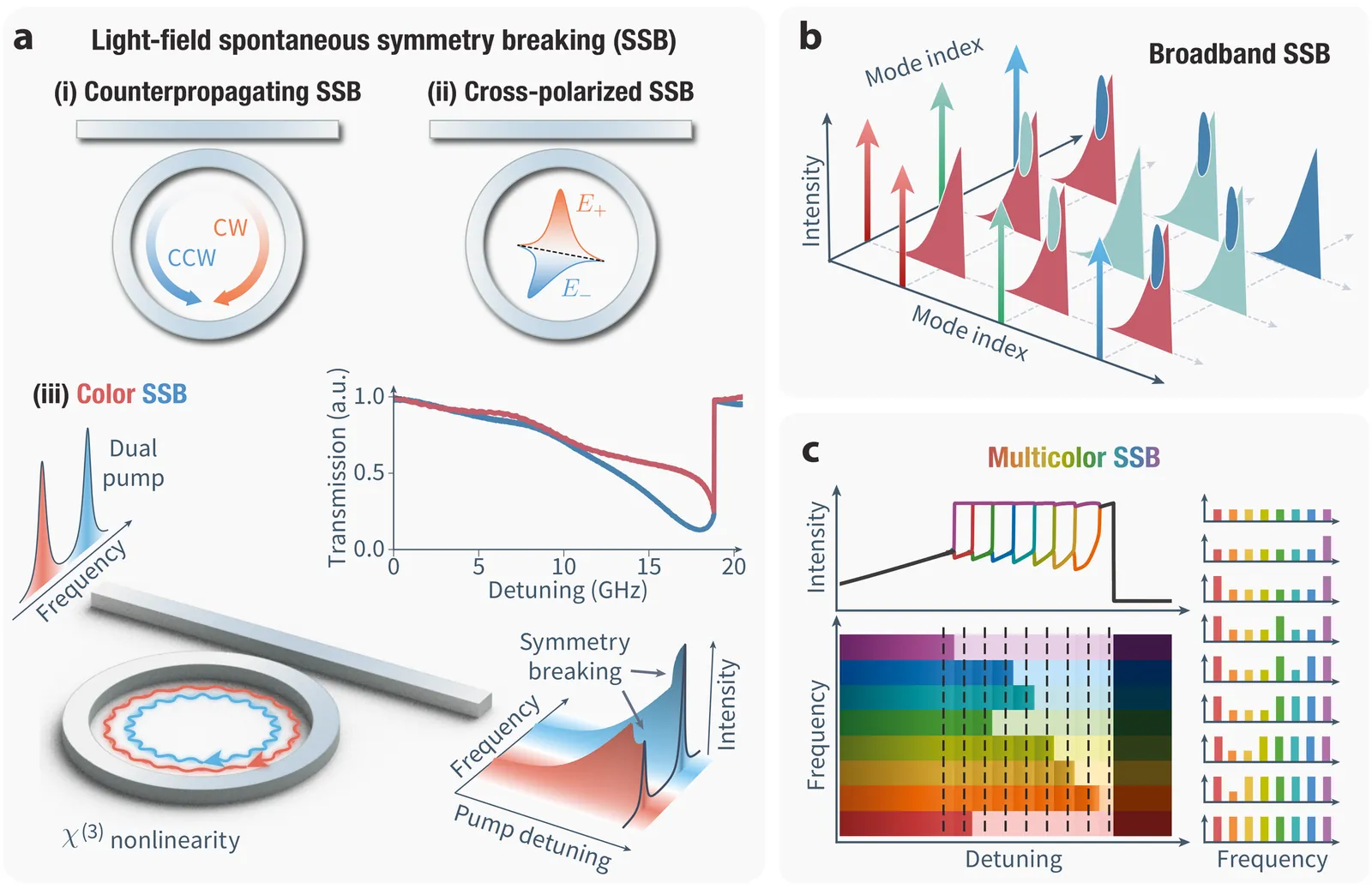
Spontaneous symmetry breaking leads to diverse phenomena across the natural sciences, from the Higgs mechanism in particle physics to superconductors and collective animal behavior. In photonic systems, the symmetry of light states can be broken when two optical fields interact through the Kerr nonlinearity, as shown in early demonstrations with counterpropagating and cross-polarized modes. Here, we report the first observation of color symmetry breaking in an integrated silicon nitride microring, where spontaneous power imbalance arises between optical mode at different wavelengths, mediated by the Kerr effect. The threshold power for this effect is as low as 19 mW. By examining the system's homogeneous states, we further demonstrate a Kerr-based nonlinear activation-function generator that produces sigmoid-, quadratic-, and leaky-ReLU-like responses. These findings reveal previously unexplored nonlinear dynamics in dual-pumped Kerr resonators and establish new pathways towards compact, all-optical neuromorphic circuits.
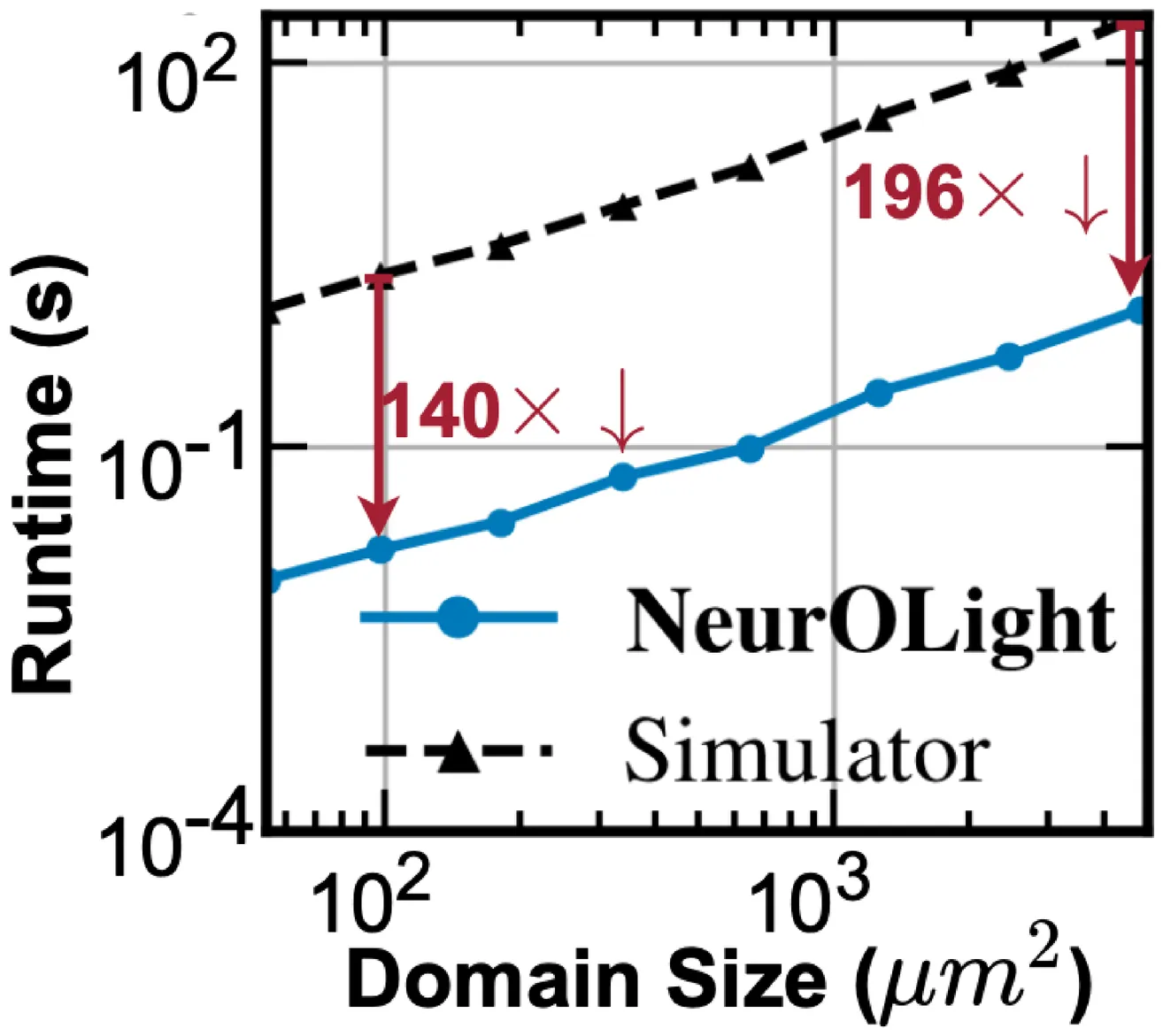
Photonics is becoming a cornerstone technology for high-performance AI systems and scientific computing, offering unparalleled speed, parallelism, and energy efficiency. Despite this promise, the design and deployment of electronic-photonic AI systems remain highly challenging due to a steep learning curve across multiple layers, spanning device physics, circuit design, system architecture, and AI algorithms. The absence of a mature electronic-photonic design automation (EPDA) toolchain leads to long, inefficient design cycles and limits cross-disciplinary innovation and co-evolution. In this work, we present a cross-layer co-design and automation framework aimed at democratizing photonic AI system development. We begin by introducing our architecture designs for scalable photonic edge AI and Transformer inference, followed by SimPhony, an open-source modeling tool for rapid EPIC AI system evaluation and design-space exploration. We then highlight advances in AI-enabled photonic design automation, including physical AI-based Maxwell solvers, a fabrication-aware inverse design framework, and a scalable inverse training algorithm for meta-optical neural networks, enabling a scalable EPDA stack for next-generation electronic-photonic AI systems.
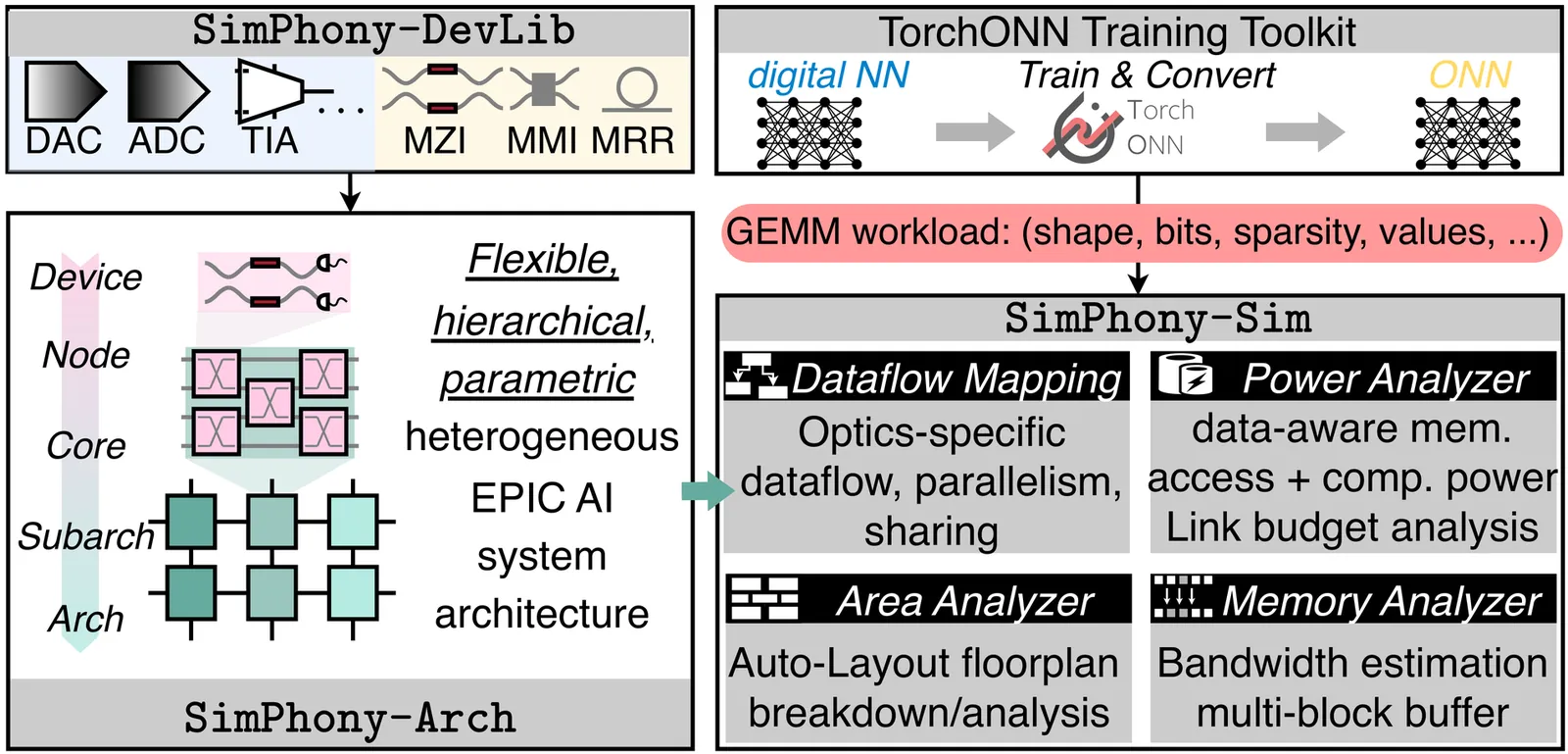
In this work, we identify three considerations that are essential for realizing practical photonic AI systems at scale: (1) dynamic tensor operation support for modern models rather than only weight-static kernels, especially for attention/Transformer-style workloads; (2) systematic management of conversion, control, and data-movement overheads, where multiplexing and dataflow must amortize electronic costs instead of letting ADC/DAC and I/O dominate; and (3) robustness under hardware non-idealities that become more severe as integration density grows. To study these coupled tradeoffs quantitatively, and to ensure they remain meaningful under real implementation constraints, we build a cross-layer toolchain that supports photonic AI design from early exploration to physical realization. SimPhony provides implementation-aware modeling and rapid cross-layer evaluation, translating physical costs into system-level metrics so architectural decisions are grounded in realistic assumptions. ADEPT and ADEPT-Z enable end-to-end circuit and topology exploration, connecting system objectives to feasible photonic fabrics under practical device and circuit constraints. Finally, Apollo and LiDAR provide scalable photonic physical design automation, turning candidate circuits into manufacturable layouts while accounting for routing, thermal, and crosstalk constraints.

In this work, we develop a mathematical theory for the photonic Hall effect and prove the existence of guided electromagnetic waves at the interface of two honeycomb photonic crystals. The guided wave resembles the edge states in electronic systems: it is induced by the topological Hall effect, and the wave propagates along the interface but not in the bulk media. Starting from a symmetric honeycomb photonic crystal that attains Dirac points at the high-symmetry points of the Brillouin zone, $K$ and $K'$, we introduce two classes of perturbations for the periodic medium. The perturbations lift the Dirac degeneracy, forming a spectral band valley at the points $K$ and $K'$ with well-defined topological phase that depends on the sign of the perturbation parameters. By employing the layer potential techniques and spectral analysis, we investigate the existence of guided wave along an interface when two honeycomb photonic crystals are glued together. In particular, we elucidate the relationship between the existence of the interface mode and the nature of perturbations imposed on the two periodic media separated by the interface.
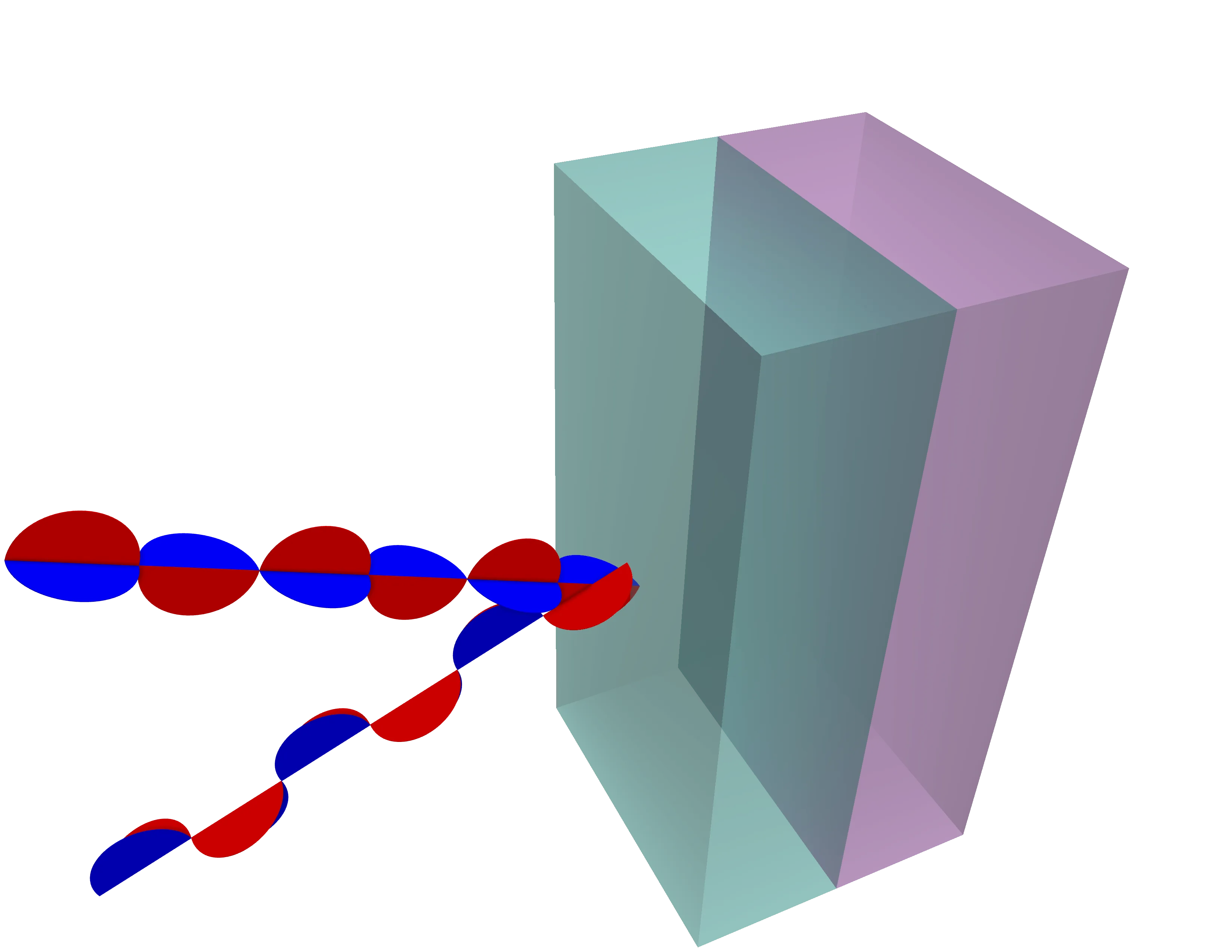
This paper investigates the unique properties of PT-symmetric Topological Weyl Semimetals (TWS) within the framework of non-Hermitian physics, focusing on their potential for generating topological lasers. By exploring the role of spectral singularities and their relationship to exceptional points, we examine how these materials, characterized by Weyl nodes and topologically protected surface states, can support novel optical phenomena such as unidirectional propagation and enhanced lasing. Through a theoretical model based on the transfer matrix approach, we reveal how the interplay between the PT symmetry and the axion term introduces new dynamics, leading to 12 distinct topological laser configurations. The study also investigates the impact of the $θ$-term on spectral singularities, showing how it quantizes the system's gain values and influences the topological properties of the lasers. By applying our model to the TaAs material, a known Weyl semimetal, we uncover previously unreported effects, demonstrating the potential of PT-symmetric TWS materials for advanced optoelectronic applications. We show that the axion-induced cyclotron-like Hall current in a PT-symmetric TWS medium, revealing its topological characteristics and distinct flow patterns in the gain and loss regions, which serve as indicators of the system's topological symmetry. Our findings open new avenues for the development of robust, tunable, and efficient topological lasers with applications in quantum information processing and beyond.
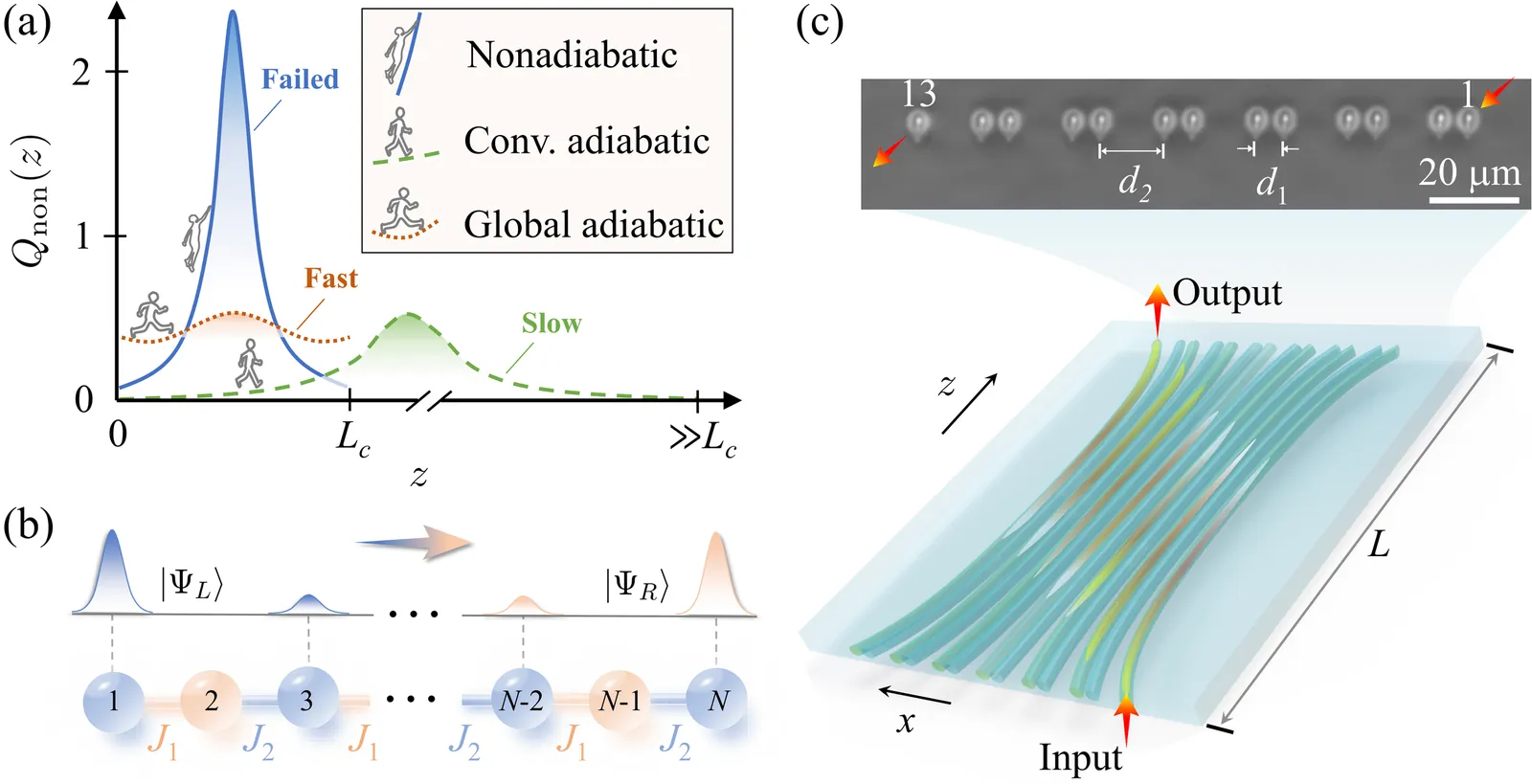
Adiabatic topological pumping promises robust transport of energy and information, but its speed is fundamentally limited by the instantaneous adiabatic condition, which demands prohibitively slow parameter variations. Here we develop a paradigm shift from instantaneous to global adiabaticity. We derive a global adiabatic criterion (GAC), which sets an absolute fidelity bound by controlling the root-mean-square value of nonadiabaticity factor. We further introduce a fluctuation-suppression acceleration criterion, which minimizes spatial inhomogeneity and allows us to safely increase the mean nonadiabaticity. Experimentally, we implement this principle in femtosecond-laser-written photonic Su-Schrieffer-Heeger waveguide arrays via scalable power-law coupling modulation. Our accelerated topological pumping achieves >0.95 fidelity over a fivefold reduced device length compared to the conventional scheme, exhibits the predicted linear scaling with the system size, and maintains robust performance across a >400 nm bandwidth. This principle of GAC provides a universal design rule for fast, compact, and robust adiabatic devices across quantum and classical topological platforms.
The energy-transfer efficiency of the natural photosynthesis system seems to be perfectly optimized during the evolution for millions of years. However, how to enhance the efficiency in the artificial light-harvesting systems is still unclear. In this paper, we investigate the energy-transfer process in the photosystem I (PSI). When there is no effective coupling between the outer antenna (OA) and the reaction center (RC), the two light-harvesting networks are disconnected and thus the energy transfer is inefficient. In order to repair these disconnected networks, we introduce a bridge with three sites between them. We find that by modulating the level structure of the 3-site bridge to be resonant, the energy transfer via the dark state will be enhanced and even outperform the original PSI. Our discoveries may shed light on the designing mechanism of artificial light-harvesting systems.
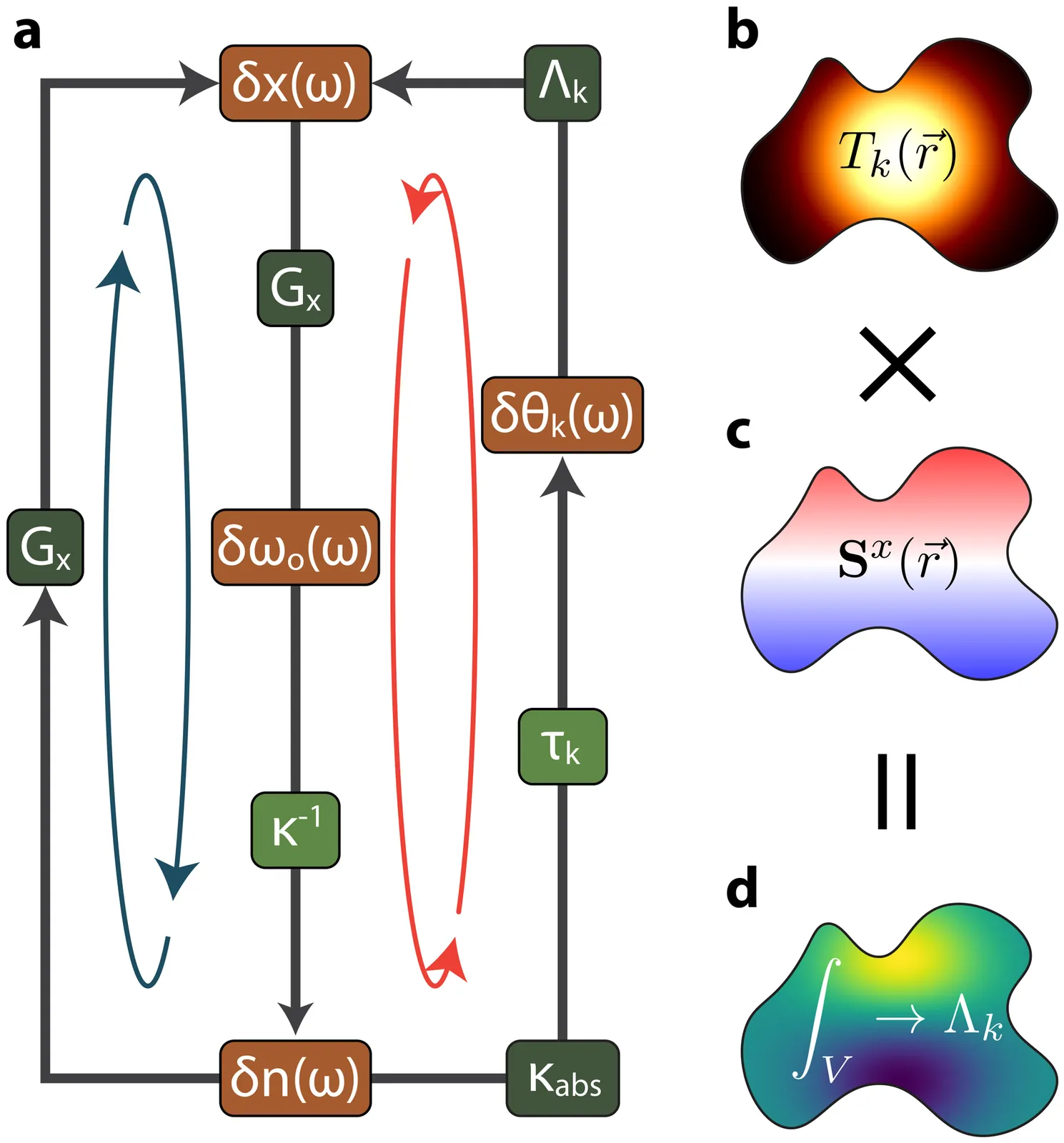
In micro- and nanoscale optomechanical systems, radiation pressure interactions are often complemented or impeded by photothermal forces arising from thermal strain induced by optical heating. We show that the sign and magnitude of the photothermal force can be engineered through deterministic nanoscale structural design, by considering the overlap of temperature and modal strain profiles. We demonstrate this capability experimentally in a specific system: a nanobeam zipper cavity by changing the geometry of its supporting tethers. A single design parameter, corresponding to a nanoscale geometry change, controls the magnitude of the photothermal backaction and even its sign. These insights will allow engineering the combined photothermal and radiation pressure forces in nano-optomechanical systems, such that backaction-induced linewidth variations are deterministically minimized if needed, or maximized for applications that require cooling or amplification at specific laser detuning.
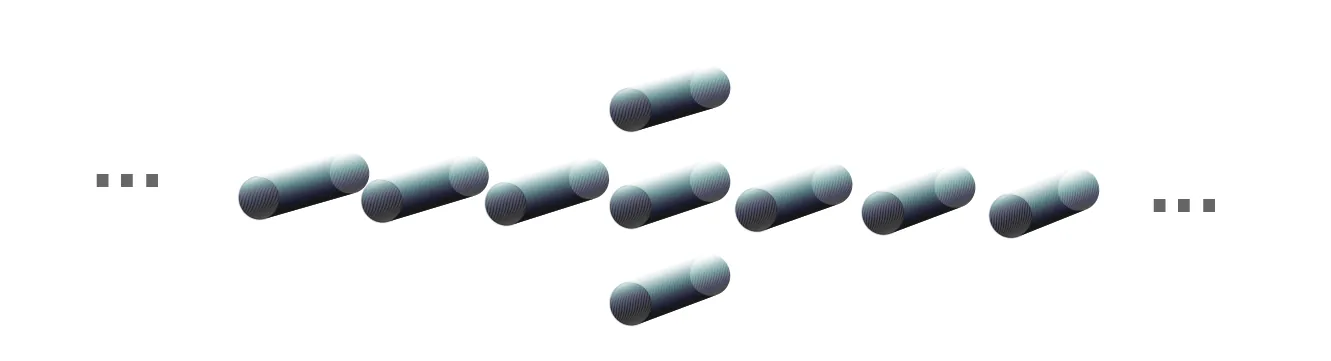
This paper presents a rigorous mathematical analysis for symmetry-based Bound States in the Continuum (BICs) in optical waveguide arrays. Different from existing research, we consider a finite system of horizontally and equidistantly aligned waveguides and transform the wave propagation problem into Nonorthogonal Coupled-Mode Equations (NCME), rather than adopting the tight-binding approximation or orthogonal coupled-mode equations. We derive the exact expressions of the overlap integrals and coupling coefficients by utilizing the addition theorems of Bessel functions. We then generalize the discussion to an infinite waveguide array and rigorously characterize the dispersion relation and continuum with the help of theories in harmonic analysis. In the second part of the paper, we give a strict proof of the existence of BICs in the aforementioned waveguide system with two additional identical vertical waveguides aligned symmetrically above and below the horizontal waveguide array. We further numerically demonstrate the transition from a perfect BIC to a leaky mode by introducing a symmetry-breaking refractive index perturbation and quantitatively analyze the resulting radiation losses. This work gives a comprehensive study of symmetry-protected BICs and provides an efficient and precise computational model for designing such BICs devices.
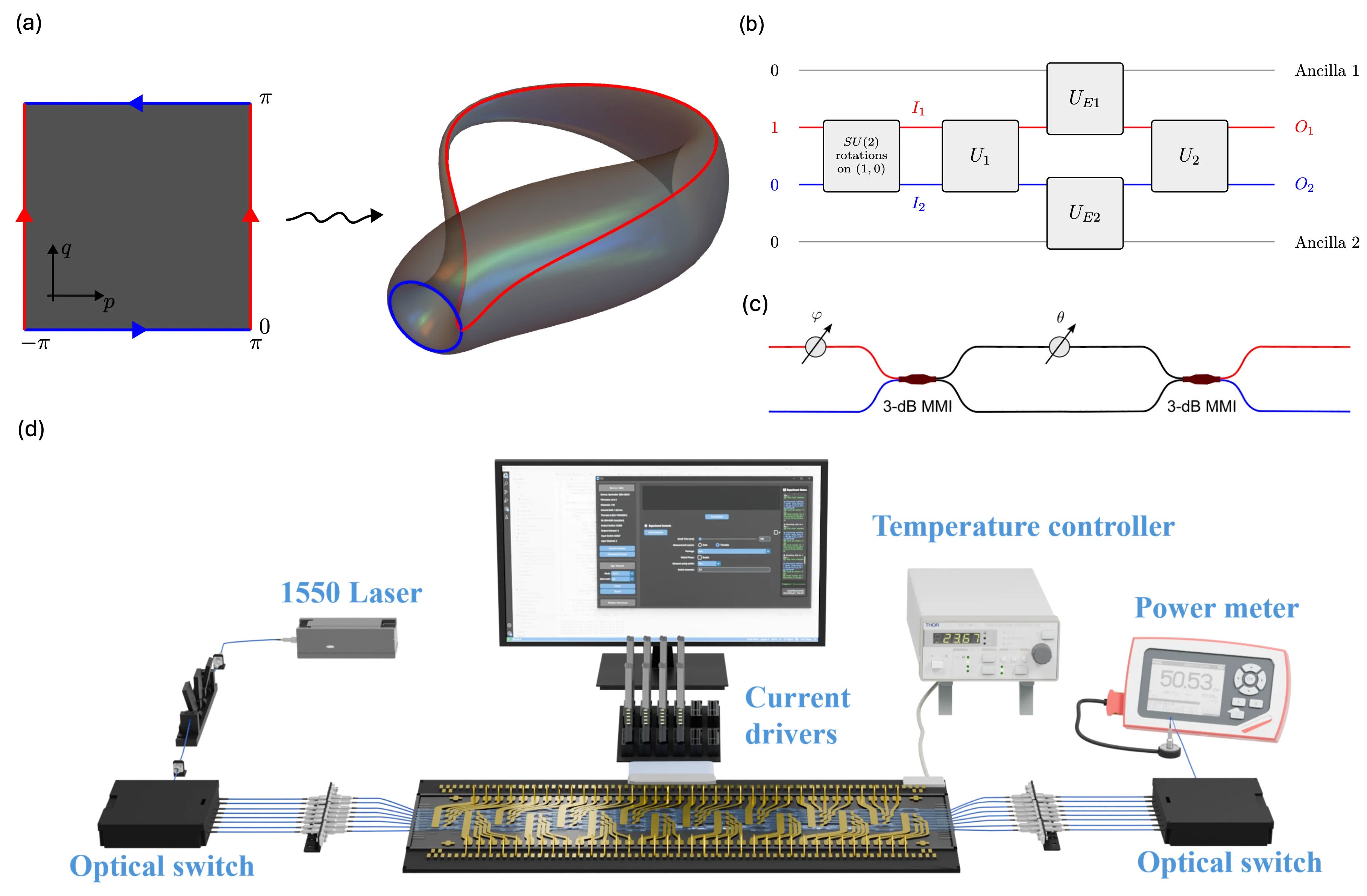
Non-Hermitian physics has unlocked a wealth of unconventional wave phenomena beyond the reach of Hermitian systems, with exceptional points (EPs) driving enhanced sensitivity, nonreciprocal transport, and topological behavior unique to non-Hermitian degeneracies. Here, we present a scalable and reconfigurable silicon photonic integrated circuit capable of emulating arbitrary non-Hermitian time evolution with high precision. Using this programmable platform, we implement a two-band non-Hermitian Hamiltonian defined on a Klein-bottle topology a nonorientable parameter space that enables exceptional phases forbidden on orientable manifolds. Through an on-chip amplitude-and-phase reconstruction protocol, we retrieve the full complex Hamiltonian at multiple points in parameter space and experimentally map the associated Fermi arc where the imaginary eigenvalue gap closes. The orientation of the measured Fermi arc reveals a nontrivial exceptional topology: it implies the presence of same-charge EPs (or an EP monopole) that cannot annihilate locally on the Klein bottle. Our results demonstrate the first photonic realization of exceptional topology on a nonorientable manifold and establish a versatile platform for exploring exotic non-Hermitian and topological models relevant to classical and quantum photonics.
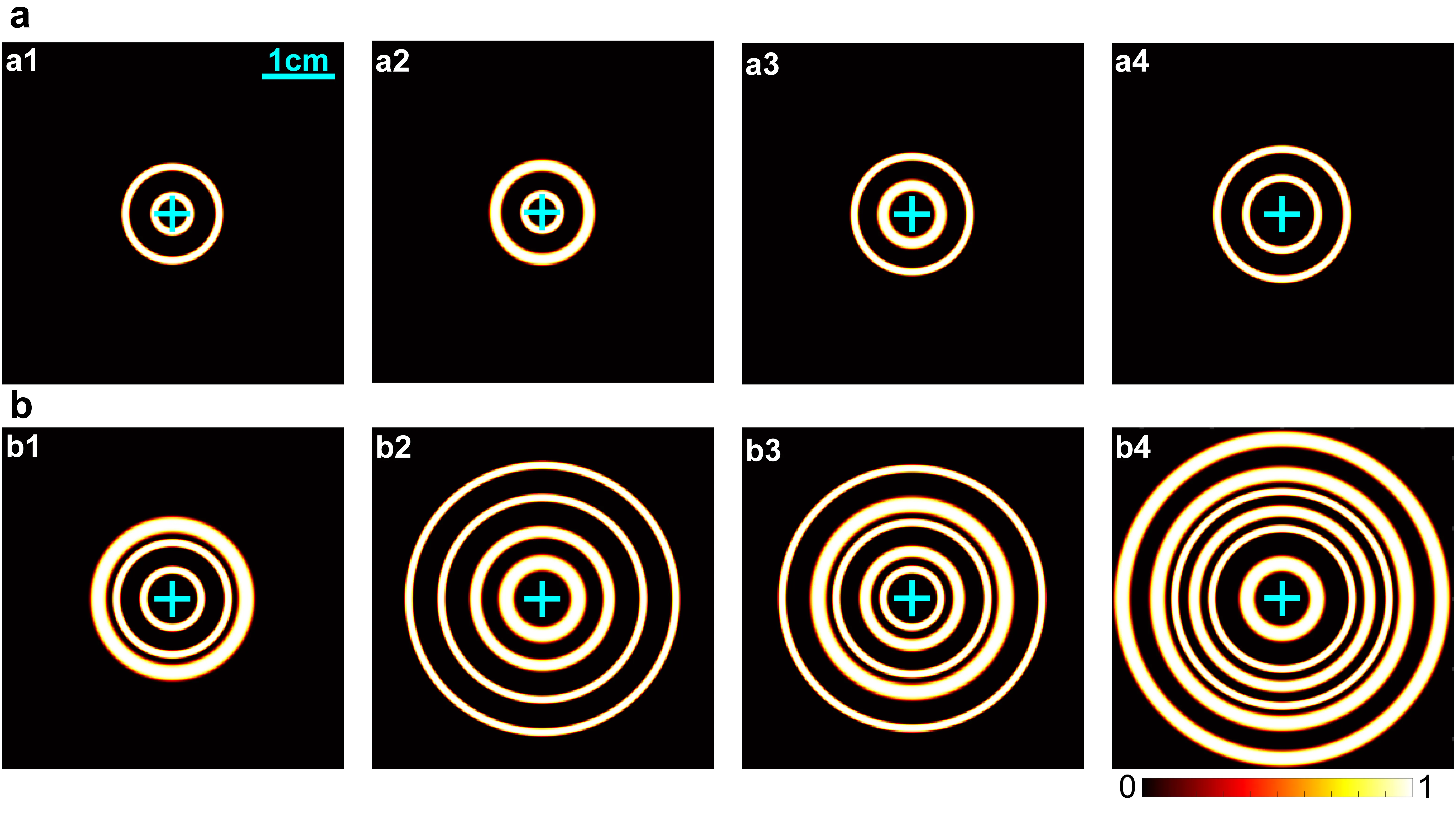
Atmospheric turbulence imposes a fundamental limitation across a broad range of applications, including optical imaging, remote sensing, and free-space optical communication. Recent advances in adaptive optics, wavefront shaping, and machine learning, driven by synergistic progress in fundamental theories, optoelectronic hardware, and computational algorithms, have demonstrated substantial potential in mitigating turbulence-induced distortions. Recently, active convolved illumination (ACI) was proposed as a versatile and physics-driven technique for transmitting structured light beams with minimal distortion through highly challenging turbulent regimes. While distinct in its formulation, ACI shares conceptual similarities with other physics-driven distortion correction approaches and stands to benefit from complementary integration with data-driven deep learning (DL) models. Inspired by recent work coupling deep learning with traditional turbulence mitigation strategies, the present work investigates the feasibility of integrating ACI with neural network-based methods. We outline a conceptual framework for coupling ACI with data-driven models and identify conditions under which learned representations can meaningfully support ACI's correlation-injection mechanism. As a representative example, we employ a convolutional neural network (CNN) together with a transfer-learning approach to examine how a learned model may operate in tandem with ACI. This exploratory study demonstrates feasible implementation pathways and establishes an early foundation for assessing the potential of future ACI-DL hybrid architectures, representing a step toward evaluating broader synergistic interactions between ACI and modern DL models.